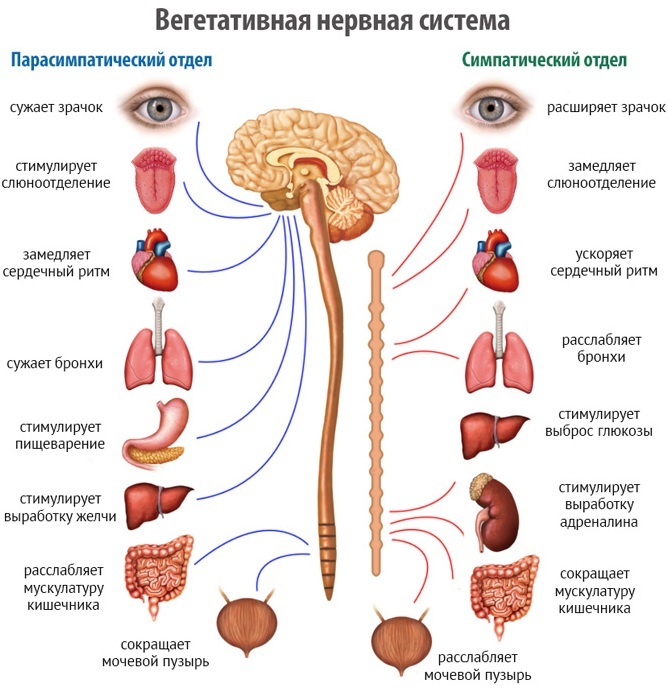
VSD is autonomic dysfunction (it is also often called vegetative dystonia), which is characterized by a violation of the functionality of the autonomic nervous system. In fact, pathology is a whole complex of symptoms and manifestations, the causes of which can be very different.
Until now, in the medical field, there are disputes about whether it is possible to attribute VSD to pathologies at all and to make a similar diagnosis for patients. Some people think that autonomic dysfunction is just a mental problem.
Nevertheless, about 10-15% of children and about 70% of the adult population suffer from VSD. Therefore, some experts call such symptoms only a manifestation of minor deviations that cannot be called a disease.
Other doctors (there are much more of them), on the contrary, are inclined to believe that this manifestation is a serious pathology that requires treatment.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about VSD
Views
There are several types of IRR:
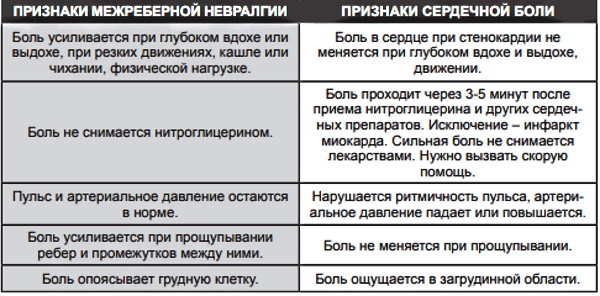
- Cardiac. The patient has a heartbeat of up to 90 beats / min. In this case, a person complains of severe pain in the region of the heart. Or, conversely, the heart rate slows down to 50-60 beats / min. There may also be signs of arrhythmia, increased sweating.
- Hypotonic. In this case, the patient experiences a rather sharp decrease in blood pressure (blood pressure), which can reach up to 100 mm. rt. Art. Additional symptoms include sweating, constant chills, weakness, and pale skin. It becomes difficult for a person to breathe, he complains of disturbances in the functioning of the intestines (diarrhea, heartburn).
- Hypertensive. The main symptom of this type of VSD is a severe headache. Also, patients complain of the appearance of a shroud or goosebumps, nausea, vomiting, and loss of appetite. At the same time, there are signs of severe nervous overstrain. A person experiences fear, but cannot explain what exactly he is afraid of. Sweating increases, coordination is impaired. This manifestation of VSD differs from hypertension in that it is not necessary to take medications with an autonomic disorder. The attack usually goes away after the person has calmed down and got some rest.
- Vagotonic. The main symptom of this form of pathology is shortness of breath. Also, patients have a slow heartbeat, increased salivation. Often there is a decrease in blood pressure, problems with the work of the gastrointestinal tract appear.
- Mixed. This type of pathology occurs most often in medical practice. Symptoms in this case may include manifestations of several types of VSD at once. Additional symptoms often appear, for example, meteorological dependence, sleep problems. But most often, patients note the presence of irritability, headaches, panic attacks, and blood pressure surges. This seriously complicates the process of making a diagnosis, since the patient complains of many different symptoms at once. Therefore, in this case, a whole range of diagnostic measures is required.
Stages and degrees
According to the severity of the disease, there are 3 degrees of severity of the disease:
-
Easy (also called latent or latent). The patient has no symptoms of symptoms. Occasionally, there may be headaches and chest pains in the region of the heart. As a rule, this occurs after physical exertion or nervous strain, so a person does not attach importance to such symptoms. With an easy stage of pathology, vegetative-vascular crises do not occur. But even if they do happen (it happens very rarely), then there may be a break of several years between the two attacks.

- Average. In this case, the patient pays attention to more pronounced symptoms. For example, a person complains of general weakness and decreased performance. With moderate severity of VSD, crises may occur more often. After an exacerbation, a very short period of remission is observed.
-
Heavy. The patient is temporarily disabled, he may even be prescribed inpatient treatment. Symptoms in the severe stage are pronounced. Vegetative-vascular crises occur very often.

Specialists pay special attention to the stage of exacerbation. As a rule, it is seasonal. The deterioration of the patient's condition can be observed in the same period of the year. In female patients, exacerbation often occurs during menstruation or pregnancy.
| Season | Influence on a person with VSD |
| Winter | Exacerbation of VSD most often affects people with low immunity, those who often suffer from seasonal infectious diseases. |
| Spring | An exacerbation of the condition may be associated with psychological exhaustion or hypovitaminosis. This is due to a change in the length of daylight hours. A person becomes more lethargic, apathetic, panic attacks appear more often, pressure drops. |
| Summer | Exacerbation is caused by increased air temperature or humidity. Patients with VSD often complain of light-headedness, breathing problems. |
| Autumn | VSD is aggravated against the background of a depressive state, lethargy, depression. |
Vegetative dysfunction is a pathology that is subdivided into several more types. For example, an IRR can be generalized, systemic, or local. The latter type is distinguished by serious lesions of the peripheral NA. Generalized pathology manifests itself in the form of disorders affecting the so-called suprasegmental vegetative structures.
Symptoms
The symptoms of VSD may differ depending on the individual patient, the reasons that led to the pathology, the season and many other factors. Therefore, the symptomatology of vegetative-vascular dystonia is called variable.
However, experts have divided the symptoms into 2 main groups:
- 1Group. The patient complains of general symptoms. These include increased body temperature and sweating, increased anxiety, tremors of the limbs. Patients report that they literally feel their heart beating.
- Group 2. The symptoms are more specific. For example, a patient may be diagnosed with organ or system dysfunction on only one side of the body.
Autonomic dysfunction is a disease characterized by subjective symptoms that are not always detected during diagnostic measures.
These symptoms include:
- frequent dizziness and headaches;
- attacks of nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation;
- shortness of breath, angina pectoris and heaviness in the region of the heart;

- fainting;
- impotence in men and dysmenorrhea in women;
- bad mood, constant weakness, decreased performance;
- unpleasant sensations in the body, the appearance of "creeping creeps";
- swelling of the face after sleep;
- a constant feeling of fear of death;
- problems with urination.
As a rule, symptoms are grouped into syndromes. Their classification was developed by Nikitin and Savitsky. It is based on three syndromes: cardiac, hypertensive, and hypotensive.
Reasons for the appearance
Depending on the specific type of VSD, the following factors can be distinguished that affect the development of pathology:
- With the vagotonic type, the main reason is hormonal changes in the body. That is why this type of pathology is often found in adolescent children. Also, VSD of this type belongs to the category of hereditary pathologies, so the risk of the disease is much higher in those people who have relatives suffering from autonomic dysfunction.
- Sympathicotonic VSD is diagnosed more often in people of lean physique. As a rule, such patients are more faced with a strong adrenaline rush, which provokes a rapid heart rate. Also, this type of pathology occurs in those who suffer from nervous disorders and neuroses.
- Hypertensive autonomic dysfunction is usually associated with the tone of the sympathetic nervous system.
- Hypotonic VSD often occurs against the background of an increased tone of the parasympathetic nervous system. The vessels are in a relaxed state, which provokes a decrease in pressure. Patients often complain of headaches and a constant feeling of fatigue. This type of vegetative-vascular dystonia differs in that an exacerbation can occur against the background of physical or nervous overstrain.
- The cardiac form of the disease appears as a result of the development of pathology affecting the work of the cardiovascular apparatus. Doctors differentiate this type of VSD with heart diseases, such as coronary artery disease or myocardial infarction.
- VSD of the mixed type can appear from a variety of factors. For example, excitation in the sympathetic division of the ANS can lead to the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia.
Vegetative dysfunction can also be triggered by hormonal changes. This is a fairly common cause of VSD in adolescents.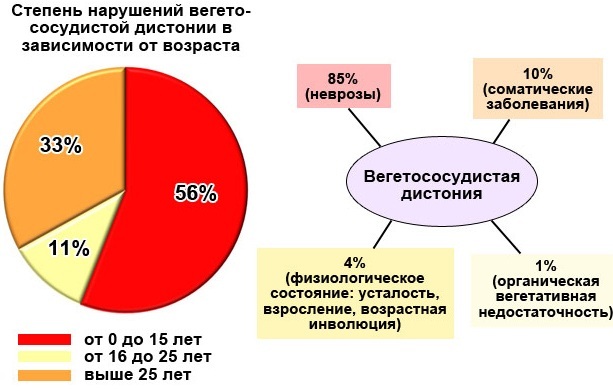
In addition, schoolchildren and students often suffer from overwork and nervous tension, which is caused by the preparation for exams and the learning process itself. At the same time, many adolescents lead a sedentary lifestyle, which also becomes a factor causing IRR.
In older patients, pathology can develop due to chronic diseases (for example, pancreatitis, peptic ulcer). Also, the cause of VSD can be alcohol abuse and smoking.
Another reason for the appearance of this syndrome is associated with mental and somatic disorders that were previously diagnosed in the patient. In this case, vegetative-vascular dystonia is a secondary dysfunction. Somatic diseases include arterial hypertension, gastrointestinal diseases. Mental disorders can manifest themselves in the form of depression, panic attacks.
There is a list of additional factors that can trigger the development of this disease.
For example, VSD can develop due to:
- improper sleep patterns, physical activity at work;
- high weight or even obesity of 1-3 degrees;
- decreased physical activity (VSD is often found in office workers) or too long stay at the computer, TV;
- sleep disorders, insomnia;
- chronic pathology that is at the stage of decompensation or infectious disease;
- immunodeficiency;
- constant stress;
- taking narcotic drugs or strong drugs of the psychostimulating category.
Diagnostics
Vegetative dysfunction is a pathology that is very difficult to diagnose due to the fact that there is no clear etiology of this disease. Accordingly, research begins to be carried out almost blindly.
First of all, the doctor should conduct a detailed examination and carefully examine the symptoms that the patient complains about. It is equally important to exclude cardiovascular diseases, since often the symptoms of VSD are the same as in heart diseases. At the next stage, the doctor must conduct a study of the respiratory system for the presence of possible pathologies.
Standard diagnostics include the following steps:
- Collecting anamnesis. It is important to tell your doctor about your parents' health problems. For example, did any of them have cardiovascular diseases before the age of 55?
- Determination of blood pressure and heart rate.
- Conducting electrocardiography and echocardiography.
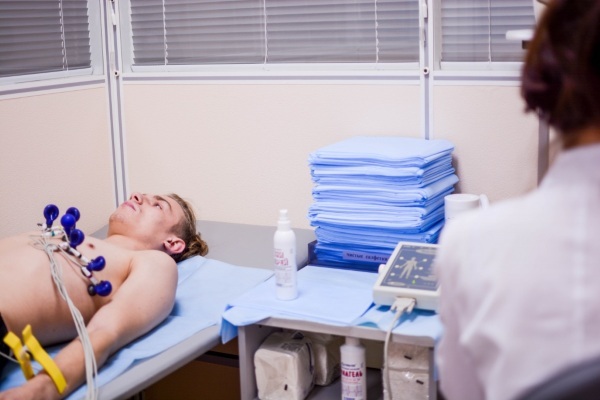
- Performing a general and biochemical blood test. This will allow to exclude organ pathologies, which led to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms.
- General analysis of urine.
- Radiography. The doctor should examine the chest organs.
- Bicycle ergometry. This study allows you to assess the patient's heart rate and rule out some diseases that could be a cause of concern.
Much attention is paid to differential diagnostics. As a rule, all the necessary research can be performed at the district clinic free of charge.
When to see a doctor
Which doctor you need to contact for diagnosis and treatment depends largely on the specific symptomatology. Typically, the patient visits a therapist first.
This doctor, on the basis of a person's complaints, directs him to a narrow-profile specialist:
- Gastroenterologist. An appointment with this doctor is sent for vomiting, intestinal colic, constipation and flatulence. Very often, with VSD, irritable bowel syndrome develops (the patient constantly thinks that he has diarrhea). The gastroenterologist directs the patient for ultrasound, CT or MRI. Endoscopy and, if necessary, biopsy are also performed.
- To a cardiologist. The patient is referred to this specialist if he has signs of tachycardia, bradycardia or other heart rhythm disturbances, pain and heaviness in the region of the heart or on the left side of the body.
- To a neurologist. This is a doctor who is directly involved in the treatment and diagnosis of VSD. People who have pronounced signs of dysfunction of the nervous department are referred to a neurologist. In this case, the patient has symptoms of neurosis. These signs include increased sweating, a constant feeling of anxiety, aggressive behavior, loss of strength, and persistent headaches.
- Psychologist. The specialist conducts an initial consultation, examines the cerebrospinal fluid, directs the patient to an ultrasound scan with the performance of Doppler ultrasonography of the cerebral vessels. Additionally, a duplex brain scan and X-ray examination of the spine are performed.
- To the urologist. This specialist is referred to those patients who complain of frequent urge to urinate, pain in the kidneys, discomfort in the lumbar region, insomnia.
- Endocrinologist. If the pathology was caused by a malfunction of the hormonal background, then the patient complains of a sharp loss or gain in weight, fatigue, sleep problems, and jumps in body temperature. Also, people show signs of neurosis, mood swings, sweating, and a feeling of thirst.
Prophylaxis
In order to prevent the development of pathology, the following recommendations must be followed:
- 1 time in 6 months to undergo a general examination of the body;
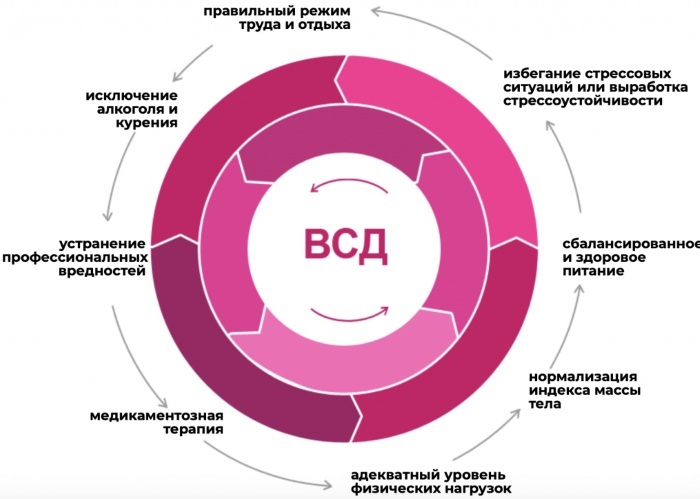
- timely treat infectious, somatic and endocrine diseases;
- do not lead a sedentary lifestyle, get enough sleep, do not do heavy physical work;
- take multivitamins (especially in the cold season and in spring, when many have allergies);
- do not abuse smoking and drinking alcohol;
- avoid stressful situations.
Treatment methods
Autonomic dysfunction is a medical condition for which there is no specific treatment. If the patient has symptoms of other pathologies that could provoke a complication in the form of VSD, then primary diseases must be treated.
If no pathologies were found during the diagnosis, then, as a rule, therapy includes taking sedatives, vitamins, and dieting. All these activities are aimed at improving the state of the nervous system.
Medications
Standard treatment for VSD includes taking several drugs, which are prescribed by the doctor:
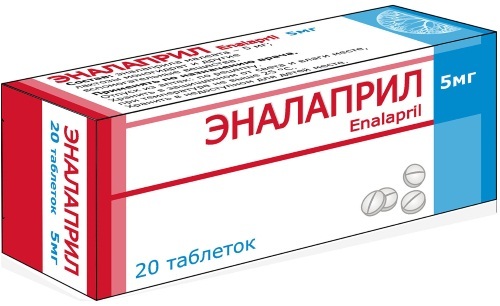
- With a cardiac form of pathology, prescribe Enalapril. It is an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor. The drug can be taken strictly according to the doctor's prescription, as it has side effects in the form of severe dizziness. It is necessary to take the drug at 2.5 mg per day. After a few days, the dose may be increased, but more than 80 mg should not be taken per day. The cost of the drug is about 20-30 rubles.
- Melaxen prescribed in case of heart rhythm failure against the background of the flowing VSD. This is a melatonin-type drug. It is recommended to take this remedy only for adults 1 tab / day half an hour before bedtime. You can take no more than 2 tablets per day. The cost of the drug is about 650 rubles.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe:
- Antidepressants. As a rule, drugs of this type are prescribed for severe forms of VSD.
- Psychotropic drugs.
- Beta blockers.
- Anti-asthenic drugs.
- B vitamins.
Traditional methods
There are several options for treatment with folk remedies:
- With clay. For this method of treatment, only purified clay without impurities and dirt is suitable (you can buy this only at a pharmacy). It must be diluted with water (1 tbsp. l. per glass of warm water) and take daily, reducing the amount of clay every day. You need to take the product until the dosage of clay is 1 tsp. l. After that, you need to take a break.
- From severe headaches with VSD will help baths with mustard powder.
 It should also be purchased from a pharmacy. To relieve pain symptoms and general relaxation, add 5 tbsp. To a small container of hot water. l. tablespoons of mustard powder. You should get a mass similar in consistency to thick sour cream. The mixture prepared in this way must be poured into a bath of water, the temperature of which should be about 39 ° C. In the bath, you need to lie down for about 7-10 minutes, after which you must immediately wrap yourself in a towel and lie under the blanket. To improve the effectiveness of this method, it is recommended to drink hot tea after taking a bath. However, you should not perform such procedures every day. A hot bath with mustard can be done 2-3 times a week.
It should also be purchased from a pharmacy. To relieve pain symptoms and general relaxation, add 5 tbsp. To a small container of hot water. l. tablespoons of mustard powder. You should get a mass similar in consistency to thick sour cream. The mixture prepared in this way must be poured into a bath of water, the temperature of which should be about 39 ° C. In the bath, you need to lie down for about 7-10 minutes, after which you must immediately wrap yourself in a towel and lie under the blanket. To improve the effectiveness of this method, it is recommended to drink hot tea after taking a bath. However, you should not perform such procedures every day. A hot bath with mustard can be done 2-3 times a week. - Tea with cognac. Unlike previous methods, this treatment is not suitable for children. Adults with VSD who suffer from a decrease in blood pressure in the morning are advised to drink daily a mug of hot strong tea with the addition of 1 tsp. l. cognac.
Other methods
Phytotherapy has found wide application in the treatment of VSD.
For the prevention and treatment of pathology, natural remedies are used:
- Adaptogens. These drugs include infusion of ginseng, lemongrass, and Siberian ginseng. Drugs of this type stimulate metabolism, increase immunity and bioenergetics.
- Valerian, yarrow, and thyme help to reduce general anxiety, improve sleep and psycho-emotional state. Also, these plants have a positive effect on the heart rate, stabilizing it. Means of this type can be given to children. The dosage in this case depends on the patient's age (how old the child is, as many drops of the drug are needed). Adults are advised to take these remedies three times a day, 20-30 drops diluted in a little water.
Physiotherapy will help get rid of the symptoms that bring physical discomfort. One of her most effective treatments is electrotherapy. To relieve unpleasant symptoms, magnetic and electric fields are used.
Also, electrophoresis and galvanization can be attributed to this category of therapeutic measures. The first type of treatment is applicable to patients suffering from hypertensive syndromes and cardiac arrhythmias. Galvanization is necessary to stimulate metabolic and trophic processes. It also improves blood circulation.
In addition, physiotherapy includes:
-
Electric sleep. Similar treatment is used for the hypotensive form of the VSD. Therapeutic procedures are carried out every day. The course of treatment is 20 days.
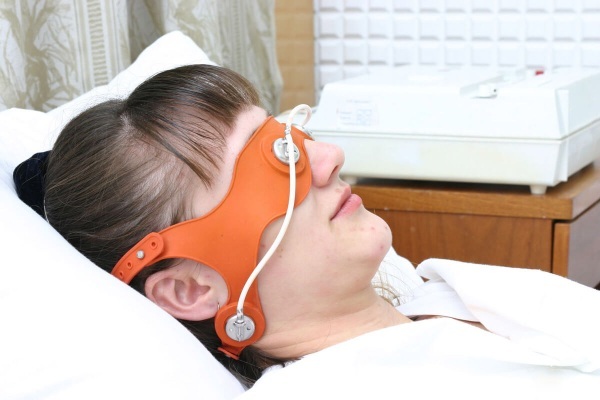
- Aeroionotherapy. In this case, special aeronizers are used, which are suitable for individual and collective use. In fact, we are talking about the ionization of the air in the room. It is saturated with negatively charged ions, which has a positive effect on the condition of patients. Thanks to this treatment, blood pressure and heart rate stabilize, headaches decrease, and weakness disappears.
Possible complications
If left untreated, the patient may develop a paroxysmal state. In this case, the person needs urgent medical attention. This condition is very dangerous because it provokes the strongest panic attacks and vegetative crises.
This condition manifests itself:
- excessive sweating;
- rapid heart rate (heartbeat can be up to 90 beats / min);
- shortness of breath, choking;
- strong fear of death.
Symptoms become less pronounced between attacks. However, if left untreated, seizures will become more frequent.
As a rule, autonomic dysfunction does not flare up immediately, so there is ample time for a correct diagnosis. This pathology responds well to treatment. At the same time, in order to get rid of mild manifestations of the disease, you do not need to resort to taking potent drugs. Natural remedies are often sufficient.
Video about VSD
Malysheva about vegetative-vascular dystonia: