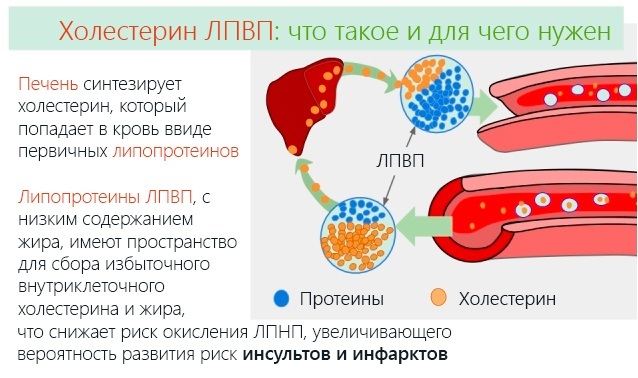
Lymphocytes are an important component of human immunity; they represent a separate group of leukocytes produced by the bone marrow and transported to the blood plasma. The increased content of lymphocytes indicates the activation of the body's natural defense reaction to the negative effects of pathogenic microorganisms.
Lymphocytosis is not a disease, but rather a condition in which there is a high level of lymphocytes (white blood cells). A similar phenomenon often occurs in children, and the reason for this is the presence of any inflammatory processes in the body. That is, the role of lymphocytes is to recognize foreign agents and form a protective response on them.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Reasons for the appearance
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prophylaxis
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
- 8.2 Traditional methods
- 8.3 Other methods
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about lymphocytosis
Views
Children are most often exposed to negative external influences (infections, bacteria, viruses). An increase or decrease in the level of important blood components, in particular leukocytes, helps to resist the development of diseases. They develop a persistent immune response to damaging microorganisms, which allows you to quickly and effectively cope with various infections.
The condition in which a high level of lymphocytes is diagnosed (lymphocytosis) is divided into two types:
- absolute;
- relative.
Types of lymphocytosis and their characteristics.
| Type of lymphocytosis | Description | What is he talking about |
| Absolute | There is an absolute increase in lymphocytes per liter of blood. Speaks about the presence of an infectious lesion in the body. The dynamics of the level shows the growth of the component throughout the entire period of the course of the disease. | The condition indicates the presence of:
|
| Relative | An increase in lymphocytes as a percentage of other blood components. This happens often, indicates a recent infectious disease, that the patient is in the recovery stage, or the beginning of an infectious lesion. | The condition speaks of the beginning or end of such pathologies:
|

Often, the relative form of lymphocytosis does not require treatment; this condition is considered the norm for the body and immunity. The absolute form, as a rule, indicates an existing pathological process that requires immediate differentiation and treatment.
Lymphocytosis in children (the causes are determined by further diagnosis) of the relative type is considered the norm for children under the age of 2 years. In adolescents, the percentage of an increase in lymphocytes in relation to other blood components cannot exceed 37%.
Stages and degrees
In medical practice, there is another classification of lymphocytosis, reflecting the severity of the problem:
- reactive - the reaction of the immune system to an infectious disease;
-
malignant
 - indicates the presence of a lymphoproliferative disease, which includes lymphoma and lymphoblastic leukemia.
- indicates the presence of a lymphoproliferative disease, which includes lymphoma and lymphoblastic leukemia.
From the above, we can conclude that an increase in the level of lymphocytes may indicate that the body is able to fight against infectious infections. But in practice, this is often completely different. A change in the concentration of a substance indicates the presence of any problem, which the doctor must find out after a full diagnosis.
The malignant degree is dangerous for the life of children, therefore, early diagnosis makes it possible to stop the development of complex disease-causing processes in a timely manner.
Symptoms
Lymphocytosis in children has clinical manifestations depending on the cause that provoked the growth of white cells. Their number can only be determined by conducting a blood test.
In very young patients, this condition is accompanied by impaired respiratory function:
- shortness of breath with bouts of shortness of breath;
- lack of oxygen supply, accompanied by heavy irregular breathing.
The reactive degree of leukocytosis has the following signs:
- inflammation and enlargement of the lymph nodes;
- an increase in the size of the spleen and liver.
Similar manifestations can occur with neoplasms of any nature (malignant or benign).
Lymphocytosis caused by infection mainly manifests itself as follows:
- catarrhal affection of the nasopharynx and pharynx;
- pain in the abdominal region;
- hyperthermia.
There is no definite clinical picture in cases of lymphocytosis, however, the symptoms of the condition completely depend on the cause.
With an infectious lesion in children, it appears:
- general weakness;
- lethargy;
- rashes;
- high body temperature, up to fever;
- enlargement and redness of the tonsils.
With infectious lymphocytosis, it is important to stop the further spread of the infection in a timely manner, since this form can very quickly lead to the most irreparable consequences.
Lymphocytosis in children, the causes of which are associated with neutropenia, indicates serious inflammation in the body. However, not always a combination of two pathological conditions can lead to serious consequences. Often, as the child grows up, this condition returns to normal.
Reasons for the appearance
Often, excessive physical activity or frequent stress can lead to an increase in lymphocytes.
An excess of lymphocyte counts can mean serious adult illnesses, such as:
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- sarcoma;
- cytomegalovirus infection;
- tuberculosis;
- measles, chickenpox, rubella;
- toxoplasmosis;
- whooping cough;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- syphilis;
- disorder of the peripheral and central NS.
There are many more reasons that become a provoking factor for lymphocytosis:
- avitaminosis;
- blood transfusion;
- prem of some specific dosage forms;
- HIV;
- prolonged exposure to the open sun;
- poor quality food;
- respiratory infections;
- reaction to vaccination.

The peculiarity of the blood formula is that after recovery, the analysis may show an increased number of lymphocytes for some time. This is diagnosed as relative lymphocytosis. You should not worry in this case, as this is considered the norm. Gradually, in a healthy body, the level of the substance will decrease.
Lymphocytosis in children with more serious causes can be life-threatening. So, if an increased concentration of white cells in the blood is diagnosed, it is important to immediately exclude the likelihood of the development of malignant mechanisms in the bone marrow and hematopoietic system.
The most common cancer causes are:
- acute and chronic lymphoblastic leukemia;
- lymphoma;
- lymphogranulomatosis;
- lymphosarcoma;
- myeloma.
Diagnostics
Lymphocytosis in children (the reasons are found out only after additional diagnostics) is an excess of the norm of white cells in the blood plasma. To detect a change in the concentration of lymphocytes, it is enough just to make a general and biochemical blood test.
But in order to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the cause that provoked such a leap of substance, it is necessary to make an extensive diagnostics, the purpose of which is:
- examine the bone marrow;
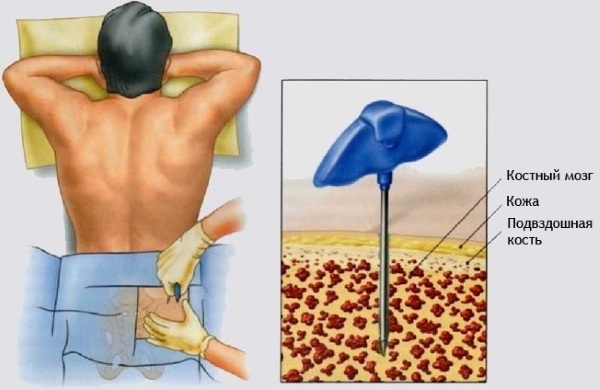
- investigate the immune response;
- find out the type of infectious agent.
For this, patients undergo:
- Ultrasound;
- chest x-ray;
- CT;
- MRI.
These examination methods make it possible to reveal the presence of an inflammatory process, changes in structures internal organs, diffuse and focal lesions in the body, which provoke an increase in the level lymphocytes.
To exclude the likelihood of developing malignant processes, the patient is assigned immunophenotyping.
In order for the blood test to show the correct result, it is necessary to adhere to special recommendations before submitting the biomaterial:
- do not take food 12 hours before the analysis (the exception is infants, their blood is taken 2 hours after feeding);
- do not drink water 2 hours before the procedure;
- if the child is taking any medications, it is necessary to inform the attending physician, perhaps some time before the analysis, the medication will be canceled.
For the accuracy of the diagnosis, patients are assigned other laboratory tests:
- blood chemistry;
- urine analysis;
- sputum cytology;
- coagulogram;
- analysis for markers of various types of hepatitis;
- blood test for HIV and RW;
- tests for tuberculosis;
- bacterial culture of biomaterials of the nasal cavity and pharynx;
- tumor markers.
Lymphocyte count for children of different age groups: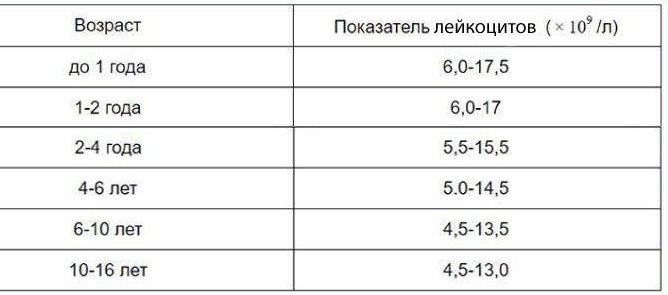
| Child's age | 5 days | 10 days | 1 month | 12 months | 5 years | 10 years | 15 years |
| Lymphocyte content in relation to other blood components,% | 30-50 | 40-60 | 45-60 | 45-60 | 35-55 | 30-45 | 30-45 |
When to see a doctor
Initially, the child is examined by a pediatrician. As a rule, parents consult a doctor if there are any alarming signs (general weakness, lethargy, high fever, reddening of the mucous membranes, enlarged lymph nodes, etc.). After taking the history and assessing the patient's health, the doctor will order a blood test.
The presence of a viral disease is indicated by characteristic symptoms and an increase in the level of lymphocytes and ESR. If, along with the above parameters, there is an increase in monocytes, this will be evidence that a chronic viral process is present in the body.
With prolonged forms of infection, patients are referred for analysis, which determines the number of activated β-cells. If this indicator is higher than normal, this may indicate an autoimmune disorder.
The pronounced degree of leukocytosis gives rise to further examination of the child in order to find out his immune response and the presence of tumor formations. Separately, a bone marrow study may be prescribed.
After a preliminary diagnosis has been made, the child will need to consult other highly specialized specialists (surgeon, infectious disease specialist, hematologist, oncologist, nephrologist, ENT, rheumatologist).
Prophylaxis
An increase in lymphocyte count is usually associated with a lack of immune defense in the child. Therefore, prevention is aimed at eliminating all possible provoking factors that stimulate an increase in the level of lymphocytes.
In order to protect the child from lymphocytosis, it is necessary to exclude such moments from his life:
- regular stress;
- poor quality food;
- high physical activity;
- hypothermia;
- lack of walks in the fresh air;
- prolonged exposure to the open sun.
If the child still has the first alarming symptoms, you should consult a doctor in the early stages and undergo adequate treatment aimed at eliminating the cause.
Treatment methods
There is no definite tactic for the treatment of lymphocytosis, since this condition is not considered a disease as such. This is just a condition that is triggered by a number of reasons. Accordingly, therapy is determined depending on the results of additional diagnostics. In each case, an individual treatment approach is developed.
The purpose of the treatment measures:
- identification of the cause and its adequate treatment;
- relief of symptoms;
- restoration of the body in complex pathologies;
- prevention of the development of severe and life-threatening conditions.
The need for hospitalization arises when:
- severe forms of primary pathologies;
- the need to isolate the child from others;
- accession of a secondary disease;
- the risk of developing serious complications;
- a history of chronic processes that aggravate the patient's health;
- the inability to carry out treatment at home;
- ineffectiveness of outpatient therapy for an extended period.
Medications
There is no specific tactics for drug treatment of lymphocytosis, since this condition is a consequence of other diseases. Having found out the reason, the doctor prescribes treatment, taking into account the characteristics of the organism, the presence of acute symptoms, individual tolerance of drugs and other things.
Treatment tactics for various diseases:
| Disease group | Conservative therapy |
| Oncopathology | Radiation therapy, chemotherapy and cytostatic drugs are prescribed. |
| Viral lesion | The use of M2 channel blockers, interferon, neuroaminidase inhibitors. |
| Bacterial infections | Treatment is carried out with antibacterial agents. |
| Fungal infections | Antifungal medicines are used. |
| Inflammatory processes | Hormonal agents, NSAIDs, combined pharmacological preparations are prescribed. |
| Hyperthermia over 38 degrees | Medicines of the anilide group are used. |
If the etiology of lymphocytosis after the first tests is not established, the patient is hospitalized in order to isolate from others and find out the exact cause of the condition.
Traditional methods
Treatment of lymphocytosis with traditional medicine is possible only after consultation and approval of the attending physician. Often, medicinal herbs quite effectively cope with emerging unpleasant symptoms, relieve inflammation, and improve the general well-being and activity of the child.
However, it is worth using such treatment only in combination with drugs. Independent use of folk remedies is allowed only as a prophylaxis.
Traditional medicines that strengthen the immune system, suppress inflammation, relieve symptoms, improve well-being, thereby reducing the level of lymphocytes in the blood.
| Means | Preparation | Application |
| Rowan and rosehip | Take 25 wild rose and rowan berries, pour 1 glass of boiling water. Infuse for 15-20 minutes. | Take as vitamin tea 1 time per day. |
| Black currant and rose hips | Take 50 g of berries of medicinal plants, pour 400 ml of boiling water over them. Insist 20 minutes. | Take orally during the day, 100 ml every 4 hours. |
| Lungwort medicinal | 2 tbsp. l. dry raw materials pour 0.5 liters of boiling water and place in a thermos. Leave to brew for 40 minutes. Strain. | Take orally 120 ml of infusion 3 times a day before meals. |
| Herbal collection | Mix:
Select from the resulting mixture 3 tbsp. l. raw materials, place it in a thermos (1 l), pour boiling water. Leave to infuse for about 2 hours. |
In the morning on an empty stomach, drink 1 glass of the medicine, then during the day drink 0.5 glasses every 3 hours. |
Before using any medicine based on medicinal plants, you should consult your doctor.
Other methods
Lymphocytosis, as a rule, occurs against the background of insufficient immunity. Often the cause is vitamin B12 deficiency. In this case, the problem is solved by injecting a solution of vitamin B12 intramuscularly. To compensate for the deficiency of this substance, it is recommended to include in the diet such foods as beef liver, fish, chicken yolks, and dairy products.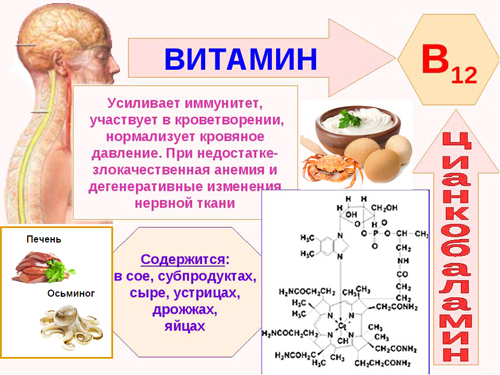
If the cause of the condition is myeloma, leukemia, or other oncological processes, the child is prescribed a course of chemotherapy or radiation therapy. In difficult situations, when such a tactic does not give a positive result, the need for a bone marrow transplant is determined.
Proper nutrition is the key to excellent health and strong immunity. Therefore, when detecting lymphocytosis, doctors recommend adjusting the diet.
The following foods will help reduce the level of lymphocytes:
- oat groats;
- fresh red or green vegetables;
- walnuts;
- legumes;
- dates;
- bananas;
- apricots;
- fermented milk products.
The specified list of products not only restores the norm of the substance, but also helps to cleanse the intestines and blood from toxic and other negatively affecting substances.
Fried, too fatty, salty, spicy and smoked foods should be excluded from the diet.
Possible complications
The insidiousness of lymphocytosis is that the condition is a consequence of the pathology in the body. Therefore, in addition to the indicator of the level of lymphocytes, it is necessary to pay attention to other test results and the manifested symptoms. At the slightest suspicion of the development of any disease, parents need to seek medical help.
Timely identification of the problem can prevent the further development of complex disease-causing processes.
Complications with untimely treatment can be as follows:
- transformation of the disease into a chronic form;
- development of malignant processes;
- damage to the body by infectious and bacterial infections.
Lymphocytosis in children is always provoked by leukemia
The prognosis of recovery depends entirely on the disease that provoked such a condition and the timeliness of the treatment begun.
The younger generation is quite vulnerable to any pathological impact, especially a serious danger lies in wait for young children under 3 years of age. Lymphocytosis is a condition caused by the active work of the immune system in children.
When a pathological cause appears, bone marrow cells begin to actively produce lymphocytes, which recognize foreign agents and form a stable immune response against them.
With a relative increase in the substance, parents should not worry, since over time, the level of lymphocytes will recover, and the child will become completely healthy. But with absolute lymphocytosis, you need to undergo extensive diagnostics and accurately determine the possible cause.
Video about lymphocytosis
Komarovsky about the increase in leukocytes: