Monocytosis in the blood in an adult is a pathological indicator and indicates the development of a serious illness. This can be an inflammatory process, viral pathology, or cell damage. Changes in indicators indicate that the leukocytes present are unable to cope independently with pathological processes.
The causes of the increased level of blood cells (monocytes) will help determine a comprehensive diagnosis. Based on the results of the examination, the therapist will diagnose and, if necessary, prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Record content:
- 1 Views
- 2 Symptoms and Signs
- 3 Causes
- 4 Diagnostics
-
5 Treatment methods
- 5.1 Drug therapy
- 5.2 Folk remedies
- 5.3 Diet
- 5.4 Operation
- 6 Possible consequences and complications
- 7 Video about monocytosis
Views
Depending on the provoking factor, monocytosis in adults in the blood is classified as follows:
- Relative. The pathological condition is characterized by an increase in the percentage of monocytes in the blood in relation to other blood cells. Relative monocytosis occurs as a result of active multiplication of intracellular organisms (viruses, fungi, bacteria). In most cases, this type of monocytosis is detected in a person after severe stress or treatment for a cold.
- Absolute. Monocytosis in this case provides for an absolute increase in blood cells in the human blood. This also increases the level of leukocytes. The change in indicators occurs during the period of the body's immune response to the ingress of a bacterial infection. The same thing happens with the development of malignant processes. Absolute monocytosis requires a comprehensive and thorough diagnosis.
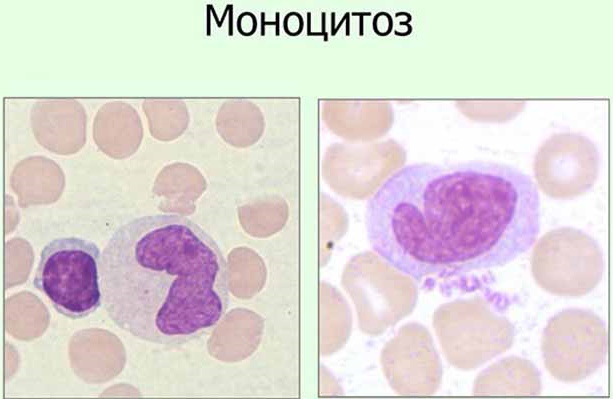
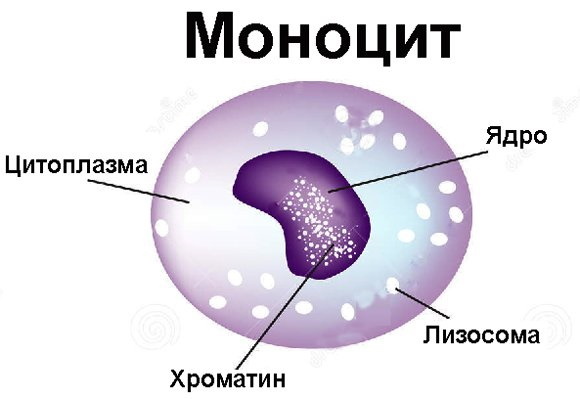 After therapy, patients donate blood for analysis so that the doctor can assess the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment. If, at the same time, an increase in the level of monocytes in the blood of an adult is observed for a long time, it means that the disease has become chronic. The patient was not fully treated or did not exactly follow the recommendations of the specialist.
After therapy, patients donate blood for analysis so that the doctor can assess the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment. If, at the same time, an increase in the level of monocytes in the blood of an adult is observed for a long time, it means that the disease has become chronic. The patient was not fully treated or did not exactly follow the recommendations of the specialist.
Symptoms and Signs
The clinical picture of monocytosis in adults depends on the provoking source. It is important for the attending physician to tell about all existing complaints so that the specialist makes a preliminary diagnosis and prescribes the most informative examination. Monocytosis, as a secondary factor, does not provoke certain symptoms.
But a doctor's consultation will be required if the following symptoms appear:
- for no apparent reason, body weight decreases sharply;
- appetite worsens or is completely absent;
- a person is worried about constant fatigue, general weakness in the body;
- panic attacks, emotional agitation, anxiety occur;
- stool is disturbed;
- feces contain blood impurities;
- there is a pain syndrome in the abdomen, which does not help to eliminate drugs;
- taste preferences change, there is an aversion to meat products;
- the mucous membranes are covered with boils or pimples;
- rashes appear on the skin;
- worried about discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- redness, rashes appear in the genital area;
- characteristic discharge comes out of the genital canals.
The person becomes irritable, sleep disturbed, insomnia is present. The work of the digestive system organs is accompanied by loud characteristic sounds. Muscles and joints ache. In some situations, a person is worried about a strong dry cough, during which sputum is released with impurities of blood.
Causes
Monocytosis in the blood in adults does not always provoke serious diseases. In some situations, the triggering mechanism is physiological reasons. A physician therapist will help to establish an accurate diagnosis by prescribing a comprehensive diagnosis for the patient.
| Name | Description |
| Physiological causes |
|
| Pathological |
|
Monocytosis in the blood in adults (the reasons for the increase in the concentration of blood cells will allow the examination to be established) more often is the result of a pathological process, which is accompanied by concomitant symptoms and requires treatment. In the absence of timely therapy, the risk of developing serious complications increases, since the disease will gradually progress.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic method for determining a high level of blood cells is a complete blood count. After the results obtained, the doctor, guided by the existing information, prescribes additional examination methods for making an accurate diagnosis:
| Name | Description |
| Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | The most informative method that will help determine pathological foci with high accuracy and identify the defeat of neighboring areas. |
| Computed tomogram (CT) | X-ray examination method, with the help of which the internal organs are viewed in layers. CT scan helps to establish the disease at an early stage of development and the exact area of localization of pathological processes. |
| Bone marrow puncture | The bone marrow is harvested from the pelvic or sternum area. Experts in laboratory conditions carefully study the material for the detection of malignant processes. |
| Lymph node biopsy | An invasive diagnostic method, during which the tissue of the lymph nodes is taken for histological examination. The results will help detect malignant cells. |
| Blood chemistry | The results of the study will help assess the condition of the blood and the functioning of internal organs. The inflammatory process is always accompanied by a change in the composition of the blood. |
| Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) | Internal organs are examined, where the specialist presumably suspects the development of pathological processes. |
It is important to determine the disease against which the concentration of monocytes in the blood of a person has increased. The tactics of treatment also depend on the results of the study.
With an incorrectly selected therapy, the patient will face negative complications. A person may also need additional advice from other specialized doctors, taking into account the data obtained after diagnosis (cardiologist, gynecologist, infectious disease specialist, endocrinologist, oncologist).
Treatment methods
Restoring the level of monocytes requires complex therapy, taking into account the main reason, which negatively affected the concentration of blood cells. The profile doctor prescribes medications, in the absence of contraindications, he allows the use of folk remedies. An obligatory stage in the treatment of monocytosis is dietary nutrition.
Drug therapy
First of all, the patient needs to ensure bed rest and complete rest. The specialist prescribes medications, taking into account the pathological processes that provoked the development of monocytosis. It is important to adhere strictly to the dosages in order to eliminate the likelihood of side effects.
Monocytosis in the blood in adults (the causes of the pathological condition must be determined at an early stage of the development of the disease in order to prevent complications) is treated with the following drugs:
| Drug group | Name | Application |
| Immunomodulators | Tiloron, Galavit | Medicines increase the body's defenses and strengthen the fight against pathogenic factors. The tablets are recommended to be taken orally and washed down with water. The dosage of the drug depends on the patient's condition and is 1.25-2.5 mg every 48 hours. Immunodeficiency states require taking the medication once a week for 1.5 months. |
| Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs | Ibuprofen, Paracetamol | The dosage of the drug is selected for patients on an individual basis, depending on the diagnosis. Adults are prescribed 400-800 mg 3-4 times a day. The tablets should be swallowed whole without chewing and washed down with plenty of water. |
| Antibacterial drugs | Cefazolin, Spiramycin | Medicines are prescribed to patients when the human body is affected by a bacterial infection. The drug is administered intramuscularly or intravenously. The dosage depends on the patient's condition and is 0.5-2 g once a day. The standard course of therapy lasts 7-10 days. |
| Immunosuppressants | Methotrexate, Cyclophosphamide | Drugs are prescribed to patients with a pronounced and prolonged inflammatory process. The tablets are taken orally, washed down with water. The course of treatment and the regimen of therapy depends on the patient's condition. The dosage is 10-25 mg 1-2 times a week. |
| Glucocorticosteroids | Prednisolone, Methylprednisolone | Medicines are used for chronic pathological changes in the human body. The therapeutic dosage is 4-6 tablets per day. Maintenance dosage involves taking 1-2 tablets. |
The defeat of the nose and throat requires the additional use of antiseptics. It is necessary to flush the nasal passages and gargle. If the cause of monocytosis is malignant processes, chemotherapy is given. The drugs are taken orally or injected directly into the cerebrospinal fluid area.
Folk remedies
Unconventional methods can be used with elevated monocytes, if the cause of the change in the level is not pathological processes. It is necessary to discuss therapy with your doctor in order to prevent the occurrence of an allergic reaction or individual sensitivity.
Monocytosis in the blood in adults, the causes of which are not related to pathological factors, allows the use of the following folk remedies:
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Field horsetail | Pour 1 tbsp. dry herbs with hot water (1 tbsp.). Leave for 40 minutes and strain. | The ready-made infusion is recommended to be consumed inside in 50 ml. For taste, you can add a small amount of natural honey. |
| Linden | Dry plant flowers (1 tablespoon) pour boiling water (1 tablespoon). Put the resulting mass on medium heat and simmer for another 10 minutes. Insist 5 minutes and drain. | The finished product must be drunk before meals for 30 minutes, 2-3 tbsp. per day. Linden reduces the level of monocytes and leukocytes, an increase in which provoked colds. |
| Tincture of thorns | Pour plant berries (1 kg) with clean water (2 l). Grind the resulting mass well and leave for 24 hours in a dark place. Then put on medium heat, boil for 1 hour and strain. For taste, you can add a little natural honey. | Blackthorn tincture activates the body's immune forces, purifies the blood. It is recommended to use it internally, 50 ml before meals, 30 minutes. |
| Healing collection | Mix the leaves of strawberry, birch and raspberry in equal parts. Brew 3-4 tablespoons. collection with boiling water (3 tbsp.). Insist 3 hours and strain. | The finished drink should be taken orally in 0.5 tbsp. before eating. |

It is important to use folk remedies in combination with traditional medicines and strictly after consulting your doctor. It is impossible to cure the disease with only recipes of healers and healers, which provoked an increase in the concentration of blood cells.
Diet
The quality of blood in the human body depends on the food consumed. With the development of pathological processes, it is necessary to maintain immunity with a properly composed diet.
| Featured Products | Prohibited foods |
|
|
In the presence of monocytosis, the nutritionist recommends adhering to the following rules:
- Eat less sugar. Foods that are high in glucose contribute to the development of diabetes. It is better to refrain from various sweets, refined sugar and sweet tea.
- Refusal of alcohol is mandatory. Alcoholic beverages exacerbate health problems, against the background of which the progression of the inflammatory process occurs.
- It is necessary to add fatty fish to the diet, in which omega-3 acids are present.

- Dietary supplements that contain fish oil from cod liver help to reduce the number of monocytes in the blood. The same goes for curcumin, a compound that reduces the number of monocytes in the blood and reduces inflammation. Found in turmeric root.
An active lifestyle, physical activity within reasonable limits will help maintain the required level of monocytes in the blood. For health and disease prevention, you need fresh air in your living quarters, frequent and long walks in the park, forest. It is necessary to adhere to the drinking regime.
Operation
Monocytosis in the blood in adults (complex diagnostics will help determine the causes of pathological changes) sometimes requires surgical intervention. Surgical treatment for patients is prescribed when serious complications appear or in the case of a diagnosis of tumor neoplasms.
The same applies to congenital abnormalities and the lack of a positive result after the use of drug therapy. The operation involves a stem cell transplant from a donor. The method of treatment is used in extremely rare situations, since there is a high probability of death.
Possible consequences and complications
Monocytosis in adults is not an independent disease, but a specific indicator. A high level of blood cells will allow you to suspect a disease and conduct an examination. Complications can be different, including death, especially if the cause of the change in parameters is a serious pathology.
A high level of monocytes provokes the following changes:
- the blood circulation process is disrupted;
- the risk of developing atherosclerosis increases;
- reduced blood flow to the heart muscle threatens the development of heart disease.
Monocytosis also negatively affects the condition of the walls of blood vessels. Damage to them can be a complication. The prognosis depends on the severity of the underlying disease, as a result of which the concentration of blood cells has changed. Timely diagnostics and correctly selected therapy will help to increase the chances of a full recovery.
Monocytes are essential cells in the human immune system. They are necessary to protect against various kinds of infectious diseases. Monocytosis in human blood can be the result of physiological or pathological effects.
A thorough diagnosis will help establish the root cause of an adult's disorder. If necessary, treatment is prescribed by a specialized doctor, referring to the results of the examination.
Video about monocytosis
Monocytosis under a microscope:


