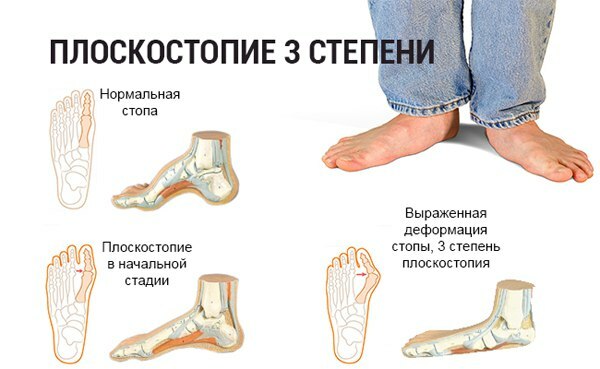
Flat feet 3 degrees - This is a pathological change in the shape of the foot, which is expressed in the omission of its transverse, as well as the longitudinal arch. The severity of the deformity of the lower limb is measured in degrees, and is determined by the results of a diagnostic examination.
Grade 3 flat feet is considered the most severe stage of this disease, which develops due to the extreme neglect of the disease. Such a curvature of the foot is possible only if for a long period of time the person did not take any measures aimed at treating the pathology.
Grade 3 flat feet are equally often diagnosed in men and women of all age groups. This disease of the musculoskeletal system can be congenital, or acquired at a certain stage of independent life. The main danger of grade 3 flat feet is that the patient's foot has a critical degree of curvature.
In this regard, there is a violation of the functions of the lower limb, concomitant diseases of the spine, knee and hip joints develop. Further progression of grade 3 flat feet leads to the fact that the person becomes limited in the vision of an active lifestyle, is deprived of the opportunity to independently move for long distance.
Record content:
-
1 Views
- 1.1 Transverse flat feet
- 1.2 Longitudinal flat feet
- 1.3 Congenital
- 1.4 Traumatic
- 1.5 Paralytic
- 1.6 Rachitic
- 1.7 Static
- 2 Symptoms and Signs
- 3 Causes
- 4 Diagnostics
-
5 Treatment methods
- 5.1 Plaster cast
- 5.2 Use of orthopedic products
-
5.3 Performing medical gymnastics
- 5.3.1 Closure of socks and heels
- 5.3.2 Rotation of the feet
- 5.3.3 Roller rolling
- 5.4 Surgery
- 6 Possible consequences and complications
- 7 Flatfoot videos
Views
Flat feet of grade 3 (the degree of curvature of the foot is determined by an orthopedic surgeon or surgeon) has several varieties. Each type of this disease is accompanied by painful symptoms that appear while walking or performing other active movements.
Transverse flat feet
Grade 3 transverse flat feet is characterized by the fact that the anterior arch of the plantar part of the leg becomes completely flat. At the same time, its frontal segment rests on the surface of the head of 5 metatarsal bones, which take the form of a fan-shaped divergence. At this stage, there is a reduction in the length of the feet. The first toe of the lower extremity has signs of external curvature.
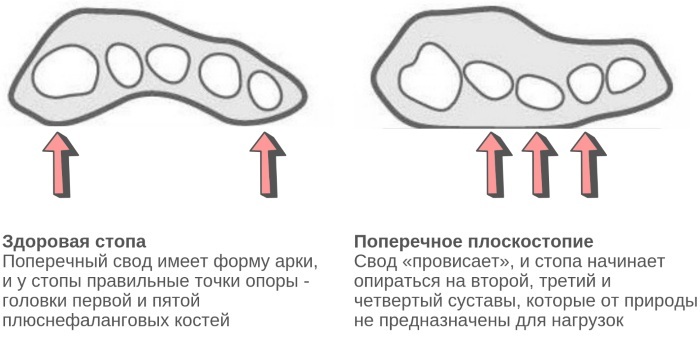
The middle toe undergoes hammer deformation. According to medical statistics, a transverse view of flat feet occurs in 55.22% of patients, who seek medical help with signs of curvature of the foot. This pathology of the musculoskeletal system is most often diagnosed in people aged 35 to 50 years.
Longitudinal flat feet
Flat feet of the longitudinal type are distinguished by the fact that in the conditions of this disease, the plantar part of the leg is completely in contact with the floor surface. There is a gradual increase in the length of the foot. During the diagnostic examination, it is found that the longitudinal arch of the lower limb is strongly flattened.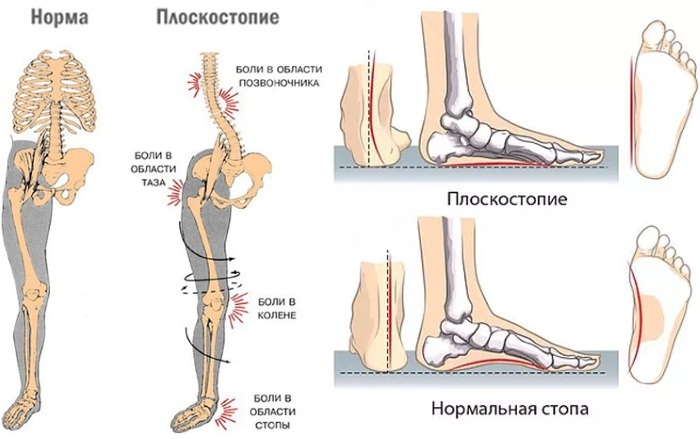
This type of disease is most often found in young people aged 16 to 25 years. At the same time, the longitudinal view of flat feet in men is diagnosed much less often than in women. Statistical data indicate that this type of lower limb disease accounts for about 29.4% of all cases of deformity changes in the feet.
Congenital
Congenital flat feet occurs in 3% of infants. Diagnosis of this disease in children under 6 years of age is complicated by the anatomical features of the foot structure. This is due to the fact that at this stage of development in almost every child, the plantar part of the leg initially has a flatter shape.
Therefore, children who have the first signs of flattening of the foot should be examined by an experienced and qualified orthopedic doctor. Timely detected flat feet of the 3rd degree enables doctors and parents of the child prevent further progression of the disease with the development of concomitant pathologies musculoskeletal system.
Traumatic
Traumatic flat feet belongs to the category of acquired deformities of the lower extremities. This pathology occurs after a person has received a severe fracture of the tarsal bones, ankles, and heels. A distinctive feature of flat feet of a traumatic origin is that it develops gradually.
Over a long period of time, there are no obvious signs of critical deformity of the feet. The lack of proper treatment and an effective rehabilitation scheme leads to the appearance of flat feet of the 3rd degree of severity.
Paralytic
Flat feet of grade 3 (degrees of foot deformity can be detected during a preliminary examination by a doctor) of the paralytic type occurs due to severe pathology of the lower extremities. In most cases, the painful condition of the legs is caused by the negative consequences of previous polio.
In this situation, the development of grade 3 flat feet occurs due to the paralysis of the muscle tissues of the sole and the muscles of the lower leg. This type of pathology practically does not lend itself to physiotherapeutic, drug and surgical treatment, as it is associated with dysfunctional disorders of the peripheral nerves.
Rachitic
Rachitic flat feet most often affects children whose musculoskeletal system suffers from lack of vitamin D, metabolic disorders associated with inadequate absorption of calcium salts and phosphorus.
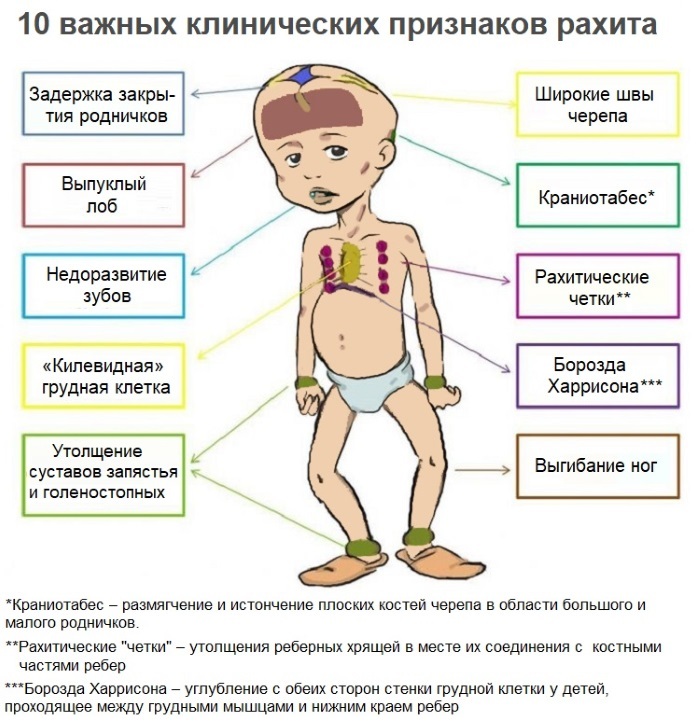
In this regard, under the load of the patient's body weight, the flattening of the too soft and weakened bones of the plantar part of the leg occurs. This pathology affects children of the younger age group. The main danger of rickets flat feet of the 3rd degree of severity is the irreversibility of pathological changes in the foot.
Static
Static flat feet is one of the most common types of this disease. This type of painful condition of the lower extremities occurs due to the initial weakness of the muscles of the foot, lower leg, as well as connective and bone tissue.
The static type of flat feet of the 3rd degree of severity develops under the influence of various factors. In this case, a sharp increase in body weight, a sedentary lifestyle, daily and long-term stay in an upright position is possible.
Symptoms and Signs
Flat feet 3 degrees (degrees of curvature of the foot affects the patient's gait) can be detected by the manifestation of the following symptoms:
- uneven abrasion of the heels of shoes with premature wear of the inner part of the sole;
- an increase in the length or width of the foot, which indicates deformational changes in the bone tissue of the leg (in most cases, the patient has to buy shoes 1-2 sizes larger than the previous one);
- severe clubfoot;
- change in gait towards its heaviness;
- various posture disorders associated with improper positioning of the foot;
- curvature of the toes;
- deformation changes in the plantar part of the leg with its complete flattening;
- disproportionate physical development of the muscle tissues of the lower leg and the rest of the lower extremities;
- sharp or aching pain in the plantar part of the foot, which bothers the patient at the time of performing active movements;
- deformation of the structure of the knee joints, which also affects the appearance of the legs and the quality of the patient's gait.
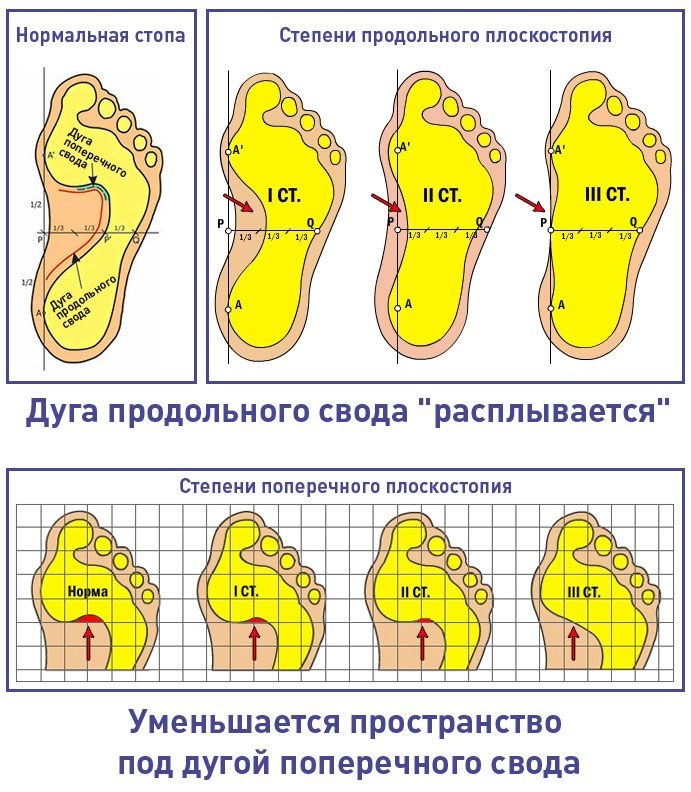 External symptoms of grade 3 flat feet are detected by performing a preliminary examination of the foot. The characteristic signs of this pathology are already acquired deformities of the bone and connective tissue of the lower limb.
External symptoms of grade 3 flat feet are detected by performing a preliminary examination of the foot. The characteristic signs of this pathology are already acquired deformities of the bone and connective tissue of the lower limb.
In most cases, a patient with flat feet of the 3rd degree of severity is not able to carry out independent movement without the use of special orthopedic shoes, which reduce the static load on the plantar part of the leg.
Causes
Grade 3 flat feet (degrees of foot deformity can be determined using an X-ray) occurs under the influence of negative environmental factors. The table below describes the main causes that can cause the development of this disease of the lower extremities.
| Causes of flat feet | Characteristics of pathological factors |
| Lack of physical activity | The lack of a full load on the muscular system of the foot and lower leg leads to an incorrect formation of the plantar part of the foot. This reason for the development of grade 3 flat feet is quite common in people with a sedentary lifestyle. |
| Genetic predisposition | Medical statistics indicate that about 3% of men and women get flat feet as a hereditary disease of the musculoskeletal system. In this case, the disease can manifest itself at any stage of a person's life. Flat feet of the 3rd degree of the genetic nature of origin is very difficult to respond to all types of treatment. |
| Rickets | Rickets, which struck the human body in early childhood, leads to deformation flattening of the foot due to the weakness of the bone tissue of the legs. In this case, grade 3 flat feet acts as a complication of an already existing disease of the musculoskeletal system. |
| Wearing uncomfortable shoes | Daily walking in high heels, using poor-quality or uncomfortable shoes, causes gradual deformation of the plantar part of the foot. At risk are women who prefer high-heeled shoes and sandals, men who wear sneakers and moccasins with completely flat soles every day. |
| Overweight | It has been scientifically proven that obese people experience critical flattening of the foot several times more often than men and women of normal weight. This is due to the fact that excess body weight creates an additional load on the plantar part of the foot. |
| Polio | Polio is a disease that affects the nervous system of the body. In this case, the development of grade 3 flat feet occurs due to partial or complete paralysis of the muscle tissues of the foot and lower leg. The muscles of this part of the body are constantly in a state of hypertonicity, which disrupts the process of correct formation of the plantar part of the leg. |
| Heavy physical activity | People who daily have to spend a long time in an upright position, standing on their feet, doing heavy physical work, also quite often face the appearance of flat feet. The pathology is aggravated if, in conditions of such a lifestyle, a person wears shoes with completely flat soles. |

Grade 3 flat feet do not appear suddenly. Quite often, the occurrence of a critical curvature of the foot is associated with a person's inactivity. For example, if the disease was previously at stages 1 and 2 of its development, but at this stage no action was taken to prevent further progression of the disease.
Diagnostics
A diagnosis of grade 3 flat feet is made based on the results of a physical examination of the patient's lower extremities by an orthopedic surgeon or surgeon. In addition to visual examination, the patient is prescribed X-ray of the feet with the creation of a load in the standing position. In this case, the image of the lower extremities is performed in 2 projections.
The doctor who diagnoses the patient determines the anatomically correct position of the ankle in relation to the foot. The reaction of the musculature of the arches to the created physical activity, the patient's gait, the peculiarity of the wear of the sole of the shoe are taken into account.
Decoding of X-rays of the lateral and direct projection of the feet is carried out by a radiologist. The diagnosis of grade 3 flat feet is made in a patient whose deformity angle is between 1 and 2 metatarsal bones reached the level of 20 degrees, and the pathological deviation of the 1st toe is within 40 degrees.
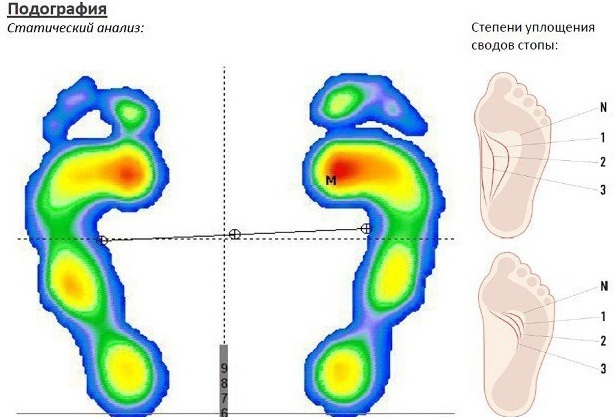
X-ray examination is a prerequisite for diagnosis. If concomitant complications of the disease are found that have affected other parts of the musculoskeletal system, additional examination methods can be used in the form of MRI, ultrasound.
Treatment methods
Therapy of grade 3 flat feet is complex. The main task of the attending physician and the patient himself is to prevent further progression of the disease. And also the creation of the most favorable conditions for the elimination of deformation changes in the foot.
Plaster cast
The use of plaster casts is carried out in relation to children who have been diagnosed with congenital flat feet. In this case, the child's lower limb is cast in order to stop further flattening of the foot, as well as to give the plantar part of the leg an anatomically correct shape. The duration of wearing a plaster cast is determined by the doctor.
Use of orthopedic products
This method of therapy for grade 3 flat feet involves the daily wearing of insoles or shoes, the shape of which is characterized by the presence of bulges affecting the patient's flat sole. Under the influence of orthopedic products, signs of flattening of the foot are gradually eliminated, and high-quality prevention of further progression of the disease is performed.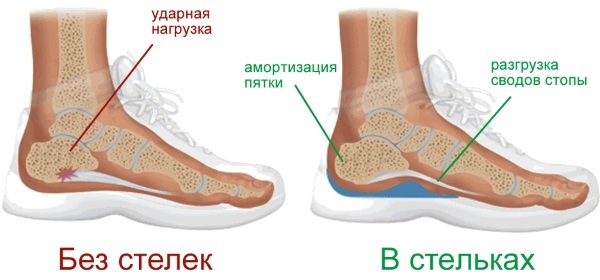
Orthopedic shoes and insoles are made to order, taking into account the individual needs of each patient. The wearing of corrective products of this type can last for several years, depending on the nature and severity of the pathological process.
Performing medical gymnastics
Regular exercise of remedial gymnastics for the legs, which is combined with wearing orthopedic shoes, allows you to achieve positive results in correcting deformation changes in the foot.
Closure of socks and heels
This exercise is aimed at improving local circulation and stimulating the plantar leg to regain its anatomically correct shape.
The principle of performing therapeutic exercises of this type is as follows:
- Legs must be placed shoulder-width apart.
- The feet turn to the sides.
- After that, it is necessary to alternately close the heels and socks.
It is recommended to do at least 12 reps in 3 sets. Before starting the exercise, you should carry out a high-quality warm-up of the ankle joint.
Rotation of the feet
To complete this exercise, you will need to sit down in a chair, and then follow the following sequence of actions:
- Fix the heels to the floor surface by lifting the rest of the sole.
- Perform circular movements with the feet to the left and right sides.
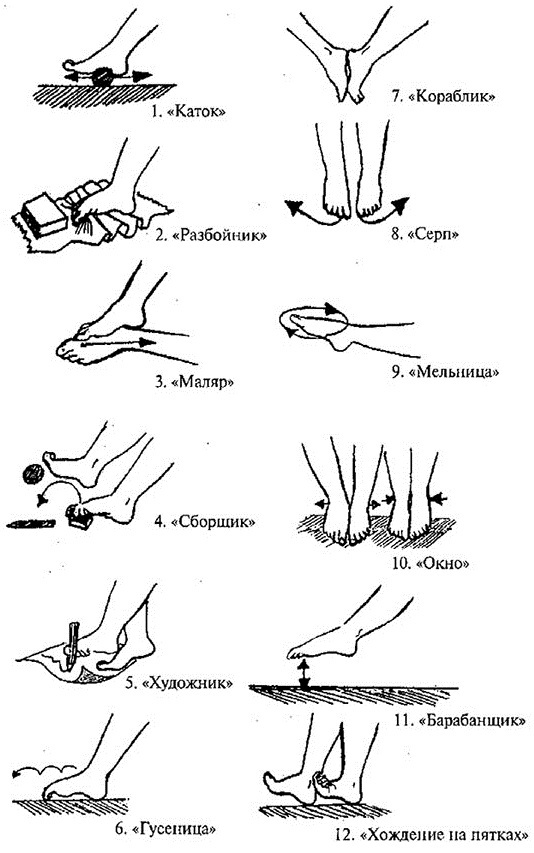 For each leg, you need to do 12 reps in 3 sets. The main goal of this exercise is to prevent further deformation changes in the calcaneus.
For each leg, you need to do 12 reps in 3 sets. The main goal of this exercise is to prevent further deformation changes in the calcaneus.
Roller rolling
Rolling the roller with the plantar part of the leg is an effective physiotherapy exercise, which runs like this:
- You must sit in a chair or chair.
- Put a special roller made of hard and durable material on the floor. At home, you can also use an absolutely round log, or a glass bottle.
- The plantar part of the lower extremities is installed on the surface of a roller or other device, and then rhythmic movements are performed to roll these objects with the feet of the feet.
This exercise is recommended to be performed daily 2-3 times a day with a therapeutic session duration of at least 40-60 minutes. If you follow these rules, you can count on achieving a positive result.
Surgery
Surgical operation is a radical method of therapy that is used in if the correction of grade 3 flat feet is impossible with the help of physiotherapy and orthopedic products. Surgical intervention is performed under the influence of general anesthesia in the sterile conditions of the surgical department.
With the help of medical instruments, the surgeon gives the patient's feet an anatomically correct shape, eliminating the signs of deformational changes. In this case, the method of superimposing corrective metal structures can be used, which direct the bone tissue of the leg at a certain angle of development.
Possible consequences and complications
The lack of timely measures for the prevention and treatment of flattening of the foot can lead to the fact that flat feet of grade 3 will entail the development of the following complications:
- chronic pain inside the hip, ankle and knee joints;
- heavy and unnatural gait;
- severe clubfoot, which will be especially pronounced while walking;
- abnormal lengthening of the foot and toes;
- periodic ingrowth of the thumbnail, the removal of which requires surgical intervention;
- the foot is too wide;
- deformation of the structure of the knee joints;
- increased tendency to develop osteoarthritis;
- poor posture, as well as a high likelihood of scoliosis;
- the inability to move independently over long distances due to the feeling of constant pain in the plantar part of the foot;
- problems with maintaining balance and frequent falls from their own height;
- disability associated with partial or complete disability, which is caused by severe and irreversible deformities of the feet.
It is possible to prevent the development of the above consequences only if the treatment of the first signs of flat feet is started on time, preventing the transition of the disease into complicated forms.
Grade 3 flat feet is a pathology of the musculoskeletal system, in which there is a progressive flattening of the arch of the plantar part of the leg. Diagnosis of this disease is carried out by an orthopedic doctor or surgeon. The main method of examining patients with signs of grade 3 flat feet is foot radiography using frontal and lateral projections.
In this case, the patient's legs should be under load. X-rays are deciphered, during which the degree of curvature of the 1st and 2nd metatarsal bones, as well as the 1st toe of the lower limb, is measured.
Flatfoot videos
Komarovsky on how to treat flat feet: