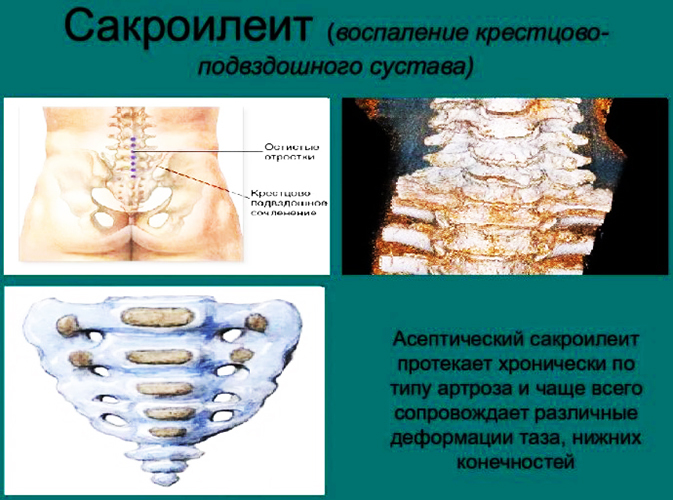
Sacroiliitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the region of the sacroiliac joint and is accompanied by painful sensations and decreased joint mobility or the spine.
Record content:
- 1 Classification of sacroiliitis
- 2 Stages of the disease
-
3 Causes of pain in the sacrum
- 3.1 Ankylosing spondylitis
- 3.2 Rheumatoid arthritis
- 3.3 Psoriatic arthritis
- 3.4 Enteropathic arthritis
- 3.5 Bone and ligament injuries
- 3.6 Sacroiliac joint infection
- 3.7 Tumor process
-
4 Sacroiliitis symptoms
- 4.1 With aseptic arthritis (rheumatological pathology)
- 4.2 With joint injury
- 4.3 With an infection of the joint
- 4.4 With a tumor process
-
5 Analyzes and diagnostics
- 5.1 Radiological signs of sacroiliitis
- 5.2 Magnetic resonance imaging
- 5.3 Laboratory analysis
-
6 Sacroiliitis treatment
- 6.1 Medicines
- 6.2 Physiotherapy
- 6.3 Operations
- 6.4 Diet
- 7 Consequences and complications, prognosis
- 8 Disease video
Classification of sacroiliitis
Pathology is divided into several types depending on the nature and area of the inflammatory process.
By prevalence:
- Synovitis - the disease develops in the area of the synovial membranes.
- Panarthritis - pathology affects all areas of the articular system.
- Osteoarthritis - the disease is formed in the superficial part of the joints.
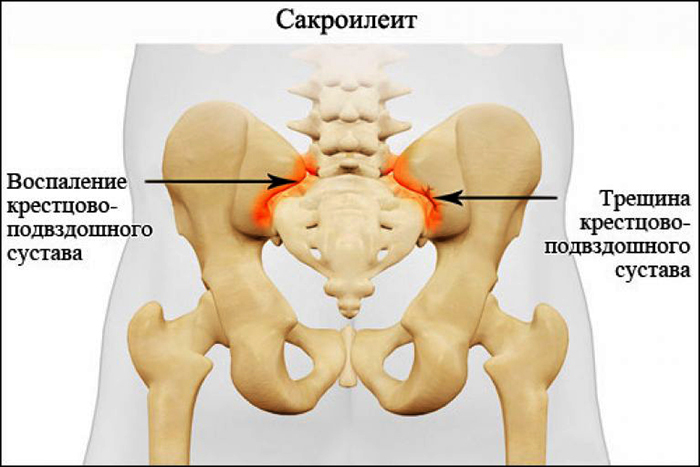
Classification (by the nature of the pathology):
- nonspecific or purulent sacroiliitis;
- specific - in this case, the process develops against the background of syphilitic, brucellosis or tuberculous disease;
- aseptic or infectious-allergic - in most cases, pathology is formed against the background of autoimmune disorders;
- non-infectious - can develop as a result of injuries, injuries, congenital defects and anomalies, as well as disruptions in metabolic processes.
Same the disease is subdivided into unilateral and bilateral sacroiliitis. In turn, the first form can be left-sided and right-sided. The bilateral type of the disease is divided, depending on the severity, into stages 1, 2 and 3.
Stages of the disease
The pathological process is also divided into stages depending on the area of the lesion and the accompanying symptoms.
Stages of the disease:
- 0 stage. It is considered normal, there are no abnormalities in the surface of the joints.
- Stage 1. At this stage, there is an uneven surface in the joints. In this case, in the central part of the joint, small seals form in the area of the trabeculae and bone substance.
- Stage 2 (initial sacroiliitis). With this type of disease, gradual (minor) changes occur in the area of connective tissue located under the articular cartilage. Expansion (alternating with narrowing) of the gap between the joints is also noted. As a result, minor erosive and sclerotic processes may occur.
- Stage 3 (active form of the disease). This type of pathology is characterized by the following manifestations: violation of the integrity of the edges in the joint and its surface, narrowing of the density of the joint, in rare cases, cysts may occur in the subchondral bones.
- Stage 4. At this stage, complete ankylosis of the joints and its constituent structural elements develops.
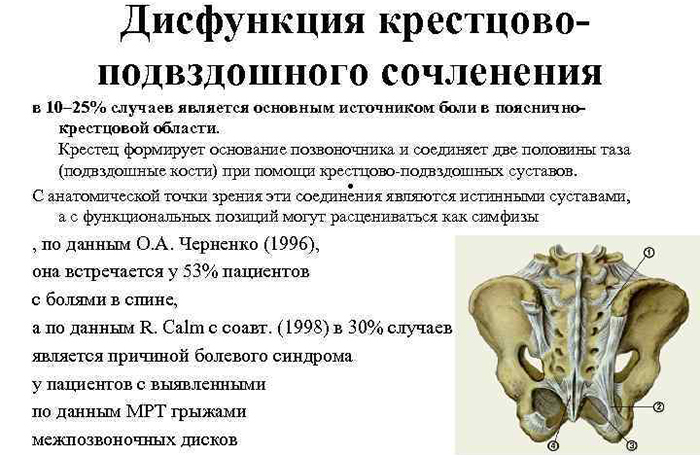
The effectiveness of therapy depends on the stage of development of the disease. In this case, the method of treatment at different stages may differ.
Causes of pain in the sacrum
Sacroiliitis of the sacroiliac joint in the overwhelming majority of cases is accompanied by pain. In this case, the causes of pain may differ depending on the form of the disease.
Ankylosing spondylitis
At the moment, the exact cause of ankylosing spondylitis has not been established. However, the main provoking factor is considered to be a hereditary predisposition or abnormalities in the genetic structure.

Pain syndrome in this pathology is associated with the development of inflammatory processes in the area of the articular surface, as well as damage to the connective tissue frame located in other organs.
Rheumatoid arthritis
This type of disease is systemic and chronic. The exact cause of the pathology has not yet been established. It is believed that the disease occurs as a result of autoimmune disorders that lead to the development of inflammation in certain joints.
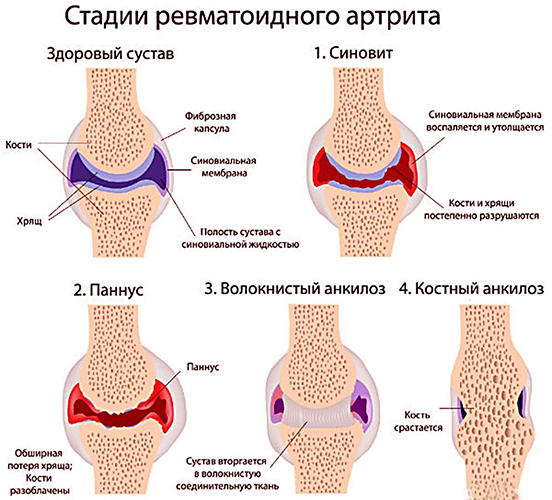
The mechanism of action is associated with negative external influences (tobacco, alcohol, trauma, infectious diseases), as a result of which an autoimmune reaction occurs. Against this background, the body begins to attack both foreign and its own cells.
Psoriatic arthritis
This form of pathology develops against the background of psoriasis. Psoriatic plaques affect certain areas of the skin, against the background of which the disease affects the articular system. The main cause of the disease is autoimmune disorders that cause inflammation and soreness.
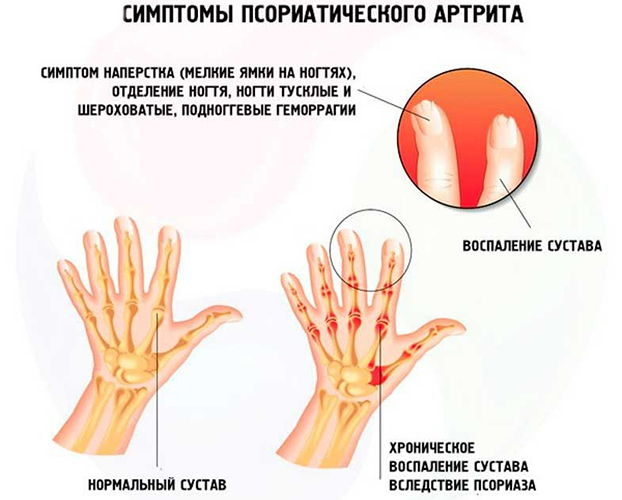
Psoriatic arthritis occurs in 1/3 of all psoriasis patients.
Enteropathic arthritis
This form of the disease is formed as a result of existing gastrointestinal disorders of a bacterial or inflammatory nature.
Causes:
- Crohn's disease;
- nonspecific ulcerative colitis;
- intestinal bacterial lesions - shigella, salmonella, clostridia, campylobacter, yersinia;
- parasitic invasions - giardiasis, ascariasis, strongyloidosis.
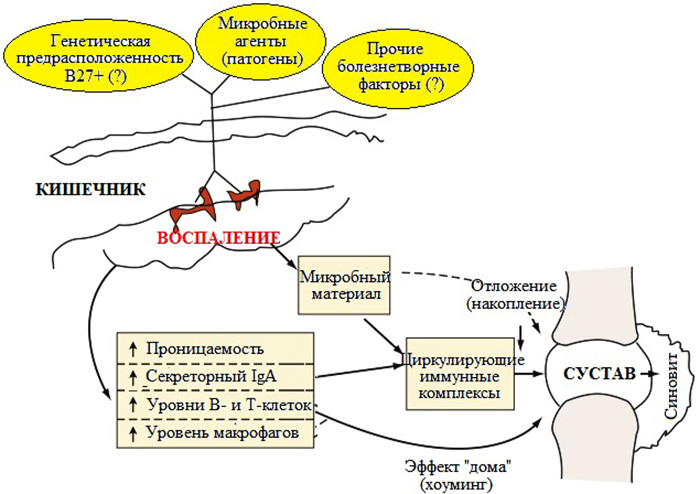
Microorganisms cause inflammation and pain. Also, pathology can occur due to hereditary (genetic) predisposition.
Bone and ligament injuries
This form of the disease is formed as a result of injury to the sacroiliac region. Against the background of trauma, an autoimmune reaction can occur, which leads to the development of inflammation and other unpleasant symptoms.
Sacroiliac joint infection
This type of pathological disorder develops against the background of infectious diseases occurring in the body. Most often, the disease occurs as a result of infections such as tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis.
The process is accompanied by the formation of pus, which accumulates between the surfaces of the joints, which leads to the development of inflammation and a deterioration in well-being.
Tumor process
The main reason is the development of neoplasms that cause metastatic reactions, accompanied by severe pain. At the same time, there is a significant narrowing of the joint space, which causes friction and leads to pain.
Sacroiliitis symptoms
Sacroiliitis of the sacroiliac joint has its own developmental characteristics and symptoms. Moreover, each form of the disease has its own manifestations and symptoms.
With aseptic arthritis (rheumatological pathology)
Aseptic arthritis is characterized by a pronounced severity of symptoms in the morning or after rest. In this case, after movement, the soreness decreases.
Symptoms:
- chronic back pain;
- stiffness in the lumbar region;
- fast fatiguability;
- increased subfebrile body temperature;
- the development of osteoporosis.
In rare cases, kyphosis may occur against the background of the disease.
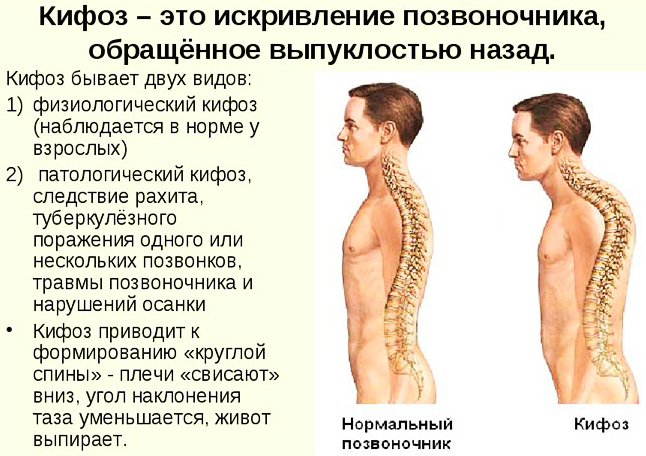
Also, the disease can be accompanied by visual disturbances, disorders of the cardiovascular system, pulmonary diseases, neurological disorders or renal pathologies.
With joint injury
The severity of symptoms in trauma depends on the duration of exposure and the intensity of the trauma.
Symptoms:
- pain syndrome;
- the formation of puffiness;
- hyperemia in the area of injury;
- hematomas;
- wound surface - bruising and bleeding.
In indirect forms of damage, bone fractures and injury to other organs can occur.
With an infection of the joint
With the infectious development of sacroiliitis, the symptoms are extensive and pronounced, since, in addition to inflammatory reactions, other processes develop due to the influence of the products of the vital activity of pathogens on the body person.
Symptoms:
- intense pain in the area of the damaged joint;
- increase in overall body temperature;
- malaise;
- headaches;
- chills;
- body aches;
- increased sweating;
- intoxication of the body;
- the formation of abscesses.
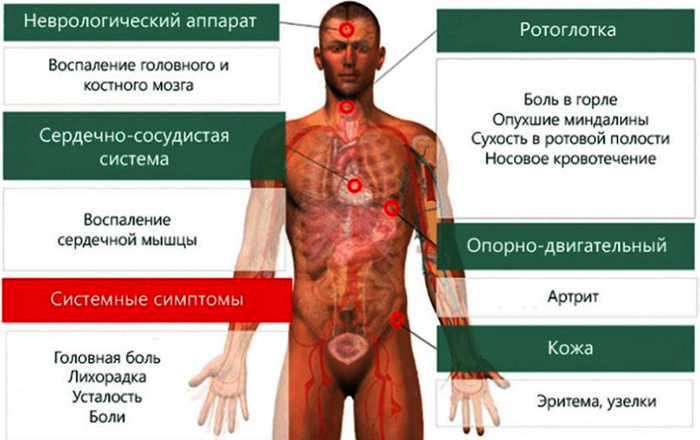
Signs and their severity may also depend on the specific pathogen that triggered the development of the disease.
With a tumor process
With neoplasms, the disease does not have a clear clinical picture, since the symptoms depend on metastatic reactions and the affected organ. Thus, severe pain in the area of another organ, cough with bloody discharge, soreness in the epigastric region, attacks of shortness of breath, and stool disorders may occur.
Analyzes and diagnostics
Sacroiliitis occurring in the region of the sacroiliac joint can be determined by concomitant symptoms during a visual examination by a specialist. It is possible to identify and establish a specific form of pathology only with the help of additional laboratory and instrumental studies.
Radiological signs of sacroiliitis
Radiological diagnostics is based on exposure to gamma radiation, which makes it possible to obtain an image of the problem area on a film or computer monitor.
Types of radiological examination:
- Simple.
- CT scan.
This diagnostics allows you to determine the following symptoms:
- the degree of narrowing of the joint space;
- the presence of changes in the area of the articular surface - contour, density, unevenness;
- the degree of compaction of bone tissue;
- erosive or sclerotic lesion;
- the presence of osteoporosis;
- the formation of purulent masses.
If necessary or if the method is not informative, additional studies may be prescribed.
Magnetic resonance imaging
This type of diagnosis is more informative than X-ray and is used if it is necessary to check soft tissues, as well as tissues that contain a large amount of fluid.
The study allows you to determine the presence of fatty deposits in the area of the bone marrow located near the focus inflammation, as well as the formation of inflammatory reactions in the area of muscle tissue, tendons or ligaments apparatus.
Laboratory analysis
Laboratory studies make it possible to determine the presence of inflammatory reactions and the factor of involvement of other neighboring organs in the pathological process.
The analysis is carried out in order to establish the following signs:
- erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR);
- quantitative content of C-reactive protein;
- the level of leukocytes;
- the presence of antibodies.
In some cases or with a hereditary predisposition, an antigen test is performed.
Sacroiliitis treatment
Sacroiliitis of the sacroiliac joint in most cases requires drug treatment. In more severe cases, surgery may be prescribed.
Medicines
The main and main method of therapy is medication., the action of which is aimed at reducing inflammatory processes and reducing the severity of pain.
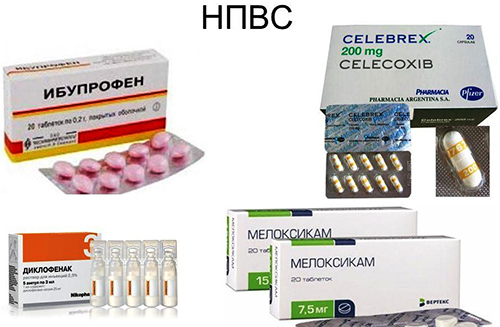
These drugs are divided into several main groups:
- NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs). The most commonly prescribed drugs are: Diclofenac, Ibuprofen, Nimesulide. The drugs have a similar mechanism of action and have anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects. The dosage is determined by the attending physician.
- Other anti-inflammatory drugs. This group of drugs includes Sulfasalazine. The medication has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
- Tumor necrosis factor antagonists. List of drugs: Adalimumab and Infliximab. They are used only with the permission of the attending physician.
- Steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These drugs include Prednisolone and Dexamethasone. Both drugs have a pronounced anti-inflammatory, antipyretic and anti-allergic effect.
For infectious forms of pathology, antibacterial drugs are additionally prescribed:
| Name of the drug | Mechanism of action | Mode of application |
| Ceftriaxone | The drug has a depressing effect on bacterial cell membranes, which leads to the death of microorganisms. | The agent is administered intravenously or intramuscularly. The daily dosage is from 0.5 to 1 g, no more than 2 times a day. |
| Clarithromycin | The agent causes a disruption in the production of protein compounds in the bacterial cell. | Capsules are taken orally 2 times a day. The duration of the course is set by the specialist. |
| Vancomycin | The action of the drug is aimed at blocking the multiplication of microorganisms by suppressing the production of nucleic acids. | The solution is administered intravenously as an infusion. The dosage is determined by the attending physician. |
Anti-TB drugs such as Kanamycin or Thioacetazone may also be used.
The dosage and duration of therapy is set individually by the attending physician.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy in most cases is prescribed for the rheumatoid form of the disease.
Procedures:
- Laser exposure. This type of treatment contributes to the saturation of cells and tissues of the body with oxygen and leads to a decrease in inflammatory processes.
- Infrared radiation treatment. This method helps to strengthen the immune system, accelerates regeneration, relieves inflammation, and reduces infiltrative blackouts.
- Magnetic treatment. The action of the magnetic field is aimed at eliminating inflammation and accelerating metabolic processes.
- Phonophoresis. This method of treatment allows you to effectively inject drugs into the body.
As a supplement, various gymnastic exercises can be prescribed to increase the mobility of the joints and relieve their stiffness.
Operations
Sacroiliitis of the sacroiliac joint in some cases requires urgent surgical intervention. Surgical treatment is prescribed in cases of severe disease, accompanied by the formation of purulent masses. To remove the contents, the painful area is opened, cleaned of pus, treated with an antiseptic solution, and then a bandage is applied.
Surgical operations are also indicated in cases of serious injury and partial / complete destruction of the joint. In this case, special pins or spokes are installed.
Diet
There are no restrictions on adherence to dietary regimens in patients with sacroiliitis. If necessary or in cases of development of a disease caused by damage to the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to additionally consult a doctor.
Consequences and complications, prognosis
With a delay in treatment or its complete absence, severe complications can develop.
Possible consequences:
- functional disorders of the affected joint;
- partial or complete destruction of bone structures, especially in the presence of tuberculosis infection;
- ankylosis, complete lack of joint mobility;
- destructive changes in the bones;
- the formation of cracks in the iliac region;
- septic lesion of the peritoneum or pelvic organs.
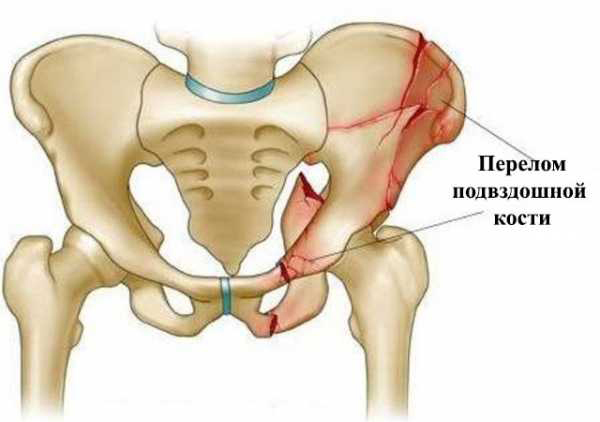
In severe cases, pathology can lead to disability. At the initial stages of the disease, the prognosis for complete recovery is favorable, since in the first stages, in the overwhelming majority of cases, it is possible to preserve all the functions of the joint.
In chronic forms of sacroiliitis, developing in the region of the sacroiliac joint, the prognosis depends on the methods of treatment and timely referral to a specialist. Therefore, at the first signs of illness, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor.
Disease video
Diagnostics and treatment of sacroiliitis:



