Beta-adrenomimetics effective in the presence of coronary heart disease, hypoglycemic coma, bronchospasm. After entering the body, the components of the drug bind to beta-adrenergic receptors in the smooth muscles of the heart muscle, bronchi, uterus and vascular tissue.
The mechanism of action of this group of medications involves an effect on beta cells, due to which physiological processes are activated: the production of the hormone adrenaline and neurotransmitter is stimulated dopamine.
After the use of beta-adrenergic agonists, it is possible to achieve an increase in blood pressure, an increase in the intensity of contraction of the heart muscle, and an improvement in bronchial conduction.
Record content:
- 1 Physiological role of β-adrenergic receptors
- 2 What are B-adrenergic agonists?
- 3 Mechanism of action in the body
- 4 Advantages and disadvantages
- 5 Classification of beta-adrenergic agonists, types of medicines
- 6 Indications for the use of B-adrenergic agonists
- 7 Contraindications
- 8 Side effects
- 9 Overdose
- 10 Precautions and special instructions
-
11 List of drugs, dosage regimen, prices
- 11.1 Tablet forms of drugs
- 11.2 Solutions for injection and inhalation
- 12 Video about beta adrenomimetics
Physiological role of β-adrenergic receptors
The universal adrenergic agonist is adrenaline, since it is he who is responsible for the stimulation of all 4 subtypes of adrenergic receptors. Norepinephrine stimulates: 1, 2 and 1. 1-adrenergic receptors are under the control of dopamine. Additionally, this neurotransmitter stimulates its own dopaminergic receptors. Otherwise, the person's condition gradually deteriorates.
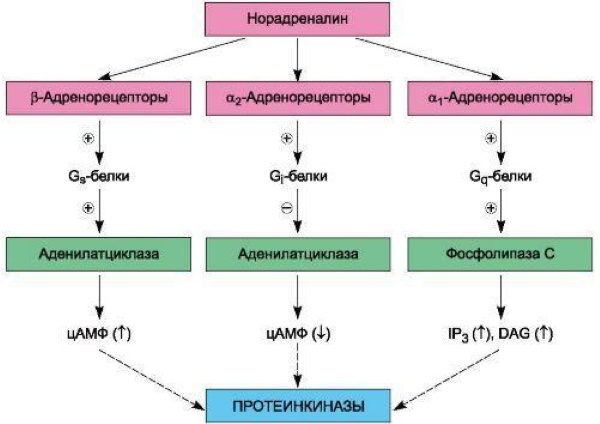
Beta-adrenergic receptors are located in adipose tissue, heart, as well as in renin-secreting cells that make up the juxtaglomerular apparatus of kidney nephrons. In the case of their excitation, the heart begins to contract more often, and atrioventricular conductivity increases.
All beta agonists are cyclic adenosine monophosphate dependent. As a result of the use of adrenal stimulants in the fatty tissue, the metabolic process is enhanced breakdown of triglycerides, thereby increasing the concentration of free fatty acids in plasma blood.
In such conditions, the kidneys synthesize renin (a protein-breaking enzyme) much better, due to which the production of a peptide hormone occurs, and the vascular tone increases. Beta-adrenergic receptors are located in almost all organs. For example, in the heart, uterus, central nervous system, blood vessels.
Their stimulation allows for a gradual improvement in bronchial conduction. B-adrenergic receptors increase blood glucose and reduce the tone of the uterus, which is very important during the period of gestation.
What are B-adrenergic agonists?
The category of B-adrenostimulants includes various medications that are used in modern medicine to combat diseases of the cardiovascular system and respiratory tract. In the patient's body, the components of the drug bind to beta receptors, a large number of which are found in the heart muscle, vascular tissue, and bronchial muscles.
Due to this, cells are stimulated, important physiological processes are activated. But it is forbidden to take such medications on your own, since an effective treatment regimen is selected for each patient individually.

Against the background of the use of B-adrenostimulants, tachycardia develops, which significantly reduces the likelihood of using these drugs to relieve bronchospasm. But selective beta-2-agonists have received huge demand in the treatment of bronchial asthma and other obstructive pulmonary diseases. For example, emphysema, chronic bronchitis.
Mechanism of action in the body
The existing beta-agonists are subdivided into B1 and B2 adrenostimulants. When interacting with receptors, these drugs activate many physiological processes in the body.
Beta-adrenostimulants have the following properties:
- Increases blood pressure. This effect is due to the stimulation of the RAAS.
- They improve the conductivity and automatism of the heart muscle (the ability to rhythmic contraction without any visible irritation under the influence of impulses arising in the organ itself).
- Accelerate lipolysis. As a result of regular use of B1-adrenostimulants, fatty acids are formed in the patient's blood.
- Increase the rhythm and strength of the heart.
All these changes in the patient's body occur against the background of binding of adrenostimulants to B1 receptors. They are found not only in the heart, blood vessels and adipose tissue, but also in the peri-glomerular cells of the kidneys.

B2-adrenergic agonists have the following mechanism of action:
- Accelerate muscle glycogenolysis, due to which skeletal muscles contract much faster.
- Improves bronchial conductivity. This effect is due to the gradual relaxation of smooth muscles.
- In liver cells, glycogenolysis is accelerated, which increases the concentration of glucose in the blood.
- Relaxation of the myometrium of the uterus occurs.
B-adrenostimulants have a wide range of applications. With proper use, medicines from this category can get rid of the painful symptoms of diagnosed diseases, significantly improving the patient's quality of life.
Advantages and disadvantages
Beta-adrenomimetics (the mechanism of action of these drugs involves the stimulation of beta cells in the human body, which positively affects the work of internal organs) are implemented in the form of solutions for intravenous administration and inhalation, powders, tablets.
If the patient is prescribed inhalation, then only 20% of the total dose will go to the lungs. The dosage of the drug depends on the form of the diagnosed pathology and the patient's condition.
B-adrenergic agonists have the following positive characteristics:
- Tones up blood vessels.
- Beta-adrenostimulants can be prescribed for patients with low HDL cholesterol.
- Produce an anticoagulant effect.
- The drugs are highly effective when the content of triglycerides in the patient's body is increased.
- They stop the inflammatory process.
- Effective in the presence of metabolic syndrome.
- Fight free radicals.
Long-term treatment with B-adrenomimetics reduces the concentration of lipoproteins in the blood, and also improves the state of blood vessels.
Beta-agonists can provoke the development of adverse reactions, which is why you need to make sure that there are no contraindications before using the drug.
Among the main disadvantages of this category of drugs, one can single out the fact that they often cause gagging, diarrhea, and flatulence in patients. In some cases, the emotional state may worsen, the development of depression is not excluded.
Classification of beta-adrenergic agonists, types of medicines
Beta-adrenomimetics (the mechanism of action of drugs from this category allows you to cope with atrial fibrillation arrhythmia, which is the most complex form of heart rhythm disturbance) is usually divided into several groups.
There are 3 categories of B-agonists in total:
- Selective beta-1-adrenergic agonists. These drugs are in great demand in the intensive care and cardiology departments.
- Non-selective beta-adrenostimulants.
- Selective B2-adrenergic agonists. Medicines from this category are in great demand in the field of combating pathologies that affect the respiratory system. The drugs can have both short and long-term principles of action.

Non-selective adrenostimulants are used in a short course to improve atrioventricular conduction and increase heart rate in bradycardia. Medicines can achieve a positive inotropic effect. Some drugs are taken in a short course for acute heart failure, which is associated with myocarditis, myocardial infarction.
Uncontrolled use of drugs increases the likelihood of patient death.
For the rapid elimination of attacks in chronic diseases of the respiratory tract, B-2 adrenostimulants are used. Intravenously, the patient is injected with Terbutaline or Fenoterol to gradually reduce the intensity and frequency of contractions of the muscle structures of the uterus, when there is a great threat of premature birth.
Drugs in this category are often combined in the same bottle with glucocorticosteroids to combat asthma.
Indications for the use of B-adrenergic agonists
Beta-adrenomimetics (the mechanism of action of medications due to a gradual increase in the tone of blood vessels allows you to achieve an anti-shock effect) of a non-selective principle of action are rarely used in modern medicine. Previously, these drugs were used to normalize the heart rate, improve cardiac conduction.
But in laboratory conditions, specialists have been able to determine that selective B-agonists are no less effective, but at the same time cause fewer side reactions. These medications are more practical to use, since their constituent components affect only the damaged organ.
Among the main indications for the use of beta-adrenostimulants, the following diseases and conditions can be distinguished:
- Hypoglycemic coma.
- Severe ischemic heart disease (CHD).
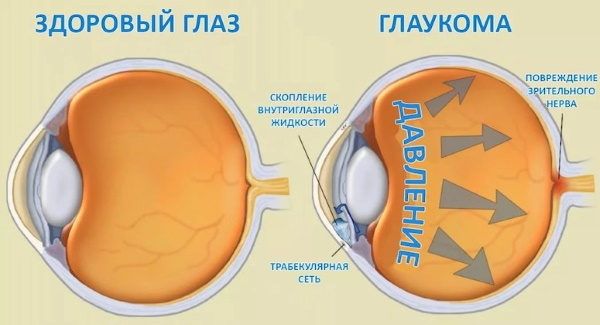
- Inflammatory diseases of the mucous membrane of the visual apparatus, nose.
- Glaucoma.
- Acute heart failure.
- Collapse (a life-threatening condition characterized by a drop in blood pressure and impaired blood supply to vital organs).
- Shock of various etiologies, drop in blood pressure indicators to a critical level, sudden cardiac arrest.
- Bronchial asthma and other diseases of the respiratory system, which are accompanied by bronchospasm.
- Conducting local anesthesia.
- Decompensated heart defects.
Short-term use of beta-2-adrenergic agonists by healthy people can achieve a short-term increase in physical endurance.
This effect is due to the fact that the components of medications improve the functioning of the bronchi, which makes the body easier to cope with stress. B2-adrenomimetics are often used by professional athletes (for example, cyclists).
Contraindications
Beta-agonists may not be used in all patients. Most of all contraindications for use are non-selective B-agonists. These drugs can cause tremors, hyperglycemia, tachycardia, and central nervous system agitation.
The mechanism of action of B-agonists is based on the stimulation of beta-receptors, which makes it possible to achieve tocolytic, bronchodilatory and inotropic effects. Correctly selected drugs help to reduce the intensity of the release of inflammatory mediators by mast cells and basophils, thereby increasing the lumen of the bronchi.
Beta-1-adrenergic agonists belong to the category of potent drugs, which is why only a qualified doctor can prescribe them. They are not used if the patient has subaortic stenosis, ventricular arrhythmias, or pheochromocytoma. B1 agonists should not be used for cardiac tamponade.
Before using beta-2-adrenergic agonists, the following contraindications should be considered:
- Diabetes.
- Individual intolerance to beta-adrenergic agonists.
- Children's age (up to 2 years old).
- The presence of inflammatory processes in the myocardium.
- Abnormal heart rhythm.
- Pregnancy, which is complicated by placental abruption, internal bleeding, the threat of premature birth.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Aortic stenosis.
- Renal, liver failure.
- Arterial hypertension.
With caution, beta-adrenergic agonists are prescribed to those patients who are taking medicines for dry cough. B-agonists are prohibited for use in acute kidney disease (eg, aldosteronism).
Modern beta-2-adrenergic agonists in 98% of all cases are well tolerated by the patient's body. Due to the reduced risk of adverse reactions and the possibility of reducing the minimum dosage drug therapy allows you to achieve good results in the fight against decompensated defects hearts.
Side effects
Beta-adrenomimetics (the mechanism of action of drugs allows you to enhance the work of the B-receptors of the vascular walls and internal organs, which helps to improve cardiac conduction) in isolated cases can worsen the condition the patient. Most often this occurs as a result of non-compliance with the treatment regimen recommended by the attending physician.
B-adrenomimetics can provoke the following side reactions:
- Neurotoxic complications. As a result of the use of Ephedrine, Adrenaline, the patient may experience: insomnia, agitation, tremors of the extremities, acute headaches, discomfort in the region of the heart.
- Sudden vasoconstrictor action. Stroke, hypertensive crisis, acute heart failure may occur, followed by the development of pulmonary edema.
- Arrhythmogenic action, which is fraught with various cardiac arrhythmias.
- Dilation of the pupils.
- Stool disorder.
- Dry mouth.
- Development of allergic reactions.
- Nausea, vomiting.

In case of adverse reactions, the patient should stop taking the drug and seek advice from the attending physician in order to choose a safer analog with him.
Overdose
Overdose cases of beta-adrenergic agonists are extremely rare in medical practice. Due to a significant excess of the recommended dosage of the drug, the patient may experience the following symptoms.
Scroll:
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Diarrhea.
- Tachycardia.
- Worsening attacks of suffocation (pulmonary closure syndrome).
- Headaches.
- Hypokalemia.
- Increased sweating.
- Increased fatigue.
- Myalgia.
- Retention of urine.
- Confusion of consciousness.
- Increased body temperature.
- Paradoxical bronchospasm.
- Chills.
- Coughing fits.
- Itching and burning of the skin, Quincke's edema.

If the patient inadvertently took a large dose of the drug, then you need to rinse the stomach and take an effective sorbent (for example, activated carbon). To reduce the likelihood of a deterioration in well-being, the patient should seek qualified help from the attending physician, who, if necessary, will prescribe symptomatic treatment.
Precautions and special instructions
Beta-adrenomimetics can be used with caution in patients diagnosed with severe diseases. cardiovascular system, hyperthyroidism, prostatic hypertrophy and urinary tract obstruction. If the patient develops rapidly progressing shortness of breath, you should immediately seek medical help.
Symptomatic treatment may be more effective than regular use of B-adrenergic agonists by those patients who are diagnosed with bronchial asthma or moderate form of chronic obstructive pathology lungs. Additionally, it may be necessary to strengthen anti-inflammatory therapy to control the inflammatory process of the airways.
In isolated cases, after the use of beta-adrenergic agonists, patients are worried about complications from the visual system. For example, an increase in intraocular pressure, the development of mydriasis and angle-closure glaucoma, acute pain in the eyeball. Such symptoms can occur after contact with the eyes of the drug.
To avoid negative consequences, the patient should carefully study the instructions before using beta-agonists in the form of aerosols.
If the patient has decreased visual acuity, pain in the eye and redness of the mucous membrane, then these symptoms may indicate an acute attack of angle-closure glaucoma. In this case, together with B-adrenergic agonists, you need to use eye drops that will help narrow the pupil.

Before using the drug, you must consult an ophthalmologist. If the patient has a history of cystic fibrosis, then as a result of the use of beta-agonists, various disorders of the work of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract may occur. In this case, the gastroenterologist will have to find a safe analogue.
List of drugs, dosage regimen, prices
Beta-agonists are in great demand in traditional medicine, as they are highly effective in the fight against cardiac and pulmonary pathologies.
Some drugs from this category are used in the intensive care unit. For example, Dobutamine. Various beta-adrenergic agonists have gained demand in gynecological practice.
Tablet forms of drugs
Beta-adrenomimetics in the form of oral tablets are often used to combat bronchial asthma, cardiac crises and other diseases. The treatment regimen and dosage depend on the patient's diagnosis and general condition.
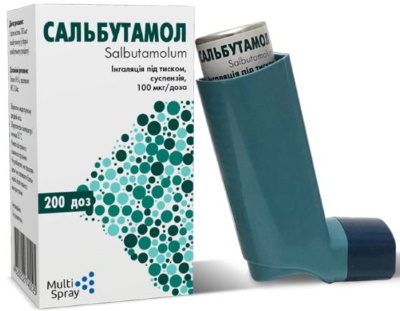
| Drug name | Description | Average cost (rub.) |
Salmo |
Salbutamol is used as an active ingredient. The drug is indicated for airway obstruction provoked by bronchial asthma or chronic bronchitis. Adults and children over 12 years old should take the drug 2 tablets 3-4 times a day. The duration of treatment is determined on an individual basis. | 110 |
Salbutamol |
Salbutamol is added to the preparation as the main active ingredient. The drug is indicated for all forms of bronchial asthma, reversible airway obstruction in chronic pulmonary emphysema and bronchitis. Salbutamol is prescribed to pregnant women when there is a high risk of premature birth. It is recommended to take the drug 2-4 mg maximum 4 times a day. The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor. | 130 |
It is forbidden to use B-adrenergic agonists without preliminary examination and consultation with the attending physician. Otherwise, the patient's condition may deteriorate significantly, which will require more radical treatment.
Solutions for injection and inhalation
B-adrenomimetics in the form of solutions with precise dosage are used for effective relief and prevention of bronchospasm in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and bronchial asthma. A large dosage of the drug is needed for pronounced edema and inflammation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract.
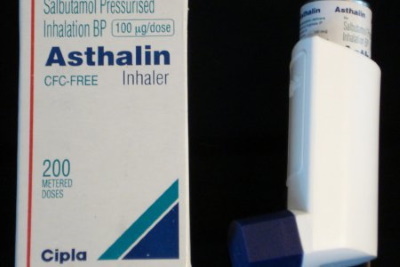
| Drug name | Description | Average cost in Russia (rubles) |
Astalin |
Salbutamol sulfate is used as an active ingredient. The drug is intended for the prevention and relief of bronchospasm in bronchial asthma, pulmonary emphysema. To obtain a positive therapeutic effect, adults and children over 12 years old need to take 100-200 μg of the drug (1-2 inhalation doses). The daily dosage of the drug should not exceed 1200 mcg. | 155 |
Fenoterol |
The active component of the solution is fenoterol. The drug is indicated for hypertonicity of the uterus, bronchial asthma, chronic bronchitis of a spastic nature. In gynecology, the drug Fenoterol is prescribed to those women who are at risk of premature birth. When using the medicine by inhalation, a single dosage is 200 mcg. When administered intravenously, the initial dose should not exceed 50 mcg. The duration of treatment depends on the patient's condition. | 340 |
Before buying beta-adrenergic agonists, you need to study the instructions, as well as consult with your doctor. In modern B2-agonists, the mechanism of action is associated with the stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors, due to which the muscles of the bronchi relax, and the work of the heart muscle is enhanced.
Subject to the recommended dosage and frequency of use of the drug, the likelihood of adverse reactions is practically excluded.
Video about beta adrenomimetics
Features of drugs adrenomimetics: