Payr's syndrome is bowel diseasecharacterized by various symptoms. Pain and constipation are most common. In this case, complications may occur - peritonitis, ischemic damage to the intestinal wall, and more. Therefore, adults need to know the symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment of pathology.
Record content:
- 1 General information
- 2 Causes
- 3 Classification
- 4 Symptoms
- 5 What is the danger of the syndrome, complications
- 6 Diagnostics
- 7 Diet treatment
-
8 Conservative treatment
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Physiotherapy
- 9 Forecast
- 10 Payr Syndrome Videos
General information
Food that a person eats is digested in the stomach. It then enters the small intestine as a thick paste (chyme). The mass is affected by bile, intestinal juice, an enzyme. When the chyme moves through the small intestine, it gradually breaks down, absorbing nutrients and salts into the blood. Further, the masses enter the large intestine.
Residual water, nutrients and salts are absorbed there. That is, the chyme becomes dehydrated and turns into feces. In the large intestine, undigested components are utilized. For example, toxins, carbon dioxide. Disposal is carried out at the expense of the liver. Additionally, feces are pushed to the anus to remove it from the body.
The large intestine has several sections (blind, colon, rectum). The longest is the colon. Its diameter can reach 6 cm.
The colon has sections:
- Ascending segment. Its localization is the right side of the abdomen. The ascending segment rises towards the liver and bends at an angle of about 90 degrees. The length of the department is 20 cm.
- Cross segment. The length of the department can reach 50 - 60 cm. This part of the intestine is the longest. The transverse segment reaches the spleen (located in the left hypochondrium), then bends and passes into the descending part.
- Descending segment. Its length is from 10 to 30 cm. The average value is 23 cm. The segment is located in the left abdomen.
- Sigmoid colon. Located on the left side in the retroperitoneal space. The name comes from the fact that the gut is similar to the letter S. The length of the department is from 54 to 55 cm. But hesitation is allowed. Possible sizes are from 15 to 70 cm.
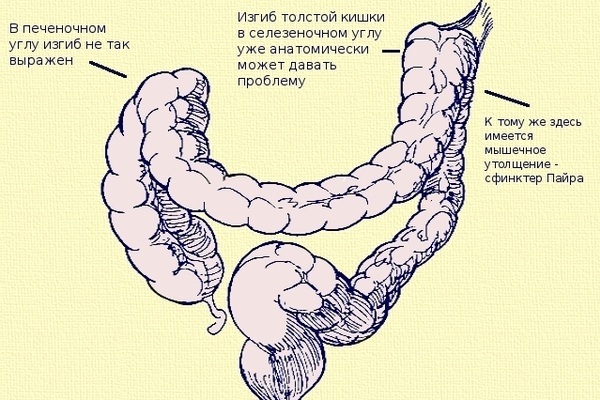
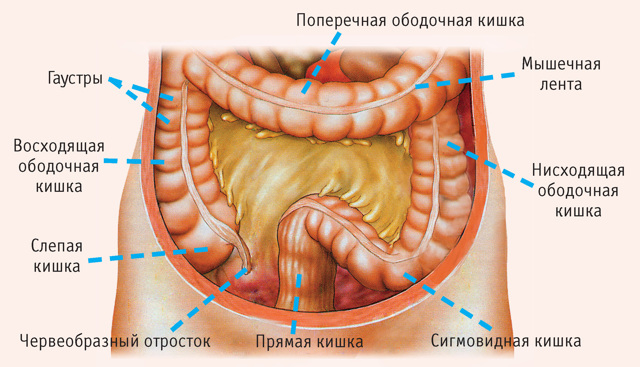 Next comes the rectum. In this section, the formation of feces is completed, the masses are removed from the body through the anus. Payr's syndrome in adults is a condition in which the second flexure of the colon (located in the spleen) increases in size. That is, it deviates from physiology.
Next comes the rectum. In this section, the formation of feces is completed, the masses are removed from the body through the anus. Payr's syndrome in adults is a condition in which the second flexure of the colon (located in the spleen) increases in size. That is, it deviates from physiology.
And also a pathological bend is formed in the place where the transverse colon passes into the descending colon. Feces cannot quickly leave the body and make room for new masses, a congestion appears. Another name for pathology is splenic angle syndrome.
The disease was first described by the German surgeon Erwin Pyr. This was in 1905. Compared to boys, girls had pathology 3-4 times more often.
Causes
Payr's syndrome is a congenital disorder. Until the end, it was not possible to establish the causes that lead to pathology. It is believed that the onset of the syndrome is associated with a combination of several factors. Gastroenterologists, proctologists, surgeons have identified possible causes that cause pathology. They are shown in the table.
| Causes contributing to the appearance of the syndrome | Description |
| Dysontogenetic factors | Payr's syndrome can appear when the following factors affect the fetus:
|
| Hereditary collagenopathies | When examining patients with Payr's syndrome, the prevalence of type III collagen was revealed. Thus, fibromuscular dysplasia is manifested (not associated with atherosclerosis or inflammation, it implies local stenosis or multiple narrowing of the vessel due to the thickening of its wall). At the same time, the following diseases can be determined in people:
Additionally, other signs are possible, indicating the weakness of the connective tissue. |
Classification
Payr's syndrome has a classification.
The following stages of the disease are distinguished:
- Compensated. This stage can be characterized by exacerbations that rarely occur. Pain is mild or absent. To improve a person's well-being and eliminate the symptoms of the disease, it is enough to follow a diet. The stage occurs in 15 - 16% of patients.
- Subcompensated. In this case, the use of drugs and physiotherapy is required. This stage is common - in 70% of cases.
- Decompensated. Conservative treatment is useless as it will be ineffective. At this stage, a person has strong painful sensations of a cramping character. In addition, symptoms of intoxication appear (disruption of the functioning of internal organs due to exposure to toxic substances). The stage occurs in 14 - 16% of patients.
Symptoms
Payr's syndrome in adults has symptoms that are similar to other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). Therefore, doctors often make a mistake with the diagnosis and prescribe the wrong treatment.
Symptoms that may indicate the syndrome:
-
Abdominal pain. A symptom that is common in this syndrome. Localization of pain - left hypochondrium. After eating or physical activity, the symptom becomes more pronounced. The pain can change its location and radiate to the heart or lower back (left half). The unpleasant sensations are strong. The pain may recur several times a week or month. Additionally, patients note that the discomfort increases as they grow older. The pain decreases when the person lies down horizontally.

- Chronic constipation. The symptom can last more than 5 days in a row. With prolonged constipation, the pain sensations increase.
- Dyspeptic manifestations. This point includes nausea, periodic vomiting, a feeling of early satiety. Additionally, there is heaviness in the abdomen, gas formation increases, appetite worsens.
- Violation of the general condition. This item is characterized by pain in the head, reduced performance, irritability. Additionally, body weight decreases (due to intoxication), shortness of breath appears and heart rate increases.
What is the danger of the syndrome, complications
Normally, the act of defecation should be carried out daily to remove toxic substances from the body. With a delay in feces, they are absorbed into the bloodstream, intoxication develops. This is the main danger of Payr's syndrome. Due to intoxication, the immune defense decreases, the body becomes susceptible to various diseases.
Additionally, solid masses irritate the intestinal mucosa, ulcers are possible. And if a person is pushing hard so that feces leave the body through the rectum, the development of hemorrhoids is allowed (inflammation, thrombosis, pathological expansion of hemorrhoidal veins, which form nodes around the straight intestines).
Additionally, colonoptosis cannot be ruled out - prolapse of the colon. As a result, it is possible to develop acute intestinal obstruction and volvulus (sometimes).
Additional complications that cannot be ruled out in Payr syndrome:
- ischemic damage to the intestinal wall - pathology associated with blockage or narrowing of the intestinal arteries, as a result there is a possibility of necrosis (cell death) of the organ;
- peritonitis - inflammation of the sheets of the peritoneum (parietal and visceral) due to exposure to food, intestinal contents, microbes;
- reflux ileitis - occurs in 85% of patients with Payr's syndrome, is characterized by inflammation of the ileum (end section of the small intestine), associated with the constant reflux of feces from the cecum into the ileum;
-
colitis - appears in 60% of cases, is characterized by inflammation of the colon, leading to atrophy of the mucous membrane and impaired functionality of organs.
The likelihood of complications increases with untimely or incorrectly prescribed therapy.
Diagnostics
Payr's syndrome, which can be found in a child or adult, needs diagnosis. The examination allows you to determine the disease and prescribe therapy.
Before referring a patient for diagnosis, a gastroenterologist:
- Conducts a survey. The specialist asks questions that relate to symptoms, concomitant diseases.
- Measures indicators. The doctor pays attention to blood pressure, pulse, temperature.
- Conducts examination and palpation. The specialist examines the patient's skin, probes the abdominal cavity.
Additionally, the gastroenterologist may advise you to visit a proctologist (in case of hemorrhoids) and a surgeon (if surgery is necessary). And also the person is prescribed a referral for examination. Diagnostic methods are shown in the table.
| Name | Description |
| Blood analysis | This study is one of the main methods of laboratory diagnostics, which allows you to assess the general condition of the body. If you suspect Payr's syndrome, a clinical blood test is prescribed. It allows you to identify inflammation, infection, swelling. The result sheet indicates the number of different indicators (hemoglobin, erythrocytes and others). Additionally, the doctor may prescribe a blood donation to determine the following indicators:
To perform the study, capillary (from a finger) or venous blood is taken. The result is considered more accurate if a vein biomaterial was used. With Payr's syndrome, there are changes in the following indicators:
|
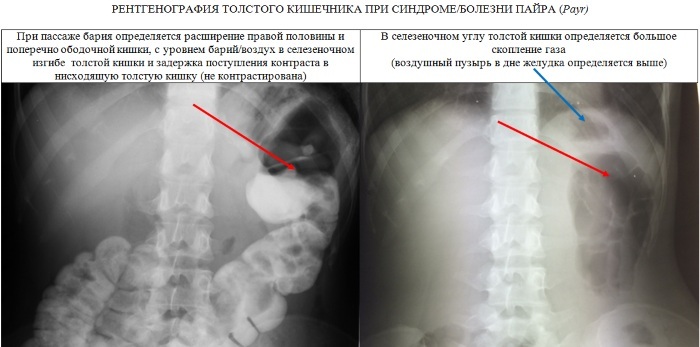
| Irrigoscopy | Study of the large intestine, which allows you to examine the organ, to determine the functionality of individual sections.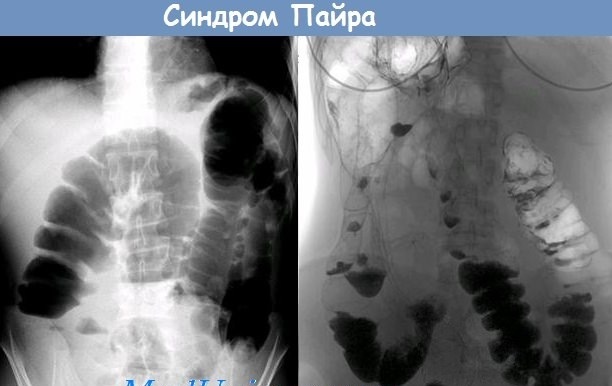 There are 3 options for irrigoscopy:
Stages of the procedure: 1. The patient takes off his clothes below the waist and lies on his side on the couch. The person is asked to bend their knees and press them against their stomach. 2. An enema tip is inserted into the rectum. There is contrast in the device. Most often, a barium mixture is used (barium sulfate is dissolved in water). During the introduction of the substance, the healthcare professional may ask the patient to roll over onto the other side, stomach, or back. When contrast is received, a series of images is taken. 3. When distributing the substance, a general picture is taken. 4. The patient is asked to have a bowel movement. 5. A snapshot is taken to assess bowel function. 6. If double contrasting is performed, the intestines are filled with air and a picture is taken. Irrigoscopy takes 20 - 50 minutes. |
| Doppler ultrasound of the vessels of the abdominal cavity (USDG) | A procedure that allows you to examine the blood flow in the vessels of the abdominal cavity. With the help of the USDG it is possible to determine:
The method is based on the ability of ultrasonic waves to be reflected from blood vessels. During research, everything is visible on the screen in real time. Moreover, a medical professional can measure the speed and uniformity of blood flow. Stages of the USDG: 1. The man takes off his clothes to the waist and lies down on the couch. 2. Gel is applied to the abdominal cavity to improve visualization. 3. An ultrasound probe is guided over the abdominal cavity. If necessary, during the examination, the healthcare professional may ask the patient to roll over on his side and hold his breath. 4. The person is asked to wipe off the skin. The duration of the procedure is from 20 to 60 minutes. |
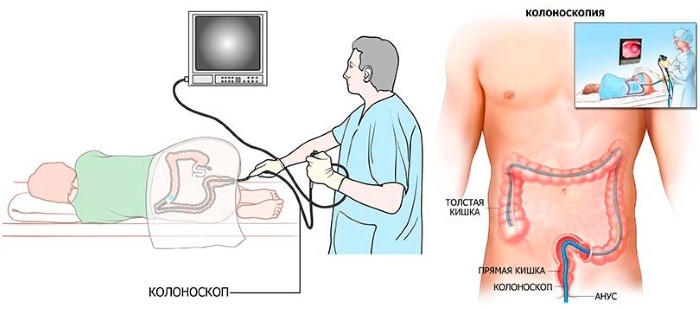
| Colonoscopy | The method involves the study of the large intestine. With the help of a colonoscopy, it is possible to examine in detail the mucous membrane of an organ. Additionally allowed:
The procedure is performed using a colonoscope. The device is a soft and bendable probe equipped with a video camera and lighting. The camera transmits the image to the screen in real time, and it is also possible to take a picture of a separate area of the intestine. In addition, the kit includes a tube for air injection and forceps for taking a tissue sample. When performing the study, it is possible to use anesthesia. For example, if the patient has a low pain sensitivity threshold or has a fear of the procedure.
Stages of the procedure: 1. The patient is asked to remove the clothing below the waist and lie on the couch with his legs bent. 2. If necessary, an anesthetic drug is administered. 3. The anal opening is treated with an antiseptic. 4. A colonoscope is inserted into the rectum and gradually advanced, observing the process through a monitor. If necessary, air is injected to straighten the intestinal folds. 5. After the end of the examination, the equipment is removed from the anus. The research takes 15 - 40 minutes. |
| Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen | The study is based on X-ray radiation. With the help of CT, it is possible to obtain high-quality images in three-dimensional projection. If it is necessary to improve visualization, a contrast agent is injected into the human body before examination. With the help of MRI, it is possible to identify various diseases of the abdominal cavity, including formations (ulcers, tumors). Stages of the procedure: 1. The patient is asked to undress to the waist and lie on a couch. 2. If necessary, inject a contrast agent. 3. The couch is positioned in relation to the study area. 4. Research begins. It is important to lie still during the operation of the tomograph. If necessary, the person may be asked to hold their breath. 5. After the tomograph has finished work, the person can get dressed. The duration of the procedure is from 20 to 40 minutes. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen | The survey is based on magnetic radiation. With the help of the procedure, it is possible to obtain high-quality images in three-dimensional projection. MRI allows you to detect diseases of the abdominal cavity, including formations (ulcer, tumor). If it is necessary to improve visualization, a contrast agent is injected into the human body. The stages of an MRI scan depend on the type of tomograph: 1. Open. A person needs to take off his clothes to the waist, lie on the couch, above which the tomograph is located. If necessary, inject a contrast agent. The tomograph begins its work. During the study, it is necessary to be motionless. Additionally, you may be asked to hold your breath. The person can get dressed when the work of the tomograph is finished. This type of MRI is performed for people with a fear of a confined space (claustrophobia), weighing more than 120 kg. 2. Closed. The man undresses to the waist, lies down on the couch. If necessary, inject a contrast agent. The couch slides into the apparatus, the tomograph starts its work. When examining, you need to lie still. If necessary, the person may be asked to hold their breath. After the tomograph has finished its work, the patient is allowed to get dressed. Abdominal MRI takes 30-50 minutes. |
| Colon histology | The method allows you to determine the presence of tumors of a benign and malignant nature. Additionally, according to the results of histology, it is possible to determine colitis and other gastrointestinal diseases. First, a biopsy is taken, that is, a tissue sample is taken. Then histology is done - this is a study of the biomaterial under a microscope. |
Each study requires adherence to the preparatory rules. They will be recommended by a specialist. The cost of diagnostics is different. It all depends on the list of procedures, city, organization. Therefore, the price must be checked at the clinic.
You can get diagnostics free of charge. To do this, you need to contact the clinic with a compulsory health insurance policy (MHI).
Diet treatment
Payr's syndrome in adults requires proper nutrition.
Diet principles:
- eat 5 - 6 times a day with breaks of 3 - 4 hours;
- do not exceed the serving size (150 - 300 g);
- eat at the same time - for example, have breakfast at 8:00, lunch at 12:00, and so on;
- steam, boil or bake food in the oven;
- replace fatty foods with low-calorie ones - for example, buy not pork, but chicken or turkey;
- reduce the amount of sweet;
- exclude salty, fried, smoked;
- do not forget about the drinking regime - at least 1.5 liters of clean non-carbonated water per day;
- exclude strong coffee and tea, alcoholic beverages - it is better to replace products with green tea, compote, juice;
- add fruits and vegetables, cereals to the diet.
Conservative treatment
In order to alleviate a person's condition, conservative therapy can be prescribed for the disease.
Namely:
- taking medications;
- use of physical therapy.
The method of treatment must be selected by a specialist. The doctor takes into account the stage of the disease, the manifestation of symptoms, the individual characteristics of the organism.
Medications
Payr's syndrome in adults is a medical condition in which medications can be prescribed. Medicines can eliminate negative symptoms and alleviate a person's condition. The table lists the drugs that are prescribed for Payr's syndrome.

| Group name | Effect of application | List of funds |
| Laxatives | The drugs contribute to the excretion of feces from the body. | Guttalax, Microlax, Duphalac |
| Antispasmodics | Medication can help reduce smooth muscle spasms. | No-shpa, Duspatalin, Trimedat |
| Antiemetic | Medicines in this group eliminate vomiting and nausea. | Metoclopramide, Cerucal, Motilium |
| Carminative | The drugs fight increased gas production in the gastrointestinal tract. | Espumisan, Sub Simplex, Motelegaz Forte |
| Sedatives | Means normalize the emotional state of a person, eliminate irritability. | Novo-Passit, Persen, Tenoten |
| Antacid | The drugs form a protective layer on the gastrointestinal mucosa. Additionally, antacids promote the elimination of toxins, gases and microorganisms from the digestive tract. And also medications normalize the output of feces. | Phosphalugel, Almagel, Rennie |
| Analgesics | Means eliminate pain. | Analgin, Paracetamol |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) | The drugs reduce inflammation, pain, and fever. | Nurofen, Dexalgin, Pentalgin |
| B vitamins | The funds restore the deficit, since in case of a disease, a deficiency of B vitamins develops due to impaired absorption. Additionally, this group of drugs restores liver function. | Kombilipen, Milgamma |
Physiotherapy
To reduce the intensity of pain, the doctor may refer the patient to physical therapy (the effect of natural factors on the body).
With Payr's syndrome, the following methods are used:
- electrophoresis - the effect on the body of constant electrical impulses;
- iontophoresis - the use of low voltage current;
- paraffin therapy - the effect of heated paraffin as a heat compress;
- diathermy - heating of tissues with high currents;
- UHF therapy - exposure of the body to a high-frequency electromagnetic field;
- massage therapy - impact on soft tissues with the help of a specialist's hands.
Forecast
The prognosis for recovery depends on the timeliness of diagnosis and the correct choice of therapy. According to statistics, after the appointment of complex treatment, the condition improved in 85% of patients with Payr's syndrome. Therefore, with proper therapy, the prognosis is favorable. When the syndrome is in its late stages, the likelihood of complications increases.
A disease in which a pathological bend is formed in the place where the transverse colon passes into the descending colon is Payr's syndrome. The disease is hereditary. Symptoms include prolonged constipation, abdominal pain, and vomiting. To clarify the diagnosis, an examination is carried out.
After receiving the results, the adult is prescribed treatment, which may include adherence to proper nutrition, taking medications, and using physical therapy. If a late stage of the syndrome is identified, conservative treatment will be ineffective, and surgery will be required.
The most important thing is to reduce the likelihood of complications. To do this, you need to consult a doctor when symptoms of the disease appear in order to diagnose and prescribe therapy in a timely manner.
Payr Syndrome Videos
Bowel problems, Payr syndrome:

 Types of pain relief:
Types of pain relief: