Meningitis is an acute infectious disease, which can provoke serious inflammation of the lining of the spinal cord, as well as the brain. Infection can be caused by bacteria, fungi and viruses. You can prevent the disease or stop it at an early stage if you introduce a vaccine against this pathology.
Record content:
- 1 What is meningitis and how is it dangerous?
- 2 Sources of infection, symptoms
-
3 Vaccination against meningococcal infection
- 3.1 Active emergency immunization
- 3.2 Passive emergency immunization
- 3.3 Vaccination of high-risk contingents
- 4 The mechanism of action of vaccinations
- 5 Duration of the protective effect
- 6 Is revaccination necessary?
- 7 Who needs meningococcal immunization?
- 8 At what age are children and adults vaccinated against meningococcus?
-
9 Is it necessary to get vaccinated: pros and cons
- 9.1 Pros and cons of vaccinating a child
- 10 Vaccination schedule
- 11 How much does a vaccine cost - average prices
- 12 Free vaccinations
- 13 Vaccines against meningococci
- 14 Which meningococcal vaccine is best for children?
- 15 How is the vaccine done?
- 16 When vaccination is contraindicated
- 17 Possible side reactions
- 18 Well-being after vaccination and the possibility of complications
- 19 Meningitis vaccine video
What is meningitis and how is it dangerous?
Meningitis is a neuroinfectious pathology. The most difficult is the so-called reactive meningitis. It proceeds very quickly, and it is often possible to diagnose it already at the stage of serious complications.
It is very important to start treatment as early as the first day after the onset of primary symptoms. Otherwise, the patient may lose sight and hearing. Sometimes meningitis can lead to coma and even death.
If we talk about the types of meningitis, then it can be divided into two broad categories:
- Primary. This type of pathology is characterized by the fact that it is not possible to immediately identify the defeat of the meninges.
-
Secondary. Such meningitis, as a rule, is a complication after the underlying disease (for example, after otitis media and other pathologies). This type of meningitis develops for an extremely long time and may not appear for a long time. However, sooner or later, pathology leads to damage to the lining of the brain.
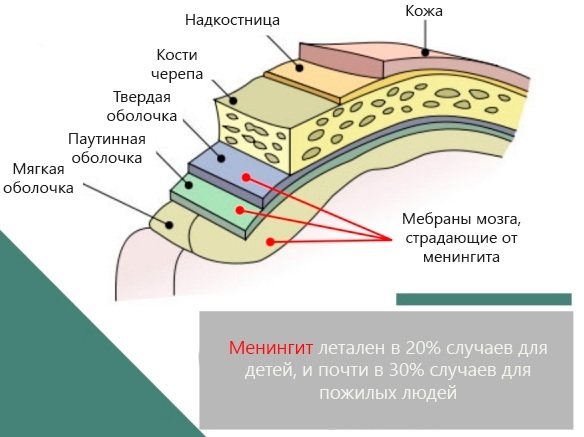
The main danger of pathology is that it can develop in just a few days and cause a very serious defeat. There is also the so-called tuberculous meningitis, which does not appear at all for several weeks. However, the body is actively developing.
Sources of infection, symptoms
The causative agents of meningitis are divided into several categories. They are viral, fungal, and bacterial. Viral meningitis very often develops against the background of other infections.
For example, it can be diagnosed with chickenpox, rubella, and also with damage to the meninges. Sometimes it is a complication after a flu or other illness. Also among the viral pathogens of meningitis, the herpes virus can be noted.
The danger is bacterial meningitis. It occurs against the background of any purulent process in the body. For example, this type of meningitis can develop against the background of pneumonia, an infected burn, sore throat, abscesses, and more.
In most cases, meningitis is caused by microorganisms that trigger the development of meningitis. That is why this pathology is also called meningococcus. You can even get infected with this virus by airborne droplets.
The main danger of this infection is that meningitis is very similar in symptoms to a common respiratory viral infection. That is, a person has a slight runny nose, the throat turns red, and a cough develops.
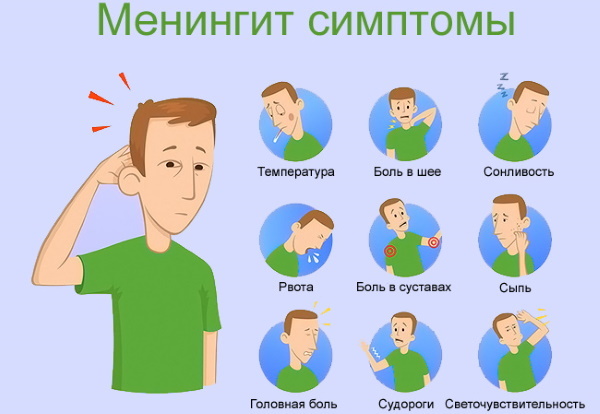
In addition to the standard symptoms (sore throat, colds on the lips and other signs), a very severe headache appears. The pain attacks are so severe that the patient does not even pay attention to other symptoms. Vomiting and nausea may accompany the headache.
If such a symptom appears, the patient must be hospitalized immediately. Another noticeable sign of meningitis is that when a person's body temperature rises against the background of a viral diseases, in addition there are very strong pains in the neck and back, and the pain syndrome increases with each movement heads.
Drowsiness and confusion are the main signs of a cold. However, if, in addition, the patient has bouts of vomiting and nausea, then this may also be the first signal of the development of meningitis. You also need to immediately call an ambulance if the patient has seizures (no matter how intense and prolonged).
Children under 1 year of age should be especially closely monitored. In this case, when meningitis occurs, they immediately experience a whole range of symptoms. As a rule, very young children develop a fever and cry monotonously.
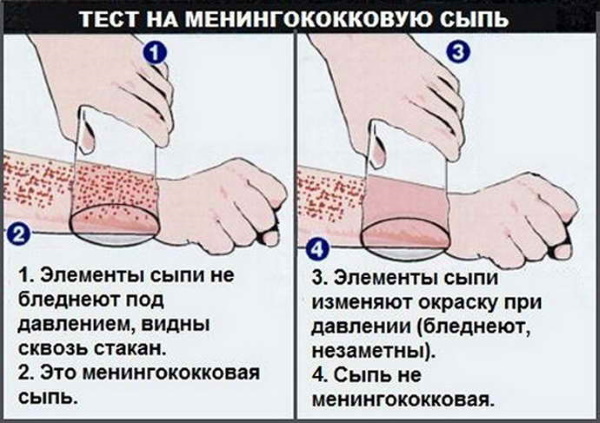
On external examination, it is easy to identify bulging fontanelle. Also, a symptom of meningococcus is a rash that appears at the same time as fever.
Vaccination against meningococcal infection
This type of vaccination is optional. That is, it is not included in the list of required injections. As a rule, such vaccinations begin to be prescribed en masse only if an epidemic is registered.
This means that when 20 cases of this pathology are diagnosed per 100,000 people, preventive measures may be required. As a rule, massive vaccinations against meningococcus are prescribed for children aged 1.5-8 years. If there is a serious risk of an epidemic, then at least 85% of the population is vaccinated.
The meningococcal vaccine is the most beneficial and safest solution if the disease threatens a large number of people. Thanks to the vaccine, antibodies are stimulated, which, if a real threat appears, will destroy the infection at the very initial stage of its formation.
Active emergency immunization
Similar activities are carried out in those areas where foci of meningococcal infection have been registered. Also, active emergency immunization is required in places where at least one patient with a generalized form of meningitis (meningococcemia) has been registered.
Before performing this type of vaccination, it is necessary to establish the serogroup of meningococci, which provoke the development of the disease. However, if we are talking about a possible epidemic, then there is no time for additional research. In this case, vaccination is prescribed without prior determination of the meningococcal serogroup.
If a person (in this case he is called a contact person), has been in contact with a patient suffering from meningitis, then the patient also needs to be vaccinated for this type of meningitis within the first five days after contact with an infected person human.
In this case, it is required to determine the exact serogroup of the patient's meningococci. Moreover, if the contact person has nasopharyngitis, then this condition does not apply to a contraindication to vaccination. However, this is only possible if the person has a normal body temperature.
If a person has already had a mild form of the disease, then vaccination is allowed only a month after the patient has fully recovered. Provided that the person has suffered from a severe form of meningitis, the injection is prescribed no earlier than after 3 months after complete recovery and if the neurologist has not identified any contraindications.
Passive emergency immunization
This type of vaccination is prescribed if a patient has meningococci with a serogroup that does not correspond to standard vaccines. In this case, the patient is injected with a normal immunoglobulin. This procedure must be performed within 7 days after the first detection of the disease.
Vaccination of high-risk contingents
This is a prophylactic vaccination that is performed in a situation where it is necessary to prevent the spread of an infectious disease, as well as during the formation of group immunity in children aged from 1.5 years. This type of vaccination is intended for children who have been in preschool and other educational institutions for a long time.
The mechanism of action of vaccinations
The meningococcal vaccine can be multi-component or single-component. In the second case, the vaccine contains the serum of only one pathogen. In multiple formulations, serum of a larger number of pathogens is used, thanks to which the immune system forms protection against several types of bacteria at once.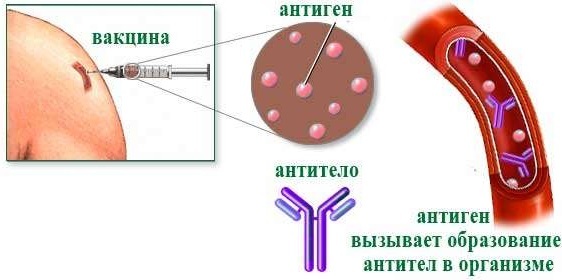
As a rule, after a single-component injection, the immune system develops the necessary antibodies already on the fifth day. Such immunization is very effective against certain pathogens. If we are talking about multiple vaccinations, then the formation of antibodies occurs in 2 weeks.
As soon as the serum enters the body, serious biological and chemical processes begin to take place in it. First of all, the immune system detects the pathogen that was injected, recognizes it and starts producing antibodies.
It is also worth noting that children under 1 year old, as a rule, are not prescribed such vaccinations. The fact is that at this age the immunological reactivity is not yet fully developed, therefore this type of vaccination is prescribed only at a later age. However, there are exceptions (for example, during an epidemic) when children are injected with serum from 3 months.
Duration of the protective effect
The duration of the vaccine may differ depending on the specific drug and the types of pathogens. Some vaccinations can form lifelong immunity, accordingly, re-vaccination is not required.
It is worth noting that if such an immunization is made to a child, then in this case the likelihood of developing meningitis decreases to 0.1%. Even if the infection does occur, then in this case there will be no complications or negative consequences.
Is revaccination necessary?
A single vaccination allows you to activate the protective functions of specific immunity. In this case, re-administration of the serum is usually not required. However, it all depends on the age of the patient. If the first vaccination was made at a too young age, for example, when the child was 3 months old, then revaccination is needed.
It is also worth considering that the same person is allowed to inject serum no more than 1 time in 3 years.
Who needs meningococcal immunization?
The vaccine, which is prescribed for meningococcal infection, is required if, for example, there is a person around the child who already has meningitis. In this case, the risk of contracting pathology is 95%.
On the other hand, in developed countries, immunization for the development of meningitis is not always carried out, since the pathology is practically completely eliminated, so the risk of meeting on the street (or in your environment) a person with a similar disease is reduced to minimum.
When deciding on the need for vaccination, you should pay attention to the fact that drugs for vaccinations are very effective and quite easily tolerated by the body, even when it comes to small child.
It is also worth protecting against possible infection if a person soon plans to visit the so-called dangerous meningitis zones (for example, Africa). When traveling to such countries, it is recommended to be vaccinated before the trip.
Also at risk are students who live in dormitories, conscripts, employees of medical institutions.
At what age are children and adults vaccinated against meningococcus?
There is no consensus on this matter. The fact is that some experts are sure that as soon as the child reaches the age of two, there is absolutely no point in this vaccination. However, this theory has not been confirmed.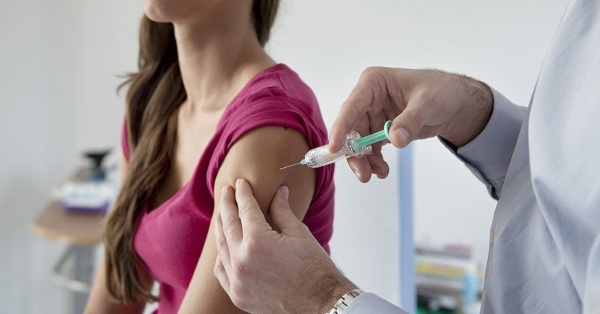
Other doctors, on the contrary, are inclined to believe that up to 1.5-2 years old, such a procedure cannot be performed, since the child's immune system has not yet fully formed. This means that she simply will not be able to give a stable reaction to the injected drug. Therefore, if the vaccination was performed before the age of two, it will have to be repeated twice.
The procedure is first performed at the age of 3 months. Newborn babies who are breastfed are protected from such infections, thanks to special antibodies that enter the body along with the mother's milk.
Re-injection of serum is carried out when the patient reaches 3 years of age. Only in this case can you be sure that the necessary antibodies have been developed in the body.
If we talk about adults, then in this case there are no serious age restrictions.
Is it necessary to get vaccinated: pros and cons
The vaccine against meningococcal disease is not mandatory, so the decision is made by the person himself or his parents. However, there are many factors to consider.
For example, this type of vaccination is recommended in several situations:
- If any of the parents in childhood or more adulthood suffered from meningitis, then the child should definitely be vaccinated.
- Vaccination is carried out if a person constantly suffers from various pathologies affecting the upper respiratory tract. In this case, the vaccine activates the immune system and strengthens the body.
- If the doctor cannot determine exactly why the patient has a particular disease of the nasopharynx. In this case, the vaccine is prescribed just in case, since the symptoms of meningitis are very similar to the typical manifestations of colds.
It is also worth noting that vaccination is the only treatment available for meningococcal infection. In some countries of the world, vaccination is mandatory in order to exclude possible deaths from meningitis in the population.
Pros and cons of vaccinating a child
If we talk about the benefits of vaccination for children, then it is worth paying attention to the fact that today many children quite often get sick during the year. If in this case, vaccination is carried out, then it will positively affect the state of the immune system. In this case, the protective functions of the body are strengthened and, accordingly, the child stops getting sick so often.

If we talk about the disadvantages of this procedure, then many people are afraid that a small amount of pathogenic microorganisms will be introduced into the child's body, which just cause meningitis. However, this volume is so insignificant that there is no reason to fear the occurrence of pathology. In addition, there are no active microorganisms in the serum.
Vaccination schedule
It all depends on the age of the patient and when the decision was made to administer the serum:
- When vaccinated at 3 months, serum is injected 3 times with an interval of 1.5 months. Next, you need to perform revaccination, which is performed at 1.5 years.
- If the doctor prescribed vaccination at 6 months, then in this case only 2 vaccinations are performed with an interval of 1.5 months. Revaccination is performed 1 year after the last serum injection.
- When it comes to older children and adults, a single vaccine is used. It is administered only once as directed by a doctor.
How much does a vaccine cost - average prices
Vaccinations can be carried out both in a district medical institution and in a private clinic. The cost of the drug varies from 250 to 7000 rubles. This price range is due to the type of bacteria to which antibodies must be synthesized. Also, the price is influenced by the manufacturer of the drug and the amount of serum that the doctor prescribes.
The vaccine can only be purchased with a prescription. If the patient has applied to a private institution, then the cost will be increased, since an additional examination will be required.
Free vaccinations
The vaccine against meningococcal disease can be introduced free of charge only under special conditions:
- If there is a danger of a meningitis epidemic in the village.
- If the child spends a lot of time in kindergarten, where there are patients with meningitis.
- Provided that the incidence rate is increased in the region.
- When diagnosing immunodeficiency in a child.
Vaccines against meningococci
On the territory of the Russian Federation, you can get different types of vaccines that are produced in different countries.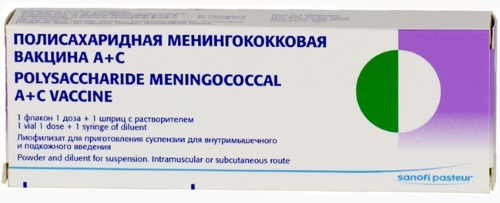
| Vaccine name and manufacturer | What type of meningococcus is assigned | Peculiarities |
| Meningococcal vaccine (Russia) | A + C | Does not protect against purulent meningitis. Serum is allowed to be administered to patients from 1.5 years old. After 3 years, revaccination will be required. |
| Meningo (France, firm "Aventis Pasteur") | A + C | Serum can prevent the development of cerebrospinal meningitis. It is used for adults and children from 1.5 years old. |
| Mantsevax (Belgium, GlaxoSmithKline) | A + C + W + Y | Used for children aged 2 years and older and adults. Also, this serum is necessarily prescribed to pilgrims heading to Mecca. |
| Menaktra (USA, Sanofi Pasteur Inc.) | A + C + W-153 + Y | Forms a very stable immunity to various serogroups of meningococcus. The drug is recommended for children from 2 years old and adults up to 55 years old. |
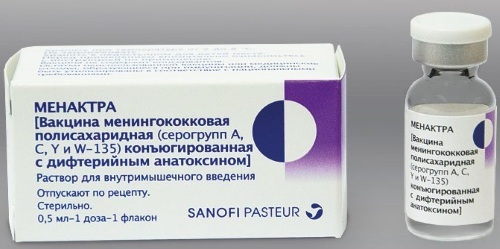
Group A and C drugs are characterized by a relatively low degree of immunity development. The more serogroups the drug covers, the more types of antibodies the patient's body can create.
Which meningococcal vaccine is best for children?
Most of the drugs are allowed for children aged 1.5-2 years. All vaccines described earlier are safe for children, as they do not contain live microorganisms. That is, the serum is not capable of provoking the development of meningitis.
If we talk about which remedy is considered the best for the child, then the attending physician will be able to recommend the exact drug. Most parents give preference to foreign-made drugs, since they have more a wide spectrum of action and allow the production of antibodies from different types of meningococcal infections.
How is the vaccine done?
The doctor usually administers the meningococcal vaccine intramuscularly. Subcutaneous administration is also allowed. The tool is a dry substance that dissolves with the liquid attached to it.
The vaccine is given in the front of the thigh or forearm. This serum cannot be injected into the gluteus muscle. The same applies to other areas of accumulation of subcutaneous fat.
When vaccination is contraindicated
Vaccination against meningitis is allowed not only to healthy adults and children, but also to those who already suffer from any pathologies. Vaccination is performed for mild meningitis. However, this type of vaccination is not performed if the patient suffers from an acute infectious disease in which there is an increased body temperature.
Also, serum should not be administered in case of exacerbation of chronic pathology, as well as if a person suffers from an allergic reaction to the drugs that are part of the vaccine.
Possible side reactions
This is a pretty broad topic as it all depends on many factors. First of all, the doctor must assess the general well-being of the person; he also needs to study the drug that is planned to be administered.
Despite the fact that the injection procedure is extremely simple, you need to be confident in the professionalism of the doctor. Vaccination of this type does not threaten serious consequences. However, in some situations, the body may react negatively to the injected drug.
For example, some patients after the procedure often complain of chills, fever, weakness, drowsiness and muscle pain. Also, some develop swelling, minor skin rashes and a small induration in the area where the drug was injected.
However, most of these side effects disappear after a few days. The only exception is the seal at the injection site, which can bother for several more weeks. But such a reaction of the body is considered quite normal.
Also, experts prefer not to prescribe injections against meningitis if the patient has difficulty breathing, swelling in the mouth, tachycardia.
If hemophilic serum is used, then in this case, local side effects appear in 10% of patients. These include the blanching of the skin, the appearance of rashes. However, the ailment disappears very quickly.
Well-being after vaccination and the possibility of complications
As a rule, patients tolerate the administration of the vaccine quite easily. Sometimes the first days there may be weakness and general malaise. A similar reaction is caused by the fact that the immune system recognized the injected drug and began to actively produce antibodies.
The vaccine does not cause complications. In addition, additional drug therapy for meningococcal infection will not be required. The only danger can arise in the event of an allergic reaction.
In this case, it is necessary to take an antihistamine drug. However, this happens extremely rarely, since before the administration of serum, the doctor determines whether its components are irritants for the body of a particular patient.
Meningitis vaccine video
Komarovsky will tell you whether it is worth doing a vaccine for meningitis:



