There are many diseases of female reproductive organs that can seriously affect not only the ability to conceive a child, but also lead to serious complications. One of the most unusual at this time is ovarian teratoma. This new growth amazes and frightens with one's appearance. Scientists from around the world are trying to establish the real cause of this unusual disease.
Contents of
- 1 What is the ovarian teratoma?
- 1.1 Video on ovarian teratoma in the program of Elena Malysheva "Live healthy"
- 2 Causes and risk factors
- 3 Tumor types and their features
- 3.1 Mature teratoma
- 3.2 Immature teratoma
- 3.3 Ovarian taurate with malignant transformation
- 4 Symptoms and signs
- 4.1 Video on the teratoma in the program "Monsters inside me"
- 5 Diagnosis of the disease
- 5.1 Mature teratoma on ultrasound
- 6 Treatment of the teratoma of the ovary
- 6.1 Operation to remove the terOvarian volumes
- 6.1.1 Surgical removal of teratoma
- 6.1.2 Laparoscopic removal of teratoma
- 6.1.3 Chemotherapy and irradiation
- 6.2 Postoperative recovery
- 6.3 Treatment and precautions during pregnancy
- 6.1 Operation to remove the terOvarian volumes
- 7 Consequences and complications
- 8 Effect on the planning of pregnancy
- 9 Reviews
What is an ovarian teratoma?
Teratoma is a special neoplasm, which is classified as lipid-cell. It is customary to refer it to germinogenic tumors that develop from primary germ cells of sexual glands. Its feature is a heterogeneous structure, since each of the parts develops from different embryonic sheets. As a result of this tumor formation can grow real hair and even teeth. In rare cases, doctors detected eyeballs and rudiments of limbs, which gave the tumors a resemblance to a terrible and ugly living being. It is because of the appalling appearance that this formation was called teratoma, from the Latin word teras - monster.
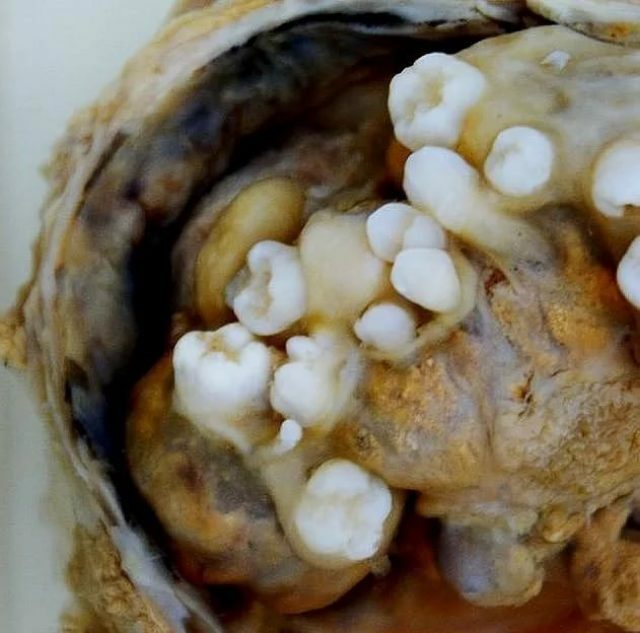
When removing the teratoma of the ovary, teeth, hair and other formations are found.
Teratoma is considered a benign neoplasm and rarely degenerates into a malignant tumor.
There are many synonyms for the ovarian teratoma:
- embryo;
- parasitic fetus;
- tridermoma;
- is a complex cellular tumor;
- mixed teratogenic formation;
- monodermoma.
Such a large number of names indicates that the teratoma remains a mysterious disease, the exact causes of which have not yet been fully explored.
Video on ovarian teratoma in Elena Malysheva's program "Live Healthily"
Causes and Risk Factors of
Currently, there are no real reasons for the formation of an ovarian teratoma. One of the most common versions of the scientists consider the violation of embryogenesis due to chromosomal abnormalities.
The most common cause of teratoma is considered to be chromosomal abnormalities
There is also an interesting theory that a teratoma develops in pathological processes during the development of identical twins, when one fetus absorbs the other.
In addition to this, the following possible reasons for the formation of teratomas are highlighted:
- sharp hormonal failures;
- beginning or end of the menstrual cycle;
- contraceptive use;
- surgical operations on female genital organs.
Tumor types and their features
Teratoma can be located on the left or right ovary. Most of all, it appears immediately from two sides. The most commonly encountered right-sided teratoma, which is due to the special anatomical structure of the female reproductive system. It is from this side that the blood supply is the most active. Left-sided teratoma occurs less frequently, since ovulation occurs less frequently in this ovary. Because of the reduced load in this side, all kinds of cysts and tumors are formed to a lesser degree.
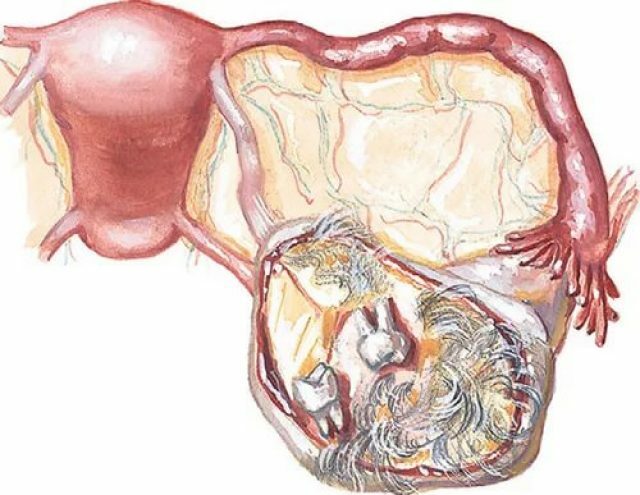
Teratoma is most often formed on the right ovary
. According to the histological structure, several types of teratomas are distinguished:
- mature;
- is immature;
- with transformation into a malignant tumor.
Mature teratoma
This type of embryo develops from clearly differentiated germ cells. In its structure, it can be of three types.
- Single is usually small in size, rarely contains hair and bone elements.
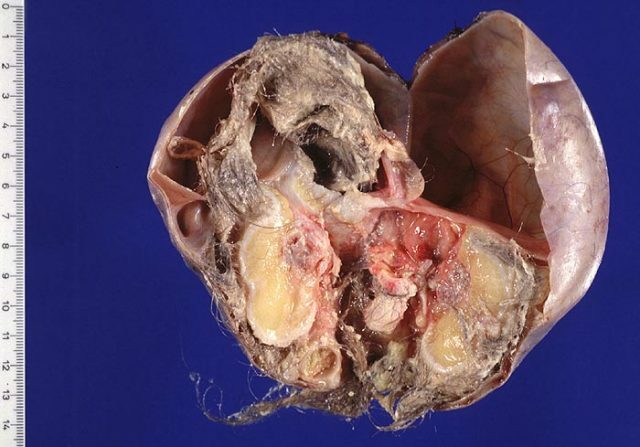
- Whole or solid can reach very large sizes and in detailed study, cartilage, bone tissue and fluid-filled vesicles are found. It is not homogeneous and, when examined, its surface is often bumpy and very dense to the touch.
- Cystic teratoma of the ovary is a large accumulation of blisters filled with a grayish and yellowish liquid, and cells of sebaceous and sweat glands are also found. Between them can lie nerve, fat and muscle tissue, cells of the intestine. This kind of teratom represents a great danger, since it can reach gigantic proportions and promotes the twisting of the base of the tumor, which leads to tissue necrosis. It usually occurs on the right ovary.
Immature teratoma
This type of education is considered transitional and it tends to degenerate into a malignant teratoblastoma. Consists of low-differentiated cells that form mesenchymal and nerve tissue sections. Immature teratoma is rare, only 3% of all patients after histological evaluation establish this diagnosis.
The main danger is the rapid spread of the tumor process during degeneration into teratoblastoma, promoted by blood flow and lymph flow. Most often, this disease is found in girls aged 17-26 years. The surface of this tumor is smooth, prone to quickly necrotic and bleed. In this case, cartilage and epithelial cells are not found in the composition. Very often immature teratoma appears with gliomatosis and promotes the spread of metastases to nearby organs.
Ovarian Teratoma with Malignant Transformation
This type of teratoma is the rarest and is necessarily accompanied by a cancers formation. After taking a tumor sample for histology, melanoma, adenocarcinoma and other malignant diseases are diagnosed in patients. In the ovaries can be found cells that are characteristic of thyroid cancer.
Symptoms and signs
Typically, a teratoma is a single formation with smooth contours, the size of which rarely exceeds 15 centimeters.
Mature teratoma of the ovary has its clinical manifestations:
- , they are often found in girls of different ages, including even in newborns;
- is the most common location - in the right ovary, in front of the uterus;
- small teratomas are difficult to detect with ultrasound;
- is an asymptomatic course of the disease;
- Acute pain in the abdomen appears only when suppuration and torsion of the legs of the teratoma.
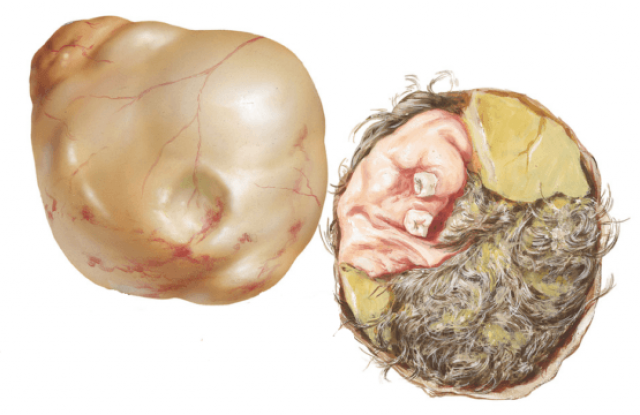
Teratoma very often remains asymptomatic until it reaches a large size
If the teratoma has reached a large size and is more than seven centimeters in length, then the following symptoms may be observed in patients:
- pelvic organs are displaced;
- pain in the right or left side, a feeling of heaviness;
- difficulty with urination, up to dysuria;
- defecation, it becomes painful, often constipation;
- in the place where the teratoma grows, the abdomen may increase in size;
- marked anemia in tumors of large size;
- weakness, increased fatigue, drowsiness with immature teratoma;
- fever with suppuration and necrosis.
Manifestations with left-sided and right-sided teratomas are no different than localization of pain. In most cases, the disease is asymptomatic until the tumor reaches a large size. Most often, the established diagnosis is a surprise to patients and is revealed during preventive examinations.
Sometimes the first time a teratoma is detected after childbirth, as a changed hormonal background can stimulate the tumor to augmented growth.
Video about the teratoma in the program "Monsters inside me"
Diagnosis of the disease
At the first suspicions of the appearance of tumors in the pelvic organs, women should contact a gynecologist. In the beginning the doctor will collect anamnesis, clarify the existing complaints, the symptoms of the diseases and conduct a bimanual examination of the vagina and cervix. Also, an examination will be carried out with the help of special gynecological mirrors.
Then ultrasound diagnosis of pelvic organs is mandatory. Also, this study helps to identify the pathology of intrauterine development of the fetus, if a woman is pregnant.
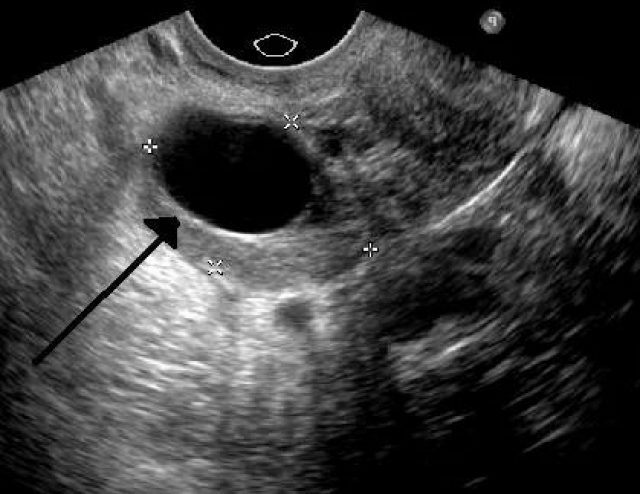
Ultrasound reveals large blackouts that may indicate the development of the teratoma
Additionally, the following instrumental diagnostic methods may be prescribed:
- fluoroscopy, which also examines other organs to detect possible metastasis;
- Doplerography for the study of blood supply to neoplasm;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging for obtaining layered images of internal organs;
- puncture of the abdominal area with fence material for histological examination of tumor tissues;
- Irrigoscopy or colon examination with a special contrast agent for suspected tumors in this area;
- sigmoidoscopy, examination with the help of a special chamber of the inside of the rectum.
A blood test can also be administered to determine the presence of placenta antigens and oncomarkers, such as chorionic gonadotropin, alpha-fetoprotein.
Mature teratoma on ultrasound
Treatment of teratoma of the ovary
Teratoma does not respond to conservative treatment and most patients are assigned to prompt removal of the tumor.
Ovarian teratoma removal operation
In almost all cases of detection of ovarian teratoma, women are assigned a surgical procedure to remove it, in order to avoid a possible degeneration into a malignant tumor. There are several options for surgical intervention:
- laparoscopic enucleation, in which only tumor cells are eliminated;
- partial removal of the ovary with a teratoma, to preserve the childbearing function;
- complete resection of the uterus and ovaries to reduce the risk of formation of oncological tumors in the menopause.
Before assigning the date of surgery, the patient must pass the following tests and undergo the necessary tests:
- general blood test with study of the group and Rh factor;
- biochemical blood test;
- coagulogram for determining the rate of clotting of blood;
- blood test for the content of antibodies to HIV, hepatitis and some other sexually transmitted diseases;
- ECG or electrocardiogram for studying the work of the heart;
- a general swab from the vagina to detect inflammation and the presence of sexually transmitted diseases;
- additional tests for doctors of different orientations in the presence of special indications.
Surgical removal of teratoma
For particularly large tumors, surgery with a standard surgical incision in the abdominal region may be prescribed. The doctor carefully examines the organs of the small pelvis for the presence of other tumors, adhesions and inflammatory processes. After removal of the teratoma, abdominal sanitation is performed. The time of the procedure is about one hour, after which the patient is stitched.
After removal of the tumors in this way, a fairly pronounced scar may remain on the skin and the recovery time of the patient can be significantly increased. The risk of bleeding and stitching is also increased.
Laparoscopic removal of teratoma
In most cases, a laparoscopic operation is required, after which only small incisions remain, not more than 2-3 cm in length. This method is minimally invasive and consists of three punctures through which the camera and instruments for the operation are inserted. If multiple tumors are found that have affected most of the reproductive organs, patients are removed not only from the teratoma itself, but also from the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus.
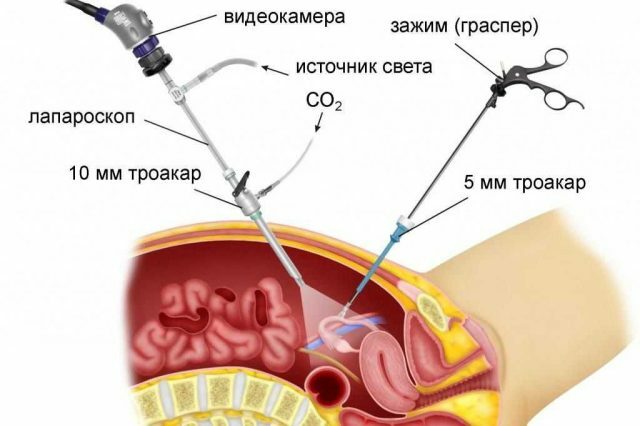
When laparoscopic operation, small incisions are made, through which instruments and a special chamber
are introduced. There are many advantages in carrying out laparoscopic removal of tumors:
- is more likely to preserve the childbearing function;
- minimal trauma of skin;
- shorter recovery period;
- minimal risk of complications and blood loss;
- additional pelvic examination with an optical instrument;
- minimal risk of formation of adhesions due to the absence of intestinal injuries.
Usually, the operation is carried out 5-10 days after the end of the month.
Chemotherapy and irradiation
If a malignant formation has been diagnosed after a tumor has been removed from a tumor, patients may be prescribed chemotherapy, radiation, or taking antitumor medication. Also, patients can be prescribed hormone therapy if the neoplasm has been found to be receptors that are sensitive to hormones. Chemotherapy is carried out with the help of special preparations containing platinum( Cisplatinum, Platidiam, Platinol).
Postoperative recovery of
Two days after surgery, patients are allowed to get out of bed and move. Approximately five days before discharge from the hospital, seams are removed. Patients should observe a sparing regimen for at least a week at home, try to relax more and make easy walks. It is better to refrain from sexual relations for a month and a half after the operation to avoid possible ruptures and internal bleeding.
Treatment and precautions during pregnancy
Self-medication during pregnancy is excluded, as this can lead to miscarriage and even death in the mother. A woman must strictly follow all the advice of a doctor. It is necessary to implement the following recommendations:
- monthly undergo a follow-up examination at a gynecologist and perform ultrasound diagnosis;
- to avoid sudden movements, slopes, turns;
- If there is pain in the abdomen from the side of the teratoma, immediately consult a doctor.
If the indication and large size of the teratoma is not earlier than the seventeenth week of pregnancy, it is possible to carry out laporascopic removal of the tumor. However, in the event of necrosis and torsion of the base of the teratoma, the operation is performed at any time.
If the tumor size is small, you can remove it during caesarean section, or several months after natural delivery.
Consequences and complications of
The prognosis of teratoma treatment is often favorable, in 98% of all cases there is a complete cure for the disease that has arisen. Only 2-3% of patients have a tumor degenerating into a malignant tumor. At an early detection of a cancerous tumor, the chance of recovery is high enough. In the absence of timely treatment, the following complications may occur:
- degeneration of the teratoma into a malignant tumor;
- metastasis to other internal organs;
- torsion of the leg of the tumor;
- tissue necrosis;
- rupture of the lesion;
- internal bleeding;
- peritonitis due to ingestion of the contents of the cyst into the abdominal cavity;
- a violation of the functions of the pelvic organs due to squeezing.
Influence on pregnancy planning
Tumors of large size can seriously affect the ability to conceive a child and to bear it. Very often there are cases of intrauterine fetal death and spontaneous miscarriage. However, pregnancy with teratoma is possible if special conditions are observed:
- tumor is mature;
- there are no other ovarian neoplasms;
- the size of the teratoma does not exceed five centimeters;
- there are no other concomitant diseases of internal organs.
During pregnancy, when a teratoma is detected, a thorough thorough examination of the gynecologist and ultrasound diagnosis are necessary in order to respond in a timely manner to any changes in its size and location.
Reviews
The prognosis of treatment with teratoma is often favorable, but most patients fear this diagnosis due to the appearance of the tumor, which is not in vain named after a monster or beast. Teeth, cartilage, hair, muscle and nerve tissue, and sometimes even eyeballs pierce the tumor. To this day, teratoma causes a lot of controversy about the reasons for its origin. Virtually all patients need to undergo surgical removal of the tumor in order to avoid further complications.