Leukopenia is a blood disorder characterized by a decrease in the number of leukocytes in a unit of blood volume. There are many reasons for the development of leukopenia in adults - from poor nutrition to genetic abnormalities.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Stages and degrees
- 3 Symptoms
- 4 Causes of occurrence
- 5 Diagnostics
- 6 When to see a doctor
- 7 Prevention
-
8 Treatment methods
- 8.1 Medications
-
8.2 Folk methods
- 8.2.1 Rosehip decoction
- 8.2.2 Beetroot with honey
- 8.2.3 Drink with lemon and honey
- 8.2.4 Broth of oats
- 8.2.5 Decoction of birch buds
- 8.2.6 Vitamin Blend
- 8.3 Diet therapy
- 8.4 Bone marrow transplantation
- 8.5 Administration of colony-stimulating factors
- 8.6 Suspension of other treatments
- 9 Possible complications
- 10 Video about leukopenia
Views
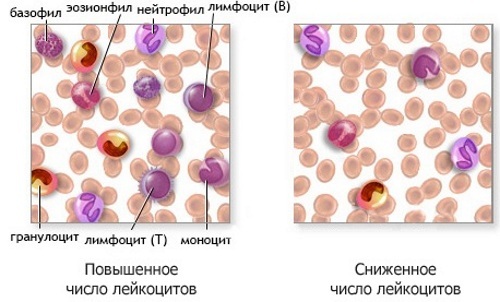
Leukopenia (causes in adults can be congenital or acquired) is divided into 2 large groups:
- Absolute - there is a uniform decrease in the level of all types of leukocytes in the blood.
- Relative (redistributive) - there is a decrease in one or more types of leukocytes.
The blood contains 5 types of leukocytes, and the relative form of leukopenia is divided
by 5 subspecies, depending on which type of blood cells are reduced:- Neutropenia - there is a decrease in neutrophils (responsible for the absorption and destruction of foreign substances and taking part in the inflammatory reaction), which make up 60-70% of all leukocytes.
- Lymphopenia - there is a decrease in the level of leukocytes (responsible for the production of antibodies to infectious agents), which make up 20-45% of the total mass of leukocytes in the blood.
- Monocytopenia - the number of monocytes decreases (the content in the blood is from 1 to 8%). Monocytes are responsible for recognizing substances foreign to the body and "teach" this to other types of leukocytes.
- Eosinopenia - the level of eosinophils, which are responsible for the fight against multicellular parasites, decreases (the content in the blood is from 0.5 to 2%).
-
Basopenia - there is a decrease in the number of basophils involved in the development of allergic reactions (the content in the blood is up to 0.5%).
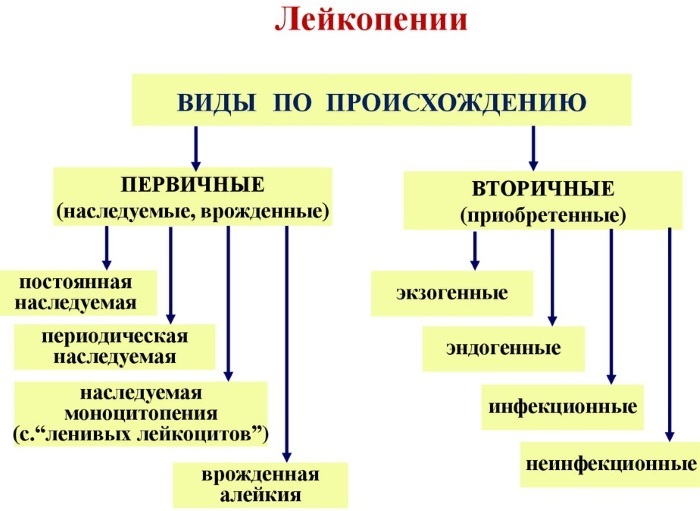
The following forms of leukopenia are also distinguished:
| By the shape of the flow | |
| Sharp | The fall in the level of leukocytes occurs suddenly and lasts no more than 3 months. |
| Chronic | The level of leukocytes in the blood is kept at a low level for more than 3 months. |
| By etymology | |
| Congenital (primary) | Leukopenia is caused by genetic disorders and congenital abnormalities. |
| Acquired (secondary) | The disease develops as a result of various pathologies that occur during life. |
In rare cases, leukopenia is the norm - this is a physiological feature of the patient's body (this form of the disease is called physiological).
Stages and degrees
Doctors identify 3 main stages in the development of leukopenia, depending on the level of decrease in leukocytes in the blood:
-
Initial degree (the level of leukocytes decreases to 1-1.5 * 109/л). At this stage, there are no symptoms of pathology, the likelihood of complications is minimal, or complications are mild. The difficulty lies in the fact that due to the absence of symptoms, a person is not aware of the presence of pathology; it can be detected by chance during a blood test.
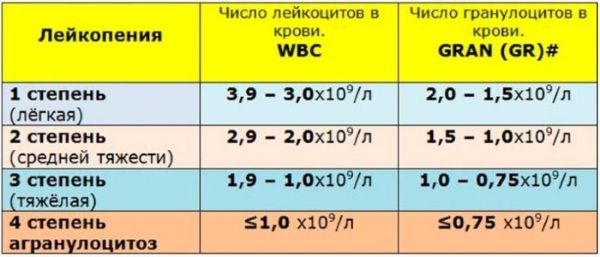
- Moderate leukopenia (the level of leukocytes decreases to 0.5-1 * 109/л). This stage of the disease is critical, as it poses a threat to further human health.
- Severe leukopenia (the level of leukocytes in the blood is less than 500 * 109/л). This degree of pathology, also called "agranulocytosis", entails severe complications and a rapid and complete decrease in immunity.
Symptoms
Leukocytes are shaped blood cells, the main function of which is to protect the body from various bacteria, viruses and fungi. Therefore, with a decrease in their number, the body becomes more susceptible to infectious agents, a person begins to get sick more often.
Leukopenia (the causes of occurrence in adults and children are different), in mainly accompanied by symptoms characteristic of an infectious process in the body:
- increased body temperature for no reason (usually not higher than 37 ° C, while the person feels good, and there are no other symptoms);
- constant weakness, fatigue;
- chills or sweating;
- headache;
- heart palpitations;
- dizziness;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- lack of appetite;
- frequent sore throats, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, which do not pass for a long time;
- stomatitis, inflammatory diseases of the mucous membranes, which do not heal for a long time;
- frequent herpes;
- enlargement of the liver or spleen;
- inflammatory processes in the internal organs.
Causes of occurrence
There are many causes of leukopenia in adults.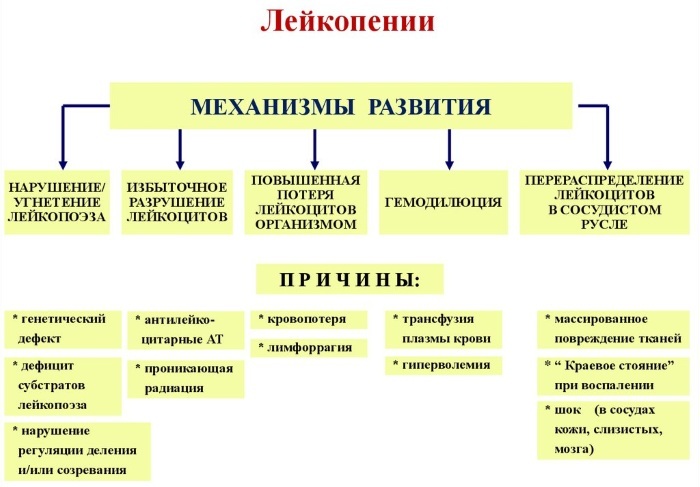
These include:
- genetic disorders and congenital bone marrow diseases;
- hereditary factor (if someone in the family had leukopenia, in particular, of genetic origin, then the patient is very likely to have this disease as well);
- acquired diseases of the bone marrow;
- disorders of hematopoiesis;
- autoimmune disorders;
- the effect of certain medications;
- intoxication with salts of heavy metals, toxic chemical compounds;
- infectious pathologies (tuberculosis, HIV infection and AIDS, cytomegalovirus and hepatitis reduce the level of leukocytes in the blood);
- lack of essential vitamins and minerals in the body caused by malnutrition;
- the effect on the body of radiation, microwave rays, x-rays;
- large blood loss;
- strong psycho-emotional shocks (indirect influence).
Very often, a decrease in the level of leukocytes in the blood is observed in patients with cancer, in particular leukemia (blood cancer). Oncological pathologies and methods of their therapy (radiation therapy, radiotherapy, chemotherapy) strongly affect the decrease in the number of leukocytes in the blood and lead to a deterioration in immunity.
Diagnostics
Most often, leukopenia is detected when conducting a general detailed blood test during a routine examination. Or a person notices that his immune system is weakened and turns to a doctor who prescribes an analysis.
To find out the cause of the pathology, as well as to identify complications of leukopenia, the following group of examinations is prescribed:
| Immunoassay blood test (immunogram) | Allows you to detect the presence of antibodies to certain infectious agents. |
| Blood chemistry | It is necessary for the determination of certain liver enzymes in the blood. |
| Blood test for rheumatoid factor | Helps to identify the presence of an autoimmune disease that affects the decrease in the level of leukocytes in the blood. |
| HIV test | It is necessary to identify HIV infection that can cause leukopenia. |
| Bone marrow puncture | It is carried out only in exceptional cases when it is not possible to establish the cause of the development of leukopenia. For the study, bone marrow punctate is taken and examined by the cytological method for the presence of any organ diseases. |
For a reliable result, tests are repeated after a few weeks. You may also need an ultrasound scan of any organ or soft tissue (if an infectious-inflammatory process is suspected) or an MRI of the brain.
When to see a doctor
If a person rarely had colds, viral-bacterial and fungal diseases before, but noticed that he has recently become more ill with them, then he needs to visit a general practitioner. The therapist will write a referral for a blood test, based on the results of which he will decide whether to send the patient to a hematologist (specialist in diseases of the blood and hematopoietic organs).
A timely visit to the doctor helps to stop the progression of leukopenia, prevent complications and identify the presence of concomitant diseases that may be the cause or effect of a reduced amount leukocytes.
Prevention
If a person has leukopenia due to genetic disorders or congenital (hereditary), then he should carefully follow the rules prevention to prevent infectious complications:
- take drugs that stimulate the synthesis of leukocytes in accordance with all the instructions of the attending physician;
- in the presence of inflammatory, infectious (viral, bacterial, fungal) diseases, immediately consult a doctor and begin immediate treatment;
- observe sanitary and hygienic standards, use antiseptics and sanitizers to prevent infection of the body;
- eat well, eat foods rich in vitamins and minerals, avoid nutrient deficiencies;
- use soft toothbrushes (to prevent damage to the gums), electric razors (so as not to cut the skin);
- do not squeeze out pimples, do not comb the skin;
- wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly with soap and scald with boiling water, subject meat and offal to full heat treatment;
- wearing medical masks in public places.
Treatment methods
Treatment of leukopenia is primarily aimed at eliminating the causes and increasing the level of leukocytes in the blood. Also, treatment is carried out, the purpose of which is to strengthen the protective functions of the body and prevent complications.
Medications
Leukopenia (causes of occurrence in adults affect the choice of further therapy) is treated comprehensively with the use of various groups of medicines:
| Group of drugs | Action | Release form | Names of funds |
| Leukopoiesis stimulants | They stimulate the activity of the bone marrow and the formation of leukocytes, enhance immunity and accelerate the regenerative processes in the body. | Injection | Sodium Nucleinat, Granogen, Leukostim, Pentoxil. |
| Immunomodulators | They stimulate the protective functions of the body, strengthen the immune system. | Tablets, capsules, injections, external agents. | Immunal, Isoprinosine. |
| Vitamin and mineral complexes or individual vitamin supplements | Eliminate the deficiency of vitamins and minerals in the body, strengthen the immune system, improve the general condition of the patient. | Tablets, capsules, drops, injection | "Ascorbic acid", "Alphabet", "Complivit". |
| Antibacterial drugs (antibiotics) | They have an antibacterial effect and are used in case of bacterial infections caused by leukopenia. | Tablets, solutions for injections, powders for suspension preparation. | Erythromycin, Avelox, Zinnat. |
| Glucocorticosteroids | Hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs. | Injections, tablets. | "Hydrocortisone", "Prednisolone", "Betamethasone". |
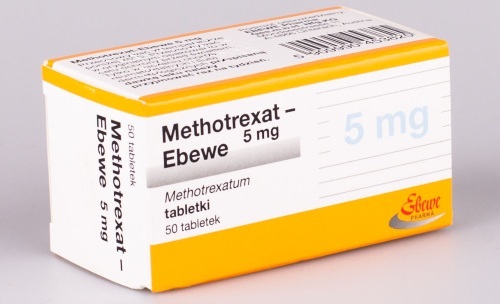
| Immunosuppressants | Suppress the functions of the body's immune system. They are used only if leukopenia is caused by an autoimmune disorder. | Injections, tablets. | “Methotrexate”, “Azathioprine”. |
Also, drugs are prescribed, depending on the cause of the leukopenia. Therapy is selected individually for each patient, depending on the form and stage of the disease.
Folk methods
Folk remedies for leukopenia help to strengthen the immune system, increase the level of leukocytes in the blood, and help restore the body's strength. Some of the methods are helpful in the presence of infectious complications.
Rosehip decoction
Rosehips are rich in vitamin C, which is necessary to strengthen the immune system and maintain the strength of the body. Also, the berry has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. To prepare rosehip broth you will need: 2 tbsp. l. dry rose hips, 2 glasses of water.
The cooking process is as follows:
- The fruits must be chopped and placed in a saucepan.
- In a separate saucepan, boil water and pour it over the fruits, put the mixture on low heat.
- Boil the broth for 5 minutes, then remove from heat and cool, then strain.

You need to take a decoction of 50-70 ml per day for 2 weeks. Then you should take a break for 1-2 weeks and repeat the course of treatment.
Beetroot with honey
Beetroot, due to the content of useful substances in it, stimulates the production of leukocytes, helps to eliminate anemia and cleanses the blood. And honey has anti-inflammatory properties and strengthens the immune system.
For cooking, you need to take 1 raw beets, wash and peel them. Then the beets should be chopped in a blender and mixed with 2 tbsp. l. honey. You need to eat this salad 2-3 times a week for 2 months.
Drink with lemon and honey
Such a drink is useful to everyone, even healthy people - it helps to increase immunity, cleanses the body of toxins, and reduces the severity of inflammatory processes.
To prepare a drink you need:
- Dissolve 0.5 tsp in 1 glass of warm water. l. any honey.
- Then add 2-3 tsp. l. lemon juice.
- Stir everything thoroughly and drink in slow sips.
You need to drink such a drink immediately after waking up (or after brushing your teeth) for 20-30 minutes. before breakfast. It is recommended to do this on an ongoing basis.
Broth of oats
Oatmeal is most beneficial for chemotherapy-induced leukopenia. To prepare the broth, you will need 3 tbsp. l. oat grains and 0.5 liters of water.
Cooking process:
- The grains must be poured with water and placed on fire.
- Bring the mixture to a boil, then reduce heat and simmer the broth over low heat for 15 minutes.
- After 15 minutes. the broth should be removed from the heat, wrapped and cooled in this form.

You need to take the broth for ½ cup 3 times a day for 30 minutes. before meals.
Decoction of birch buds
The broth is useful for bacterial and fungal infections, as it has a pronounced antimicrobial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory effect. It also helps in the fight against parasites.
To prepare the broth you should:
- 1 tbsp. l. birch buds should be placed in a glass container and pour 200 ml of hot water.
- The container must be placed in a water bath, closed with a lid and infused (stirring occasionally) for 15 minutes.
- Then the broth must be removed from the heat, cooled and filtered.
It is necessary to take a broth in 1-2 tbsp. l. 3 times a day for 30 minutes. before eating. The course of treatment is 2 weeks.
Vitamin Blend
This product contains a huge amount of vitamins and minerals, helps to strengthen the immune system.
For cooking you will need:
- peeled walnuts - 250 g;
- dried apricots - 250 g;
- raisins - 200 g;
- lemons - 3 pcs.;
- honey - 1.5 tbsp. l.
Nuts, dried apricots, raisins and lemon (always with zest) must be scrolled through a meat grinder or chopped in a blender and mixed with honey. The mass should be placed in a glass jar and stored in the refrigerator. Take 3 times a day for 1 month.
Diet therapy
Diet therapy is important in the treatment of leukopenia, as it helps prevent the development of complications, relieve the patient's condition, help the body recover after chemotherapy or radiation therapy and strengthen immunity. Also, some foods contribute to an increase in the level of white blood cells in a person's blood.
It is recommended to exclude foods heavy for digestion, fried and fatty foods (including fatty soups), flour, yeast and confectionery products from the diet. Only a small amount of red wine is allowed from alcohol outside of periods of exacerbation of infections.
The following foods should prevail in the diet:
- fruits and vegetables (especially citrus fruits, kiwi, red peppers, broccoli and cabbage);
- berries (black currant, rose hips, sea buckthorn - leaders in the content of ascorbic acid);
- greens (the richest in vitamin C are parsley and dill);
- whole grain cereals and breads;
- vegetable broths;
- legumes;
- nuts (no more than 10 nuts per day);
- honey (no more than 1-2 tsp. l. in a day);
- lean meats, poultry and fish;
- seafood;
- fermented milk products (except milk).
Food must be baked, stewed or boiled. It is recommended to drink more liquid (mainly water), freshly squeezed juices, herbal teas, fruit drinks and compotes (preferably without sugar) are allowed.
Foods that increase the level of leukocytes in the blood:
- fruits, vegetables and berries of red and purple color;
- beet juice;
- liver (in limited quantities);
- beans;
- lard (in limited quantities).
Bone marrow transplantation
Bone marrow stem cell transplantation is performed for severe leukopenia, when the above methods of therapy do not help. In this case, the transplanted stem cells become a source of new leukocytes and eliminate the deficiency of blood cells.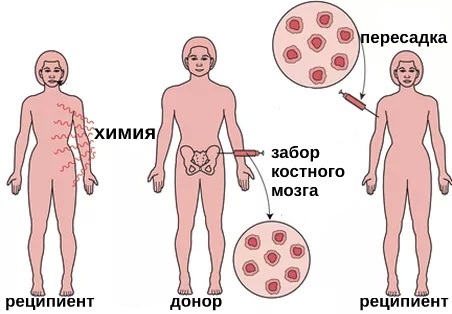
Bone marrow transplants are also used to treat leukemia, which causes a decrease in white blood cells. To do this, first, chemotherapy or radiation therapy is carried out in order to suppress the functions of the patient's own bone marrow, and then donor cells are transplanted.
Administration of colony-stimulating factors
The use of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor is controversial. However, this method of treatment helps to reduce the severity and duration of some forms of leukopenia in cancer patients.
Before the administration of the drug, a thorough diagnosis is carried out under the supervision of a hematologist and the risks are assessed.
Suspension of other treatments
If leukopenia is caused by chemotherapy, radio or radiation therapy, as well as taking medications drugs, then in some cases treatment is suspended so that the bone marrow can produce new leukocytes. The decision to suspend treatment is made depending on the patient's condition, the severity of the disease, the importance of taking medications.
Possible complications
Leukopenia (causes of occurrence in adults affect the number of which type of white blood cells will decrease) leads to a decrease in immunity and the body's susceptibility to various infections.
In the absence of treatment for the disease, the patient faces the following complications:
- frequent colds;
- frequent infections of various kinds;
- sepsis;
- tissue necrosis as a result of soft tissue infection;
- toxic shock;
- death due to infection.
With the timely initiation of therapy, the prognosis of treatment is favorable, but success depends on the causes and form of the disease.
Leukopenia in adults is a dangerous pathology that can greatly complicate a person's life or lead to death. The causes of the disease can be different and the success of treatment and complete recovery depends on them.
Video about leukopenia
Pathophysiology of white blood:


