Epilepsy is a pathology of the nervous system of a chronic nature, which is manifested by seizures, severe impairment of respiratory, sensory, autonomic and mental functions.
It is impossible to stop the onset of seizures. But, properly selected treatment can reduce their number and significantly improve the patient's quality of life.

The diagnosis is made on the basis of multiple recurring seizures. A single episode does not give grounds to assert that the patient has epilepsy. The disease is associated with the occurrence of excessive neuronal connections
Record content:
-
1 Views
- 1.1 Tonic-clonic
- 1.2 Absances
- 1.3 Myoclonic
- 1.4 Tonic
- 1.5 Clonic
- 1.6 Atonic
- 1.7 Simple focal
- 1.8 Complex focal
- 2 Symptoms and Signs
- 3 Causes
-
4 Diagnostics
- 4.1 Electroencephalography (EEG)
- 4.2 Computed tomography (CT)
- 4.3 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- 4.4 General blood analysis
- 4.5 Biochemical blood test
- 4.6 General urine analysis
-
5 Treatment methods
-
5.1 Medicines
- 5.1.1 Phenobarbital
- 5.1.2 Phenytoin
- 5.1.3 Ethosuximide
- 5.1.4 Lamotrigine
- 5.1.5 Topiramate
- 5.1.6 Clonazepam
-
5.2 Folk remedies
- 5.2.1 Infusion of motherwort and wormwood
- 5.2.2 Infusion of lemon balm, St. John's wort and motherwort
- 5.2.3 Infusion of medicinal valerian
- 5.2.4 Oregano decoction
- 5.3 Exercise therapy
- 5.4 Hardware physiotherapy
- 5.5 Hydrotherapy
- 5.6 Diet
-
5.1 Medicines
- 6 Possible consequences and complications
- 7 Epilepsy Videos
Views
In medicine, there are several classifications of the disease, the main of which is associated with the etiology of epileptic syndromes:
| Idiopathic epilepsy | Due to genetic factors. |
| Symptomatic epilepsy | Associated with secondary brain lesions - tumor, trauma, cyst. |
| Cryptogenic epilepsy | The reasons for the appearance have not been established. |
According to the age of patients, the following forms of the disease are distinguished:
- forms of newborns (up to 3 months);
- infant (up to 1 year old);
- children (up to 6 years old);
- youth (12-14 years old).
By the extent of the involvement of the cerebral hemispheres, 2 groups of seizures are distinguished:
- Generalized - both hemispheres are involved;
- Focal - limited areas of the brain are involved.
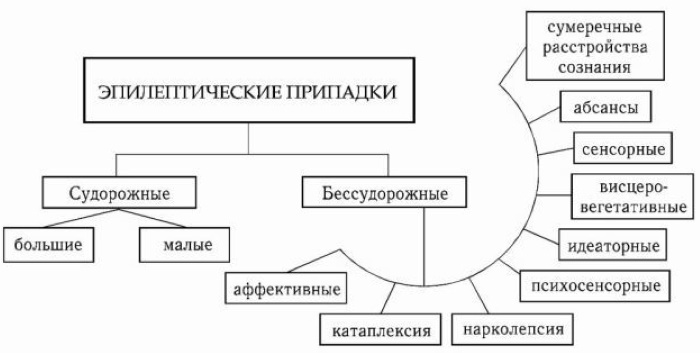
Each of the groups is subdivided into types:
| Generalized | Focal |
| · Tonic-clonic; · Absences; · Myoclonic; · Tonic; · Clonic; · Atonic. |
· Simple; · Complex. |
Tonic-clonic
They are bilateral symmetrical motor seizures characterized by loss of consciousness. The attack consists of 2 phases - muscle tone and rhythmic twitching.
At this time, the human body tenses and stretches, the limbs take a bent position. He falls to the ground convulsing. Urinary incontinence may occur. Foam comes out of the mouth. The attack lasts a few minutes.
Absances
Short attacks of 2-5 seconds with impaired consciousness, but without loss of consciousness. Most often found in childhood and adolescence. From 2-3 to 50-100 seizures can be observed per day.

There are 2 types of absences:
- simple - are manifested by fading for 2-3 seconds and with an abrupt stop of the activity being performed.
- complex - accompanied by temporary motor anomalies.
Myoclonic
Represented by single or repeated tremors of the limbs. A person may unknowingly throw objects in their hands or fall on their buttocks while sitting on a chair.
Tonic
Twitching not only of the limbs, but also of parts of the body, accompanied by muscle tension. The duration of the attacks does not exceed 25 seconds. There may be eye rolling or shortness of breath due to tension in all muscles.
Clonic
Rare attacks, expressed by repeated twitching and muscle spasm. The period of muscle tension is abruptly replaced by relaxation. The attack lasts 5-10 seconds.
Atonic
Expressed in sudden falls without convulsions. This is due to a sharp loss of muscle tone. The attack lasts 10-15 seconds.
Simple focal
Seizures are not associated with loss of consciousness. A person may feel sharp abdominal pains, headaches, or see “flies” and spots in front of his eyes. You may also experience sudden feelings of increased anxiety or euphoria. Sometimes such an attack precedes a complex focal attack.
Complex focal
An attack consists of 3 phases:
- sudden cessation of the activity being performed (the gaze becomes unconscious, the consciousness is clouded)
- the beginning of automatic uncontrolled actions - twitching, smacking lips, fiddling with clothes or accessories;
- exit from unconsciousness and disorientation in space.
Symptoms and Signs
Epilepsy (treatment, to stop seizures with the help of which is associated with medications) manifests itself in different ways, depending on the form and type.

The first signs of idiopathic epilepsy appear at the age of 5-15 years. Symptomatic epilepsy can occur at any age. Signs of any type of pathology are associated with impaired consciousness and muscle tension.
Scientists identify 4 characteristics inherent in seizures:
- sudden onset of an attack;
- short duration - from 2 seconds to 2 minutes;
- the ability of the attack to stop on its own;
- the stereotypical nature of the seizures.
The most difficult manifestations are tonic-clonic seizures, the development scenario of which is the same in all cases:
- The onset of an attack is associated with difficulty breathing. The patient may moan, scream, or bite their tongue. Then he loses consciousness, falls. The patient's head is thrown back, the limbs are extended.
- After 10-20 seconds, muscle contraction and relaxation begins, which is accompanied by involuntary urination. Foam comes out of the patient's mouth. The eyes roll.
- After 30-60 seconds, muscle contractions stop, the person returns to consciousness. He is disoriented, his thoughts are confused.
In other forms of epilepsy, loss of consciousness is not observed.
Attacks can be expressed:
- numbness of the limbs;
- momentary clouding of consciousness;
- gustatory and auditory hallucinations;
- optical illusions;
- disorientation in space;
- smacking his lips;
- active rotation of the head from side to side.
Causes
Epilepsy can be hereditary or acquired. One of the main causes of pathology is called a violation of the activity of genes that are responsible for the work of sodium, potassium, hydrogen channels in the nerve cell.

It sharply increases its activity, triggers certain processes in the brain, which provokes the appearance of seizures. Epilepsy can be caused both by genetic abnormalities that affect the functioning of nerve cells, and by specific genes that provoke the development of the disease.
The causes of acquired epilepsy are:
- traumatic brain damage;
- brain tumors;
- transferred meningitis or encephalitis;
- intoxication with harmful substances - mercury, lead, carbon monoxide;
- stroke.
Diagnostics
Epilepsy (treatment, it is possible to stop seizures with the help of which, it is prescribed after the examination) involves a careful collection of anamnesis to make the correct diagnosis. Diagnostics consists of laboratory and instrumental research methods.

The initial stage of the examination consists of an oral questioning at a neurologist's appointment. The doctor clarifies the circumstances in which the attack occurred, finds out what sensations preceded it and how long the attack itself lasted.
If the patient finds it difficult to answer the questions, a person who has witnessed an epileptic seizure is interviewed. Also, the doctor determines the presence of concomitant pathologies or abnormalities.
Among the instrumental research methods, the most valuable are:
Electroencephalography (EEG)
Electroencephalography (EEG) is a diagnostic method for studying the state of the brain substance. Examinations are carried out using a special device in the form of metal electrodes, which are applied to the scalp. The device detects brain vibrations, amplifies and depicts them on a monitor or paper in the form of waves.
In patients with epilepsy, epileptiform activity is observed. Brain vibrations are sharp waves and peaks that stand out against the background of normal activity.
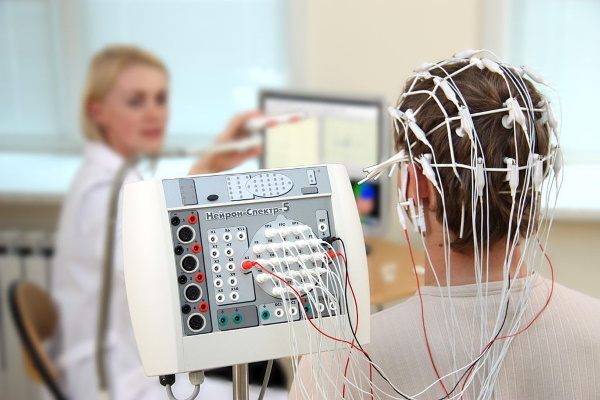
EEG allows you to understand in which part of the brain the pathological discharge originates, which becomes the cause of the attack. No special training is required to conduct the study. The cost of diagnostics is 2500-4000 rubles.
Computed tomography (CT)
Computed tomography (CT) - X-ray examination with taking step-by-step images and creating a complete picture of the area being examined. The rays that are projected by the X-ray tube of the tomograph affect the area under study at different angles.
The sensors of the device receive data on layer-by-layer scanning, which are processed and supplied in the form of an image. The picture shows abnormalities in the structure of the brain - scars, hemorrhages, damage caused by trauma. The duration of the study is 3-5 minutes. CT cost - 3500-4000 rubles.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a high-resolution 3D visualization of internal organs. When conducting an MRI, the state of the structures of the brain is assessed, the features of its structure are revealed.
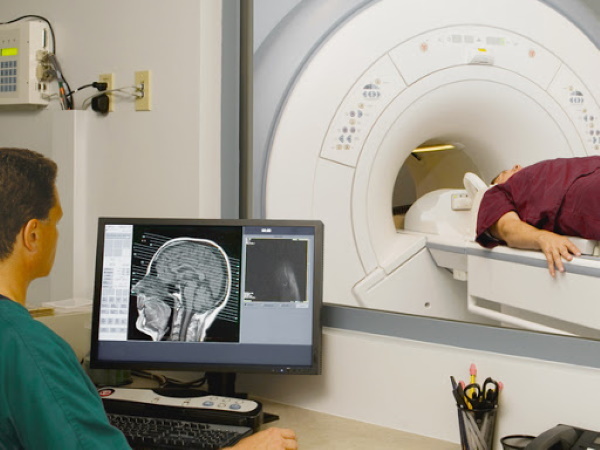
MRI is used for symptomatic epilepsy caused by structural changes in the brain. The MRI machine is a large cylinder with holes. The patient is positioned on a movable table inside the device. A device that sends and receives radio waves is attached around the circumference of the head.
The tomograph takes a series of images, which are further deciphered. The procedure takes about 20-30 minutes. The cost of an MRI scan is from 6,000 rubles. To identify the nature of an epileptic seizure, in addition to describing clinical manifestations and instrumental diagnostic methods, laboratory tests are prescribed:
General blood analysis
A general blood test is a medical analysis that allows you to assess the content of hemoglobin in the blood, as well as erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets and also to study the color index. For research, venous or capillary blood is used. The cost of the analysis is 250-300 rubles.
Biochemical blood test
A biochemical blood test is carried out to assess the general condition of the body. The analysis reveals indicators such as total protein, urea, creatine, cholesterol, bilirubin and amylase. Venous blood is used as a biomaterial. Analysis price - 400-600 rubles.
General urine analysis
General urine analysis is a study that determines a number of chemical and organoleptic characteristics of urine.
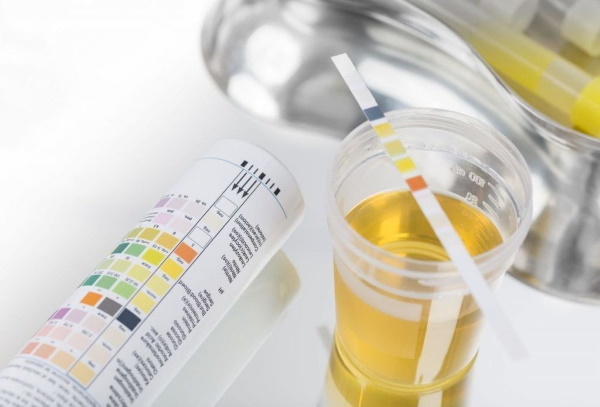

The odor, foaminess, transparency of the biomaterial, as well as density, acidity, the presence of sugar, protein and ketone bodies are assessed. Analysis cost - 200 rubles.
Treatment methods
Epilepsy (treatment, with the help of which to stop seizures, consists of a set of measures) has different forms of manifestation, therefore, the appointment of therapy has an individual character.
The selection of medicines is carried out taking into account the age characteristics of the patient, the nature and duration of the attacks, the presence of concomitant diseases.
Medicines
Epilepsy is treated with anticonvulsant drugs. As means of this group, different pharmacological actions are used - barbiturates or tranquilizers. They weaken the processes of excitation and enhance the processes of inhibition in the central nervous system.
Modern anticonvulsants are divided into basic therapy and new generation drugs.
Basic therapy drugs include the following drugs.
Phenobarbital
Phenobarbital is a hypnotic and sedative drug that reduces the excitability of neurons of the epileptogenic focus and the spread of nerve impulses. It has anticonvulsant, muscle relaxant and antispasmodic effects.

Adults are prescribed 50-100 mg 2 times a day. The duration of treatment is determined individually.
Phenytoin
Phenytoin is a non-sedating anticonvulsant. The drug does not provoke depression of the central nervous system. It has a membrane stabilizing, antiarrhythmic and hypotensive effect.
The agent is prescribed orally after meals for 0.1-0.3 g. The drug has a long half-life of 22 hours, so it should be taken no more than 2 times a day.
Ethosuximide
Etosuximide is a pill formulation that reduces the incidence of minor seizures and epileptiform seizures. The action of the remedy is due to the suppression of the motor centers of the cerebral cortex.
The dosage of the drug is determined individually. The starting dose for adults is 5-10 mg per kg of body weight. Then the dose is increased by 5 mg per 1 kg of body weight every week. The maximum daily dose is 30 mg per 1 kg of body weight.
Lamotrigine
Lamotrigine is an anticonvulsant drug that reduces the pathological activity of neurons without suppressing their functions. It is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration of the drug in the blood is observed 2-3 hours after administration.
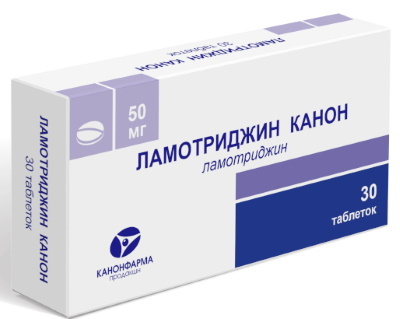
Adults and children over 12 years old are prescribed 25 mg 1 time per day for 14 days. Then the dose is increased to 50 mg for another 2 weeks.
Topiramate
Topiramate is a drug belonging to the class of sulfate-substituted monosaccharides. The tool blocks and suppresses the excessive activity of neural connections. The drug is prescribed as monotherapy.
Adults should take 25 mg of topiramate at bedtime for 1 week. Then the dose is exceeded by 25-50 mg per day. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 500 mg per day.
Clonazepam
Clonazepam - tablets that have sedative, muscle relaxant and anticonvulsant effects. In large quantities, it causes a number of side effects: drowsiness, dizziness, weakness, impaired memory and speech.
Adults are prescribed 1.5 mg of the drug, divided into 3 doses. Every 3 days, the dosage is increased by 0.5-1 mg.
Folk remedies
Epilepsy (a treatment to stop seizures with the help of which can be based on the use of folk recipes) lends itself to therapy with special herbs. For the treatment of pathology, there are many schemes, the selection of which is carried out individually.
In combinations, the following plants are most often used:
- calamus;
- arnica;
- valerian;
- oregano;
- St. John's wort;
- melissa;
- motherwort.

The listed plants have anticonvulsant, sedative, muscle relaxant properties. Preparations based on herbal ingredients are taken within 4-12 months. During the treatment period, the regimens and combinations may change. The most effective folk remedies include:
Infusion of motherwort and wormwood
You need to take 20 g of angelica root, 10 medicinal valerian, 10 g of motherwort and 20 g of wormwood. Mix dry ingredients in a separate container. 3 g of the resulting mixture must be poured with 1 glass of boiling water, cover with a lid and let it brew for 1 hour. The infusion should be taken 3 times a day for 1 glass.
Infusion of lemon balm, St. John's wort and motherwort
It is necessary to mix 10 g of oregano herb, 5 g of lemon balm, 20 g of St. John's wort and 10 g of motherwort. 1 hour l. the resulting dry mixture should be poured with 1 glass of boiling water and let it brew for about 1 tsp. Take 150 ml 3 times a day.
Infusion of medicinal valerian
You should take 1 tbsp. l. chopped grass roots, pour 200 ml of boiling water and let it brew for 8 hours. It is necessary to take the infusion 3 times a day for 1 tsp. l.
Oregano decoction
20 g of dry grass must be poured with 1 glass of hot water and boiled over low heat for 10-15 minutes. You need to take the broth 3 times a day, 50 ml. Epilepsy affects the patient's emotional state by creating stressful situations.
The use of herbs in the treatment of epilepsy helps to get rid of increased anxiety, fatigue, and fears. Customized herbal regimens not only improve emotional instability, but also help stop seizures over time.

Physiotherapy is actively used to treat symptomatic epilepsy. Medical rehabilitation of patients is carried out after the removal of the acute period, when the number of attacks per month does not exceed 2.
The recovery program is formed using:
- Exercise therapy;
- hardware physiotherapy;
- hydrotherapy;
- diet therapy.
Exercise therapy
Exercise therapy allows you to balance the processes of excitation and inhibition in the brain, strengthen the body's systems and expand its adaptive capabilities. Exercise therapy is performed against the background of anticonvulsant therapy. Classes are presented in the form of collective remedial gymnastics.
Patients perform a set of special exercises, the action of which is aimed at relaxing and stretching the muscles. Correct breathing is also important. The duration of the lessons does not exceed 30 minutes.
Hardware physiotherapy
Hardware physiotherapy is represented by impulse electrotherapy, which is carried out using constant impulse currents. The procedure is carried out in combination with electrophoresis. The physiotherapy course consists of 15-20 sessions. You can repeat it every 3 months.
Hydrotherapy
Hydrotherapy - therapy using warm relaxing baths with the addition of powdery or liquid pine needle extract. The duration of the bath is 10-15 minutes. The course consists of 10-15 procedures.
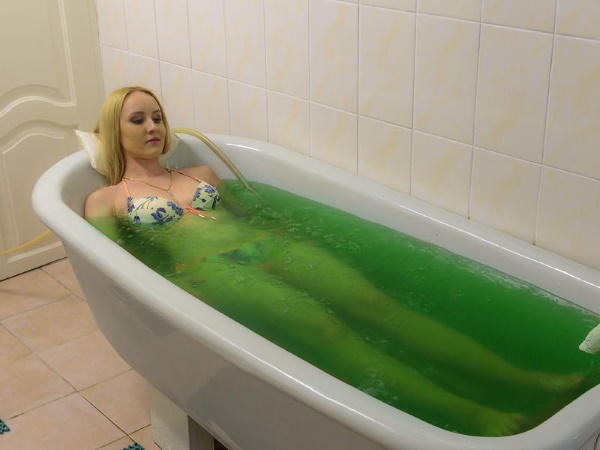

Also, for the treatment of pathology, sage, valerian and iodine-bromine baths are used.
Diet
The diet is a balanced, balanced diet. Patients are prohibited from drinking coffee, strong tea, and alcoholic beverages. You should also limit the use of spicy, fatty foods, legumes and fast carbohydrates.
Possible consequences and complications
Lack of medical therapy in the presence of a disease can lead to the development of complications:
- aspiration pneumonia - occurs when the remains of vomit, food or small objects enter the lungs during an attack;
- status epilepticus - constantly recurring seizures, when one seizure is superimposed on another and there are threats to the patient's life;
- mental disorders - depression, increased aggressiveness, isolation.
Epilepsy has more than 48 forms of manifestation. Epileptic seizures occur in different ways in different people - with loss of consciousness and without, with fading eyes, twitching, convulsions or auditory hallucinations.
With the help of well-chosen treatment and constant medication, frequent episodes of seizures can be stopped and the patient's quality of life can be significantly improved.
Epilepsy Videos
Types of epilepsy seizures: