Biliary dyskinesia Is a disease of a functional nature associated with a malfunction of the gallbladder and its ducts. In children, pathology can manifest itself by a slowdown in the outflow of bile to the duodenum, or, conversely, by the intake of bile secretion in excessive quantities. This leads to disruption of the digestive process and a deterioration in the absorption of beneficial nutrients.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms and Signs
- 4 Causes
-
5 Diagnostics
- 5.1 Instrumental
- 5.2 Laboratory
-
6 Treatment methods
-
6.1 Drug treatment
- 6.1.1 Pain relievers
- 6.1.2 Choleretic drugs
- 6.2 Folk remedies
- 6.3 Food
- 6.4 Physiotherapy
-
6.1 Drug treatment
- 7 Possible consequences and complications
- 8 Dyskinesia Videos
Views
The main function of the gallbladder is to excrete bile produced by the liver cells. Normally, bile enters the digestive tract and provides digestive processes in the small intestine. However, if the gallbladder motility is impaired, this does not happen.
Depending on the volume of bile secretion produced in children, there are 3 main forms of manifestation of pathology: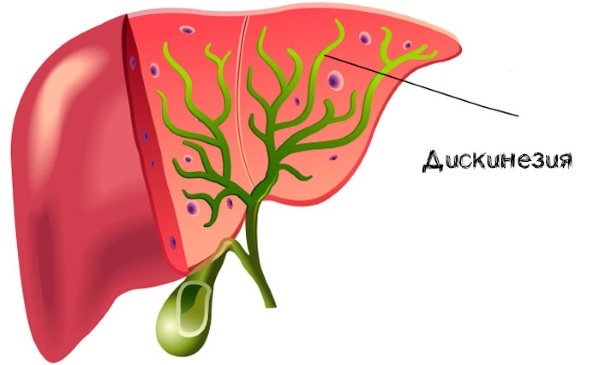
| Hypomotor | Hypermotor | Mixed |
| The muscles of the gallbladder do not contract strongly enough, as a result of which there is a slowdown in the outflow of bile. | The muscle tissue of the organ contracts rapidly and in an uncoordinated manner, which is why bile is produced in excessive quantities. | Combines signs of two types of dyskinesia. |
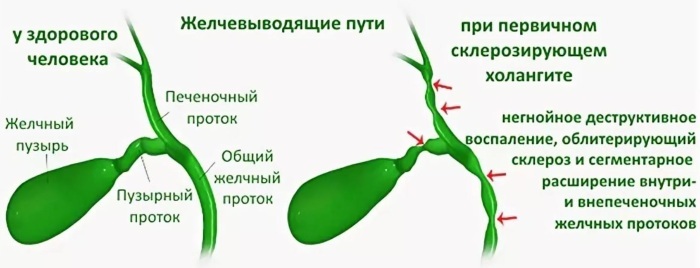
Also, primary and secondary dyskinesias are distinguished.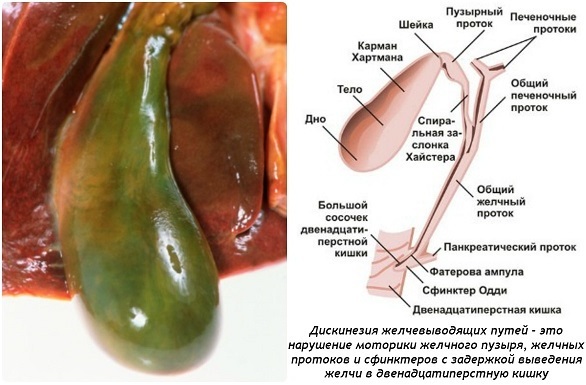
Primary dysfunction is associated with functional abnormalities such as:
- neurosis;
- vegetative dystonia;
- psychosomatic syndrome;
- neuro-arthric anomaly.
Secondary dyskinesia is associated with organic diseases of neighboring organs - the liver, pancreas, as well as hormonal disorders.
Stages and degrees
According to the degree of damage to the sphincter of Oddi, located in the terminal section of the bile duct, dyskinesia is distinguished:
- I degree. Significant disturbances in the outflow of bile with signs of liver damage.
- II degree. Expansion of the duct system.
- III degree. The presence of pain in the absence of laboratory signs of the disease.
Symptoms and Signs
Biliary dyskinesia in children manifests itself in different ways, depending on the form of the disease. With hypermotor dyskinesia, spastic contractions of the gallbladder walls are observed.
This provokes the onset of acute, cramping pain that lasts for a short time. The onset of an attack is associated with a sudden increase in gallbladder pressure after a diet disorder. Pain occurs and intensifies 1-1.5 hours after eating.
Hypermotor DVP provokes the following symptoms:
- attacks of acute pain in the epigastric region and in the hypochondrium;
- bitterness in the mouth in the morning;
- loss of appetite;
- discoloration of feces;
- nausea;
- irritability;
- yellow coating on the tongue.
With hypomotoroia of DVP, the gallbladder contracts sluggishly. The attacks of pain are mild, protracted and can last from 2-3 hours to several days.
This form of dyskinesia is characterized by:
- aching pain in the right hypochondrium;
- feeling of fullness in the abdomen;
- belching with air;
- frequent constipation.
At the same time, at the time of a painful attack, the following is observed:
- excessive sweating;
- pallor of the skin;
- dizziness;
- heart palpitations.
Both hypomotor and hypermotor dyskinesias are recurrent. There are periods of exacerbation and remission. Attacks are associated with stressful situations or emotional stress.
In interictal periods, the child's condition is satisfactory. There may be rare aching pains in the gallbladder area.
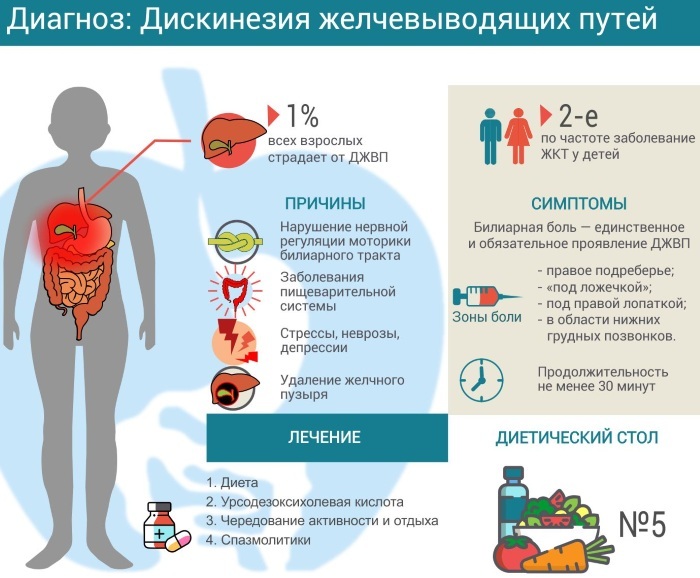
Causes
Dyskinesia develops against the background of other diseases, as well as under the influence of external factors that increase the likelihood of the development of pathology.
In children, the disease is associated with malfunctions in the central nervous system and disorders of the autonomic system of the body. Attacks are often associated with stressful situations or emotional overstrain, since it is these conditions that lead to involuntary contractions of the gallbladder. As a result, in the area of the biliary tract, bile accumulates and thickens, losing its functional properties.
| External factors | Diseases of other organs and systems | Abnormalities in the structure of the gallbladder |
|
|
|
Diagnostics
Biliary dyskinesia in children is manifested by attacks of biliary pain, which is important to differentiate from other types of pain sensations provoked by neighboring organs. For this purpose, a thorough examination of the child is required. The main methods for diagnosing the disease include instrumental and laboratory research methods.
Instrumental
If a child is suspected of having DVT, the following diagnostic methods are shown:
-
Ultrasound of the abdominal organs.
 Includes examination and assessment of the state of organs - pancreas, spleen, liver. The doctor measures the gallbladder and ducts, assesses the state of the vessels of the internal organs. The study is carried out on an empty stomach: eating is prohibited 6 hours before the start of the diagnosis. It is recommended to follow a diet 3 days before the ultrasound scan. Foods that enhance intestinal motility should be excluded. The examination is carried out in the morning and lasts about 30-40 minutes. Cost - 1500-2000 rubles.
Includes examination and assessment of the state of organs - pancreas, spleen, liver. The doctor measures the gallbladder and ducts, assesses the state of the vessels of the internal organs. The study is carried out on an empty stomach: eating is prohibited 6 hours before the start of the diagnosis. It is recommended to follow a diet 3 days before the ultrasound scan. Foods that enhance intestinal motility should be excluded. The examination is carried out in the morning and lasts about 30-40 minutes. Cost - 1500-2000 rubles. - Esophagogastroduodenoscopy. A method for examining the esophagus, stomach and duodenum, which allows you to visually assess the state of the mucous membrane of the upper gastrointestinal tract. The examination is carried out using an endoscope, which is inserted into the esophagus. The endoscope camera transmits the image of the mucous membranes to the monitor screen, while the video is recorded. EGDS is carried out in the first half of the day on an empty stomach, after 19 hours from the moment of the last meal. If the study is carried out in the afternoon, you can eat a light breakfast. Cost - from 1700 rubles.
- X-ray of the gallbladder. Diagnosis is carried out using a contrast agent that contains iodine. Contrast X-ray allows you to assess the shape, size, location of the gallbladder. A low-fat diet is recommended for the child 24 hours before the examination. On the eve of the procedure, it is necessary to take a contrast agent. After 17 hours, a study can be carried out, since the substances of the drug penetrate into the bile and the shadow of the gallbladder is visible on the roentgenogram. If there is no shadow, this indicates an obstruction of the bile ducts. The cost of the procedure is from 1800 rubles.
Laboratory
When making a diagnosis, laboratory tests play an important role.
The child needs to pass the following tests:
- Clinical blood test. A study that allows you to assess the content of hemoglobin, the number of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets. For analysis, venous or capillary blood is used. Special preparation for the study is not required. It is enough not to eat food for 8 hours, as well as to exclude physical and emotional stress 30 minutes before collecting the biomaterial. The results of the analysis can be handled throughout the day. Cost - 200-350 rubles.
-
Blood chemistry. The study, which is carried out to determine the state of the organs and systems of the child. The analysis allows you to assess the indicators of total protein, glucose, urea, bilirubin, cholesterol and amylase in the blood. The collection of biomaterial is carried out from a vein. It is forbidden to eat food 8-12 hours before the test. Also, the child needs to provide comfortable conditions for a stable emotional state. Research cost - from 700 rubles.
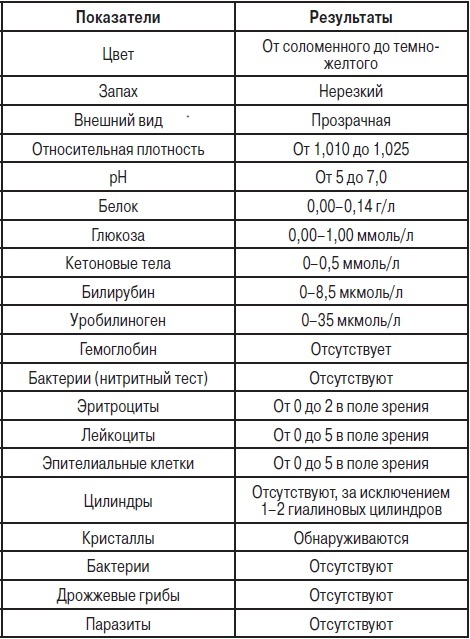
- General urine analysis. The study is carried out to study the physical and chemical characteristics of urine. For the analysis, it is preferable to use morning urine collected in a container. The urine should be collected after a thorough toilet of the external genitalia. It is necessary to deliver the biomaterial to the laboratory within 1.5-3 hours from the moment of collection. Before taking the analysis, it is not recommended to eat coloring food. Research cost - 200-400 rubles.
Treatment methods
Treatment of dyskinesia should be comprehensive and include not only the appointment of medications, but also other measures: diet, physiotherapy, normalization of sleep and rest. Since disorders of the autonomic and central nervous systems play a key role in the etiology of VAD, therapy should be aimed at restoring their full functioning.
Drug treatment
The choice of drug treatment for dyskinesia in children depends on the type of dysfunction and the presence of comorbidities.
The treatment program includes the following stages:
- correction of motor disorders of the gallbladder;
- improving the flowing properties of bile;
- normalization of the nervous system.
To alleviate the child's condition, the following groups of drugs are used:
- pain relievers;
- choleretic agents;
- enzyme preparations.
Pain relievers
Pain relievers can help reduce the manifestations of pain.
The most commonly used:
-
Noshpa - antispasmodic agent in the form of tablets. The active ingredient is drotaverine. The drug relaxes the smooth muscles of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary tract. Approved for use by children over the age of 6 years. Dosage regimen: 6-12 years - 1 table. 1-2 times a day, children over 12 years old - 1 table. 2-4 times a day. Price - 200 rubles. per packing.
- Trimedat - antispasmodic agent in the form of tablets, designed to relieve pain associated with functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and gallbladder. Children aged 3-5 years need to take 25 mg of the drug 3 times a day. Children 5-12 years old - 50 mg 3 times a day. The duration of treatment is determined individually. The cost of tablets is from 350 rubles.
- Buscopan - tablets that have a local spasmolytic effect on the muscles of the internal organs. The drug is taken orally with water. The product is intended for children over 6 years old. Dosage regimen: 1-2 tablets. 3-4 times a day. Price - from 450 rubles.
Choleretic drugs
Choleretic drugs are subdivided into choleretics and cholekinetics. Choleretics increase the concentration of bile acids. Cholekinetics stimulate contraction of the gallbladder and reduce pressure in the biliary system. Often these drugs are homeopathic.
These include:
- Galsten - homeopathic drops, which include milk thistle, dandelion, celandine. The drug should be taken 30 minutes before meals. The initial dose is 10 drops every 1 hour, but not more than 4 times a day. Drops are used in pure form or diluted in 1 tbsp. l. water. After the severity of symptoms decreases, the number of doses is reduced to 3 times a day. Cost - from 500 rubles.
- Hofitol - homeopathic preparation with choleretic and diuretic effect based on dry extract of field artichoke. Children over 6 years of age are prescribed 1-2 tables. 2 times a day after meals. The course of treatment is 10-14 days. Price - from 470 rubles.
- Odeston - a choleretic agent in the form of tablets. The drug is taken orally after meals. Children aged 7 years and older are prescribed 1 table. 1-3 times a day. The duration of treatment is 2-3 weeks. Cost - 400 rubles.
Enzyme preparations allow you to cope with digestive disorders associated with the disorder of fat emulsification.
Most often used:
-
Creon 10000 - the drug is in the form of enteric capsules. Improves the digestion process and reduces the symptoms of enzyme deficiency. The agent is taken orally during meals. The dosage regimen depends on the weight of the child and is 1000 lipase units per 1 kg under the age of 4 years, and 500 lipase units per 1 kg for children over 4 years of age. Cost - from 300 rubles.
Creon 10000 for children - Mezim forte - a digestive enzyme agent in the form of tablets. The enzymes included in the product digest proteins, fats and carbohydrates better, which contributes to their complete absorption in the intestine. The dosage regimen for children is determined individually. Cost - from 70 rubles.
Folk remedies
Dyskinesia of the biliary tract in children is a pathology for the treatment of which traditional medicine methods are suitable, provided that they are part of complex therapy.
In case of illness, choleretic and soothing herbs are used. Calamus, artichoke, dandelion root, barberry, immortelle, mint, valerian are well suited for these purposes. Decoctions and infusions for oral administration are prepared from the herbs listed.
The most popular recipes are:
- Mix in a bowl for 1 tsp. l. sandy immortelle flowers, chamomile flowers, St. John's wort and dandelion root. 1 tbsp. l. the resulting dry mixture must be poured with 200 ml of boiling water, cover the container with a lid and let it brew for 30 minutes. You need to take the infusion 2 times a day, 100 ml 30 minutes before meals.
- 2 tbsp. l. corn stigmas should be poured with 500 ml of boiling water and let it brew for 1-2 hours. The resulting infusion must be taken 2 times a day, 0.5 cups half an hour before meals.
- Mix in a container for 1 tsp. l. wormwood and peppermint. You should take 1 tbsp. l. the resulting dry mixture and pour 2 cups of boiling water, then set in a water bath and simmer for 30 minutes. The resulting broth must be cooled and filtered. Take 1 tbsp. l. 2 times a day 30 minutes before meals.
- 30 ml of olive oil should be mixed with 1 tsp. l. lemon juice. You need to take the mixture 3 times a day before meals.
- 3 fruits of black radish must be peeled and grated on a fine grater, and then squeezed out with cheesecloth. The resulting juice should be taken after meals for 1 tsp. l. 3 times a day.
- 1 tbsp. l. marsh calamus, you need to pour 1 glass of boiling water and let the mixture brew for 1 hour. Then the mixture should be cooled and filtered. You need to take a decoction of 50 ml before meals 3 times a day.
Food
Biliary dyskinesia is a pathology for the treatment of which children need to adhere to a diet. For any form of disease, small patients are shown fractional meals (5-6 meals).
You should refuse:
- fried and fatty foods;
- smoked meats;
- conservation and pickles;
- carbonated drinks;
- fast food.
It is also forbidden to eat foods that cause contraction of the gallbladder:
- spices;
- mushrooms;
- fatty fish;
- onion;
- garlic;
- sorrel.

You should exclude the use of products that provoke gas formation:
- legumes;
- White bread;
- sweets.
Physiotherapy
Additional treatments include physiotherapy.
Techniques are used that are aimed at normalizing the work of the central nervous and autonomic systems:
- Exercise therapy. Classes are carried out 40-60 minutes after eating. The exercises are performed while lying on the left side or standing on all fours. In this case, it is necessary to breathe with the diaphragm, since such breathing provides drainage of the biliary tract. The number of repetitions for each exercise is 4-6 times. Movements are performed at a slow pace. Classes are conducted among groups of 4-5 people. The duration of exercise therapy is 1.5-2 months.
- Magnesia electrophoresis. The drug is administered using direct current. The procedure allows you to relax smooth muscles, relieve nervous tension and improve bile outflow. The procedure takes 6-15 minutes. The duration of the course is 10-20 procedures.
- Paraffin applications. The procedure is prescribed in the absence of acute events. Applications are applied to the liver area, which improves blood circulation, eliminates spasm of the biliary tract and improves bile outflow. The procedures are carried out every other day for a course of 8-15 applications.
- Inductothermy. A procedure, the essence of which is the effect of a high frequency alternating magnetic field on parts of the body. As a result, the blood supply in the capillaries is activated, which leads to an increase in lymph flow and metabolic processes. The degree of excitability of the nervous system decreases. The procedures are carried out daily or every other day. The duration of the 1st session is 15-30 minutes.
Possible consequences and complications
Dyskinesia of the biliary tract in children can lead to complications if it is not treated promptly.
The consequences of the disease include:
- the formation of stones in the bile ducts;
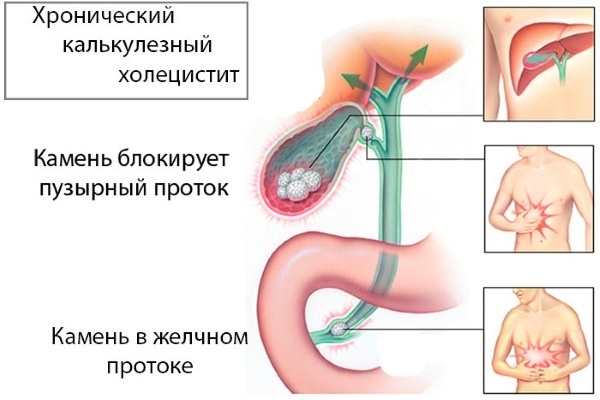
- biliary pancreatitis;
- chronic cholecystitis;
- inflammation of the bile ducts;
- weight loss.
Biliary dyskinesia is a pathology with a favorable prognosis. In children, the disease proceeds in waves, with periods of exacerbation and improvement. Drug therapy and adherence to diet relieves the condition of the child, introducing the disease into a state of prolonged remission.
Dyskinesia Videos
Biliary dyskinesia: