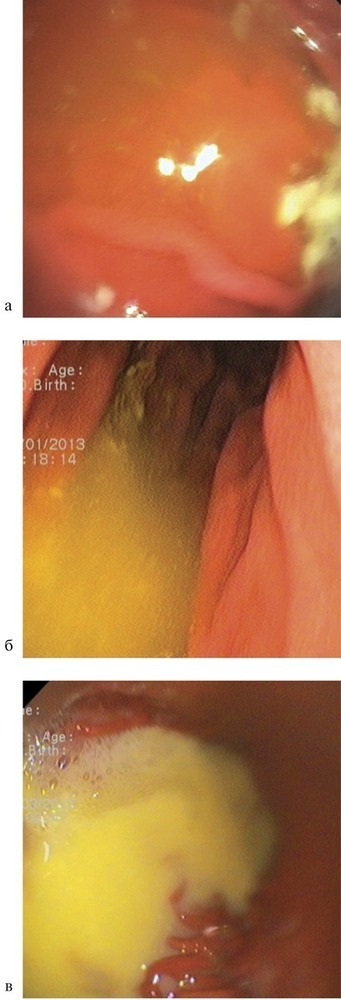
GHR or duodenogastric reflux is a disorder of the digestive system, which is associated with the ingestion of contents from the small intestine (duodenum 12) into the stomach. Most often, the condition indicates a pathology of the gastrointestinal tract, but can be diagnosed as an independent ailment (in 15 - 30% of cases). You need to know how to treat GHD in order to get rid of it in a timely manner.
Record content:
- 1 Tissue damage classification
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms and Signs
- 4 Causes
- 5 Diagnostics
-
6 Treatment methods
- 6.1 Medications
- 6.2 Traditional therapy
- 6.3 Proper nutrition
- 6.4 Exercises
- 6.5 Surgery
- 7 Possible consequences and complications
- 8 Video about DGR
Tissue damage classification
Duodenogastric reflux (treatment involves the use of drugs) has a classification.
The following types of tissue damage exist:
- superficial - changes in the epithelium are reversible;
- catarrhal - inflammation of the upper layers of the digestive organs occurs;
- erosive - the formation of defects on the mucous membrane of the digestive organs;
- biliary - a violation of the outflow of bile from the bladder into the small intestine.
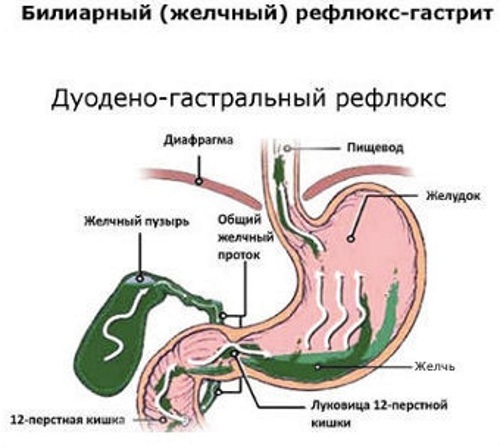
Biliary duodenogastric reflux
Upon occurrence, the ailment can be acute or chronic. In the first case, the symptoms appear vividly. Chronic GHR is characterized by periods of remission (remission), when symptoms are absent or decrease in intensity, as well as exacerbations.
Stages and degrees
The disorder has an additional classification.
Degrees of GDR development:
- First. Another name is a weak degree. It is characterized by a slight displacement of the contents from the intestine. The degree occurs in 50% of patients with GHD.
- Second. An additional name is a moderate degree. The amount of fluid that is thrown into the stomach increases.
- Third. Another name is pronounced degree. Deep changes develop, accompanied by vivid clinical symptoms.
Symptoms and Signs
GHD is a disorder characterized by certain symptoms.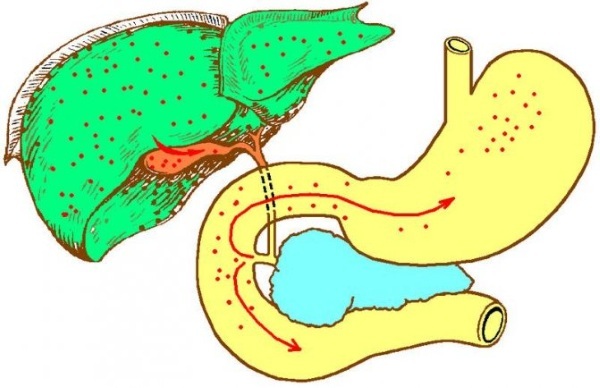
Most often, the following symptoms occur:
- burning sensation;
- pain in the abdomen (can be given to the chest);
- belching, in which sour vomit may be slightly released;
- heartburn;
- discomfort when swallowing food or drinking liquids;
- change in taste;
- bitter taste in the mouth;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- plaque on the tongue, which has a yellow color - the symptom is present even with proper oral care;
- distension of the stomach - there is a feeling of overflow of the organ;
- increased gas production in the stomach;
- insufficient production of saliva in the mouth;
- lack of appetite;
- dry cough;
- hoarseness or loss of voice (rare);
- decreased performance;
- general weakness;
- nausea;
- discharge of vomit with food debris;
- pallor of the skin.
Causes
Duodenogastric reflux can be associated with various causes.
The most common signs affecting the onset of GDR are:
- insufficient functionality (weakened closure ability) of the pyloric sphincter (separates the stomach from the duodenum 12);
- increased motility of the duodenum;
- congenital anomalies in the child's digestive system;
- biliary dyskinesia (biliary tract dyskinesia) - impaired separation of bile into the intestine;
- duodenostasis - duodenal obstruction;
- neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract;
- hernia of the diaphragm - displacement of the abdominal organs into the chest cavity through a hole in the diaphragm;
- cholecystitis - inflammation of the gallbladder;
- pancreatitis - inflammation of the pancreas;
- Botkin's disease (hepatitis A) - an infectious liver disease;
- duodenitis - inflammation of the duodenum (most often the mucous membrane of the organ is affected);
- gastroduodenitis - inflammation of the mucous membrane of the stomach and duodenum;
- peptic ulcer - a defect in the gastric mucosa, which is formed under the action of hydrochloric acid;
- gastritis - inflammation of the stomach lining;
- surgical interventions on the gastrointestinal tract - for example, reducing the stomach, removing the gallbladder, and more.
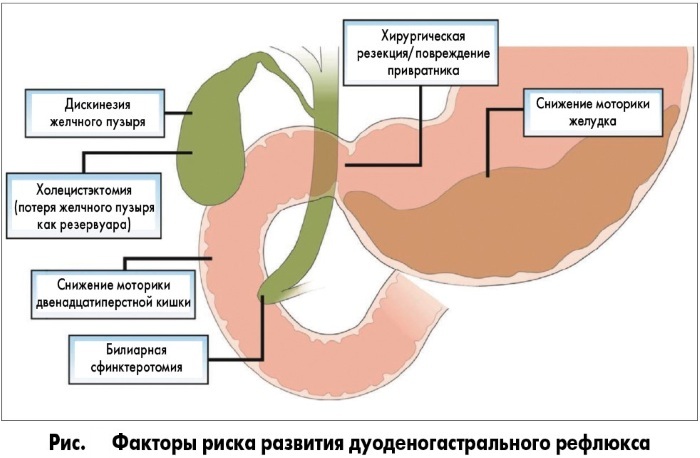
Additionally, risk factors are identified that increase the likelihood of GHD.
Their list:
- unhealthy diet - overeating, the predominance of fatty and spicy foods;
- bad habits - smoking, drinking alcohol and drugs;
- age category - the older a person becomes, the higher the likelihood of GDR;
- overweight;
- diabetes;
- uncontrolled use of various drugs - the likelihood of GHR increases with the use of painkillers and choleretic drugs;
- performing a diagnostic study in the gastrointestinal tract;
- late pregnancy - due to the enlarged uterus, the abdominal organs are compressed and their functionality is impaired;
- the use by a woman (when carrying a fetus) of drugs that are prohibited during pregnancy;
- frequent stress;
- lack of rest and proper sleep.
Diagnostics
Duodenogastric reflux (treatment includes medication) is a disorder that needs diagnosis. With the help of an examination, it is possible to establish the cause of the onset of symptoms.
Duodenogastric reflux is in the competence of a gastroenterologist - a doctor who identifies and treats diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). If a visit to this specialist is not possible, it is allowed to contact a therapist.
Before assigning diagnostics, perform the following actions:
- Interview. The doctor asks questions that relate to symptoms, concomitant diseases.
- Measurement of indicators. The specialist pays attention to blood pressure, pulse, temperature.
- Inspection. The doctor examines the patient's skin.
- Palpation. The specialist palpates the abdominal cavity to locate the pain.
Laboratory methods for the diagnosis of GDR are shown in the table.
| Name | Description |
| Complete blood count (CBC) | Research that is always assigned. The analysis is used to assess the state of human health. The result sheet indicates the value of various indicators (hemoglobin, erythrocytes and others).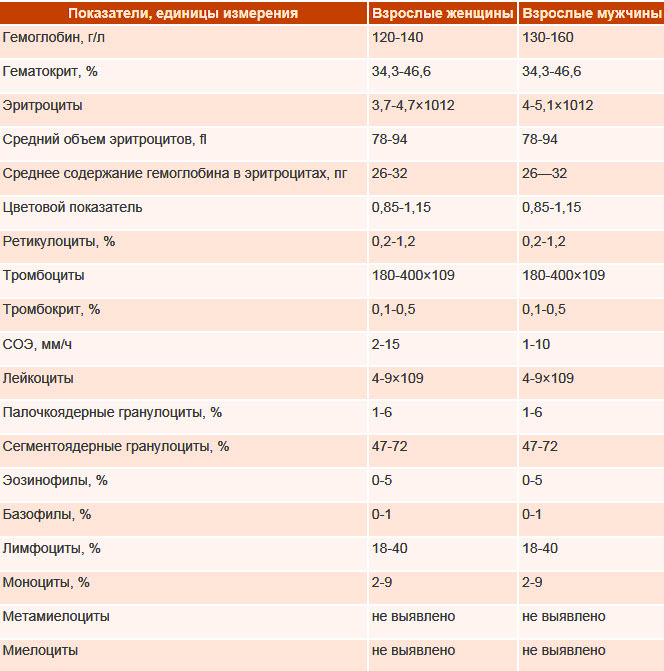 Analysis types:
Blood from a vein or finger is used as a biomaterial. The term for preparing the result is 1 working day. The cost of the analysis is from 300 to 1000 rubles. |
| General urine analysis (OAM) | The study allows you to identify various diseases. Urine is used as a biomaterial. Liquid collection stages: 1. Purchase a sterile container in advance in the pharmacy chain. 2. Wash off with warm water. If soap or other detergent is used, rinse thoroughly. 3. Drain some urine into the toilet, then, without stopping urinating, collect the liquid in a container. 4. Close the container, deliver it to the laboratory. The collected urine can be stored for no more than 2 hours at a temperature of 5 - 20 degrees. For analysis, you need to collect the morning portion of the liquid (accumulated in the bubble at night). The result sheet indicates the volume, color, odor of the biomaterial. Additionally, attention is paid to the foaminess, transparency, density. They also indicate acidity (pH), the number of indicators (erythrocytes, leukocytes, etc.). The term for preparing the result is 1 working day. The cost of the analysis is from 300 to 500 rubles. |
| Coprogram | Study of feces for diagnosing diseases of the digestive system. Stages of collecting biomaterial: 1. Purchase a sterile container in the pharmacy network. 2. Wash off with warm water. If detergent is used, rinse thoroughly. 3. Perform a bowel movement after waking up in the morning. It is better to do this not in the toilet, but in a separate container. 4. Take a stool sample that is not in contact with the walls of the container, transfer it to a sterile container. 5. Deliver the container to the laboratory. The maximum shelf life of feces in the refrigerator is up to 12 hours.
The term for preparing the result is up to 4 working days. The cost of the analysis is from 500 to 800 rubles. |
Duodenogastric reflux is a condition that needs hardware diagnostics. An examination is ordered to prescribe an effective treatment. Hardware diagnostic methods are shown in the table.
| Name | Description |
| PH metry | The method involves measuring acidity in the gastrointestinal tract. Varieties of pH metry:
The procedure is prescribed for various diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - ulcers, gastritis and more. The study involves the introduction of a flexible probe into the gastrointestinal tract. It is equipped with measuring electrodes. The probe is inserted through the mouth or nasal cavity. The cost of the procedure is from 2000 rubles. |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the abdominal cavity | The method is based on the action of ultrasound waves. They are reflected from the tissues, return to the sensor, and appear on the monitor in the form of a black-and-white picture. The procedure is performed using the transabdominal method. Stages of abdominal ultrasound: 1. The man strips to the waist and lies down on the couch. 2. The healthcare professional lubricates the abdominal skin with a special gel that improves visualization. 3. The worker drives the sensor over the skin. During the study, the physician may ask the person to hold their breath, roll over onto the other side. 4. A person wipes off the skin, receives a result sheet with a description of the study. Ultrasound is performed in 10 - 30 minutes. Research cost - from 1000 rubles. |
| Abdominal X-ray | The study is based on X-ray radiation. 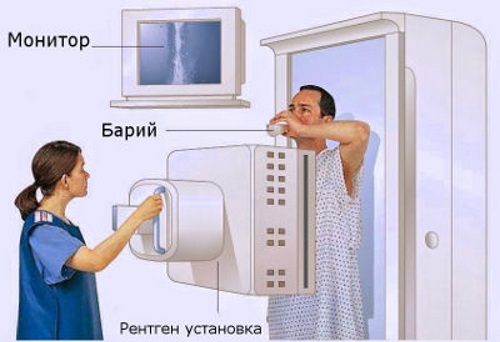 Varieties of the procedure: Varieties of the procedure:1. Plain radiography. Take 1 main picture. This type of diagnosis is used for a physical examination. Among the advantages, a small dose of radiation and a duration (1 - 5 minutes) are noted. The downside is the lack of information content. 2. Contrast radiography. Before taking a picture, a contrast agent is injected into a person's vein. The medication improves visualization. The substance spreads with the blood stream and stains the organs slightly. Among the advantages, they note a high level of visualization, the possibility of detecting neoplasms. Cons - duration (the study can be done up to 2 hours), side effects are allowed (headache, weakness, etc.). The cost of the procedure is from 1000 rubles. |
| Fibrogastrode uodenoscopy (FGDS) | The procedure involves examining the esophagus, stomach, duodenum 12 using an endoscope. The method is informative, it can detect many diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. EGD usually does not bring pain to a person. Therefore, the procedure is carried out without the use of drugs. But it is possible to use pain relievers. Stages of the FGDS: 1. If necessary, local anesthesia is administered (blocking pain impulses in the study area) or anesthesia (a person falls asleep and does not feel anything). 2. The patient is asked to lie on the couch on his left side. 3. A ring is inserted between the teeth to prevent clamping of the tube. 4. An endoscope is inserted into the mouth, which must be tried to swallow. 5. When the device reaches the stomach, the compressor expands the walls of the organ using air. 6. The electric pump cleans the stomach from its juice and bile. 7. The doctor examines the condition of the organs. 8. The endoscope is removed. If necessary, during EGD, additional biopsy material can be taken. When carrying out the procedure, you should follow all the recommendations of a specialist, pay attention to breathing (it should be slow), do not be embarrassed with abundant saliva. The duration of FGDS is no more than 20 minutes. Research cost - from 2000 rubles. |
| Electrogastroenterography | Another name is electrogastrography. The method provides for the study of the motor-evacuation function of the gastrointestinal tract. The procedure is carried out by registering the biopotentials of various parts of the gastrointestinal tract. Electrogastroenterography can be used to assess gastrointestinal motility. Stages of the procedure: 1. The man lies down on the couch. 2. 3 electrodes are attached to the abdomen (pre-lubricated with a conductive paste). 3. The recording is carried out within 60 minutes. 4. The electrodes are disconnected, they take a break for 1.5 hours, during which time the person must eat. 5. When the break is over, the electrodes are reattached and the test is repeated. The total time required for electrogastrography is up to 3 hours. Research cost - from 4000 rubles. |
| Computed tomography (CT) | The method is based on X-ray radiation. As a result, three-dimensional images of the examined organ are obtained. Unlike a conventional X-ray, the tomograph is more informative, from the images you can determine not only the presence of a pathological focus, but also identify its localization. If it is necessary to improve visualization, a contrast agent is injected into the person before the examination. Stages of abdominal CT: 1. The patient lies down on the couch. 2. The table assumes a position that corresponds to the beginning of the study area. To make the image layered, CT is started from the diaphragm. 3. When the scan is over, the person is allowed to stand up. The duration of the procedure reaches 40 - 60 minutes. The cost of CT scan of the abdominal cavity is from 2500 rubles. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | The procedure is based on electromagnetic radiation. The method of conducting depends on the type of the tomograph: 1. Open. The man lies down on the couch, over which the apparatus is located. The table assumes a position corresponding to the study area. 2. Closed. The patient lies down on a couch that slides into the tomograph. The method is not suitable for people with a fear of confined spaces (claustrophobia) and weighing more than 120 kg. If necessary, a contrast agent is injected into the person before the examination. The duration of the procedure is from 40 to 60 minutes. The cost of an MRI of the abdominal cavity is from 4000 rubles. |
| Biopsy | A procedure performed to obtain a biopsy (tissue sample) from the digestive tract. A biopsy must be prescribed if a neoplasm is suspected. After the biomaterial is taken, it is sent to the laboratory for research. Biopsy cost - from 1000 rubles. |
Before the examination, you must follow the preparatory rules. They will be recommended by a specialist, depending on the list of procedures.
It is impossible to single out any one diagnostic method and say that it is better than others. Most often, the doctor prescribes an examination that includes several procedures. Diagnostic costs may vary. It all depends on the list of procedures, city, organization. Therefore, the price must be checked in a specific clinic.
There is a possibility of free diagnostics. To do this, you need to contact the clinic with a compulsory health insurance policy (MHI).
Treatment methods
Duodenogastric reflux needs therapy. She is appointed after receiving the diagnostic results. Most often, complex treatment is used, that is, the simultaneous combination of several methods.
GHR therapy methods:
- the use of drugs;
- the use of alternative therapy;
- adherence to proper nutrition;
- doing exercise;
- carrying out a surgical operation.
Medications
Medicines can eliminate negative symptoms and improve a person's well-being. The table shows the drugs that are most often prescribed for GHD.
| Group of medicines | the effect | List of drugs |
| Antispasmodic | The drugs eliminate the spasm of the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract. | No-shpa, Drotaverin, Spazmalgon |
| Antacid | Medicines neutralize the hydrochloric acid of the stomach, protect the mucous membrane of the organ. As a result, heartburn, belching, and a feeling of fullness in the stomach decrease. |
|
| Carminative | Destroy gas bubbles. As a result, bloating in the abdomen is reduced. A group of drugs can be used before diagnostic procedures (ultrasound, X-ray) to avoid image defects. |
Espumisan, Bobotik, Sub simplex |
| Antiemetic | Medicines eliminate nausea and vomiting. | Motilium, Domperidone, Metoclopramide |
| Proton pump inhibitors | The drugs reduce the likelihood of damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa. Additionally, medications eliminate the aggressiveness of the contents of the duodenum, which is thrown into the stomach. |
|
| Antitussives | The drugs eliminate dry cough. | Libeksin, Sinekod, Terpinkod |
| From hoarseness and loss of voice | The remedy restores the voice. | Homeowox |
| General tonic | The drugs stimulate the immune defense, improve the body's tolerance of unfavorable external factors. | Ginseng tincture, viburnum syrup, Caffeine-sodium benzoate |
Medicines must be prescribed by a specialist. The doctor takes into account the individual characteristics of the body, the reason for the appearance of GDR. Additionally, take into account the information specified in the instructions for use of each drug.
Traditional therapy
Duodenogastric reflux (treatment includes exercise) is a condition in which the use of folk recipes is allowed. The products have a natural composition, but they must be used in combination with other methods. This way you can maximize the effectiveness of the treatment.
Folk recipes:
-
Linen. To prepare the recipe, you need to pour 1 tbsp. seeds 100 ml of hot water, wait for swelling and mucus secretion. Take the mixture on an empty stomach.

- Herbal mixture No. 1. To prepare the recipe, you need to take 50 g of sage and calamus root, 25 g of angelica. Then 1 tsp. pour the mixture with 1 glass of hot water, cover with a lid for 20 minutes. Filter through cheesecloth, drink. Apply the recipe 3 times a day, it is better to consume the mixture one hour after a meal.
- Herbal mixture No. 2. For cooking, you need to take an equal amount of mint, oregano and calendula. Next 1 tbsp. pour 200 ml of hot water into the mixture. Leave for 20 - 30 minutes, filter through cheesecloth. Add 1 tablespoon to the warm infusion. freshly squeezed aloe juice and 1 tsp. honey. Take the remedy 3 times a day.
Proper nutrition
Duodenogastric reflux therapy includes proper nutrition.
Diet principles:
- eat 5 - 6 times a day;
- do not exceed serving size (150 - 300 g);
- eat every 3 to 4 hours;
- exclude fried, salty, smoked;
- reduce the use of sweet and starchy foods;
- add vegetables, fruits;
- the diet should be dominated by vegetable soups, cereals in water or milk;
- replace fatty foods with low-calorie ones - for example, instead of pork, buy chicken or turkey;
- do not forget about the drinking regime - at least 1.5 liters of clean non-carbonated water per day;

- exclude strong coffee, black tea - it is better to replace drinks with green tea, compote, juice.
Exercises
The therapy can improve motor function and digestion.
Exercises for GDR:
- body turns - stand up, place your hands on your belt, turn to the right and then to the left;
- tilts - stand up, place your hands on your belt, slowly bend forward and return to the starting position;
- pulling up the knees - lie down, pull one leg bent at the knee to the stomach, repeat the same actions, but with the other leg;
- raising legs - lie down, take turns to raise straightened legs.
Do each exercise in 3 sets of 10 reps. That is, do it 10 times, then rest, and so on.
Surgery
If conservative therapy does not help or its use does not bring results, the doctor may recommend surgery. The method of carrying out and the need for the operation is determined by a specialist.
Possible consequences and complications
Duodenogastric reflux (treatment includes proper nutrition) is a condition characterized by complications. Most often, the consequences appear in the absence or untimely therapy.
Possible complications:
- erosion on the gastric mucosa;
- peptic ulcer (PUD) - a defect in the mucous membrane;
- gastroesophageal reflux - the throwing of stomach contents into the esophagus;
- stenosis (decrease in diameter) of the lumen of the esophagus, that is, the appearance of an obstacle to the normal movement of food;
- toxic-chemical gastritis with the formation of chronic inflammation;
- benign or malignant neoplasms in the digestive organs.
GHR or duodenogastric reflux is a disorder of the digestive system in which the contents of the duodenum are thrown into the stomach. The symptoms of the condition are abdominal pain, heartburn, belching. To determine GHD, the doctor prescribes an examination.
After receiving the results of the diagnosis, treatment is prescribed, which includes medicines, folk remedies and other methods. The most important thing is to reduce the likelihood of complications. To do this, you must follow the doctor's recommendations.
Video about DGR
GDR relationship with GERD:

 If the patient is constipated, the biomaterial obtained the night before can be delivered to the laboratory. A cleansing enema cannot be used, it is necessary to achieve a bowel movement naturally.
If the patient is constipated, the biomaterial obtained the night before can be delivered to the laboratory. A cleansing enema cannot be used, it is necessary to achieve a bowel movement naturally.