As a result of this dangerous pathological condition, like hemorrhagic shock, oxygen delivery to the tissues of the internal organs of the human body is disrupted.
Lack of nutrients provokes cell shock. A person in such a situation requires emergency medical assistance. The doctor will determine the severity of the pathological processes, the stage of their development. After a comprehensive diagnosis, he will select the most effective treatment.
Record content:
- 1 Definition of disease
-
2 Causes
- 2.1 In children
- 2.2 In pregnant women
-
3 Classification
- 3.1 Compensation stages
- 3.2 Shock index
- 3.3 Severity
- 4 Symptoms of the development of the disease
- 5 Diagnostic methods
- 6 Urgent care
- 7 Hemorrhagic shock treatment
- 8 Clinical guidelines
- 9 Consequences and complications
- 10 Video about hemorrhagic shock
Definition of disease
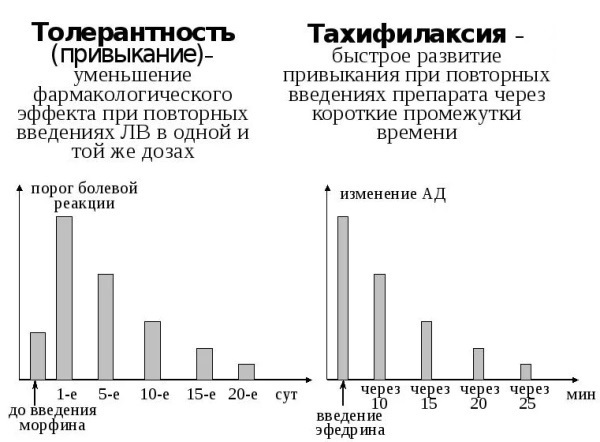
Hemorrhagic shock is the reaction of the entire human body to a large loss of blood. In medicine, this condition is called hypovolemic. Blood is a vital fluid, when reduced, the tissues of the human body experience acute oxygen deficiency.
In some situations, the human body independently compensates for blood loss due to its neurological and hormonal mechanisms. Modern medicine helps to save a person's life, even in case of overload.
If the bleeding does not stop and the lost volume is not replenished, irreversible processes occur. The cells of organs and systems of the human body die, even infusion therapy will not help save the life of the victim.
Causes
In most cases, the cause of hemorrhagic shock is a serious injury, surgery.
The severity of the pathological condition also depends on numerous factors:
- functioning of the cardiovascular system under conditions of hypoxia;
- the state of the immune system;
- how quickly blood clotting occurs;
- vascular tone and its nervous regulation.
The additional supply of oxygen to the human body also affects the severity of hemorrhagic shock.
The following factors can cause massive bleeding:
| Name | Description |
| Injury | Fracture of large bones, damage to internal organs and major blood vessels. Injuries with rupture of the liver, spleen. Damage to the aneurysm of large vessels. |
| Diseases | Heavy bleeding provokes gastric ulcer and duodenal ulcer, cirrhosis with varicose veins. The same applies to heart attack, gangrene of the lung, the formation of malignant tumors, hemorrhagic pancreatitis. |
| Gynecological reasons | Multiple or ectopic pregnancy, placental abruption or previa. Caesarean section, complications also during childbirth increase the risk of hemorrhagic shock. |
Massive bleeding is also a consequence of intrauterine death of a child, vascular embolism by amniotic fluid. In any situation, a person needs emergency medical care and a comprehensive examination, after which the doctor selects the most effective treatment.
In children
Children are more difficult to tolerate blood loss, the symptoms of hemorrhagic shock are pronounced. For a child, a 10% deficiency of circulating blood can be fatal.
The risk of hemorrhagic shock is provoked by the following factors:
- diseases against which cellular nutrition is disturbed;
- intracranial bleeding;
- damage to internal organs;
- violation of the integrity of blood vessels in the navel;
- detachment of the placenta during intrauterine development of the fetus.
Immaturity of all systems of a small organism can provoke hemorrhagic shock in newborns. Symptoms in children are the same as in adults, but more pronounced.
In pregnant women
Hemorrhagic shock is a pathological condition that is often diagnosed in women during the period of gestation or after childbirth.
The following provoking factors are the cause of acute bleeding:
- damage to the uterus, its eversion, rupture of the birth canal;
- detachment of the placenta or its dense accretion;
- atony and hypotension of the uterus;
- sheath attachment of the umbilical cord;
- hypotension of the uterus after childbirth;
- violation of the blood clotting process;
- abortion.

Placenta previa in some situations is accompanied by severe bleeding. Often hemorrhagic shock in pregnant women occurs with other concomitant pathological conditions (gestosis, chronic diseases, severe labor with ruptures).
Classification
Symptoms of hemorrhagic shock depend on the degree of circulatory disorders, the severity of heart failure. The pathological condition is assessed according to certain stages of development, scale and severity.
The doctor uses the information received during the examination to select the most effective treatment for the victim. If necessary, appoint additional tests to establish the site of the bleeding.
Compensation stages
Given the development of the pathological condition, certain stages are distinguished in acute blood loss:
| Name | Description |
| First stage | The compensation period is observed when the total blood loss is no more than 15-20%. The victim is conscious and responds adequately to what is happening. The pathological condition is accompanied by a cold snap and pallor of the skin of the lower and upper extremities. Heart rate is weak, strokes are increased, blood pressure is low. |
| Second stage | Decompensation is characterized by symptoms of brain oxygen starvation and weak cardiac output. The pathological condition occurs with acute blood loss of 25-40% of the total volume. Human consciousness is impaired, lethargy is observed. The body becomes covered with cold and sticky sweat, legs, hands become cold. Blood pressure is low, heart rate is weak, strokes are too high. Weak, shallow breathing is also accompanying clinical symptoms. The filtration function of the kidneys is reduced, as evidenced by a small volume of urine. |
| Third stage | The period is extremely difficult for the victim, when he needs resuscitation assistance. An irreversible stage, which is accompanied by pallor of the skin, a lack of consciousness in a person. It is impossible to measure the pressure and heart rate of the victim. |
At the stage of compensation, the body can independently restore the lack of blood. In the case of the rapid development of a pathological condition, compensatory reactions in the patient's body are disturbed. He will definitely need special treatment. The pathology ends with a fatal outcome if blood loss is more than 60%.
Shock index
Hemorrhagic shock is a dangerous condition, the severity of which is determined by a special shock index. The value is obtained from the ratio of heart rate and systolic pressure. In a healthy person, the indicators are below 1.
In a victim with massive bleeding, this parameter fluctuates, given the severity of the pathological condition:
| Name | Index |
| Mild degree | 1,0-1,1 |
| Medium | 1,5 |
| Heavy | 2,0 |
| Extremely heavy | 2,5 |
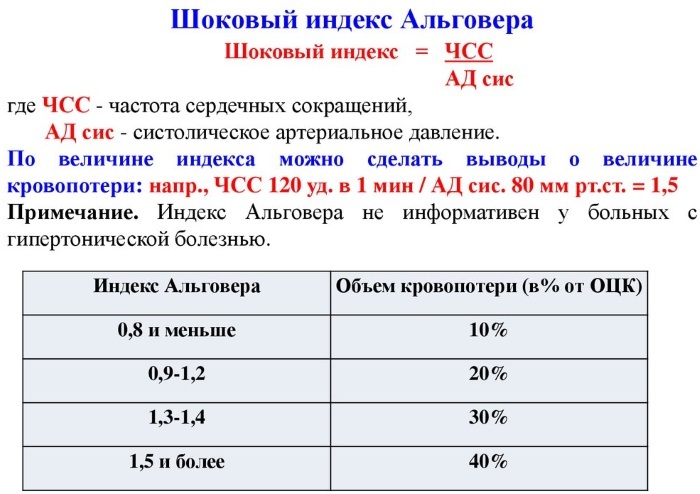
The shock index will determine the condition of the victim. Based on the results, the doctor selects treatment tactics in order to stabilize the situation and prevent possible complications.
Severity
Taking into account the severity of hemorrhagic shock, the doctor assesses the condition of the victim, selects the necessary medications to provide emergency assistance.
| Name | Description |
| I degree | Violation of the circulating blood volume is up to 15%. Blood loss is not more than 1 liter. Symptoms are absent, tachycardia is rarely observed. |
| II degree | The volume of circulating blood is reduced by 15-25%. The pathological condition is characterized by low blood pressure, heart palpitations, the presence of tachycardia and low hemoglobin values. Blood loss is no more than 1.5 liters. |
| III degree | The circulating blood deficiency is 25-35%. The skin turns pale, the lower and upper limbs of a person become cold. Blood pressure decreases, heart rate increases. Diuresis is observed, the level of hemoglobin in the blood is low. Blood loss is up to 2 liters. |
| IV degree | The circulating blood deficiency is more than 35%. Impaired consciousness is accompanied by severe hypotension, tachycardia, deterioration in hemoglobin and respiration. |
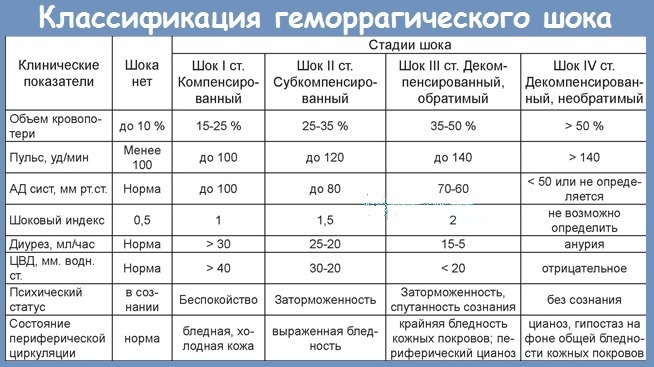
Only a specialist can determine the degree of hemorrhagic shock after medical tests and a special examination.
Symptoms of the development of the disease
The clinical signs of hemorrhagic shock depend on numerous factors, including concomitant diseases present in a person. The same applies to the rate of blood loss and the individual characteristics of the patient's body.
The pathological condition is characterized by the following clinical symptoms:
- dry mouth, nausea appears;
- there is a general weakness in the body;
- the skin turns pale, sometimes it becomes gray;
- cold sweat is released;
- the temperature of the lower and upper extremities decreases;
- acute renal failure develops;
- the amount of urine decreases;
- shortness of breath appears, which gradually increases;
- the work of the respiratory system is disrupted;
- the victim has a stable psychoemotional arousal.
The feet, hands, ears and the area of the nasolabial triangle turn blue. A person needs emergency medical care, on the speed of which his life depends.
Diagnostic methods
A doctor can establish an accurate diagnosis, taking into account the patient's condition and the degree of development of pathological processes.
To diagnose and locate massive bleeding patients are assigned instrumental examination methods:
| Name | Description |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) | The examination is assigned to patients with trauma, ultrasound allows you to identify free fluid and identify the focus of bleeding. |
| General and biochemical blood test | Measurement of hemoglobin level allows to assess the severity of hemorrhagic shock, and to confirm or exclude the development of anemia. |
| Echocardiography | Ultrasound examination of the heart helps the doctor to identify abnormalities in the functioning of the organ, to assess its condition, functioning, and tissue structure. |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | A diagnostic method that detects bleeding in the abdominal cavity or chest. |
| X-ray | The specialist examines the organs of the respiratory system, assesses their condition and functioning. |
| Laparoscopy | An informative and endoscopic diagnostic method, with the help of which the specialist gains access to the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs. In the course of medical procedures, the doctor evaluates their work and identifies damage, as well as dysfunction. |
Taking into account the results of the examination, the patient may need additional advice from other specialized doctors. It is important to differentiate bleeding, since the pathological condition is accompanied by clinical symptoms, similar to various diseases (acute pancreatitis, gastritis, malignant tumors, diverticulosis, toxic shock).
Urgent care
First aid to a victim with hemorrhagic shock involves stopping bleeding and preventing dehydration.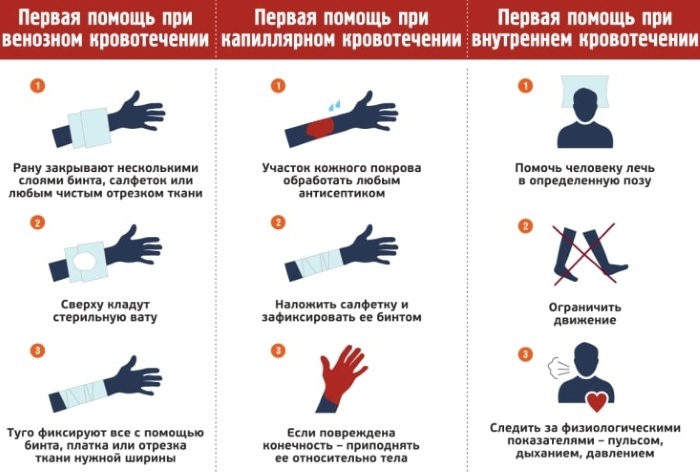
It is important to call a doctor and take the following actions before the arrival of a specialist:
- If there is a visible open wound, apply a bandage, tourniquet to squeeze the damaged blood vessel to stop the bleeding.
- The victim must lie down at all times. It is important to ensure complete immobility of the damaged area of the body.
- It is necessary to drink a person with clean water without gas and wrap him in a warm blanket, a blanket.
- Internal bleeding requires the immediate introduction of blood substitutes.
An ordinary person will not be able to establish the cause of hemorrhagic shock. In this situation, the qualified help of a specialist is required.
Hemorrhagic shock treatment
Hemorrhagic shock is treated in an inpatient department after providing the victim with first aid. The doctor prescribes medications to the patient that will help restore the stability of the hemostasis system and the blood level.
Patients are prescribed the following medications:
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Colloidal solutions | Protein, Albumin | Medicines help restore and maintain blood volume. The dosage in each case is calculated individually, taking into account the condition of the victim. The medicine is administered intravenously at a rate of 50-60 drops per minute. A single dosage depends on the condition of the person and is 100-300 ml. |
| Glucocorticoids | Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone | The recommended starting dosage for an adult is 0.5-9 mg per day. The indicated volume of the drug must be divided into 2-4 doses. |
| Hemostatic agents | Vikasol, Aminocaproic acid | The synthetic drug restores the process of blood clotting. The medicine is prescribed to patients by mouth at 15-30 mg per day. The volume of the drug should be divided into 2-3 doses. The course of treatment lasts 3-4 days, then you need to take a break for 4 days and continue therapy. |
| Crystalloids | Ringer's solution, Lactosol | The drugs correct the electrolyte composition of the plasma, eliminate dehydration. The medicine is administered intravenously through a dropper jet or at a rate of 60-80 drops per minute. The daily adult dosage is 5-20 mg / kg, it can be increased to 30-50 mg / kg. The course of therapy lasts 3-5 days. |
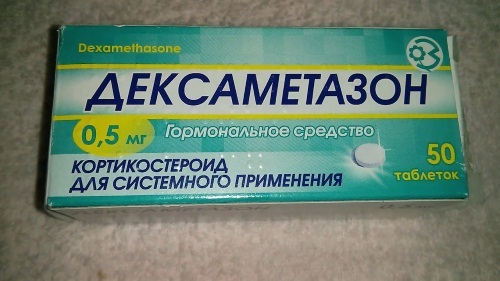
A life-threatening condition for the patient requires urgent surgical intervention (heavy bleeding in the upper gastrointestinal tract, ectopic pregnancy, placental abruption). Significant blood loss requires transfusion, if blood substitutes do not help to correct the situation.
Clinical guidelines
Stabilization of the victim's condition is not the final stage of treatment. The patient is shown an inpatient stay in order to prevent complications of hemorrhagic shock.
Clinical guidelines:
- If necessary, connect the patient to a ventilator.
- The patient needs to wear an oxygen mask.
- Severe pain syndrome requires the use of pain medications.
- To replenish blood loss and stabilize cell membranes, a special catheter is placed on the victim's peripheral veins.
Correctly selected therapy will allow not only to restore the volume of circulating blood, but also to remove toxins from the body, and normalize diuresis. The main objective of the treatment is also to improve blood circulation and cardiac output. The stabilization of the patient's condition is indicated by the restoration of blood pressure, cardiac activity, diuresis.
Consequences and complications
Hemorrhagic shock is a pathology that entails serious consequences. Their severity depends on numerous factors, including the amount of lost blood, the massiveness of the pathological process. The same applies to the physiological characteristics of the human body.
Among the serious complications of hemorrhagic shock, the following conditions should be distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| Renal failure | The disease is characterized by partial or complete disruption of the functioning of the organ. The kidneys are unable to form and pass urine. Material exchange is disrupted, which entails serious complications. |
| Brain atrophy | The pathological condition is observed in part. Brain cells quickly die, nerve and neural connections are destroyed. |
| Disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome | A severe complication of hemorrhagic shock, in which the balance of formed elements is disturbed, vascular permeability and blood circulation deteriorate. |
| Tissue hypoxia | Lungs, brain, heart suffer. The pathological condition is manifested by heart failure, mental disorders, impaired functioning of the respiratory system. |
Negative complications can occur even if an ambulance was provided to the victim in a timely manner. After hemorrhagic shock, the patient will need some time to recover.
The production of new blood takes 2-4 days. It is necessary to maintain the functioning of the heart, brain, lungs, liver. In women, after hemorrhagic shock, reproductive function worsens, for example, after removal of the organs of the reproductive system.
The lack of timely medical care and specially selected therapy for hemorrhagic shock will lead to serious consequences, including death. The risk of death remains even after the provision of emergency care to the patient. The prognosis also depends on the individual characteristics of the human body, how quickly it is able to recover on its own.
Video about hemorrhagic shock
About acute blood loss: