The need for emergency pain relief associated with the urgent implementation of diagnostic or therapeutic procedures may arise in a nursing mother at any time. However, the use of most anesthetics for her is prohibited, since, once in breast milk, they can harm the baby. Lidocaine is considered an exception to this rule.
Record content:
- 1 Indications for use
- 2 Compound
- 3 In what form is it produced
- 4 Pharmacodynamics
- 5 Pharmacokinetics
- 6 Breastfeeding
- 7 Contraindications
- 8 Overdose
- 9 Side effects
- 10 Drug interactions
- 11 Storage conditions and periods
- 12 Analogs
- 13 Video about the drug
Indications for use
Lidocaine is a popular local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic agent. It is a clear, colorless, odorless liquid. The drug is used for all types of local anesthesia (injections, applications, irrigation, drops), as well as in the complex treatment of heart diseases.
Lidocaine can be produced as:
| Release form | Application area |
| Ampoules | The main area of application of ampoules (2%) is all types of dental procedures that require anesthesia. Also, compositions of this concentration are sometimes used for simple surgical operations, when local anesthesia is sufficient, and in otolaryngology for painful examinations.
 Ampoules (10%) are required:
|
| Spray | It can be used in dentistry for simple operations on the oral mucosa. In therapy, it is used:
|
| Drops | Anesthesia with eye drops is a practice used in ophthalmology when it is necessary to carry out:
|
| Adhesive plates or plasters | They are used for the symptomatic treatment of pain in:
|
Compound
In its original form, lidocaine (white crystalline powder) is poorly soluble in water, therefore, in the drug of the same name, lidocaine hydrochloride is used as an active component.
It is a water-soluble substance that has the properties of lidocaine and is capable of:
- as an anesthetic: to reduce the permeability of the cell membranes of neurons for sodium ions, under the action of which the neuron goes into an excited state. Due to this, the signals received from the receptors located at the site of exposure to the drug lose their intensity, which is perceived by a person as a feeling of numbness;
- as an antiarrhythmic: to increase the absorption of potassium ions by cardiomyocytes, causing a slowdown and normalization of the heart rate, thereby eliminating the manifestations of arrhythmia and tachycardia.
An isotonic saline solution (sodium chloride and distilled water) is present as an auxiliary solvent in the liquid preparation. Plasters with lidocaine contain excipients, thickeners, preservatives and components that ensure the stickiness of the composition.
In what form is it produced
Lidocaine can be produced as:
- 2 ml ampoules containing 2% lidocaine solution. Each ampoule contains 40 mg of active substance. It can also be 2 ml ampoules containing 10% lidocaine solution (200 mg lidocaine hydrochloride). Glass ampoules for injection (10 pcs.) With a breaking point and a green code ring are in 2-cell blisters (5 pcs. Each), placed in a cardboard box. Packing price - 28 rubles. (2% solution), 37 rubles. (10% solution);
- spray in a plastic can with a spray, with a capacity of 38 g, (650 doses), placed in a cardboard box. Price - 28 rubles;
- eye drops 2% in a dropper tube with a capacity of 5 ml. Price - 30 rubles;
- plasters. The medicinal composition (lidocaine with the addition of thickeners and adhesives) is applied to a fabric base and covered with a PET film, which is removed before use. Plasters 1, 2 or 5 pcs. packed in boxes, price - 50 rubles.
Lidocaine in any dosage form is available exclusively by prescription.
Pharmacodynamics
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic that provides a short-term anesthetic effect. Pain relief is achieved by temporarily blocking the transmission of signals from the treated area. This is felt by the patient as a feeling of numbness.
The nature of the drug's action depends on the route of administration: with intravenous injection, 1 minute is enough for kidocaine to show analgesic qualities.
The effect lasts for 1 hour. When injected intramuscularly and with superficial local anesthesia, tissues lose sensitivity after about 15 minutes, and it takes about 20 minutes to recover. The eye drops begin to act in 2-3 minutes, providing an analgesic effect for 5-6 minutes.
Pharmacokinetics
Depending on the dose of kidocaine received and the characteristics of the anesthetized area of the body, the maximum concentration of the drug in the tissues is reached in 10-20 minutes.
Further, lidocaine is absorbed into the bloodstream. The absorption time is determined by the intensity of blood flow in this area (on average, 5-15 minutes). At the same time, about 60-80% of the active substance loses its properties, entering into a biochemical reaction with blood proteins.
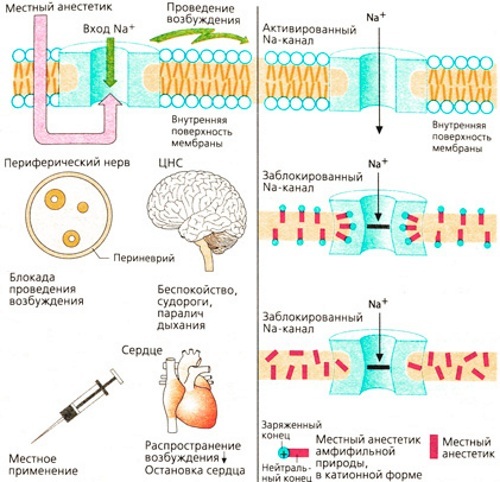
The remaining amount of lidocaine goes first to the organs that are most intensively supplied with blood (brain, liver, heart), and then to muscle and adipose tissue. After that, most of it is metabolized by the liver with the formation of metabolites of 2 types and removed from the body. A small amount of lidocaine (from 5% to 20%) is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Breastfeeding
Any drug taken by a woman during the hepatitis B period inevitably enters the child's body.
The degree of harm they cause depends on:
- concentration of the drug in breast milk;
- the mechanism of its action;
- the time required for the withdrawal of the remnants of the drug from the mother's body.
Taking these factors into account, lidocaine has the following advantages when breastfeeding:
- it enters the internal organs in small doses, since most of it, being absorbed into the blood from the injection site, binds to blood proteins. There will be an insignificant amount of it in breast milk;
- with proper use, lidocaine does not affect the work of the central nervous system and does not interfere with the work of other body systems, it cannot harm the baby;
- the duration of action of the drug is usually limited to half an hour: the disappearance of the feeling of numbness means that it has already lost its properties;
- there are lidocaine-based gels intended for children 1 year of age, which are used, for example, during the eruption of milk teeth. Its concentration in these funds is several times higher than in breast milk after injection of the drug.
Lidocaine can be considered a drug that is safe for both a nursing mother and her baby.
You can reduce the risk of complications by adhering to simple rules:
- do not try to use lidocaine on your own;
- if it is necessary to perform anesthesia, be sure to warn the doctor about the fact of breastfeeding: then he will use the composition with the lowest possible concentration of the active substance or select a safe method anesthesia;
- for "safety net" skip the next feeding, replacing it with an artificial mixture, and express the milk. By the next meal, there is no chance of lidocaine being present in breast milk.
The optimal doses, practically eliminating the risk of complications for a nursing mother and baby, depend on the method of anesthesia and the place of administration of the drug.
In the absence of contraindications, they are:
- 100-200 mg (½ ampoule or 1 ampoule of 10% solution) - with conduction anesthesia. These are intramuscular injections into the area located next to the nerve fibers, through which signals are transmitted from the area that you want to anesthetize;
- 40-60 mg (2-2.5 ampoules of 2% solution) - with intramuscular administration of lidocaine, preceding simple operations on the finger, ear, nose;
- 6 drops in each eye (three times, 2 drops with an interval of 1 min.) - when performing diagnostic ophthalmic procedures;
- 2-20 ml (1 ampoule of 2% solution) - for thermal anesthesia of the oral mucosa (applications with lidocaine);
- 400 mg - with injections in order to normalize the heart rate in arrhythmias. Injections are performed according to the following scheme: first, 50-100 mg of a 2% solution intravenously. The next day, with an interval of 3 hours - 2 injections of 100 mg of a 10% solution intramuscularly.
The maximum safe dose for an adult is 200 mg per day.
Contraindications
Lidocaine during breastfeeding can harm the woman herself or her baby if there are contraindications to the use of the drug. For this reason, before using it, a tolerance test is mandatory and the history is carefully studied.
Anesthesia with lidocaine is not possible under the following circumstances:
- excessive sensitivity to the drug;
- previous undesirable reactions to lidocaine;
- liver diseases that interfere with the full metabolism of this substance;
- a number of heart pathologies during an exacerbation;
- myasthenia gravis is a neurological disorder manifested by pathological fatigue and weakness of certain muscle groups.
With caution, the drug is prescribed to people with:
- existing chronic cardiovascular disease;
- conditions that are accompanied by impaired blood flow in the liver;
- impaired renal function;
- the patient is over 65 years old.
For the use of plates, sprays and applications with lidocaine, a contraindication is any damage to the skin on the treated area.
During pregnancy, the question of the advisability of using lidocaine should be decided by a doctor, taking into account the following factors:
- the possibility or impossibility of postponing a procedure that requires anesthesia at a later date;
- a threat to a woman's health in case of refusal of treatment;
- harm to the unborn child when performing anesthesia.
In the presence (if it is suspected) of contraindications to lidocaine in an infant, combined with the need for anesthesia for a nursing mother, the doctor, in depending on the circumstances, chooses one of the solution options:
- postpone for a while the procedure requiring anesthesia;
- use a different type of anesthetic;
- recommend skipping one feeding after the procedure, offering the baby a mixture appropriate for his age, and expressing the milk.
Overdose
When performing surface anesthesia, overdose is almost impossible.
Its concentration in the blood, tissues and internal organs increases with:
- the introduction of large doses of the drug intramuscularly;
- its repeated use;
- disruption of the lidocaine metabolism process.
Depending on the injection site, this can lead to the following undesirable phenomena:
- prolonged loss of tissue sensitivity in nearby areas of the body;
- paresthesia: tingling sensation, burning sensation;
- hyperacusis, in which any sound causes pain and discomfort;
- numbness of the tongue, impaired articulation;
- temporary decrease in visual acuity;
- tremor;
- dizziness;

- convulsions;
- disorders of the heart;
In severe cases, with the introduction of high doses of the drug intravenously, apnea and bradycardia may develop. When symptoms of an overdose appear, the administration of the drug is stopped.
To normalize the patient's condition, the following means are used:
- relieving cramps;
- supporting the work of the heart and lungs;
- accelerating the withdrawal of lidocaine from the body.
External manifestations of an overdose do not require treatment; with a decrease in the concentration of the drug in the body, they gradually weaken and disappear.
If there are signs of an overdose, a nursing mother should temporarily stop breastfeeding, and when it resumes, carefully monitor the baby's behavior.
Side effects
Lidocaine during breastfeeding, when used correctly, has practically no side effects. However, the likelihood of their appearance increases if there were contraindications or in case of an overdose.

In this case, negative reactions from certain body systems are possible:
- immune: allergies, anaphylactic shock (with repeated administration of the drug);
- nervous: nervousness, increased excitability or drowsiness, tremors, convulsions, loss of control over the muscles of the face;
- cardiovascular: increased blood pressure, bradycardia, tachycardia, arrhythmia. In severe cases, cardiac arrest;
- respiratory: breathing disorders, bronchospasm, shortness of breath, apnea;
- digestive: nausea, vomiting;
- organs of vision: a feeling of "fog" in the eyes, double vision, sometimes - temporary loss of vision, redness of the eyelids, burning sensation in the eyes;
- hearing organs: extraneous tinnitus, discomfort;
- skin: irritation, redness, rash, itching and burning.
Drug interactions
External use of lidocaine does not impose restrictions on the intake of other drugs.
When administered intramuscularly and intravenously, combinations with the following drugs are undesirable:
- Cimetidine and Propranolol, reducing the ability of the liver to metabolize lidocaine, lead to an increase in its concentration in the blood. When used together, it is necessary to reduce the dose of lidocaine;
- drugs that slow down the development of HIV infection (antiretrovirals) act in a similar way;
- diuretics, reducing the concentration of potassium in the blood, weaken the effect of lidocaine;
- local anesthetics or antiarrhythmic agents of a similar mechanism of action, when used together with lidocaine, giving an additive effect, increase its toxicity;
- some antipsychotics taken at the same time as lidocaine increase the risk of ventricular arrhythmias;
- Quinupristin and Dalfopristin are antibiotics, the action of which is based on slowing down the synthesis of proteins necessary for the vital activity of bacteria. They increase the concentration of lidocaine in the tissues of the heart, and also contribute to the appearance of this type of arrhythmia;
- muscle relaxants, taken simultaneously with lidocaine, will enhance the blockade of muscles and nerves, make more pronounced and prolonged loss of tissue sensitivity;
- Verapamil and Timolol, when used with lidocaine, can cause cardiovascular failure;
- Dopamine increases the risk of seizures after lidocaine injection;
- anti-elliptic drugs require, on the one hand, an increase in the dose of lidocaine as an anesthetic, and, on the other hand, make its antiarrhythmic properties pronounced;
- the complex effects of sedatives and lidocaine increase the effect of the anesthetic on the nervous system;
- vasoconstrictor drugs lengthen the time of elimination of lidocaine from the body;
Storage conditions and periods
The shelf life of the drug is 5 years from the date of manufacture. It is necessary to store lidocaine of any form of release in its original packaging at a temperature of 15 to 25 ° C in a dry place, protected from direct sunlight. It is prohibited to use the drug with an expired shelf life or if the package is not sealed.
Analogs
Lidocaine during breastfeeding can be replaced with analogues only after prior consultation with a doctor.
Complete analogs containing lidocaine hydrochloride as an active component are:
| A drug | Description |
| Versatis | The drug is produced in the form of plates with a sticky surface. The package contains from 1 to 30 plates. The drug is intended for local anesthesia and is used to alleviate the patient's condition with neuralgia and muscle pain of unknown etiology. Packing price for 30 pcs. - from 300 rubles. |
| Helikain | Lidocaine gel, local anesthetic. The drug is available in tubes with a capacity of 100 or 30 g, packed in cardboard boxes. It is used to perform all types of surface anesthesia in:
urology.
|
| Dinexan | Gel with local anesthetic properties. In addition to lidocaine, it contains:
It is intended for anesthesia of the oral mucosa and can be used:
The drug is sold in tubes with a volume of:
|
| Lycain | An agent based on lidocaine hydrochloride is intended for all types of local anesthesia for pain of low to moderate intensity. It is widely used:
The drug is available in the form:
|
| Luan | Gel, local anesthetic, used mainly in the performance of endoscopic diagnostic and therapeutic procedures requiring anesthesia, by applying to the mucous membrane. The drug is available in 2 types, differing in the concentration of the active substance:
|
Lidocaine, when used correctly, is a drug that is harmless to a nursing mother and her baby. It is not worth giving up the anesthesia performed with its help, given that the period of breastfeeding sometimes lasts more than a year. The disease will not wait for its end, causing much more harm than 1 injection of anesthetic.
Video about the drug
Indications and instructions for ampoules of Lidocaine:



