Dementia in adults is a pathology that occurs in old age and is characterized by disorders of the brain. Symptoms of the disease can vary depending on the type of dementia. Organic damage is often triggered by alcoholism, drug abuse, or injury.
Record content:
- 1 Dementia causes
- 2 Classification of dementia
- 3 Dementia severity
-
4 Early symptoms of dementia
- 4.1 Difficulty finding the right word
- 4.2 Anxiety, suspiciousness
- 4.3 Persistent mood swings, depression
- 4.4 Personality changes
- 4.5 Increased forgetfulness
- 4.6 Disorders of orientation in time and space
- 4.7 Loss of interest in hobbies
- 4.8 Loss of ability to follow the logic of a conversation or verbosity
- 4.9 The tendency to constantly shift, hide, accumulate objects
- 4.10 Aimlessness
-
5 The main symptoms of dementia
- 5.1 Alzheimer's type dementia
- 5.2 Senile Lewy Body Dementia
- 5.3 Symptoms of vascular dementia
- 5.4 Alcoholic dementia
- 5.5 Epileptic dementia
- 5.6 Atrophic dementia
- 5.7 Mixed dementia
- 6 Diagnosing dementia
- 7 Dementia treatment
-
8 Tips for developing early symptoms of dementia
- 8.1 Lots of traffic
- 8.2 Communication with people
- 8.3 Brain training
- 8.4 To give up smoking
- 8.5 Correct and long sleep
- 8.6 The diet
- 8.7 Prevention of vitamin deficiency
- 9 Dementia Signs Videos
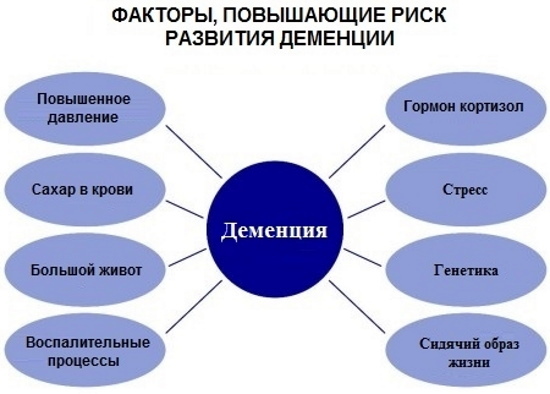
Dementia causes
Dementia in adults, symptoms of which appear gradually, occurs for a number of reasons. The main one is the development of pathologies characterized by the death of brain cells.
These include:
- neurodegenerative diseases;
- pathology of the central nervous system;
- neuronal atrophy;
- multiple sclerosis.
 Senile dementia can occur as a complication after the following pathologies:
Senile dementia can occur as a complication after the following pathologies:
- inflammation of the spinal cord and brain;
- traumatic brain injury (open and closed type);
- benign and malignant tumors;
- poisoning with medicines;
- alcohol dependence;
- high blood pressure;
- acute circulatory disorders of the brain;
- vascular atherosclerosis.
Risk factors contributing to the development of dementia include:
- lack of intellectual activity for a long time;
- obesity;
- diabetes;
- genetic predisposition (in the presence of relatives suffering from dementia).
According to statistics, dementia occurs more often in women than in men.
Classification of dementia
Dementia in adults (symptoms of pathology are presented later in the article) are classified according to the following criteria:
- localization of the lesion;
- the reason for the development.
 At the place of localization, the following types of dementia are distinguished:
At the place of localization, the following types of dementia are distinguished:
- Multifocal. Almost the entire brain is affected. The patient has a violation of mental processes responsible for the perception of information. Pathology progresses rapidly.
- Cortical-subcortical. Mixed dementia develops as a result of destruction of the subcortical structures of the brain and its cortex.
- Cortical. Dementia of this type can be attributed to Alzheimer's or Pick's disease. Characteristic symptoms include behavioral disturbances, memory lapses, and confusion.
Dementia can result from:
- Multiple sclerosis. The cause of development is the destruction of the myelin sheaths. Patients complain of memory impairment and inability to concentrate on anything.
- Epilepsy. Pathology cannot be called the root cause of dementia. The disease develops as a result of injuries sustained during a fall, after oxygen starvation and prolonged intake of phenobarbital. The patient's emotional sphere is affected, the will is completely suppressed. The manifestation of unmotivated aggression is possible.
- Trauma. Dementia with single trauma is rare. Much depends on their multiplicity.
- Alcoholism. The systematic use of alcoholic beverages in large doses leads to disruptions in the work of the parts of the brain responsible for the coordination of thinking, movement and memory. In the later stages of alcoholic insanity, the patient degrades.
- Pick or Alzheimer's disease. For pathologies, memory impairment is characteristic: brain cells atrophy. With rapid progression, the patient is completely maladjusted and disoriented.
- Vascular pathologies. A number of diseases, accompanied by impaired blood circulation in the brain, can provoke the development of vascular dementia. The characteristic symptoms include deterioration in thinking and memory, disturbances in the emotional background and various mental disorders.
 The exact causes of idiopathic dementia have not been identified. The characteristic symptom complex resembles signs of dementia of the Alzheimer's type: cognitive functions are lost, the patient complains of impaired movement and memory.
The exact causes of idiopathic dementia have not been identified. The characteristic symptom complex resembles signs of dementia of the Alzheimer's type: cognitive functions are lost, the patient complains of impaired movement and memory.
Dementia severity
Dementia in adults, the symptoms of which vary depending on the cause of development, can be classified according to the severity. Pathological manifestations appear gradually.
According to the totality of cognitive impairments, the following degrees are distinguished:
- easy;
- medium;
- heavy.
For a mild degree, the following manifestations are characteristic:
- lack of interest in your favorite hobby;
- unwillingness to communicate with others;
- the development of depression, anxiety and tearfulness;
- the emergence of a critical attitude towards oneself;
- violation of the intellectual sphere and memory;
- partial preservation of the ability to self-service;
- limitation or partial disability.
The patient's maladjustment is expressed in the refusal to take part in work, communication with loved ones. A person withdraws into himself, tries to spend more time alone and not visit crowded places. The feeling of inferiority is provoked by a slowdown in the pace of thinking, patients complain of poor memory.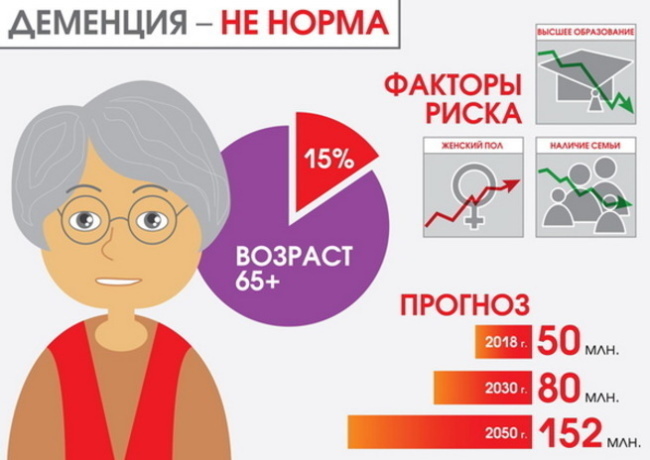
Signs of moderate dementia include:
- pickiness;
- waywardness;
- vindictiveness;
- malice;
- aggressiveness.
The patient's depressive and anxious state is aggravated. A manifestation of psychosis, accompanied by delusional ideas, is possible. The patient cannot think in detail, he is fixated on the same thought, situation for a long time. The patient ceases to navigate in time, complains of a decrease in speech, auditory and visual memory.
The patient is unable to use household appliances, he cannot open and close the door lock. A person forgets how to use a mobile phone, but retains self-service skills.
In severe dementia, there is complete emotional impoverishment. The patient's willpower is broken, he is unable to navigate in space. At this time, a person ceases to be aware of himself as a person, cognitive activity is reduced. Fragmentary facts and events are kept in memory.
Thinking is viscous, the vocabulary is scarce, the patient loses the ability to pronounce related sentences. Self-care skills are lost, the person needs foster care.
Early symptoms of dementia
Dementia in adults (symptoms will be described in more detail later in the article) is not treated.

With the help of drug therapy, it is possible to reduce the severity of characteristic signs and stabilize the patient's condition. The patient has difficulties in communication, he begins to forget important dates.
Difficulty finding the right word
Difficulty finding suitable words is considered the earliest symptom of senile dementia. A person cannot clearly express his thought; pauses slip through the dialogue. The patient needs time to find the right word and continue the conversation.
Anxiety, suspiciousness
Suspiciousness, anxiety are considered a sign of dementia, if a previously cheerful and open person began to be suspicious of close friends and relatives. The patient shows confidence, he is pursued by obsessions and thoughts. It seems to a person that those around him are prejudiced against him.
Persistent mood swings, depression
The process of destruction of brain cells is accompanied by the development of disorders from the endocrine system. In the human body, the production of hormones responsible for regulating mood is inhibited. In this case, the risk of depression is quite high.
Personality changes
Personality changes indicate the appearance of new traits in the character. A previously sociable, sociable person becomes more shy, and a cheerful person turns into a grumpy and dissatisfied person. Personality defects are accompanied by a loss of values, attitudes and specific character traits.
Increased forgetfulness
Forgetfulness is another sign of dementia. An elderly person gradually begins to forget not only important dates, but also events that have happened quite recently.
He does not remember those conversations, he is not able to remember what he ate for lunch or dinner. The patient may lose personal belongings by forgetting them on the street or in public places.
Disorders of orientation in time and space
An elderly person with dementia can no longer orientate in space and time. The patient cannot remember the date of the celebration or the day of the week. Disorientation is often accompanied by impaired consciousness: the patient ceases to recognize colleagues, friends and relatives.
Loss of interest in hobbies
Loss of interest in a hobby that used to be enjoyable and enjoyable indicates that an older person is developing dementia. The symptom is stable, over time it becomes a personality trait: the patient ceases to experience positive emotions from life.
Loss of ability to follow the logic of a conversation or verbosity
An elderly person with dementia loses the ability to focus on the other person. He is constantly distracted by what is happening around him, the conversation associated with this or that event suddenly spills over into another channel. A person cannot clearly formulate a thought and strikes into memories.
The tendency to constantly shift, hide, accumulate objects
With dementia, memory and personality degrade. An elderly person becomes suspicious, he has a need for gathering. The patient begins to accumulate pieces of furniture and clothing, to hide personal belongings (including money) from relatives. Where the cache is located, a person often forgets.
Aimlessness
With dementia, a person loses the ability to plan and focus on one object. He can leave the house for the store and return empty-handed.
The patient walks aimlessly around the house or street, asks the same questions, forgetting that he has already received answers to them earlier.
The main symptoms of dementia
Dementia in adults is an incurable disease that progresses against the background of trauma, alcoholism or vascular pathologies. The main symptoms can vary depending on the type of illness.
Alzheimer's type dementia
The disease is characterized by damage to brain cells. Most often it occurs in old age. Patients experience a partial loss of intelligence, he ceases to remember important events.
Cognitive functions are impaired, gradual degradation occurs. A person loses the ability to self-care as Alzheimer's dementia progresses.

The main symptoms of pathology are considered:
- partial loss of vision;
- violation of spatial orientation;
- loss of the ability to perform everyday tasks;
- aggressive behavior;
- absent-mindedness;
- forgetfulness;
- mood swings;
- memory impairment;
- detachment or depression.
A person feels uncomfortable even in his usual environment. As the disease progresses, the patient's condition will worsen.
Senile Lewy Body Dementia
Lewy body dementia is characterized by autonomic, motor, mental, and cognitive impairments. The disease is accompanied by neurodynamic disorders, which are manifested in the form of an inability to concentrate on something.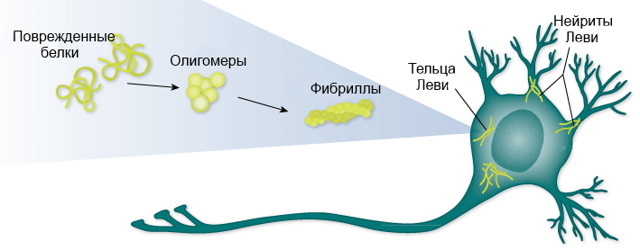
The signs of DTL include:
- delirium;
- rave;
- dissociative disorder;
- psychomotor overexcitation;
- apathy;
- visual agnosia;
- amnesia;
- bradycardia;
- depression.
In the early stages, there is an increase in tone and a hypothetical syndrome. The development of autonomic dysfunction is possible.
Symptoms of vascular dementia
Dementia of the vascular type does not always lead to disorders of the psychoemotional state.
The manifestation of neurological symptoms is possible, which include:
- bulbar disorders;
- swallowing disorders;
- epileptic seizures;
- fatigue;
- increased anxiety;
- viscosity of thinking;
- verbosity;
- emotional lability.
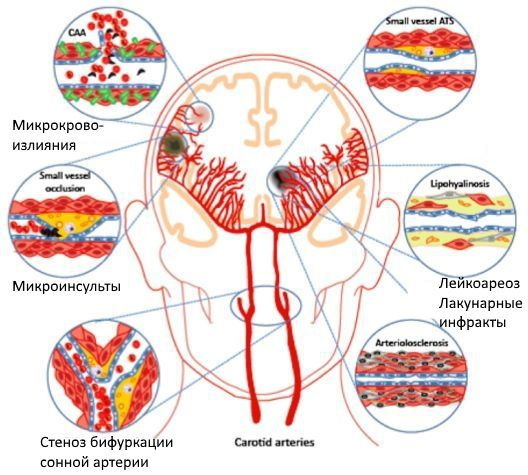 The patient becomes more irritable and deliberately provokes conflict over little things. Emotional generalized rigidity is observed in the final stage of vascular dementia.
The patient becomes more irritable and deliberately provokes conflict over little things. Emotional generalized rigidity is observed in the final stage of vascular dementia.
Alcoholic dementia
Alcohol dementia occurs with prolonged alcohol abuse. Ethyl alcohol damages brain cells by penetrating the blood-brain barrier. Alcohol dementia most often occurs in people who have been addicted to alcohol for 10 years or more.
Typical symptoms include:
- constriction of the pupils;
- incoherence of words;
- sleep disorders;
- uncontrollable craving for gathering;
- lack of self-service skills;
- constant feeling of hunger;
- inability to concentrate on something;
- spatial and temporal disorientation;
- depression;
- mood swings (from aggression to infantilism);
- amnesia.
A person with alcoholic dementia has periodic enlightenments.
For a short period, the patient tries to return to a normal lifestyle: he recognizes loved ones, speech becomes coherent, memory is restored. Periodic enlightenment occurs only in the early stages of alcohol addiction.
Epileptic dementia
This type of dementia occurs in people with epilepsy. Symptoms can vary depending on the stage of the course. The main cause of development is considered to be cerebral hypoxia that occurs during and after a seizure.
Symptoms of epileptic dementia include:
- unproductive, viscous speech;
- Difficulty thinking
- pathologically detailed speech;
- inability to express your thoughts;
- mood swings;
- anxiety;
- memory impairment;
- inhibited speech reactions.
In the early stages of epileptic dementia, a person is able to take care of himself. The patient requires moderate to severe care.
Atrophic dementia
Atrophic dementia is a classic type with the following symptoms:
- speech disorders;
- partial amnesia;
- verbosity;
- isolation;
- anxiety;
- physical degradation.
Personality breakdown is characteristic of moderate to severe dementia.
Mixed dementia
Symptoms of mixed dementia include:
- memory impairment;
- cognitive impairment;
- inability to concentrate attention;
- decrease in the productivity of intellectual work;
- spatial disorientation.
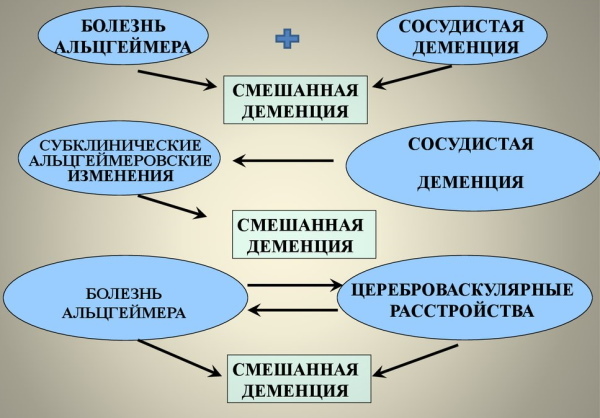 Patients with mixed dementia have a history of atherosclerosis or stroke.
Patients with mixed dementia have a history of atherosclerosis or stroke.
Diagnosing dementia
If you experience the characteristic symptoms of dementia, you should see a neurologist. During a personal visit, a specialist will study the medical history and conduct an examination. A mental test is a mandatory procedure. The doctor will ask the patient several questions to find out how well a person is oriented in time, in space, what he remembers and how he thinks.
In order to exclude diseases associated with dementia, urine and blood tests may be prescribed. Psychiatrists and gerontologists also work with the elderly. By virtue of experience, they can assess the patient's condition and prescribe supportive drug therapy. For a detailed memory check, the patient is prescribed an MRI or CT scan. The procedure detects signs of Alzheimer's.
Dementia treatment
Senile dementia is not treatable. Medication can correct the patient's behavior and temporarily improve his condition. Medicines are prescribed depending on the type of course and the severity of the disease. To reduce the manifestation of dementia, the patient is prescribed medications based on galantamine.
This category of medicines:
- has a neuroprotective effect, preventing the destruction of brain cells;
- helps to improve nerve impulses;
- restores memory and cognitive abilities.
To correct behavioral disorders, the patient is prescribed to take antipsychotics. Medicines in this category eliminate psychomotor agitation and delirium. Medications such as Haloperidol have many side effects. To relieve the patient of depression, fluoxetine-based medications are prescribed. To normalize sleep, take sleeping pills.
Tips for developing early symptoms of dementia
Behavioral disorders occurring in the early stages of senile dementia can be corrected without resorting to drug therapy.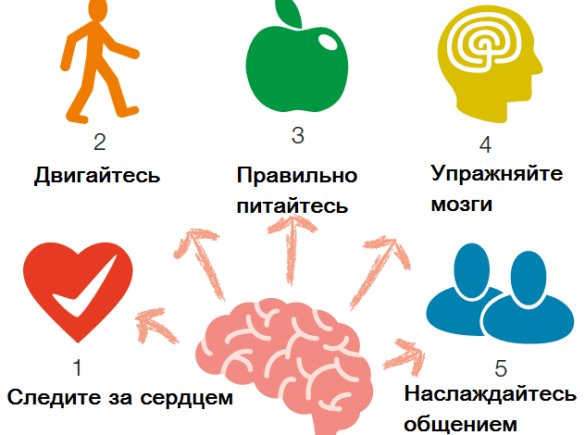
Experts recommend that older people reconsider their usual way of life.
Lots of traffic
An effective method that allows you to restore previously lost skills is regular physical education.
Outdoor exercise:
- contribute to the normalization of metabolism within tissues;
- accelerate the formation of synaptic connections;
- support vital functions at the cellular level.
Active dancing and playing sports will allow the patient to get rid of irritability and fatigue.
Communication with people
Patients suffering from senile dementia need to regularly communicate with others. This is the main condition for the social and mental development of a person.
When establishing contact with relatives, friends, neighbors and acquaintances, the patient develops the inner "I" and forms himself as a person. With dementia, the patient is deprived of the ability to interact with others. There is no logic in the reasoning, mood swings and other personal changes are observed.
To help an elderly person regain communication, it is necessary to learn to hear and listen to the patient. If the patient is not able to independently find the right word in a conversation, then you can ask him leading questions or try to build a logical chain with him.
People suffering from senile dementia see the surrounding reality distorted. You can not impose your opinion on the patient or actively persuade him.
Brain training
Brain training allows you to restore logical thinking, analytical and visual memory.
The patient can be offered:
- try to arrange things by size and color;
- find pictures in the book that depict a specific person, plant or animal;
- record a few words under dictation;
- finish a proverb or saying;
- feel a fruit, vegetable, or spice.
 To develop fine motor skills of the hands, the patient is offered to sculpt some figure out of plasticine.
To develop fine motor skills of the hands, the patient is offered to sculpt some figure out of plasticine.
To give up smoking
Smoking can cause vasoconstriction in the brain. If blood flow is disturbed, the risk of developing hypoxia is quite high. People suffering from senile dementia (regardless of type and stage) need to completely stop using tobacco products.
Correct and long sleep
It is important for the elderly to get adequate rest. A night's sleep should last at least 8 hours - during this time, the body has time to restore the spent energy. Prolonged rest allows the brain to "unload", the organ again gets the opportunity to correctly process the information received. Lack of sleep negatively affects not only the physical, but also the mental state of the patient.
The diet
Together with food, a large amount of vitamins, micro - and macroelements necessary for the normal functioning of cells enters the human body. An improper diet, frequent snacks, or partial refusal to eat can provoke disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system.
During the rehabilitation period, the patient must adhere to a therapeutic diet.
List of prohibited and permitted products:
| Category | Allowed | Forbidden |
| Vegetables | Pumpkin, zucchini, beets, cabbage, carrots. | Radish, radish, onion, garlic. |
| Fruits | Tangerines, lemons, apples, pears, avocados. | Peaches, pomegranate, pineapple, grapes, melon. |
| Cereals | Barley, semolina, buckwheat, millet. | Rice (except brown), lentils. |
| Meat and fish | Lean veal, poultry (turkey, chicken), rabbit. | Fatty meats (beef, lamb). |
| Sweets | Jam, preserves, fruit marmalade (no sugar), baked goods. | Chocolates, candies with liqueur, cakes with fat cream, cakes. |
| Sausages and smoked meats | Chicken sausage (sausages), boiled sausage, ham. | Smoked fish, fatty boiled pork, smoked bacon. |
| The drinks | Freshly squeezed fruit and vegetable juices, green tea, herbal tea, cocoa. | Alcoholic drinks (including low alcohol drinks), strong coffee, black tea. |
 If a person forgets to eat, then he needs to be carefully reminded of this. It is better to feed the patient when he is in a good mood. The diet should be dominated by semi-liquid and liquid dishes, especially if the patient has problems with swallowing. It is better to know the gastronomic preferences of the patient in advance and prepare food in accordance with them.
If a person forgets to eat, then he needs to be carefully reminded of this. It is better to feed the patient when he is in a good mood. The diet should be dominated by semi-liquid and liquid dishes, especially if the patient has problems with swallowing. It is better to know the gastronomic preferences of the patient in advance and prepare food in accordance with them.
Prevention of vitamin deficiency
To prevent vitamin deficiency, you need to eat a balanced diet and include more vegetables and fruits in the diet. You can take vitamin complexes, which are prescribed by the attending physician. Self-selection of dietary supplements is strictly prohibited: an excess of minerals or vitamins caused by taking an "inappropriate" drug can aggravate the situation.
Dementia in adults is a pathology that is diagnosed in every 5 elderly people. Symptoms appear gradually, many do not pay attention to them in time. The occurrence of delirium, hallucinations, memory and speech disorders is the reason for contacting a medical institution.
Dementia Signs Videos
Early signs of dementia: