The sacrum is one of the important parts of the spine. It is located in a person immediately behind the lumbar vertebrae and is the only fixed part.
Throughout life, the bone is exposed to various injuries, heavy loads, therefore her diseases often become a problem for patients of different ages. It is worth noting that women and men are almost equally susceptible to violations, but the former are more likely to encounter them.
Record content:
- 1 What is the sacrum
- 2 Functions
- 3 Structure
- 4 Types of diseases
- 5 Symptoms
- 6 Diagnostics
- 7 When to see a doctor
- 8 Prophylaxis
-
9 Treatment methods
- 9.1 Medications
- 9.2 Traditional methods
- 9.3 Other methods
- 10 Possible complications
- 11 Sacrum video
What is the sacrum
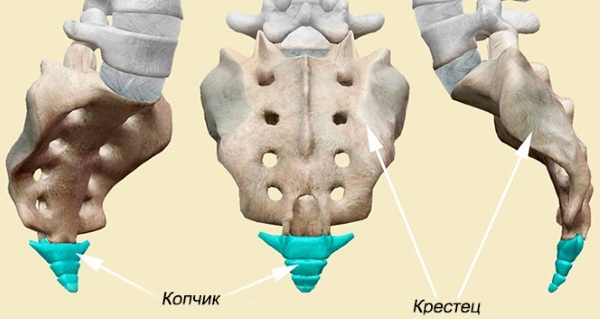
The sacrum is a section of the spinal column, which consists of 5 vertebrae, fused together into a single and motionless bone. In this case, the most important nerve endings of the spinal cord are located precisely in this section. The coccygeal vertebra, which is a rudimentary human organ, is attached to the sacrum.
Functions
The spine has several important functions in the human body.
The most significant are the following:
- The entire spinal column rests on this particular section. This explains the strength of the bone and the fusion of the vertebrae.
- The body allows you to maintain balance not only in an upright position, but also when moving.
- The bone takes part in the formation of the pelvic ring.
- Supports the pelvic organs through a strong muscular and ligamentous apparatus.
- Protects the most vulnerable part of the spinal cord from damage.
- Performs a shock-absorbing role when jumping or running.
- Prevents damage to blood vessels in case of injury.
In addition, the sacrum is the support of the entire body. With any violations in this part of the spinal column, it is possible to develop deviations from the pelvic organs, as well as extremities.
Structure
The sacrum is located in a person immediately behind the lumbar vertebrae, that is, it is one of the sections of the spine. The basis of a single bone is made up of 5 vertebrae, which are fused together by bodies and processes. The vertebra that attaches to the lumbar bones is called the base of the sacrum, and the one that joins the tailbone is called the apex.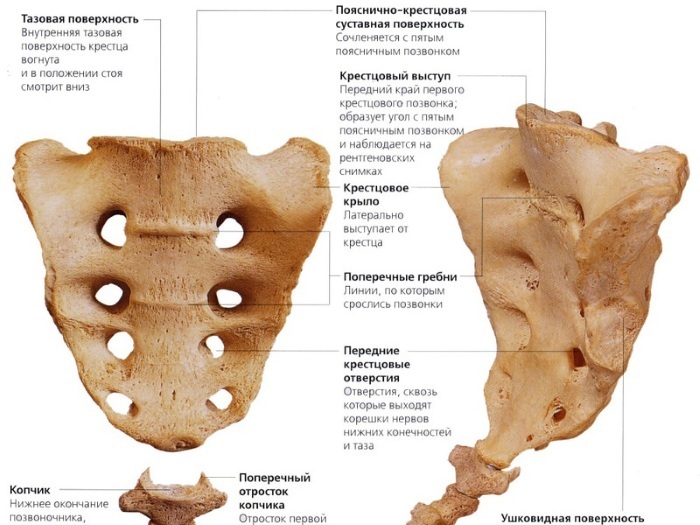
The back is represented by flat bone. In addition, the pelvic and lateral parts are distinguished in the structure. The first is attached with the help of ligaments and muscles to the pelvic bones, the second is not attached to the bones of the small pelvis. The pelvic part of the sacrum is divided into a promontory and wings.
It should be noted that the complete fusion of the vertebrae is completed at the age of 25-27 years. Up to this point, there are cartilaginous layers between them. That is why damage to this area of the spine at an early age can lead to deformation, as well as disruption of the integrity of the spinal cord. The latter provokes serious complications.
Several muscles are attached to the sacrum at once: gluteal, pear-shaped, iliac. That is why the bone takes part in maintaining balance during movement and at rest. All parts of the sacrum have grooves and depressions along which nerve endings and blood vessels pass.
Types of diseases
There are many diseases that can affect the sacrum. The most common are degenerative-dystrophic pathologies, trauma, and malignant neoplasms. In addition, bone injury can cause damage and pinching of nerve endings.
- Osteochondrosis - pathology of the cartilaginous tissue of the intervertebral discs, which affects mainly young patients. Their sacral vertebrae have not yet completely fused together, therefore, the destruction of the annulus fibrosus is possible. The disease is usually chronic, so the patient has regular exacerbations.
- Spondyloarthrosis - degenerative-dystrophic disease of bone tissue, which simultaneously affects the ligaments, cartilage tissue. In this case, there is a gradual destruction of tissues and an aggravation of the patient's condition. At an advanced stage, the patient tries to limit physical activity, since movements cause him pain.
- Tumor in the sacrum - a neoplasm in the bone tissue or in the area of the spinal cord, which may be benign or malignant. The second is more common. In this case, not only the patient's mobility is disturbed, but also the functioning of the nerve endings of the spinal cord.
- Congenital malformations of bone - pathologies manifested at an early age. Usually they become a consequence of intrauterine growth disorders. As a rule, such diseases do not respond to conservative treatment.
- Instability of the sacral bones - a disease that manifests itself at a young age, accompanied by excessive mobility of the ligaments and muscles connecting the vertebrae. In this case, the development of a violation of the pelvic organs and lower extremities is possible.
-
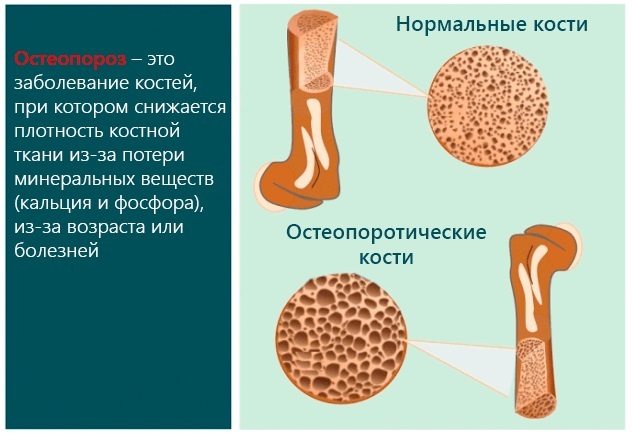
Osteoporosis - bone pathology, accompanied by the leaching of calcium from the bone tissue. As a result of this process, the bones of the sacrum become porous and brittle, which increases the likelihood of fractures.
- Sacrum fractures - a common pathology with damage to the spinal column. In case of violation of the integrity of the bones, in most cases damage to the nerve endings and blood vessels occurs, which leads to disorders on the part of the organs of the genitourinary system. Paralysis of the lower extremities often occurs.
- Radiculitis - an inflammatory disease, accompanied by pinching of the roots of nerve endings. Usually, the pathology affects the lumbar spine, but often affects the sacral spine. The disease is almost always chronic, characterized by frequent exacerbations, severe pain, and limited mobility.
- Hernia of the sacral spine - a rare disease accompanied by rupture of the fibrous ring of the intervertebral disc and the exit of the nucleus beyond its limits. The disease is not so common, which is associated with the fusion of the vertebrae in the sacral region. The risk of disease is considered to increase the risk of injury and pinching of the spinal cord.
- Osteomyelitis of the bone - a serious disease of the bone tissue, in which there is a gradual softening and the formation of a purulent cavity. Usually tubular long bones are affected, but in some cases, the inflammation goes to the sacrum.
Any of the diseases, except for a sudden fracture or other injury, proceeds in several stages with a gradual worsening of symptoms. At the initial stage, the patient may not notice the symptoms or they do not appear pronounced. The ability to work remains, and a person writes off minor discomfort to overwork and other factors.
The progressive stage is accompanied by the appearance of severe symptoms that impair mobility, reduce performance and force the patient to consult a doctor. At an advanced stage, all the signs are aggravated, the patient is often immobilized, strong medications do not help eliminate pain and other symptoms.
Usually, the pathology is successfully treated at stages 1 and 2. If the patient has postponed the visit to the doctor, therapy is complicated, prolonged and requires long-term rehabilitation. Surgery is often necessary to eliminate symptoms.
Symptoms
The sacrum is located in humans near the pelvic organs. That is why, with any pathologies, symptoms appear from the bladder, genitals. However, the symptomatology depends on the type of disease.
The most common signs of sacrum involvement are:
- Pain in the lower back and buttocks.
- Gait disorder. Outwardly, the disease manifests itself in the form of a change in posture, lameness and curvature of the spine. If you observe the gait of such a patient, it can be noted that he is trying to reduce the load on the affected area of the spine, therefore he transfers most of his body weight to one leg.
- Swelling and redness in the sacrum region. This is observed with bruising, bone fracture or neoplasm.
- Violation of urination, manifested in urinary incontinence or difficulty emptying the bladder.
- Tingling in the lower extremities, numbness, muscle weakening.
- Malnutrition of the skin of the legs, manifested in the form of pallor of the skin, the appearance of hematomas or even trophic ulcers.
- Discomfort or severe pain when moving, tilting, playing sports.
- A local increase in body temperature that develops with inflammation of tissues or muscles in the sacrum region.
- Disturbances from the intestines, manifested in the form of constipation or loose stools.
- Fatigue and inability to stay in one position for a long time.
With malignant neoplasms, as well as osteomyelitis, pain during movement and at rest becomes unbearable. Diseases are often accompanied by general symptoms such as fever, pain in muscles and joints, and a delusional state.
With radiculitis, osteochondrosis, hernia of the sacral region, severe pain is observed, radiating to the buttocks and lower extremities. When such a symptom appears, an inflammatory or degenerative-dystrophic process can be suspected. If the patient is unable to move after an injury, experts suspect a sacrum fracture.
Diagnostics
The sacrum is located in a person near important organs, therefore, it is necessary to immediately begin an examination if any abnormalities are detected. Various methods are used to diagnose pathologies.
| Method | Description | Venue and cost |
| General survey and inspection | Helps the specialist assess the general condition of the patient. He listens to complaints, identifies the alleged cause of the violation. | It is carried out in any clinic and does not require payment |
| Clinical blood test | A common diagnostic method that is used always and for any violations. | Available for public and private institutions. Price - from 200 rubles. |
| Blood chemistry | An additional blood test allows you to detect diseases of the digestive and urinary system. | It is carried out in each clinic, the cost is approximately 300 rubles. |
| X-ray of the sacral spine using a contrast agent | One of the most informative diagnostic methods, in which a specialist injects a patient with an intravenous contrast agent, the field of which makes a series of X-rays. After examining these images, the doctor makes a conclusion. Usually, the technique helps to identify osteochondrosis, osteoarthritis, osteomyelitis, hernia, fractures and other pathologies. | The technique is used in private and public institutions. The price starts from 400 rubles. |
| MRI | The most effective and informative research method, in which it is possible to identify neoplasms of the minimum size and other diseases. In this case, the specialist receives a volumetric layer-by-layer image of a specific area of the spine, which makes it possible to establish a diagnosis. | It is carried out in clinics equipped with appropriate equipment. The price starts from 1500 rubles. |
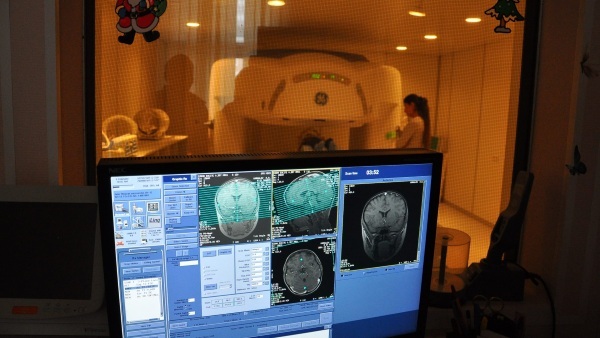
The most informative is magnetic resonance imaging, in which the doctor can almost immediately establish a diagnosis. But in any examination, several methods are used to obtain an overall picture of the patient's condition.
When to see a doctor
The sacrum is an important part of the spinal column; in humans, it is located in the immediate vicinity of many organs. That is why, if it is damaged, it is necessary to immediately consult a specialist, even if mild symptoms appear.
A neuropathologist deals with the treatment of pathologies. But during the examination, you may need to consult a therapist, nephrologist, traumatologist, surgeon.
Prophylaxis
Some sacral pathologies cannot be prevented, for example, congenital anomalies or fractures, as well as neoplasms. But many conditions are preventable. It is recommended to control body weight, not to allow its excessive increase, which will create a load on the sacral region.
In addition, patients whose professional activity is associated with a long stay in one position should strengthen their back muscles with the help of special exercises. This will prevent poor posture and displacement of the vertebrae.
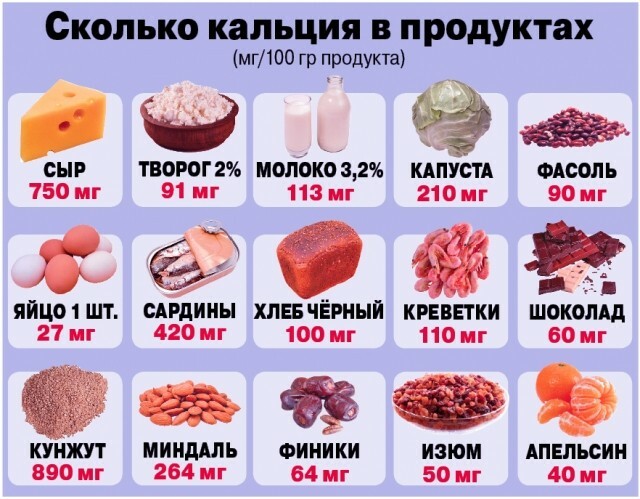
An additional method of prevention is diet correction. In this case, it is worth eating foods rich in calcium and B vitamins.
Such a menu will saturate nerve fibers and bone tissue with the necessary substances. If the patient suffers from any chronic disorders of the spine, it is necessary to regularly visit a neurologist and undergo a course of treatment to prevent complications.
Treatment methods
For the treatment of various diseases of the sacral spine, medications from different groups are used, which depends on the specific disorder. Additionally, you can use folk remedies and other methods of therapy.
Medications
Depending on the disease and the degree of its neglect, medicines from different groups are used.
Most often, the following are prescribed:
- Sumamed - an antibiotic from the macrolide group, which is often used in inflammatory diseases of the sacrum, for example, in osteomyelitis. The tool helps to destroy pathogenic bacteria and prevents their spread to other parts of the musculoskeletal system, belongs to potent drugs. It is necessary to take 2 tablets per day for 7-10 days. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. The price of the medicine is 300-500 rubles.
- Ketorol - a potent analgesic with anti-inflammatory action. Helps to eliminate pain, prevents the spread of inflammation to healthy tissues. For acute pain, an intramuscular solution is prescribed. The patient receives from 1 to 3 ml per day. In other cases, 1 tablet is prescribed 2 times a day. The duration of the course is up to 10 days. The price of the medicine is 100-200 rubles.
-
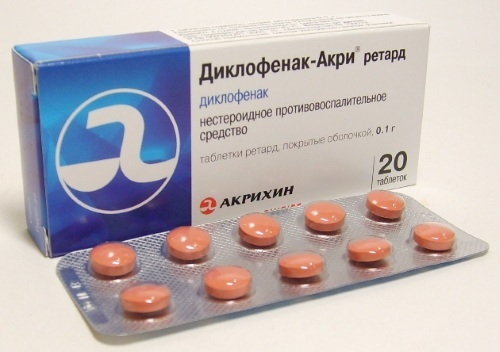
Diclofenac - a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug that helps to eliminate severe pain, and also prevents the development of complications. It is prescribed in the form of intramuscular injections and is highly effective. For 1 time, the patient is injected with 3 ml of the drug, the procedure is repeated up to 2 times a day. The duration of use is 5-10 days, depending on the severity of the symptoms. The price of 1 ampoule of the drug starts from 30 rubles.
- Pentoxifylline - a drug to expand blood vessels and improve blood circulation in the area of inflammation. Helps to normalize blood and nutrient supply, which improves tissue health. It is prescribed as a solution for intravenous administration using a dropper. For 200 ml of saline, 1 ampoule or 5 ml of the drug is taken. The procedure is carried out once a day for 10 days. The price of 1 ampoule of medication is from 15 rubles.
- Hondrolone - a drug from the group of chondroprotectors, which is administered to patients when osteochondrosis, spondyloarthrosis is detected. The product helps to restore cartilage tissue and stimulates the formation of chondrocytes. The drug is a powder for solution preparation. The solution is injected intramuscularly daily. The course consists of 25-35 injections, it should be repeated every 6 months. The price of packing the product is from 150 rubles.
In addition to these medications, the patient is often given vitamin B6 and B12 injections. They help to normalize the passage of the impulse along the nerve endings, which improves not only mobility, but also the innervation of the tissues of the limbs.
The standard course involves the introduction of 10 injections of each vitamin, but every other day, that is, the first day - pyridoxine, the next - cyanocobalamin. The price of drugs is approximately 60-80 rubles. per packing.
Traditional methods
The sacrum is located in a person in the immediate vicinity of the spinal cord. Therefore, using alternative medicine recipes can be harmful. But some remedies help relieve pain, so they are allowed for use.
- Burdock leaf compress on the sacrum area helps to eliminate swelling and pain. It is necessary to select a few large leaves and lightly beat them off until the juice appears. After that, apply to the affected area and fix with cellophane, as well as a bandage. Leave the compress for 3 hours. Repeat daily for 2 weeks.
- Broth based on calendula and mint - a good pain reliever and anti-inflammatory agent. It is necessary to separate 3 g of each ingredient, boil in 500 ml of water for 3 minutes. After insisting for 1 hour, filter, take 100 ml 2 times a day for 10 days.
-
Rubbing the sacrum area alcohol tincture of propolis is also used to relieve pain. The tincture can be prepared from 20 g of propolis and 100 ml of alcohol, leave for 2 weeks. Apply before bed to rub for 10-14 days.

Any of the prescriptions may only be used after consulting a doctor.
Other methods
Additional methods of treatment include physiotherapy exercises and massage. The methods are used only on an outpatient basis or in a hospital.
A set of exercises should be compiled by a specialist individually for each patient. They should be performed under supervision, no more than 15 minutes. In this case, the patient should not feel discomfort or pain. The minimum course consists of 20 lessons, which are held 1 time in 2-3 days.
Massage is also considered a good method for muscle recovery, preventing blood from stagnating in the sacrum area. It should be done by a professional in a medical institution, the duration of the session is 20-45 minutes. To achieve a therapeutic result, you will need at least 15 procedures.
In severe cases, when conservative therapy has failed, surgical intervention is used. The operation helps remove a hernia, growth, or cyst. The recovery period is usually long and difficult. The complexity of the operation may differ in each case.
Possible complications
If untreated, complications may develop.
The most common are the following:
- Impaired limb sensitivity.
- Rachiocampsis.
- Pinched nerve endings and paralysis of the limbs.
- Spinal cord injury.
- Complete softening of bone tissue (with osteomyelitis).
Such complications can significantly worsen the patient's condition and provoke other diseases.
The sacrum is an important part of the spinal column, which is located in a person immediately after the lumbar vertebrae. The bone plays an important role, therefore, in case of any diseases, you should not ignore the symptoms, it is better to immediately consult a doctor.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Sacrum video
Human sacrum anatomy:



