Gastroesophageal reflux (GERD) is a condition in which the contents of the stomach pass back into the esophagus. Appears more often after eating. It occurs as a result of impaired functioning of the lower alimentary sphincter (LES).
The pathological condition is accompanied by concomitant symptoms and requires the consultation of a gastroenterologist. After a comprehensive diagnosis, patients are prescribed treatment that will help eliminate violations and prevent complications.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Causes
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prevention
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Diet
- 8.4 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about GERD
Views
Gastroesophageal reflux disease affects the mucous epithelium of the esophagus and stomach. In medicine, there is a certain classification of the disease, taking into account the course of pathological processes and the area of damage to the organs of the digestive system.
| Name | Description |
| Non-erosive | The inflammatory process affects the lining of the esophagus. Small pathological foci are characterized by redness. |
| Erosive | Small erosions form on the affected areas of the mucous membrane, which can merge with each other. The pathological condition in some situations is complicated by the occurrence of bleeding. |
| Barrett's esophagus | A severe form of the disease in which all layers of the stomach are affected. |
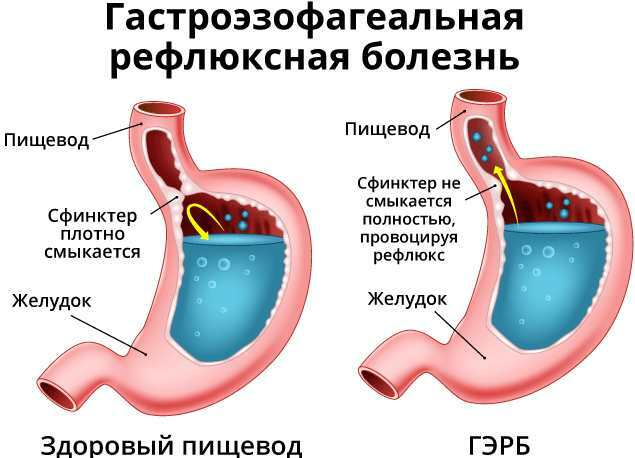
In each individual case, pathological changes are accompanied by concomitant clinical signs. They will help the gastroenterologist determine the degree of damage to the organs of the digestive system and choose the most effective treatment.
Stages and degrees
Taking into account the development of pathological processes and the boundaries of the lesion of the mucous membrane of the digestive organs, the following degrees are distinguished in medicine gastroesophageal reflux:
| Name | Description |
| I degree | The patient has complaints, and there are no pathological changes on the surface of the mucous epithelium. |
| II degree | Single shallow foci of the inflammatory process appear on the surface of the mucous layer. |
| III degree | Erosions of various depths and sizes are formed on the walls of the stomach. |
| IV degree | A peptic ulcer of the esophagus develops. A severe form of gastroesophageal reflux, against which dangerous complications may appear (bleeding, perforation of the esophageal walls, the development of a malignant tumor). |
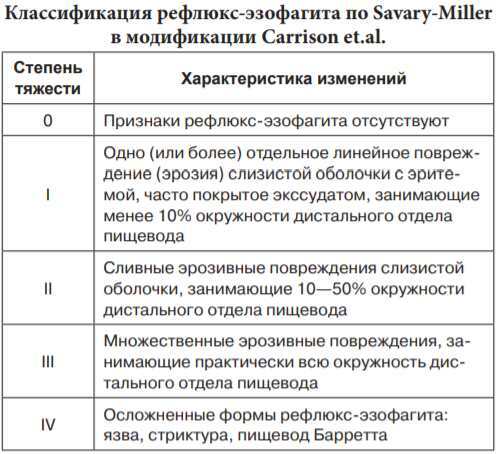
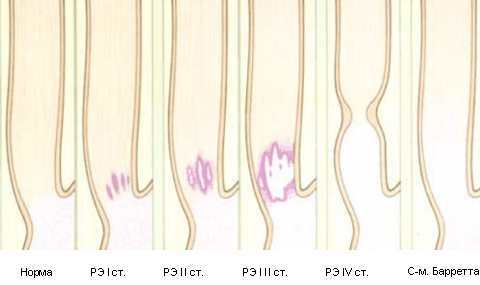
Comprehensive diagnostics, which the gastroenterologist prescribes after examining the patient, will help to determine the type of disease and the degree of development of the inflammatory process. The results of the examination are also necessary to draw up the correct treatment regimen, in the absence of which serious complications develop.
Symptoms
The clinical picture in gastroesophageal reflux disease depends on the provoking factors and the degree of damage to the organs of the digestive system. A gastroenterologist, guided by the patient's complaints, will prescribe the most informative examination for a person in order to establish the correct diagnosis.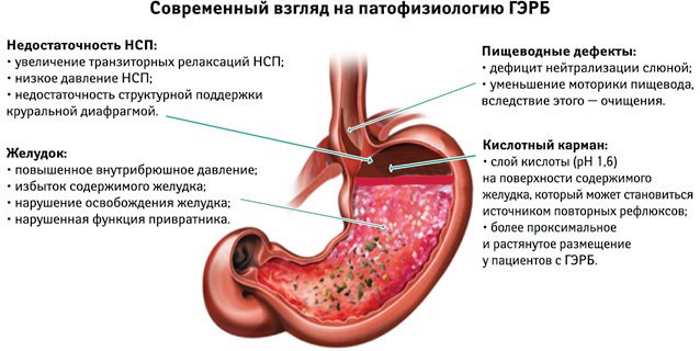
GERD (symptoms and treatment is determined by the doctor after a thorough examination of the patient) is accompanied by the following signs:
| Name | Symptoms |
| Esophageal signs |
|
| Extraesophageal manifestations |
|
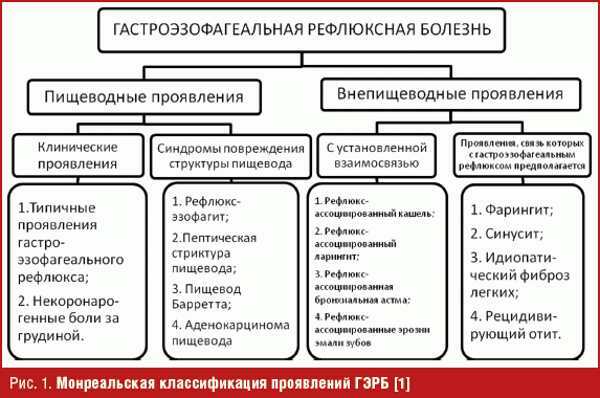
In most cases, the symptoms of GERD worsen after a meal when the patient does not follow a specially formulated diet. Many people also complain of headaches, general weakness in the body, and sleep disturbances. Patients become weather-dependent.
Causes
Gastroesophageal reflux disease, as the inflammatory process progresses, damages the mucous epithelium to varying degrees. Erosions and ulcers appear, the esophagus becomes inflamed. A serious complication of pathological processes is the proliferation of connective tissue or cell degeneration.
There are the following provoking factors against which gastroesophageal reflux occurs:
- improper nutrition;
- bad habits (abuse of alcoholic beverages and tobacco products);
- stressful situations, emotional stress, nervous exhaustion;
- extra pounds, obesity of varying degrees;
- hormonal imbalance (period of carrying a baby, menopause, menstrual cycle);
- treatment with certain drugs;
- genetic inheritance;
- damage to the esophagus;
- neuromuscular disorders of the esophagus against the background of frequent exacerbations of the inflammatory process;
- damage to the respiratory organs (bronchial asthma, obstructive bronchitis);
- great physical activity;
- prolonged stay in a forward tilted position;
- high pressure in the abdominal cavity.
A hernia of the esophageal opening of the diaphragm can also provoke the reflux of the contents of the stomach into the esophagus. The main reason is the impaired functioning of the lower esophageal sphincter as a result of neurovegetative failures.
Diagnostics
GERD (it is recommended to discuss symptoms and treatment with a gastroenterologist) requires a complex diagnostics to establish the cause of the inflammatory process and the affected area digestive organs.
Patients are assigned the following examination methods:
| Name | Description |
| pH-metry of the stomach and esophagus | The results will help determine the duration and severity of gastroesophageal reflux. |
| pH impedance measurement | Diagnostics allows you to determine acidic, slightly acidic or slightly alkaline refluxes, as well as to differentiate their structure.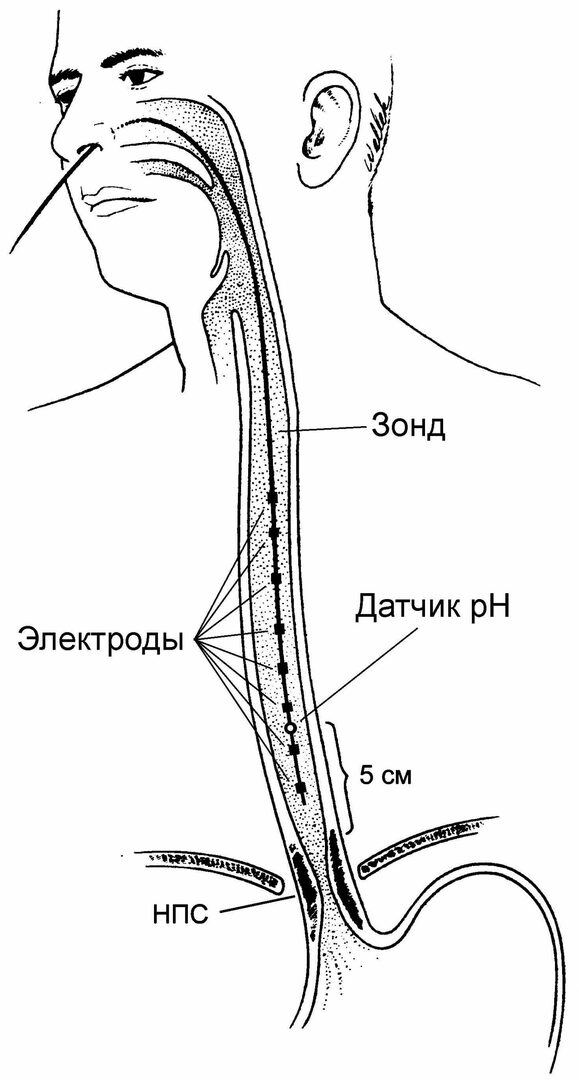
|
| Endoscopy | The doctor examines the digestive organs, determines the degree and stage of the inflammatory process. |
| X-ray | A diagnostic method that is prescribed to patients in order to exclude the development of a hernia. |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) | The specialist examines the internal organs, assesses their condition, functioning and identifies pathological processes. |
| Esophagogastro-duodenoscopy | During the examination, the doctor will take a biopsy. The taken material is examined in the laboratory. The results will help identify malignant processes. |
| Esophageal manometry | During the examination, the contractility of the esophagus and the pressure in the lower sphincter area are assessed. |
To avoid injury or injury to many patients, a gastroenterologist prescribes proton pump inhibitors. The patient drinks the medicine for a week and comes back for diagnostics. If the pathological symptoms have disappeared, the doctor assumes that the person has GERD. This diagnostic method helps if other tests did not reveal inflammation and damage to the gastric mucosa.
When to see a doctor
A gastroenterologist should be visited when the first disturbances in the work of the digestive organs appear. Timely diagnosis and correctly selected therapy will prevent serious consequences that drastically worsen the quality of human life.
It is important to undergo a comprehensive examination and differentiate the disease, since many pathologies are accompanied by similar clinical signs. Given the provoking source of GERD, the patient may need to consult other specialized specialists (pulmonologist, otolaryngologist, cardiologist, surgeon).
Prevention
To prevent gastroesophageal reflux or exacerbation of pathological processes, simple doctor's recommendations will help:
- A person needs to eat right, give preference to healthy food.
- Monitor weight, prevent weight gain.
- Completely exclude any provoking factors, against which the contents of the stomach are thrown into the esophagus (physical activity, lifting weights).
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Take medications only as directed by your doctor.
You can not try to independently treat diseases or disorders in the work of the digestive system. A gastroenterologist should establish a diagnosis, as well as prescribe medications.
Treatment methods
Complex therapy is prescribed to patients after a thorough examination. A gastroenterologist, taking into account the patient's condition and the results of diagnostics, selects the most effective methods of therapy. Medicines, folk remedies and other measures help eliminate the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux, and also improve the patient's condition.
Medicines, folk remedies and other measures help eliminate the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux, and also improve the patient's condition.
Medications
GERD (symptoms and treatment requires a full diagnosis) cannot be eliminated without traditional drugs. Drug therapy is aimed at eliminating the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux, improving the patient's quality of life.
Medicines will help restore the functioning of the digestive system and prevent complications. Patients should adhere to the prescribed dosages or carefully read the instructions before starting therapy.
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Proton pump inhibitors | Omeprazole, Rabeprazole | Medicines reduce the negative effects of stomach acid on the lining of the esophagus. The drug is preferably taken in the morning. The recommended dosage for an adult patient is 20 mg. The course of treatment lasts 2-4 weeks. |
| Antacids | Phosphalugel, Gastal | Medicines eliminate the process of throwing stomach contents into the esophagus, preventing the development of the inflammatory process. It is recommended to dilute the product with a small amount of liquid or drink it with water. Patients are prescribed 1-2 sachets 2-3 times a day. |
| Adsorbents | Smecta, Diosmectite | Means neutralize hydrochloric acid and remove bile acids. The medicine should be taken 3 g 3 times a day for 3-7 days. Stir the contents of the sachet in 0.5 tbsp. water. |
| Prokinetics | Metoclopramide, Domperidone | The drugs improve the motor-evacuation function of the digestive system organs. The medicine should be taken orally with plenty of water. Adults are prescribed 10 mg 3 times a day. |
| H2 receptor antagonists | Ranitidine, Famotidine | For adult patients, the drug is prescribed in the morning and in the evening at 0.15 g or at bedtime 0.3 g. The duration of treatment is 4-8 weeks. |
| Gastroprotectors | Sucralfat, Venter | Medicines form a certain layer on the mucous epithelium, protecting it from the negative effects of aggressive factors. Adult patients are prescribed 1 g 2 times a day. The duration of therapy is 1-1.5 months. |
| Ursodeoxycholic acid | Ursofalk, Ursosan | The capsules are recommended to be taken orally whole with a sufficient amount of water. Patients are prescribed 250 mg once a day, preferably in the evening. The course of treatment lasts 10-14 days. |
Additionally, patients are advised to use special mineral water (Kazachinskaya, Essentuki). In difficult situations, when drug therapy has not yielded a positive result or when erosions and complications appear, surgery is indicated for patients. The same goes for the formation of a stricture or scarring in the stomach area.
Traditional methods
Symptoms of GERD can be treated with unconventional treatments. Numerous herbs and natural ingredients have healing properties. Prescriptions of healers and healers can be used for GERD only in complex treatment after consulting a doctor.
It is important to choose the most effective remedy in order to exclude the occurrence of an allergic reaction or individual sensitivity.
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Aloe juice | Grind the leaves of the plant, squeeze out the juice. Mix 1 tsp. with natural honey (0.5 tsp). The resulting mass should be insisted for 2-3 hours and taken orally. | The finished medicine is recommended to be consumed in 1 tsp. after meal. Aloe juice reduces inflammation and promotes healing of damaged mucous membranes. |
| Nettle | Rinse the leaves of the plant, dry and grind. Pour with boiling water (1 tbsp.) 2 tbsp. spoons of the resulting mass. Insist and strain the solution. | The resulting product is recommended to be taken orally 2-3 times a day for 2-3 weeks. For taste, you can add a small amount of sugar or natural honey to the nettle broth (1 tsp) |
| Flax seeds | Pour 2 tbsp. seeds with boiling water (500 ml). Insist 8 hours and strain well. | A decoction of flax seeds is recommended to be taken orally 3 times a day before meals. The adult dosage is 0.5 tbsp. The course of treatment lasts 5-6 weeks. |
| Marshmallow root | Grind the plant and pour 6 g of powder with warm water (1 tbsp.). Put the resulting mass in a water bath and heat for another 30 minutes. | Ready-made marshmallow decoction is recommended to be taken chilled in 0.5 tbsp. 3 times a day. |
| Herbal collection | Mix in equal proportions marshmallow root and licorice, flax seeds and coltsfoot leaves. Pour 1 tbsp. herbal collection with boiling water (1 tbsp.). Leave for 30-40 minutes and strain. | The resulting broth should be taken orally in 1 tbsp. 5-6 times a day before meals for 30 minutes. |

With gastroesophageal reflux, it is recommended to drink a decoction made from chamomile. The plant has anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Various herbal teas in traditional medicine help damaged tissues of the mucous membrane of the stomach and esophagus to heal and recover faster. Herbs also have a calming effect.
Diet
A specially formulated diet with the development of gastroesophageal reflux will help reduce the load on the organs of the digestive system.
| Featured Products | Prohibited foods |
|
|

Eat small meals and keep food warm. Dishes should be boiled, steamed, it is also recommended to reduce salt intake.
Other methods
GERD (symptoms and treatment is determined by a gastroenterologist) requires not only complex therapy, but also changes in the patient's lifestyle.
It is necessary to adhere to the following recommendations:
- Monitor body weight, prevent the addition of extra pounds.
- It is necessary to completely abandon bad habits. Nicotine enhances the production of hydrochloric acid.
- You can not overeat and eat food before bedtime.
- Patients are advised not to wear tight belts, corsets, bandages or tight clothing. In this case, intra-abdominal pressure rises.
- You can not lift weights, load the abdominal press.
It is not recommended to take a horizontal position after eating for 1-2 hours, the risk of aggravating the disease increases. The same goes for physical activity, exercise, and forward bends of the torso.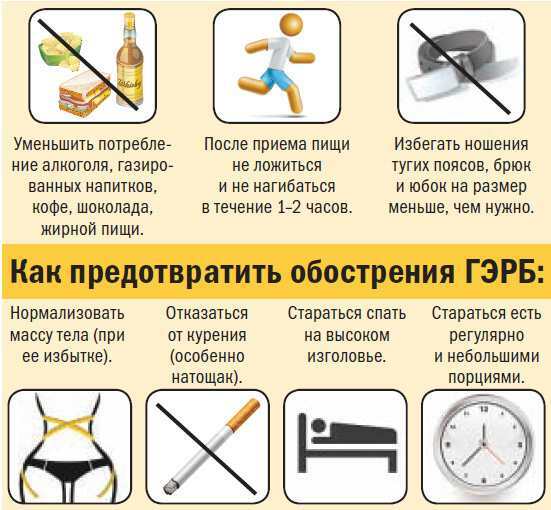
Additionally, in complex therapy, patients with GERD are advised to attend physiotherapy procedures that improve functioning digestive organs and reduce the development of the inflammatory process:
- radon baths;
- mud treatment;
- electrophoresis with antispasmodics;
- sinusoidal modulated currents.
Magnetic therapy and electrosleep eliminate the manifestations of pathological processes.
Possible complications
Gastroesophageal reflux disease should be treated under the supervision of a gastroenterologist.
Otherwise, the patient will face serious complications:
| Name | Description |
| Perforation of the stomach wall | Violation of the integrity of the walls of the stomach often occurs in the region of the mediastinal organs. As a result, sepsis develops, there is a high likelihood of respiratory arrest and the appearance of severe bleeding, due to which the patient dies. |
| Bleeding ulcers | There are overt or latent ulcers. The latter are the most dangerous for human life, they are difficult to identify, even during a medical examination. Latent bleeding prevents the doctor from making an accurate diagnosis. Improperly selected therapy can be fatal. |
| Narrowing of the lumen of the esophagus | Stenosis leads to the fact that the patient completely refuses to eat, since food is difficult to pass through the esophagus. |
A dangerous complication of GERD is the formation of adenocarcinoma, when the affected tissue degenerates and a malignant tumor develops.
GERD does not threaten a person's life if inflammation in the stomach and esophagus is treated promptly. The symptoms of the disease cannot be ignored, since complications that appear as a result of the progression of pathological changes can disrupt the usual way of life.
Video about GERD
Gastroesophageal reflux disease. Treatment:



