Hernia is a pathology of the musculoskeletal system in which the nucleus of the intervertebral disc protrudes into the spinal canal. If left untreated, a hernia can lead to disability and disability.
Record content:
- 1 Disease types
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
-
8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.2.1 Tincture of cinquefoil
- 8.2.2 Rubbing with honey and mumiyo
- 8.2.3 Fir oil
- 8.3 Physiotherapy
- 8.4 Manual therapy
- 8.5 Traction therapy
- 8.6 Surgery
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about spinal hernia
Disease types
A hernia of the spine is classified depending on the location, size, severity, visibility. Further treatment depends on the type of disease. At the site of hernia, there are cervical, thoracic and lumbosacral (depending on the level of the spinal column, on which the protrusion has formed).
The following types of pathology are also distinguished: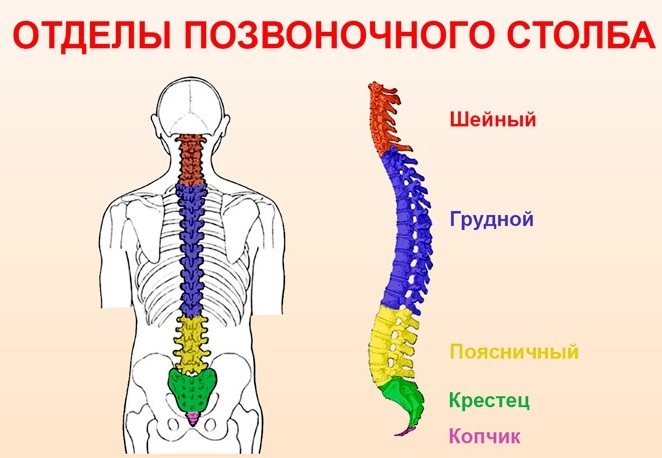
| View | Description |
| Schmorl's hernia | It is a displacement of the intervertebral disc tissue towards the adjacent vertebra. It does not pose a danger to musculoskeletal functions, but requires treatment, as it can lead to the destruction of bone tissue in the future. |
| Front | A hernia is formed on the front of the spinal column and is clearly visible on an x-ray. |
| Back | A hernia forms at the back of the vertebra and falls into the lumen of the spinal canal. Most often it is removed surgically. |
| Median and paramedian | It most often develops in the lumbosacral region (at the level of the L5-S1 vertebrae), but sometimes it can also occur in the cervical region. With the paramedian subspecies, the hernia falls into the area of the nerve root and touches it, causing painful sensations. |
| Lateral | One of the most dangerous and painful types of spinal hernias, in which the hernia tears all cartilaginous tissue and further develops in the lateral canal near the lumen of the spinal canal. |
| Foraminal and extraforaminal | The hernia is located in the foraminal opening and touches the nerve root, causing severe pain. This type of hernia is diagnosed only with computed tomography. With the extraforaminal subspecies, the hernia has a postero-lateral localization, affecting the nerves and blood vessels. |
| Sequestered | It is a pathology in which the cartilaginous tissue is displaced to the side, with the loss of an entire segment of one of the vertebrae. Treatment is only surgical. |
| Calcified | Fully or partially ossified hernia, which can only be detected by CT or MRI. |
Stages and degrees
There are only 3 stages of spinal hernia development:
- First stage. It is characterized by the formation of protrusion - when the intervertebral disc protrudes to the side without rupture of the annulus fibrosus and other structures, occupying an area up to 180 degrees from the circumference of the disc. At this stage, the pathology can be cured without surgery.
-
Second stage. The protrusion becomes more pronounced, the nucleus of the disc begins to press on the annulus fibrosus.
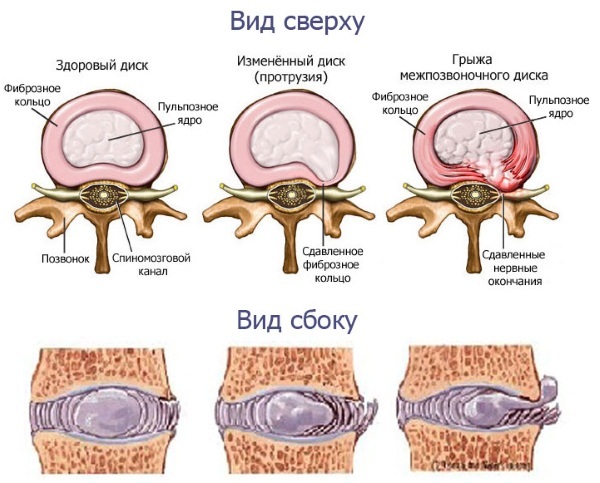
- Third stage. A rupture forms in the fibrous membrane, and its contents come out. At this stage, the treatment is only surgical.
Symptoms
A hernia of the spine, the treatment of which depends on the type and stage, manifests itself in the form of painful sensations in the spine (depending on the location). The pain can be dull, sharp or shooting in nature and intensify with physical exertion, lifting weights. Also, the patient may feel stiffness of movements when bending, squatting, in the process of getting out of bed.
Depending on the level of the spine at which the hernia is formed, neurological symptoms may appear:
| In the cervical spine | In the presence of a hernia in the cervical spine, the patient exhibits neurological symptoms due to the fact that the pathology presses on the nerves and vessels leading to the head:
|
| In the thoracic region | If the protrusion of the disc is formed in the thoracic region, then the patient feels pressing and aching pain in the sternum. Because of this, a person may think that their heart is hurting, which makes it difficult to make a diagnosis. |
| In the lumbosacral region | With this type of hernia, the pain radiates to the buttocks and hips (more often it affects only one side). The patient constantly feels numbness in the lower back, tingling sensation. Numbness and weakness in the legs may also occur. As the pathology progresses, the person begins to have problems with urination and defecation, and the menstrual cycle is disturbed in women. Men have difficulty with potency. |
Reasons for the appearance
Many factors can lead to the formation of a hernia of the spine:
- heredity;
- natural aging of the spine;
- a sedentary lifestyle (due to the constant presence in the same position, the blood supply to the spine deteriorates, which leads to malnutrition and tissue wear);

- excessive load on the spine (too frequent and strong, especially an incorrectly distributed load can lead to the formation of a hernia due to damage to the intervertebral discs; also the cause of the pathology may be frequent weight lifting);
- spinal column injuries (any injuries can lead to the formation of a hernia, but if they are cured in time, complications can be avoided);
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system (in particular, the spine); most often, degenerative pathologies of the spine (osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondyloarthrosis) lead to the formation of a hernia. Also, a hernia can be a complication of an inflammatory disease of the spine (arthritis) or nearby structures (myositis, bursitis);
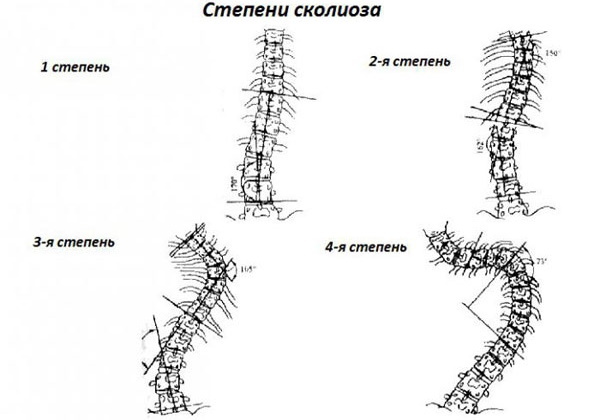
- posture disorders, scoliosis, kyphosis;
- obesity (for this reason, hernia and other pathologies develop most often in the lumbosacral region, since the body weight presses on the lower back, and it cannot cope with a strong load);
- flat feet or clubfoot (lead to an uneven load on the spinal column, which is why a hernia is formed);
- unbalanced nutrition (due to a lack of valuable substances in the diet, bones and joints can be susceptible to various diseases).
The risk of developing a hernia is especially high in office workers and people whose professional activities are associated with frequent sitting and being in the same position. Also, pathology can develop in loaders and builders due to the frequent lifting of weights.
Diagnostics
A whole group of doctors is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of hernia of the spine: an orthopedist, a surgeon, a vertebrologist. You will also need supervision by a neurologist due to the development of neurological symptoms.
First of all, you need to see an orthopedic doctor. The specialist conducts a visual examination of the spinal column, assesses the posture and looks for the presence of curvature. He should also learn about the patient's symptoms and lifestyle.
Further, special diagnostics are required. The patient is referred for an X-ray examination, which shows a decrease in the height of the intervertebral disc or the presence of osteophytes (bone growths).
The most effective method for determining a vertebral hernia is magnetic resonance imaging, which allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the spine and examine it in detail. The picture will show all changes in the structure of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. With contraindications to MRI, CT (computed tomography) is prescribed, but its effectiveness is slightly lower.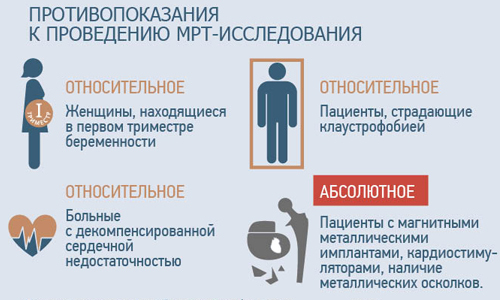
In case of serious neurological disorders, it may be necessary to study the nerve conduction of nearby tissues using electroneurography.
During the procedure, the speed of passage of nerve impulses along the nerve fibers is recorded - according to the results of the examination, it will be possible to judge the severity of neurological disorders. The procedure is painless and is carried out using special sensors.
When to see a doctor
It is necessary to consult a doctor if painful sensations in the back often appear. In the early stages, the patient may feel only a slight stiffness in the back, which intensifies after sitting or lying for a long time.
A little later, neurological symptoms may appear (depending on the location of the hernia), which require a mandatory visit to a doctor and further diagnosis. A timely visit to a specialist will help to detect not only a hernia, but also other pathologies that can cause painful sensations and neurological disorders.
Prophylaxis
A spinal hernia, the treatment of which is long and difficult, greatly affects the quality of a person's life.
Therefore, it is easier to prevent the development of pathology by observing preventive recommendations:
- Strengthen the spine with the help of special gymnastics, yoga, swimming in the pool (you can attend water aerobics courses) or special fitness programs.
- Exercise regularly to stretch your back.
- Wear comfortable shoes; people with foot pathologies are shown orthopedic shoes or insoles.
- Monitor your posture; with scoliosis or kyphosis, wear a special corset.

- Eat correct and balanced nutrition, maintain normal weight.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Avoid excessive stress on the spine, carry weights as little as possible; if you have to carry heavy things, then the weight must be distributed evenly in the right and left hands.
- When sedentary, get up regularly and do light arm and back exercises.
- Sleep on an orthopedic mattress (or choose models with medium or high firmness).
- Avoid staying in the same (especially unnatural, “hunched over”) posture for a long time.
- Avoid spinal injuries and heal them to the end.
- Prevent the development of diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Treatment methods
A hernia of the spine (treatment includes mainly conservative methods) responds well to medication and gymnastics therapy. In some cases, a decision is made about surgical intervention.
Medications
Medicinal treatment of a hernia is aimed at eliminating painful sensations, relieving neurological symptoms and stopping the inflammatory process (if any).
For this, the following types of drugs are used:
-
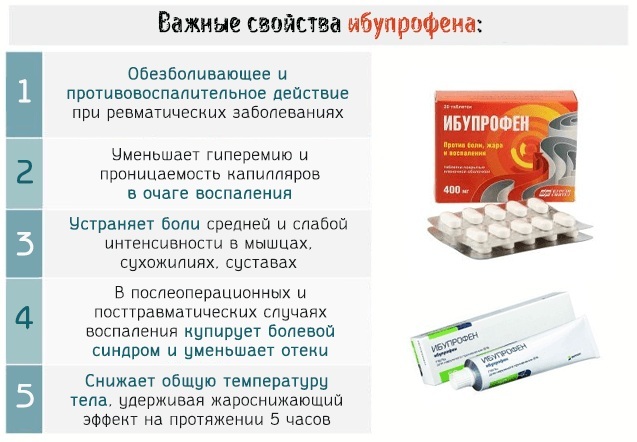
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They perform 2 tasks at once: they stop inflammation and eliminate painful sensations. Can be administered as tablets, suspensions or injections. NSAID creams and gels are less effective. The most effective means of this group are: "Ibuprofen", "Diclofenac", "Nise".
- Glucocorticosteroids. Prescribed as injections if NSAIDs are ineffective. The most commonly used drugs are "Dexamethasone", "Prednisolone".
Also, drug treatment depends on the cause of the hernia. If the pathology has arisen due to degenerative diseases, then chondroprotective drugs ("Artra", "Structum", "Don") are prescribed, which stimulate the regeneration of the cartilaginous tissue of the vertebrae.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine methods are not able to cure a spinal hernia, but can help to eliminate pain and relieve muscle spasms.
Tincture of cinquefoil
Sabelnik is a medicinal plant used in the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Tinctures from it have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects.
To prepare the tincture, it is necessary to pour 100 g of cinquefoil leaves into 1 liter of vodka or alcohol and leave for 3 weeks in a dark place, periodically shaking the container. After that, take the remedy 3 times a day for 30 minutes. before eating. The course of treatment is 14 days.
Rubbing with honey and mumiyo
Both of these products have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, enhance tissue regeneration. To prepare the product, you need to mix 1 g of mumiyo with 1 tbsp. l. honey and rub the mixture into the diseased area of the spine for 3-4 minutes. several times a day. The course of treatment is 7 days.
Fir oil
To improve the mobility of the spine, it is recommended to massage with fir oil. For the procedure, 3-4 drops of the product are enough, which must be rubbed into the affected area with gentle movements for 5 minutes. You can also add oil to massage cream.
Physiotherapy
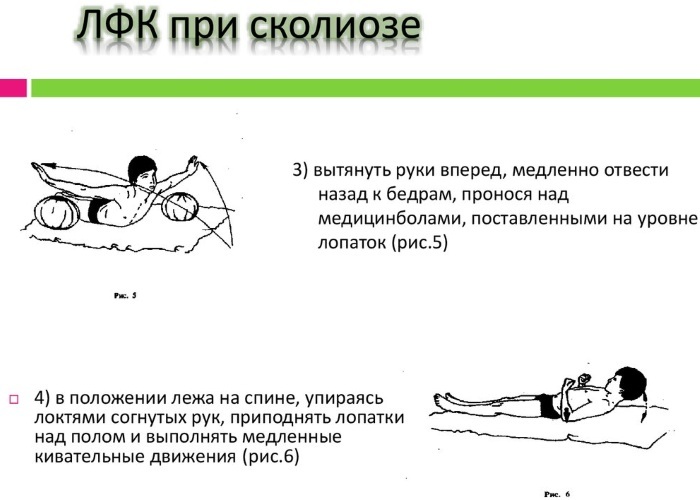
A specially developed set of exercises helps to strengthen the muscles of the back and abdomen, improve posture and relieve pain. Exercise therapy exercises reduce the load on the spinal column, but at the same time contribute to the development of the muscle corset.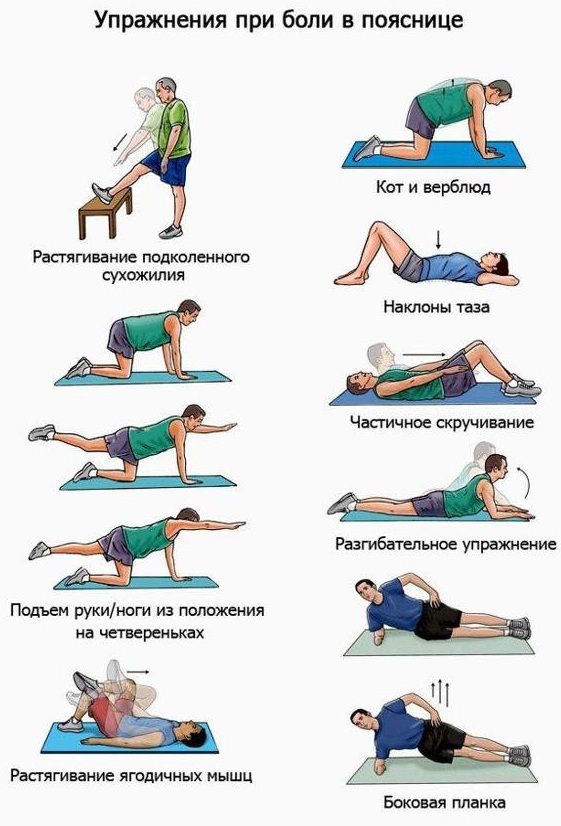
It is better to do exercise therapy in the clinic under the supervision of an instructor who will tell you how to perform the exercises correctly. After a course of remedial gymnastics in stationary conditions, you can regularly do it at home.
Manual therapy
Manual techniques are aimed at stretching and relaxing spasmodic muscles, relieving neurological symptoms and eliminating painful sensations. An experienced specialist should be engaged in manual therapy, since an insufficiently qualified master can cause additional harm to the health of the spine as a result of improper movements.
Traction therapy
Traction or traction of the spine is used in orthopedics to treat fractures and hernias.
The method is based on prolonged stretching of the vertebral muscles, resulting in:
- the distance between the vertebrae increases;
- vertebral hernias are treated (in the space near the disc, the pressure decreases and a suction effect is created - the hernia moves back to the area of the intervertebral disc);
- small and deep muscles and ligaments are developed and strengthened;
- tense and spasmodic muscles relax;
- improves blood circulation in nearby blood vessels.
In traction therapy, 3 methods are used, which have their own indications and characteristics: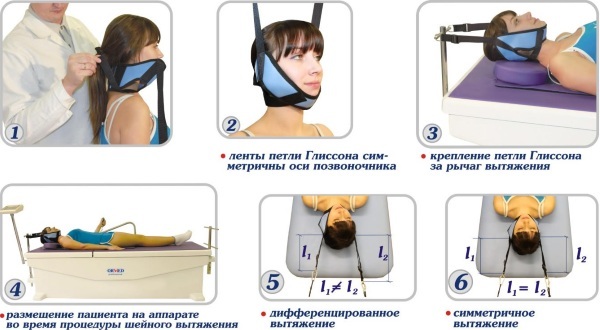
| Autogravity method | Stretching occurs under the action of a person's own body; the patient is placed on a special apparatus that lifts a certain area of the spine and makes it stretch. This method is the least traumatic and possible at home. |
| Gravity method | Based on the effects of weighting agents; it can be dry (the patient is placed on the apparatus and his spine is pulled out with straps) and underwater (a patient is attached to the legs weights are placed vertically in the water, during the procedure, the person holds onto the handrails or is fixed with straps so that he does not drown). The gravitational method can be harmful, therefore it is possible only in medical facilities under the supervision of doctors. |
| Physical exercise | Implies hanging on a horizontal bar or exercises with weights. The method is available only to physically developed people; it is also less effective, since when hanging on a horizontal bar, the upper spine and spasmodic muscles almost do not stretch. |
Surgery
Spinal hernia (treatment with surgery is performed only as a last resort) has 3 types of indications for surgical intervention:
- No indication - painful sensations are amenable to conservative treatment (medications, manual techniques, therapeutic exercises), and a hernia slightly worsens the quality of life.
- Relative indications - the operation is carried out if conservative methods of therapy do not help or recovery is required as soon as possible.
- Absolute readings - a hernia pinches the nerves and nerve roots, which causes incontinence of feces and urine, impaired potency and leads to disability.
The operation can be performed in several ways, depending on the severity, size and type of hernia: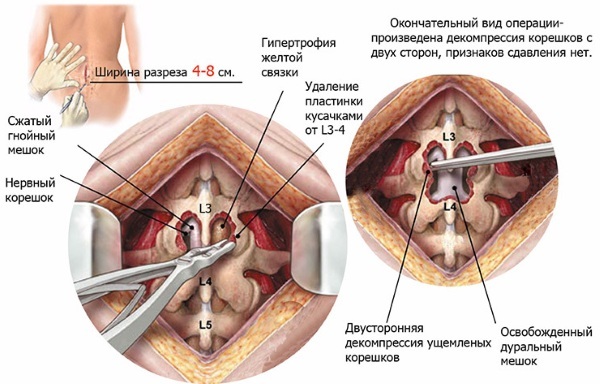
| Transfacet removal | During the operation, the hernia is removed, and the operated area is stabilized with screws and rods. It does not require special rehabilitation, after a few days the patient can lead a normal life. |
| Endoscopy | One of the least traumatic ways to remove a hernia allows you to remove the pathology through a small incision using an endoscope. The disadvantages of endoscopy include the impossibility of performing it with median hernias, since their removal requires an open anterior approach. |
| Microsurgical endoscopy | This method combines endoscopy and microsurgical manipulations. Allows to remove a hernia of any density and localization. Contraindicated in the presence of osteophytes, spinal instability and recurrent hernias. A month after the operation, the patient can lead a normal life, and before that, it is required to observe the restriction of physical activity and wear a corset to reduce the risk of complications. |
| Nucleoplasty | During nucleoplasty, there is a decrease in pressure in the nucleus of the intervertebral disc, which leads to the bulging of the annulus fibrosus and the cessation of compression of the nerve root. The following methods are used for nucleoplasty:
The operation is performed through a small puncture with the introduction of a special electrode needle. |
Possible complications
If the herniated disc is not treated, it can increase in size and begin to squeeze nearby blood vessels and nerves, which will lead to various neurological diseases.
With a cervical hernia, cerebral disturbances can occur, which greatly impair physical and mental performance; a hernia in the lumbosacral region is dangerous because it causes disorders of the pelvic organs; pathology in the thoracic spine can cause arrhythmias and heart disease.
A spinal hernia, if untreated, leads to disability and disability of a person, therefore it is important detect its symptoms in time and carry out diagnostics - this will help to maintain the health of the spine for a long time time.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Video about spinal hernia
Malysheva will talk about herniated discs: