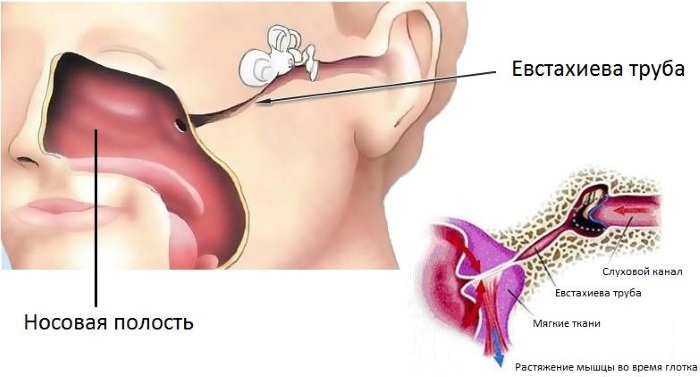
Clicking in the ears when swallowing - a rather unpleasant sensation that arises unexpectedly and manifests itself once or sporadically, in some people it causes a feeling of anxiety, while others are ignored. To find out where this strange symptom comes from, you need to understand the reasons for its appearance and the possible consequences.
The content of the article:
- 1 Reasons for the appearance
- 2 Possible diseases
- 3 Diagnostics
- 4 When to see a doctor
- 5 Prophylaxis
-
6 Treatment methods
- 6.1 Medications
- 6.2 Traditional methods
- 6.3 Other methods
- 7 Possible complications
- 8 Ear Videos
Reasons for the appearance
The causes of extraneous sounds in the ears when swallowing, chewing and yawning can be divided into 2 large groups, on which the further course of action depends:
| Causes | Classification | Peculiarities |
| Physiological - they are not accompanied by pain, do not require a visit to a doctor. | Congenital anatomical features of the jaw structure | Clicks can occur one-time or accompany a person throughout his life. |
| Spasm of the muscles of the pharynx | Occur during chewing and swallowing. | |
| Spasm of the muscles of the ear bones | May occur when swallowing, yawning. | |
| Pathological - are a deviation from the norm, accompanied by pain or other symptoms that cause discomfort. Require medical attention. | Joint pathology | Diseases of the joints, structural anomalies as a result of injuries, dislocations and other injuries of the jaw joints, loss of elasticity and fragility of the joints during the aging process. |
| Inflammatory processes | All kinds of diseases, accompanied by damage to various parts of the ear and nasopharynx. | |
| Malocclusion | Due to the uneven load on the jaw muscles, characteristic sounds may occur. The bite can be displaced due to mechanical injury (for example, as a result of an accident) or dental manipulations (poorly fitted filling, inappropriate prosthesis). |
Possible diseases
Clicking in the ear when swallowing or chewing is a common symptom that can become an alarm signal indicating the presence of the following diseases:
- Inflammatory diseases:
- otitis media is the most common cause of crackling;
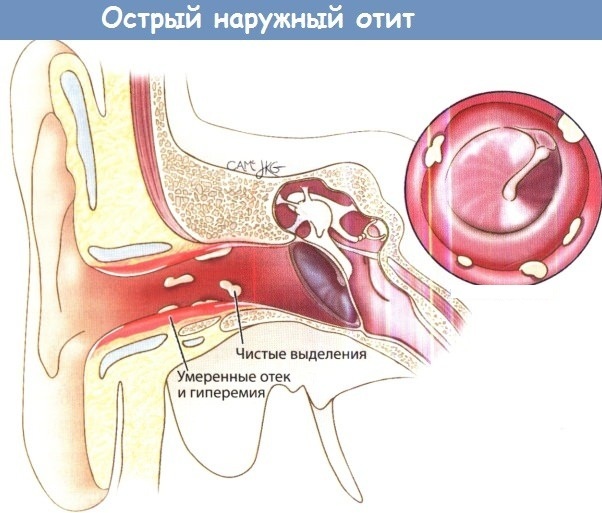
- pharyngitis - inflammation of the pharynx and auditory tube;
- colds and SARS - accompanied by swelling of the nasopharynx and increased production of mucus;
- inflammation of the oral cavity (stomatitis, herpes, candidiasis, glossitis, dysbiosis);
- Joint diseases:
- arthritis of the maxillofacial joint;
- arthrosis of the maxillofacial joint;
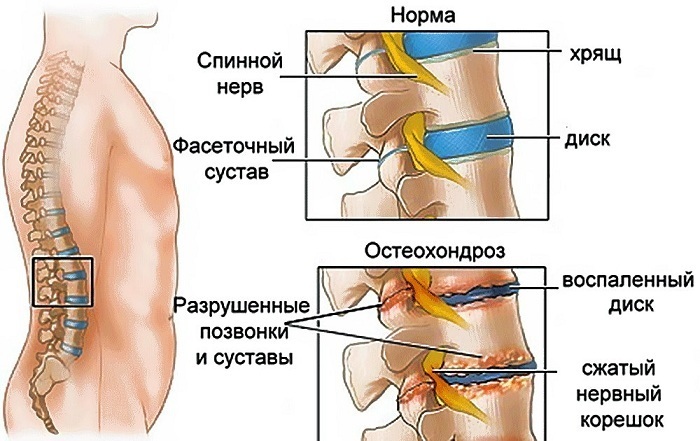
- cervical osteochondrosis.
- Other diseases, one of the symptoms of which may be clicks in the ears:
- allergic reactions, accompanied by nasopharyngeal congestion and inflammation;
- diabetes;
- jumps in blood pressure with hypertension or hypotension;
- anemia;
- sulfur plug.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of clicks in the ears involves examination of the ENT organs and is reduced to a visual examination, drawing up a general picture of the patient's health, laboratory and instrumental research, hardware methods.
- Anamnesis - collection of information about the patient, the presence of chronic and hereditary diseases, associated symptoms.
- Examination and palpation to identify pain, swelling, determining whether the color of the mucous membranes matches the norm, and the presence of purulent-serous contents in the nasopharynx and auricles.
- The examination of the nose and paranasal sinuses is carried out by the following methods:
- rhinoscopy - examination of the nasal passages and the nasal septum using a special mirror (or ear funnel for babies);
- the study of the olfactory and respiratory functions of the nose - carried out by the Voyachek method (check patency of the nasal passages) and using an olfactometer (a device for studying the reaction to odorous substances);
- nasal endoscopy - examination of the nasal passages using an endoscope equipped with a video camera (the most informative and modern diagnostic method);
- puncture of the paranasal sinuses - removal of the contents from the cavity of the nasal sinuses for laboratory research.
- Ear examination is carried out by methods:
- otoscopy - examination of the walls, cartilage, membranes of the external passage and middle ear using the ear funnel and magnifying devices;
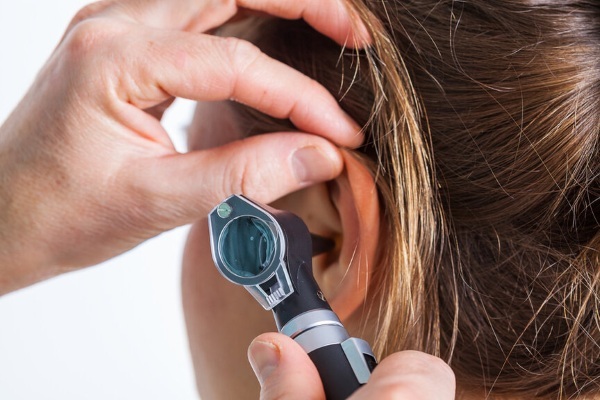
- study of the patency of the auditory tube - using the method of Toynbee, Valsalva and blowing the tubes;
- acumetry (audiometry) - the study of hearing acuity using sound waves of various frequencies.
- Throat diagnostic methods:
- pharyngoscopy - examination of the mouth and throat using special mirrors and a spatula;
- epipharyngoscopy (posterior rhinoscopy) - examination of the nasopharynx using mirrors, spatulas and dilators;
- hypopharyngoscopy - examination of the larynx with a laryngoscope or a special mirror.
It clicks in the ear when swallowing for various reasons, which general diagnostic methods will help the doctor to establish:
- laboratory blood tests (general, biochemical and serological analysis);
- laboratory tests of swabs from the nose, pharynx and ears;
- X-ray of the nose and paranasal sinuses, jaw;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the sinuses of the nose, inner and middle ear, jaw;
- arthrography;
- arthroscopy;
- computed tomography of ENT organs;
- ultrasound procedure.
When to see a doctor
Clicks in the ear, which cause discomfort when swallowing, chewing or opening the mouth, and occur repeatedly, require immediate medical attention if you have symptoms:
- ear pain;
- noise and congestion;
- nausea and dizziness;
- increased body temperature and discharge of purulent contents from the ears;
- impaired coordination of movements;
- distraction of attention.
Clicking in the ears with colds usually does not require referral to a specialist and goes away on its own after recovery. If these symptoms continue to manifest on their own, you should immediately consult a doctor.
To determine whether a doctor's help is required, one should be guided by the basic rule: spontaneous clicks without pain will pass on their own (if they are not regular), and any manifestation of pain is an alarming signal and a reason to consult a doctor.
Since the unpleasant sensations are localized in the ear, the otorhinolaryngologist is the first specialist to be visited. The doctor will form an overall picture of the patient's ENT health status and decide whether further consultation of other specialists: phonator, neurologist, dentist, surgeon, orthopedist, rheumatologist, manual therapist.
Prophylaxis
To minimize the risk of recurring symptoms of clicking in the ears and prevent the development of serious medical conditions, simple preventive measures should be followed:
- observe the hygiene of the oral cavity, nasal passages and ears;
- do not use third-party hygiene products that are not intended for these purposes;
- eat right and exercise to strengthen the immune system;
- avoid hypothermia;
- carry out the prevention of colds in the cold season;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- monitor the level of humidity in the room (especially during the heating season);
- visit the dentist periodically;
- timely treat emerging inflammations and colds;
- do not self-medicate.
Treatment methods
Clicking in the ear when swallowing with pain is a serious reason to consult a doctor for a prescription of treatment. To make it run faster, it should be combined with traditional medicine methods, after consulting a doctor.
Medications
The method for treating unpleasant tinnitus will depend on the underlying cause of the symptom.
With muscle spasms, muscle relaxants are prescribed to relieve tension:
- Baklosan - tablets are taken with meals, 5 mg 3 times a day, with a gradual increase in the daily dose to 25 - 75 mg (depending on individual indications), the cost is 250 - 550 rubles.
-
Sirdalud - Prescribe 2-4 mg of the drug 3 times a day, gradually increasing the dosage, if necessary, up to 24 mg per day. The course of treatment should not exceed 12 days. The drug has a pronounced hypnotic effect. The cost is 200 - 500 rubles.
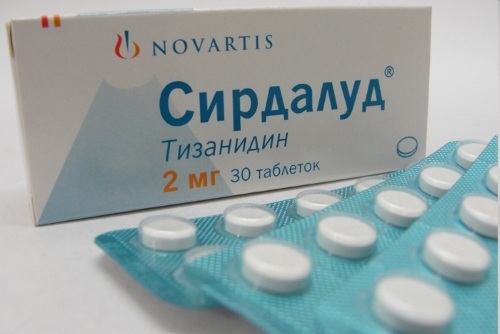
- Tizanidineand Tizanil - analogs of Sirdalud in effect and method of application, but with a more democratic price - from 130 rubles. per packing.
- Mydocalm - tablets are taken after meals, the daily dose can be 150 - 450 mg, and the course of treatment is up to 1 month. The solution is administered intravenously (100 mg per day) or intramuscularly (100-200 mg per day). The cost of the drug is 350 - 600 rubles.
ARVI treatment is based on taking:
- Antiviral drugs (Remantadin, Arbidol, Tamiflu, Teraflu, Orvirem, Isoprinosine, Viferon) - available in the form of tablets or powder, require increased intake in the first days of a cold with a gradual decrease dosage. Apply for 3 - 5 days.
- Immunostimulating drugs (Anaferon, Interferon, Ingavirin, Kagocel) - are used not only for colds, but also during epidemics of colds as prevention and strengthening immunity.
- Symptomatic drugs for:
- rinsing the nose (Aquamaris, Aqualor, Dolphin), relieving nasal congestion and swelling (Tizin, Sanorin, Afrin, Nazol, Vibrocil).
- elimination of pain and sore throat - sprays (Ingalipt, Hexoral, Miramistin, Tantum Verde, Propasol), tablets and lozenges (Lizobakt, Faringosept, Strepsils, Doctor Mom).
In the presence of an infection of bacterial origin (including with otitis media and bacterial inflammatory processes in the nasopharynx), the following are prescribed:
- Antibacterial drugs in the form of:
- drops (Polydex, Otipax, Sofradex, Normax, Anauran), which are instilled into the ears 2-3 times a day, no more than 10 days. The cost of drugs varies from 200 to 500 rubles;
- tablets and capsules, the dosage of which is selected by the doctor individually (depending on the severity of the disease), and the course of treatment cannot exceed 10-14 days:
- Amoxicillin - from 35 rubles;
- Amoxiclav - from 100 rubles;
- Augmentin - from 150 rubles;
- Azithromycin - from 70 rubles;
- Flemoxin Solutab - from 230 rubles;
- Cephalexin - from 60 rubles.
- injections - the dosage depends on the age and body weight, the severity of the disease, the course of treatment is no more than 14 days:
- Augmentin - from 135 rubles;
- Cefazolin - from 25 rubles;
- Ceftriaxone - from 23 rubles;
- Ampicillin - from 15 rubles.
Children with antibiotic therapy are prescribed drugs in the form of suspensions (Suprax, Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Macropen).
Additionally, with otitis externa, antibacterial ointments can be prescribed - Levomekol and Tetracycline.
- Anti-inflammatory and pain relievers:
-
Nise - in the form of tablets (1 tablet 2 times a day) or gel (externally, around the auricle up to 4 times a day), no more than 10 days. The cost of the drug is from 180 to 550 rubles.
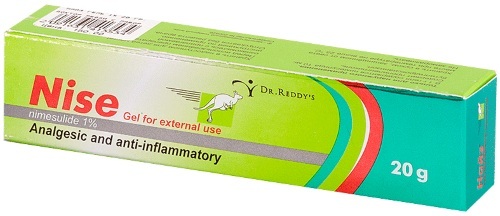
- Diclofenac - in the form of a gel or ointment up to 4 times a day, in the form of tablets - up to 150 mg a day. Cost - from 30 to 300 rubles.
- Triderm, Akriderm - hormonal anti-inflammatory ointments are used 2 times a day, no more than 3 - 4 weeks. Cost - from 150 to 900 rubles.
- Ibuklin - 3 times a day, 1 - 2 tablets. The price of the drug is from 100 to 250 rubles.
- Ibuprofen - from 200 to 800 mg per dose, up to 3-4 times a day. The course of treatment should not exceed 3 weeks. Cost - from 20 to 170 rubles.
- Ketanov - 10 - 20 mg up to 3 - 4 times a day, no more than 2 days in a row. Cost - from 50 to 200 rubles.
In the presence of fungal infections, antimicrobial ointments (Clotrimazole, Miconazole) should be used. In cases of allergic reactions or swelling of the nasopharynx, it is advisable to use antihistamines (Zodak, Zyrtec, Suprastin, Tsetrin, Loratadin, Cetirizin).
For disinfection, inflamed areas are treated with solutions of Chlorhexidine, Boric acid or Miramistin.
Traditional methods
Traditional methods of treating clicks in the ears are aimed at eliminating unpleasant symptoms with the help of warming up and massage.
With the permission of the doctor, you can apply a warming compress to the sore ear 1 - 2 times a day, up to 7 days:
- Alcoholic - mix alcohol or vodka with water in a 2: 1 ratio, apply to a gauze bandage, in which a hole for the auricle has been previously cut. Place the bandage around the ear without blocking the ear canal. Fix the bandage and do not remove it for 2 hours.
- With camphor oil - heat the oil to 40 C in a water bath and make a bandage in the same way. You can wear it without removing it for up to 6 hours.
-
With camphor alcohol - dilute alcohol with water in a ratio of 1: 2 and heat up to 40 C in a water bath, do not remove the bandage for up to 2 hours.
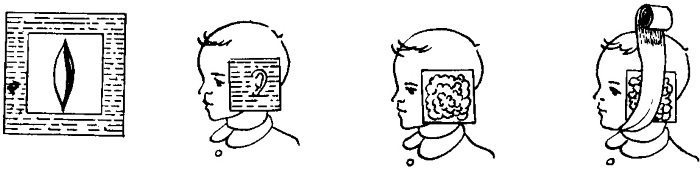
If it snaps in your ear, try a heating bandage. If the condition worsens, stop the procedure!
Before applying any warming compress, you should first lubricate the skin around the ear with a fat cream.
You can also warm your ear with salt. To do this, heat ordinary table salt (with large crystals) or sea salt in a dry frying pan for about 5 minutes, until crackling appears. Then pour the salt into a bag made of natural fabric (linen or cotton) and warm up the ears for 3 minutes. each one. After carrying out any warming procedures, it is not recommended to go outside for 2 hours.
In addition to warming up, to speed up the healing process, you can use cotton turundas dipped in aloe juice, geranium or St.John's wort broth (1 tbsp. l. per glass of water). Tampons should be left in the ears for 2 to 3 hours.
Clicks in the ear when swallowing, as a possible reaction to stress and overexertion - this is a reason for taking a relaxing bath with aromatic oils and decoctions of chamomile, calendula, string or sage. To prepare the broth, 3 tbsp is required. l. Pharmacy herbs pour 5 liters of water and boil for 10 minutes. Then insist for an hour and strain by adding the broth to the bath.
Among essential oils, the best relaxing and calming effects are:
- lavender;
- the Rose;
- geranium;
- Orange;
- mint;
- ylang-ylang;
- bergamot.
To prepare a bath, it is enough to add only 6 - 8 drops to warm water. An effective method for eliminating pain and relaxing muscles is ear massage.
It is carried out by:
- massaging the tragus and light pressure;
- stretching the auricle in different directions;
- point massage with fingers of the auricle from top to bottom;
- rubbing the earlobe;
- movements around the auricle clockwise and counterclockwise.
Particular attention should be paid to pain points; no more than 5 - 7 s are allotted for each exercise. (up to 10 approaches in 1 session). It is recommended to do massage for 3 - 5 minutes. a day, until recovery.
There are also a variety of acupressure techniques that have a targeted effect on certain organs and muscles. For their implementation, a preliminary study of the location of biologically active points is required according to special schemes and drawings.
Other methods
To achieve the maximum effect of the medications used in the treatment and to speed up the healing process, physiotherapy methods are additionally prescribed:
- physiotherapy;
- massage;
- electrophoresis;
- magnetotherapy;
- galvanization;
- ultrasound therapy;
- halotherapy;
- vibrotherapy;
- cryotherapy;
- hydromassage.
In the absence of positive dynamics with the methods of conservative treatment, surgical intervention may be required:
- septoplasty - correction of the curvature of the septum;
- tonsillectomy - removal of the tonsils;
- galvanic acoustics - cauterization of tissues with electric current pulses;
- conchotomy - excision of the nasal mucosa;
- adenoidectomy - removal of the adenoids;
- myringotomy - excision of the tympanic membrane to remove fluid;
- ultrasonic disintegration of the turbinates - cauterization of tissues using ultrasound;
- sinusitis - opening the sinuses of the upper jaw for washing and cleansing.
Possible complications
If you do not contact a specialist in a timely manner, clicks in your ears can lead to complications of ongoing diseases, the symptom of which they are:
- change in the ear membrane or its perforation;
- the development of hearing loss or hearing loss;
- the appearance of benign tumors (cholesteatoma);
- the overgrowth of otitis media and arthritis into a chronic form of the disease;
- encephalitis;
- meningitis;
- brain abscess;
- deformation of the jaw joints;
- joint stiffness and the appearance of adhesions;
- development of suppuration;
- paresis of the facial nerve;
- disruption of the digestive tract.
Clicks in the ears when swallowing is a phenomenon that often defies explanation and arises from nowhere. If they become regular and are accompanied by the manifestation of other pathological symptoms, you should not postpone the visit to the doctor until later.
Author: Anna Lalochkina
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Ear Videos
About ear and hearing diseases: