Increased body temperature always accompanies infections, but it can also manifest itself as the first symptom in cancer.
Record content:
- 1 Reasons for fluctuations in body temperature in cancer
-
2 Temperature indicators
- 2.1 High
- 2.2 Subfebrile
- 2.3 Decreased
- 3 Paraneoplastic fever
- 4 Therapeutic hyperthermia
- 5 Symptoms of hyperthermia, depending on the location of the neoplasm
- 6 Do I need to bring down the temperature?
- 7 How to behave at home when the temperature rises?
- 8 How do doctors deal with the problem?
- 9 Cancer development without fever
- 10 Video about oncology
Reasons for fluctuations in body temperature in cancer
The normal temperature of a healthy person ranges from + 36.0 ° C to + 37.3 ° C. During the day, the temperature can change, in the morning it is lower, and in the evening it can be slightly higher.
Also, temperature fluctuations in a healthy person can change depending on the hormonal background (in women), as well as under the influence of unfavorable factors. In people with an unstable nervous system, fever appears after intense experiences.
With the development of the infectious process, the body temperature also becomes elevated. But sometimes a person notices a rise in temperature, but there are no manifestations of infection.
The patient does not have a runny nose or cough, there is no sore throat, and the temperature rises. In this case, fever may be the first symptom of cancer. With increased attention you need to treat a persistent increase in body temperature, which continues for several weeks.
Temperature in cancer develops for the following reasons:
- The body's immune response to cancer cells. Tumor cells are recognized by the body as foreign, as they have an atypical structure.
- The tumor releases substances (cytokines) into the bloodstream, which contribute to the intoxication of the body and lead to intoxication syndrome. Fever is its manifestation.
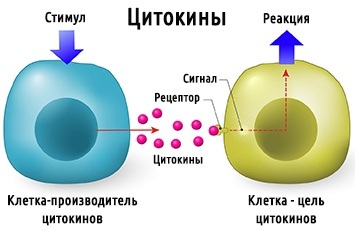
- With the development of neutropenia (a decrease in the number of cells responsible for the body's immune defense). This phenomenon occurs when an infection joins a weakened body.
The temperature in cancer patients can fluctuate. In the morning and during the day, the temperature can remain normal, and in the evening it can rise to febrile values.
In some cases, subfebrile temperature accompanies the patient throughout the entire illness. At the terminal stage of the oncological process, the temperature can remain elevated to febrile values, and also drop to low values (due to depletion of the body).
Temperature indicators
Temperature indicators can fluctuate depending on the type of tumor, its location and the extent of the process. Fever is subfebrile and febrile. These are the most common types of oncological fever. But in some cases it can be lowered. This is called hypothermia.
High
High temperature indicators range from + 38 ° С to + 42 ° С. Such indicators are called febrile.. The condition is accompanied by intoxication of the body, fever, headache. Often, high fever manifests leukemia.
Subfebrile
With this type of fever, an increase in body temperature from + 37 ° C to + 38 ° C is observed. It is accompanied by chills, poor health. May indicate a latent course of cancer. Permanent subfebrile condition can be observed for several weeks or months. But this condition is also observed during chemotherapy.
The patient may have a subfebrile temperature, both as a side effect of drugs, and during the development of an infectious process. Prolonged fever in the background or after treatment may indicate an infection.
Most often, the infection manifests itself in patients undergoing chemotherapy treatment (especially high-dose). The infectious process can be viral (most often herpes viruses), bacterial or fungal.
Decreased
It is the least common. The body temperature drops below 36 ° C and is accompanied by drowsiness, lethargy, the patient feels a breakdown. In case of cancer, such a temperature indicator may indicate sepsis (blood poisoning). After chemotherapy, the patient exhausts all of his body's defenses and therefore reacts in this way.
Paraneoplastic fever
Temperature in oncological diseases is part of the paraneoplastic syndrome, which is a clinical manifestation of the negative effects of a tumor on the body. Paraneoplastic fever is caused by the release of substances produced by the tumor. But also its decay at a late stage of the disease.
Paraneoplastic fever is most common in lung cancer, leukemia, lymphoma, breast and ovarian cancer, brain and stomach tumors. The causes of such a fever in these types of tumors are still not fully understood.
Clinical symptoms of paraneoplastic fever include fever and night sweats. The latter symptom can be so pronounced that the bed linen has to be changed several times per night.
Therapeutic hyperthermia
Therapeutic hyperthermia is a method of treating cancer. It is built on the principle of heating the site of tumor localization to + 45 ° C. It is carried out to improve the effect of the treatment. Sometimes this type of therapy is carried out as an independent type of treatment, when other methods have proved ineffective and the disease continues to progress.

In palliative care, therapeutic hyperthermia is used to improve the patient's well-being. Raising the temperature for therapeutic purposes has an analgesic effect and improves well-being.
Hyperthermia is carried out using special heating devices. The type of apparatus and the method of conducting depend on the age of the patient, the type of tumor and the degree of prevalence of the pathological process.
A local increase in temperature in the area of tumor localization has a destructive effect on pathological cells, but healthy tissues remain intact.
Cases of the use of hyperthermia in patients with sarcoma with a widespread metastatic process in the lungs are described. Within a few sessions, metastatic tumors stopped progressing in their growth. The method of treatment for hyperthermia can be local (the area of the tumor is heated) and general to the whole body.
Like other methods of treatment, hyperthermia has some contraindications, to these include:
- Exhaustion of the body.
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases.
- The infectious process is in the acute stage.
- Breakdown of the tumor.
- Growth of the tumor into the blood vessels due to the threat of bleeding.
Side effects of therapy include burns, bleeding, inflammatory reactions, edema and other local manifestations. They are temporary and go away within a few days. Other, more serious complications are rare.
The effectiveness of the use of therapeutic hyperthermia has not yet been fully proven. In some cases, it is possible to stop the growth and spread of metastases for a certain time. But this type of oncology treatment does not give a lasting effect.
This method is not used in Russia. In the United States, the method is used to treat certain groups of patients. In South Korea and China, therapeutic hyperthermia is used mainly in incurable patients (when further treatment is impossible due to the complete depletion of the body's resources).
Symptoms of hyperthermia, depending on the location of the neoplasm
Temperature can be combined with other clinical manifestations in various cancers. Depending on the location of the tumor, fever can have its own characteristics.
Generally, pronounced fever is observed in patients with hematological oncological pathologies (lymphomas, leukemia), lung cancer, melanoma, tumors of the reproductive system and breast cancer. Cancer of the brain and nervous system is also manifested by an increase in temperature, especially if a tumor formation develops in the center of thermoregulation.
The manifestation of leukemia occurs with an increase in body temperature above 38 ° C. Fever is combined with sore throat, enlarged tonsils, difficulty swallowing. The temperature rises sharply, it does not respond well to the action of antipyretic drugs. Before starting treatment, it may remain within the febrile range.
Together with fever in patients, regional lymph nodes, in this case the submandibular nodes, may increase in size. But also the disease can manifest itself without a significant increase in them.
Since the enlargement of the lymph nodes is more suitable for the clinical symptoms of lymphogranulomatosis. Leukemia is very similar in its symptoms with the manifestation of acute respiratory viral infections, tonsillitis and infectious mononucleosis. And also the patient is worried about pain in the tubular bones and muscles.
You can diagnose leukemia using a clinical blood test. In the case of acute leukemia, there will be an increase in blast cells.
With lymphomas, the body temperature often remains in subfebrile values, but as the disease progresses, it can rise above + 38 ° C. An increase in temperature is more often observed in the evening. Along with body temperature, the lymph nodes increase, mainly the cervical, supraclavicular and mediastinal lymph nodes.
Patients complain of shortness of breath, skin itching, night sweats. Profuse sweating at night, along with a rise in temperature, is one of the clearest signs of lymphomas.
Lung cancer is another malignant neoplasm that always occurs with an increase in temperature. Most often, in the early stages of the disease, the temperature remains within 37 ° C. Later, the fever becomes more pronounced. In addition to fever, patients complain of cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, and weight loss.
Brain tumors are accompanied by subfebrile fever, chills. Patients also complain of nausea and vomiting, which does not bring relief. Other classic manifestations of oncology (weight loss, weakness, fatigue).
Malignant melanoma (skin cancer) rarely presents with a fever early in the disease. First of all, patients notice the growth of the mole, its asymmetry, uneven color, as well as bleeding. Fever is typical for the last stage of the disease, when active metastasis is observed.

Tumors of the reproductive system occur with an increase in temperature to subfebrile levels already in the first stages of the disease. And often such tumors can be confused with inflammation, as there is fever, pain and discharge from the genitals. In addition, there is an increase in lymph nodes in the groin area.
In the case of cervical cancer, the temperature remains unnoticed by the patient for a long time. But with the spread of tumor cells outside the focus, the temperature rises.
For tumors of the gastrointestinal tract (cancer of the stomach, intestines), an increase in temperature up to subfebrile values, with the addition of pain syndrome, defecation disorder, nausea and vomiting.
The temperature in cancer of other localization most often remains subfebrile and does not cause serious concern to the patient.
The incidence of high temperature in some cancers:
| Leukemia | 95% |
| Lung cancer | 90% |
| Lymphoma | 80% |
| Ovarian cancer | 40% |
| Mammary cancer | 35% |
Do I need to bring down the temperature?
During the treatment of cancer, the temperature should not normally rise. If the patient notices symptoms of fever, then it means that there is a development of adverse reactions to treatment or an infectious process.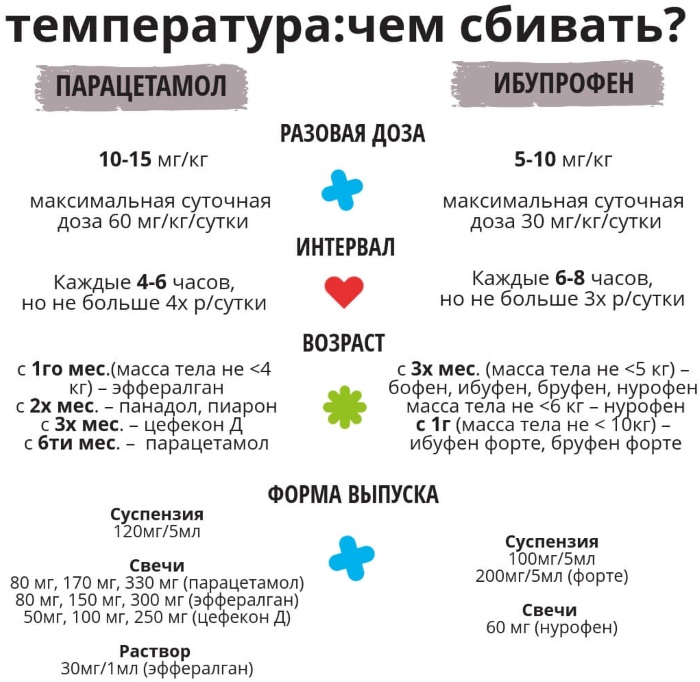
With the development of side effects on drugs, there will be no significant disturbance of well-being, and with the addition of an infection, clinical manifestations characteristic of a viral or bacterial infections.
Subfebrile temperature up to + 38 ° C can not be brought down if it does not cause significant discomfort to a person. But if other unpleasant symptoms are observed along with the temperature, then this temperature can be reduced.
The high temperature in cancer needs to be lowered. With cancer, the compensatory functions responsible for heat exchange are reduced, all the more, there will be no benefit from an increase in temperature in this case.
Therefore, it is important not to allow the temperature to rise to high values. Temperatures above + 38 ° C must be reduced. And if the patient has a history of convulsions with an increase in temperature, then in this case it is necessary to reduce it as soon as possible.
Temperature in cancer can be dangerous. Complications of high temperature can be disorders of the cardiovascular, nervous system, which can be very dangerous for a patient with cancer.
How to behave at home when the temperature rises?
When the temperature rises, it is necessary to provide an influx of fresh air in the apartment, having well ventilated the room where the patient is.
It is best to wear light clothing to prevent overheating. You can also use cooling lotions. To do this, you need to prepare warm water, moisten a towel and squeeze it well on the forehead, knee folds of the lower extremities and on the elbow folds of the upper extremities.
When the temperature rises, the patient should drink as much warm boiled water, tea, fruit drinks and fruit drinks as possible. Subject to a full-fledged drinking regime, the temperature will begin to gradually decrease.
If these measures do not help, and the temperature continues to rise, you can resort to antipyretic drugs. These include paracetamol and ibuprofen. It must be remembered that in acute leukemia, the use of aspirin is prohibited. This can lead to the development of internal bleeding.
If the fever lasts more than a day, a short-term effect is observed from medications, then you need to notify the attending physician about this. If it is impossible to contact him, then you need to call an ambulance.
How do doctors deal with the problem?
In a hospital setting, a lytic mixture is used for fever. It contains antihistamine, antispasmodic and analgesic drugs. In patients with acute leukemia, the administration of drugs is only intravenous. Since blood counts, and especially platelets, are reduced and the administration of drugs intramuscularly can lead to the development of bleeding.
After the acute attack is stopped, the reason that caused the temperature rise is considered. But usually with fever, the risk of infection is considered, in this case, the administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics is prescribed.
Since during the treatment of oncology in humans, immunity is significantly reduced, dosage of antibacterial drugs and, in addition to one, a combination of several drugs is administered funds.
The dosage of chemotherapy is adjusted. With the addition of bacterial complications, it can completely stop until the body is completely recovered. A contraindication for chemotherapy or radiation treatment is always a fever associated with the addition of an infection.
If there is a strong intoxication of the body, then detoxification therapy is carried out. To do this, a glucose solution is injected with the addition of ascorbic acid intravenously and drip. It may also require a transfusion of plasma or other drugs.
In addition, daily thermometry is carried out 2 times a day. Such control is necessary to prevent infectious complications.
Cancer development without fever
The oncological process is always associated with an increase in temperature. But sometimes a person just may not notice it. The thermometer can show + 37 ° C and not affect the patient's well-being. At the beginning of adequate therapy, the temperature should not normally rise.
If a person has a temperature without symptoms of inflammation, there are no signs of an infectious process - you need to pay close attention to this, since such a symptom can be observed with oncological diseases.
Video about oncology
Temperature is a harbinger of cancer: