Bursitis of the crow's feet Is an inflammatory disease of the synovial tendon bursa of the knee joint. The development of the syndrome is observed in both acute and chronic forms.
Record content:
- 1 Anatomy
- 2 General characteristics of pathology
- 3 Symptoms and Signs
- 4 Causes
- 5 Diagnostics
-
6 Treatment methods
- 6.1 Medicines
- 6.2 Folk remedies
- 6.3 Other funds
- 6.4 Liquid drainage
- 6.5 Treating bacterial bursitis
- 6.6 Treatment of the chronic form
- 6.7 Physical activity
- 7 Crow's foot disease video
Anatomy
The goosefoot of the knee joint is an inflammation inside the joint. This condition is often referred to as anserine bursitis. The anserina bursa lies between the tendons and the tibia.
Bursa is a small sac filled with fluid that softens friction between tendons and bones as they move relative to each other. With injuries or excessive friction of the joints, the bursa becomes inflamed and bursitis develops. Knee bursitis most often occurs in the pouch above the patella or on the inside of the knee due to frequent kneeling and repetitive running movements.
The bursa or bursa contains an aqueous fluid that is high in hyaluronic acid. They provide free movement of muscles, tendons, bones and fascia. Without a bursa, with each movement there would be much more friction, pain, and wear of the organs of the musculoskeletal system would increase.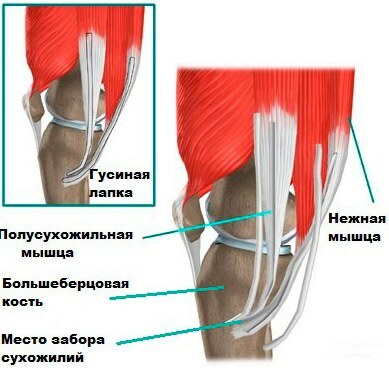
The bursa serves as a resilient, fluid-filled and free movable cushion for all the locomotor organs of the body. Bursae protect muscles, tendons, and ligaments when the knee is moved and stressed.
These are shock-absorbing organs and sliding surfaces that provide smooth movement without irritation. Bursa (bursa) are very flat, shock-absorbing sacs of connective tissue, which, like the joint capsules, are lined with a synovial membrane from the inside.
The bags release a thick elastic mass to reduce friction between tissues, and also act as cushioning cushions for tendons, muscles, bones. The inflammation of the bursa does not occur suddenly, but progresses over time. Pes Anserine tendons in the form of a crow's feet are located superficially in relation to the medial collateral ligament of the knee.
Tendons are fibrous tissues that attach muscles to bone. The thin and sartorian tendons are the adductors of the leg. They pull the leg towards the middle axis of the body. The semitendinosus muscle is part of the hamstring muscle group located at the top and back of the leg.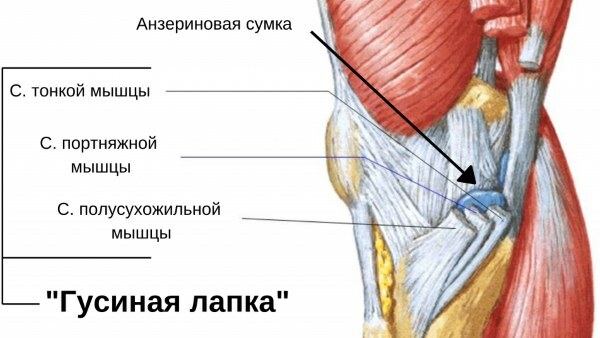
Together, the 3 muscles are the knee flexors and internal rotators. Under the pes anserinus tendon is a bursa (pes anserine).
General characteristics of pathology
Repetitive stress or friction in the tendon area contributes to the development of bursa inflammation. The bursa secretes an excessive amount of fluid and thus swells, putting pressure on the surrounding structures. The cushioning between the tendons and ligaments is compromised, causing joint irritation. All this leads to a disease - bursitis.
Bursitis in the joints causes only mild pain and discomfort and, with appropriate treatment, usually resolves in a month or less. Knee bursitis is no exception, but this syndrome may reflect a more serious underlying problem.
Especially often 3 bags on the knee are affected by bursitis:
- Bursa between the kneecap and the skin (Bursa prevatellaris). This bursa is very thin and sits between the patella and the skin.
- Bursa on the patellar tendon. Two bags lie both in front of the patellar tendon under the skin and behind the patella between the tendon and the shin bone.
- Pes anserinus bursa ("bursa of a crow's feet" inside the knee joint). The tendons of the 3 thigh muscles are attached to the inner side of the tibial head.
The goosefoot of the knee joint is an inflammation of the synovial sac at the site of attachment of 3 muscles: thin, tailor and semitendinosus, which are connected by the proximal ends on the medial side of the tibia, closer to the median plane.
Anserine bursitis develops when muscles are frequently involved in flexing and adducting the lower leg. This causes friction, increases the pressure on the bursa. Bursitis can also result from trauma. Contusion of this area leads to increased secretion of synovial fluid.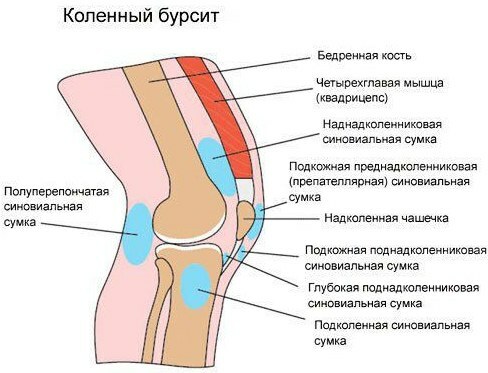
Bursa becomes inflamed, becomes painful, and over time, knee osteoarthritis develops in this place. An inflamed bursa is not a primary pathology, but a consequence of a previously suffered complication.
A knee joint that is injured due to excessive stress becomes painful. Injuries to this area are less common than other knee injuries. The muscles attached from below, in the form of a crow's feet, change their anatomical structure, because the bursa is in a state of inflammation.
Symptoms and Signs
The goosefoot of the knee joint, as a process of inflammation of the bursa, has the main symptom - pain on the inner side of the knee or in the center of the tibia, which can be exacerbated by physical load.
Bursitis is difficult to see at first. Typical symptoms are mild pain on movement and a rubbing sensation at the site of the inflamed bursa. In the case of bursitis, the affected bursa swells, causing severe joint pain.
As a result, the movement of the joint is significantly limited, the joint becomes warm. When pressed, you may feel swelling and pain. Under strong mechanical stress, the fluid in the bursa is usually stained with blood.
Clinically, anserine bursitis presents with pain, especially at night, in the medial region of the knee. Typically, patients can point their finger directly at this area when asked where the pain is most severe. A physical examination to rule out an underlying problem with the medial collateral ligament can be done with a valgus stress test.
Anserine bursitis is usually described as a small painful area at the tibial tubercle about 3.5 cm below the medial joint line.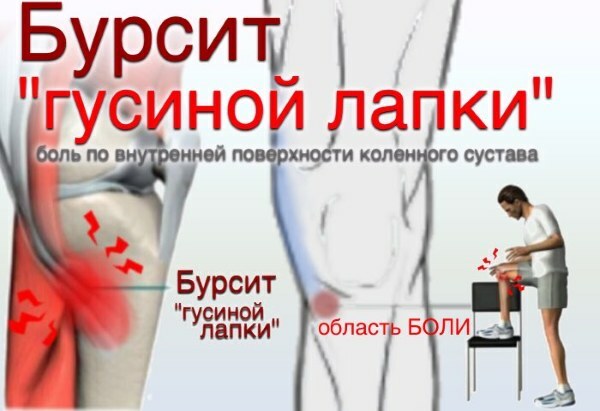
Symptoms of acute bursitis come on suddenly and are characterized by severe pain. If the bursa directly under the skin is affected, this area turns red.
Chronic bursitis presents with persistent or recurring pain. If left untreated, acute bursitis often becomes chronic.
When bursitis spreads outside the bursa, the surrounding limbs, such as the hip and lymph nodes, become swollen, reddened, and overheated. General signs of inflammation such as fever, fatigue and fatigue are also possible.
If inflammation causes an increase in body temperature, this is a sign of an additional bacterial complication. Then, in addition to immobilization, antibiotics are indicated.
Causes
Anserine bursitis is located medially, about 6 cm below the joint line between the medial insertion site collateral ligament on the plateau of the tibia and the tendon that connects the sartorian and semitendinos muscles.
The most common problem associated with anserine bursitis is osteoarthritis and abnormal gait. Increased pressure and friction from any gait disturbance affecting the knee, hip, and pelvis can lead to this form of bursitis.
Injuries and accidents can contribute to the development of bursitis, although 2 types of injury can be distinguished. If the injury is due to an external impact or collision, it can cause the bursa to fill with blood and then become inflamed. If there is an open injury near the bursa, there is a risk of bacteria entering the wound and developing bacterial bursitis.
Other causes of bursitis can be abnormal joint changes such as osteoarthritis or arthritis. The changes lead to the fact that the articular structures and, consequently, the bursa are subjected to more and more stress. Metabolic diseases, infectious diseases, can also be associated with bursitis.
The goosefoot or bursitis is often accompanied by tendonitis, which causes small tears in the tendon.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of anserine bursitis is usually clinical, and further evaluation is not necessary.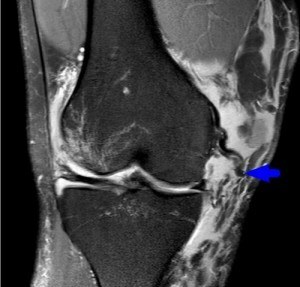
In rare cases, an additional examination is carried out.
- X-ray. Helpful in identifying a bone problem or arthritis.
- MRI. The study allows you to visualize soft tissues, such as the bursa.
- Ultrasound. Diagnostics helps to better visualize the tumor in the affected bursa.
Treatment methods
Most cases of knee bursitis resolve on their own. In the case of treatment, the main goal is to reduce the pressure on the bursa in order to speed up the healing process and maintain movement and strength in the knee.
Medicines
In some cases, medications are used to relieve pain and swelling:
| Name | Action | How to use |
Anti-inflammatory drugs | ||
| Ibuprofen | It is effective for inflammatory pains, inhibits platelet adhesion, reduces inflammation, and restores microcirculation. | With moderate pain syndrome, 1200 mg / day is prescribed. |
| Ibuprofen ointment | Apply 3-4 times / day, rubbing until completely absorbed. | |
| Paracetamol | Suppresses the Synthesis of Prostaglandins Produced by Inflammation / | A single dose is from 500 to 1000 mg, you can not use it for more than 3 days. |
| Ketoprofen | Reduces the biosynthesis of prostaglandins involved in the appearance of puffiness, pain in places of inflammation. | Tablets are taken with meals three times / day, 100 mg, capsules in the morning and afternoon, 50 mg, and in the evening - 100 mg. |
| Diclofenac | It has anti-inflammatory properties. | It is taken orally, 30 minutes before meals, 2-3 times / day, 20-50 mg. |
| Ortofen | The drug is an NSAID, has a pronounced analgesic effect. | Recommended for 1-2 tab. 2-3 times / day. |
Ointments for local effects | ||
| Nise gel | A synthetic drug for the treatment of joint pain. | Apply, without rubbing into the skin, in a thin layer, up to 3-4 times / day. |
| Fastum gel | NSAID drug for relieving muscle and joint pain of various origins. | The gel is applied no more than 2 times / day to the inflammation focus, it can be used in combination with physiotherapy. |
| Dolobene | The combined drug affects blood clotting. It is used as a decongestant and pain reliever. | Apply 2-4 times / day in a thin layer, while gently massaging the knee. |
Folk remedies
Helpful home remedies for bursitis:
- Massage to improve blood circulation, reduce swelling and reduce the feeling of stiffness in the joints.
- Ginger. Acts as a natural pain reliever due to its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties, improves blood circulation, promotes the healing process. Put 3-4 tbsp. l. grated ginger in a cotton cloth, tie and place in boiled water for 30 seconds. After cooling, apply to the affected area for about 10 minutes. Apply to the affected area 2-3 times / day.
-
Castor oil. Contains anti-inflammatory and analgesic ricinoleic acid, reduces swelling, improves joint mobility. Dip cotton cloth in cold-pressed castor oil, and then apply to the affected joint. Cover with foil, place a heating pad with hot water on top. Leave everything for 3-4 minutes. Do this compress 3-4 times a week.

- Apple vinegar. The alkaline effect ensures a balanced pH value and thus helps to reduce inflammation and relieve pain. For a compress, moisten a cotton cloth with vinegar and apply on the inflamed area of the knee for several hours.
- Willow bark. When combined with salicin, willow bark is a natural pain reliever and can reduce inflammation and minimize swelling, which supports the healing process. Insist ½ h. l. dried willow bark in a cup of hot boiled water for 15 minutes. Drink tea twice a day. The drink should not be used in conjunction with blood thinning medications.
Other funds
In addition to medicines, other methods are used:
- Rest. With knee bursitis, it is important to avoid activities that cause pain. This means a change in activity or even its complete cessation before the disappearance of the tumor.
- Cold. Applying an ice pack for 10-15 minutes every 2 hours on the inside of the knee will help reduce pain and swelling.
- Warm compresses (only for chronic bursitis or 48 hours after an attack of acute bursitis) to improve blood flow and reduce joint stiffness.
- Stretch marks. A hamstring strain is an important part of anserine bursitis rehabilitation, as the syndrome is often due to hamstring tightness, so doing simple stretching exercises is part of the healing process to relieve pressure from the bursa.
- Strengthening exercises. By strengthening the glutes, quads, and hamstrings, pressure on the muscle of the foot can be relieved.
- Physiotherapy. The doctor can assess the weak and limited areas that are contributing to the problem and develop a rehabilitation program. Treatments such as ultrasound and acupuncture are also helpful in reducing pain and inflammation in bursitis. Physiotherapy is the mainstay of treatment for the syndrome.
- Corticosteroid injections in knee joints can help reduce pain and inflammation. In addition, intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid, carboxytherapy are offered. The injection provides instant pain relief, but it should be used in conjunction with other treatments such as physical therapy and exercise to prevent the problem from returning.
- Surgery. In rare cases, if the pain persists with the above treatments, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove the bursa. It takes about 3-4 weeks to return to normal activities after surgery.
If underlying medical conditions such as arthritis, gout, tuberculosis, or gonorrhea have contributed or triggered bursitis, therapy also aims to treat those underlying conditions.
Liquid drainage
If the acute inflammation has passed and the bursa continues to feel like a cushion of water, puncture and drainage may be indicated.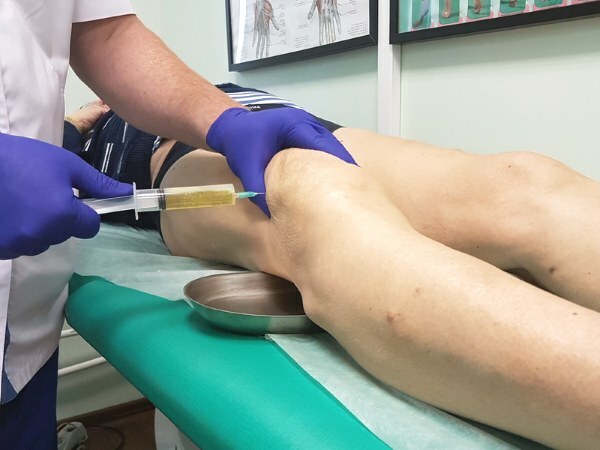 Depending on the results, you can withdraw from 1 to 40 ml of liquid, and then inject a suspension of crystalline cortisone into an empty bursa. A pressure bandage is then applied to prevent the bursa from filling up again.
Depending on the results, you can withdraw from 1 to 40 ml of liquid, and then inject a suspension of crystalline cortisone into an empty bursa. A pressure bandage is then applied to prevent the bursa from filling up again.
Treating bacterial bursitis
Bacterial bursitis, which is not amenable to immobilization and antibiotics, must be treated by surgical opening of the bursa (incision), followed by drainage of the fluid. In addition, this procedure is combined with oral antibiotics. However, complete removal of the bursa is more often required.
Treatment of the chronic form
If bursitis becomes chronic, lasts more than 3-6 weeks, it may be necessary to remove the bursa as part of a small surgical procedure, bursectomy. However, it is also associated with subsequent immobilization, possibly drainage, pressure dressings, and antibiotics.
Physical activity
As the pain subsides, you can gradually begin to return to normal activities, but you do not need to rush too much. You should start with an exercise that does not weigh heavily, such as cycling or swimming. You can return to running, but start with short distances, alternating between running and walking, gradually increasing the pace of the exercises.
A good rule of thumb to follow is the 10% rule, which gradually increases your workout by a maximum of 10% per week, whether it's distance or time.
Treatment of pain in anserine bursitis, or crow's feet, should be started as early as possible and carried out regularly. But therapy will be more effective if it is directed not only at the symptoms, but also at what causes them in the first place, otherwise the problem may return in the future.
For example, a person suffers from pain and inflammation, but the actual cause may be weakness or instability of the knee joint.
Crow's foot disease video
Crow's foot tendinitis: