 Intraventricular hemorrhage( IVH) is a pathology in which small vessels burst and bleed into the ventricles of the brain of a newborn baby.
Intraventricular hemorrhage( IVH) is a pathology in which small vessels burst and bleed into the ventricles of the brain of a newborn baby.
Ventricles are cavities in the brain that are filled with CSF( cerebrospinal fluid).A person has several and all of them are connected to each other.
The diagnosis of IVH is often given to premature babies, which is due to their physiological characteristics. The shorter the gestation period, the higher the probability of hemorrhage.
Hemorrhage does not appear just so, there must necessarily be a reason for this violation.
Contents of
- Who is at risk?
- Symptomatic
- Gravity severity
- Diagnostic methods and criteria
- Opportunities of modern medicine
- Prognosis for hemorrhage
- Preventive measures
- Correct definition of delivery tactics
- Prenatal screening
Who is at risk?
Hemorrhage in the brain of newborn babies can be due to both damage directly to the skull itself and to a lack of oxygen.
Prerequisites for IVH:
- Overlapping or, conversely, miscarriages of .Especially intracranial hemorrhages are affected premature babies, since their immature vessels still do not have sufficient support in the tissues. In children born after the term, the bones become denser and the head is not able to be configured during delivery. IVH according to statistics occurs for every fifth premature baby and every tenth child born.
- The dimensions of the fetal head do not correspond to the size of the generic pathways .In this case, the natural delivery is contraindicated, because it is fraught with trauma and hypoxia for a newborn baby.
- Severely leaking pregnancy ( fetal hypoxia, intrauterine infection with various infections).
- Complicated( prolonged or rapid) delivery of , pelvic presentation.
- Inaccurate actions of midwives during delivery of .

Based on the above, there are several risk groups.
The risk of cerebral hemorrhage in a child increases with:
- prematurity;
- low birth weight( less than 1.5 kg);
- deficiency of oxygen( hypoxia);
- trauma to the child's head during childbirth;
- complication with breathing during labor;
- infections leading to a clotting disorder.
Symptomatic symptomatology of
There are not always visible signs of hemorrhage. Also, if the child has any of the following symptoms, it is not necessarily that it is associated with IVH, they can be caused by other diseases.
The most common symptoms of intraventricular hemorrhage in infants:
- decrease or disappearance of the Moro reflex( to external stimuli);

- decreased muscle tone;
- drowsy condition;
- episodes of apnea( respiratory arrest);
- pallor of the skin, cyanosis;
- rejection of food, weakness of sucking reflexes;
- oculomotor disorders;
- is a weak and piercing scream;
- muscle twitching, convulsion;
- pareses;
- metabolic acidosis( acid-base balance disrupted);
- decrease in hematocrit or absence of its increase against the background of blood transfusion;
- the fontanel of the big sizes is intense and vybuhaet;
- coma( with severe hemorrhages, as well as concomitant hemorrhages in the cerebral cortex, significant distension of the ventricles).
Degrees of severity
There are several classifications of hemorrhages, most of them include 4 stages. Below is the gradation used most often in modern medicine:
- 1 and 2 degrees .Hemorrhage is observed in the projection of the germinal matrix and does not extend into the lumen of the lateral
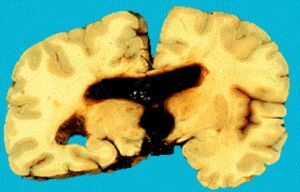 of the ventricles. In the second stage, the hemorrhage has a slightly larger size( > 1 cm) than in the first.
of the ventricles. In the second stage, the hemorrhage has a slightly larger size( > 1 cm) than in the first.
- With 3 degrees of , a hemorrhage from the germinal matrix emerges into the lumen of the lateral ventricles. As a consequence, posthemorrhagic ventriculomegaly or hydrocephalus develops. On the tomogram and the cut, there is an expansion of the ventricles, in which the elements of blood are clearly traced.
- The 4th degree of is the heaviest, the IVLC breaks into the periventricular parenchyma. Hemorrhage is observed not only in the lateral ventricles, but also in the substance of the brain.
To establish this or that degree of a hemorrhage it is possible only by means of special research.
Diagnostic methods and criteria
For diagnosis in the presence of appropriate symptoms, as a rule, ultrasound of the cerebral vessels is used( with the help of sound waves, vascular ruptures and bleeding are determined).Blood tests for anemia, metabolic acidosis, and infections are also given.
When diagnosing pathology of any degree, the specialist selects individual treatment for the patient.
Possibilities of modern medicine
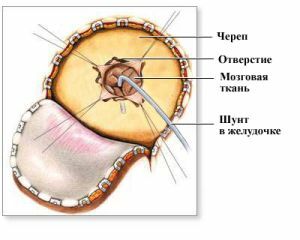 If the child has a hemorrhage in the ventricles of the brain, then he should be under the watchful eye of the medical staff. Monitoring of the condition of the baby is carried out in order to ensure its stability.
If the child has a hemorrhage in the ventricles of the brain, then he should be under the watchful eye of the medical staff. Monitoring of the condition of the baby is carried out in order to ensure its stability.
Basically, therapy with IVC is aimed at eliminating complications and consequences. If as a result of a hemorrhage there were any diseases, appropriate treatment is prescribed.
Sometimes( if too much fluid is accumulated in the brain) the following measures are taken:
- Ventricular ( via fontanel) or lumbar ( through the back) puncture .
- Ventriculoperitoneal shunting , when a special drainage tube is inserted into the ventricles. It extends under the skin to the abdominal cavity of the patient, where excess liquor is absorbed. The drainage system must always be in the body, and the tube is replaced if necessary.
It should be noted that for most patients( at levels 1 and 2 of IVH) no therapy is required, one can expect a favorable outcome.
Prognosis depending on the degree of hemorrhage
Consequences will depend on the degree of IVH and the adequacy of the actions of the medical staff:
- 1 and 2 degree hemorrhages often require no treatment. For such infants, it is necessary to observe, the probability that any neurological abnormalities will arise is not high. Cases of hydrocephalus and lethal outcome at 1 and even 2 degrees of disturbance are extremely rare.

- 3 degree .With the break of a hemorrhage into the ventricles, the probability of developing hydrocephalus increases, it can occur in about 55 percent of cases. Neurological abnormalities are observed in 35%.The lethal outcome is an average of one in five children. Patients are shown surgical intervention, and the outcome depends on the extent of the brain damage, from the location of the location( predictions are more favorable if the IVH is present in only one lobe, especially only in the frontal lobe).
- 4 degree .Unfortunately, the predictions for such a severe pathology are disappointing. Surgical intervention in this case is inevitable, and the risks of death are high - about half of infants with grade 4 IVH die. In 80% of cases, hydrocephalus develops, in 90% - neurological abnormalities.
Preventive measures
One hundred percent of the hemorrhage in the brain of a baby can not be prevented, but to reduce the risk, it is still possible and necessary to take some measures.
Correct definition of delivery tactics
Often, perinatal intracranial hemorrhage arises from birth trauma, so it is extremely important to carefully evaluate the ratio of the pelvis to the mother and the head of the fetus.
In case of a mismatch, the natural birth is contraindicated, a cesarean section is prescribed. This operation is also carried out for diseases associated with a decrease in platelets in the blood of the pregnant or fetus( poor coagulation).
In addition, in this case, special therapy is prescribed( corticosteroids, immunoglobulin, platelet mass).During childbirth it is important to monitor the child's blood pressure, you must avoid his fluctuations, so that the cerebral blood flow does not increase.
Prenatal screening
Although the research data are not mandatory for a pregnant woman, they should not be ignored.
In addition, one should know that intracranial hemorrhages are possible not only in newborn children. They can arise due to trauma at absolutely any age.