Anabolism is a type biochemical reaction in biology, in which the synthesis of complex molecules from simple precursors occurs.
Record content:
-
1 The concept of metabolism in biology
- 1.1 What is anabolism
- 1.2 What is catabolism
- 2 The relationship between anabolism and catabolism
- 3 Functions of anabolism
- 4 What happens during anabolism?
- 5 Stages of anabolism
-
6 Examples of anabolic processes
- 6.1 Protein synthesis
- 6.2 DNA synthesis
- 6.3 Bone and muscle growth
- 6.4 Synthesis of carbohydrates
- 6.5 Formation of glucose
- 6.6 Glycogen synthesis
- 6.7 Synthesis of nucleotides and fatty acids
- 7 How can you influence the rate of anabolism?
- 8 What is the connection between sleep and anabolism?
- 9 The influence of sports nutrition on the process of anabolism
- 10 Anabolic steroid
- 11 Metabolism videos
The concept of metabolism in biology
All chemical reactions in living organisms are collectively called metabolism. There are more than 5 thousand cells inside the cell. types of chemical compounds that are involved in a variety of reactions.
Metabolism can be said in another way, that it is the sum of 3 main functions:
- converting food into energy;
- converting food into building blocks for the body;
- elimination of metabolic waste.
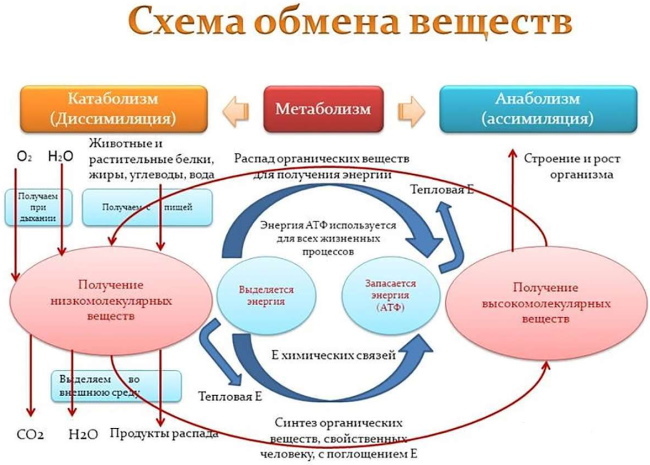
Metabolism is divided into 2 stages:
- Catabolism is the breakdown of organic matter. For example, during cellular respiration, glucose breaks down into 2 models of pyruvate.
- Anabolism is the build-up of cellular components. For example, the production of proteins and nucleic acids by the cell.
When substances decay, energy is released, and when substances are formed, energy is consumed. Taking fat as an example, when fat is broken down, energy is released. But when there is excess energy in the body, the body stores it back as fat.
What is anabolism
In anabolism, complex molecules are built from simple ones, which requires additional energy. One example is the creation of glucose from carbon dioxide. Other examples include the synthesis of proteins from amino acids or DNA strands from the building blocks of nucleic acids (nucleotides).
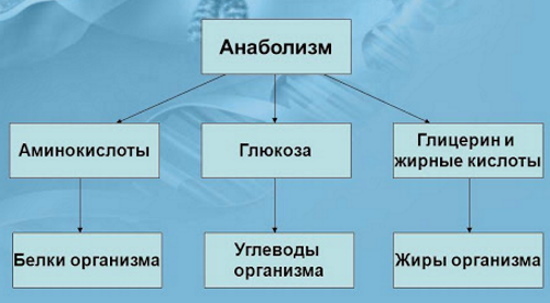
Anabolism is a natural process of plastic metabolism in biology, in which smaller and simpler molecules combine into larger and more complex substances. Using energy, the body can construct the complex chemicals it needs by combining small molecules derived from foods that humans consume.
What is catabolism
Catabolism is the process by which large and complex substances derived from foods are broken down into small and simple molecules. This releases energy.
Complex molecules in food break down, so the body can use parts of them to assemble new structures and substances necessary for life. This is a destructive process in which energy is released in the form of kinetic energy. Examples: cellular respiration, digestion, excretion.
The relationship between anabolism and catabolism
The first law of thermodynamics says that energy can neither be created nor destroyed - it can only change shape.
The main function of the body is to consume (absorb) energy and molecules from foods, transform part of it to fuel movement, support body functions, and build and maintain structures body. This is achieved by 2 types of reactions: anabolic and catabolic.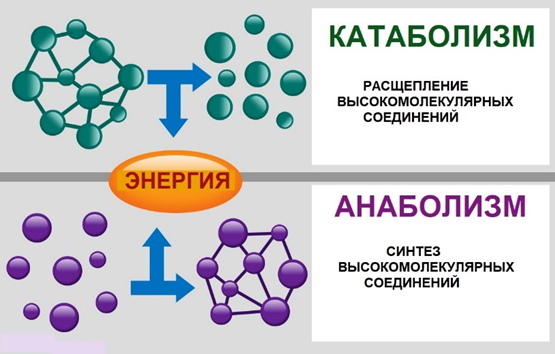
The connection between the 2 processes exists at 3 levels:
- Sources of carbon. Intermediate products of catabolism become the basis of anabolic reactions.
- Energy level. Metabolic energy is generated in the process of catabolism in the form of ATFE.
- Restorative relationship. Catabolic processes are oxidative and become donors of high-energy electrons.
Both anabolism and catabolism occur simultaneously and constantly, as a result of which a person lives. Taken together, these are 2 irreplaceable components of metabolism.
Functions of anabolism
Catabolism breaks down nutrients from foods into small blocks. In the process of anabolism, through the formation of chemical bonds between blocks or precursor molecules, macromolecules are formed, which are later used to create new cells or their structuring. Anabolism is essential for cell maintenance, growth, and development.
With the help of anabolic processes that cause cell growth and differentiation, organs and tissues are built. For example, the synthesis of complex molecules leads to an increase in body growth, expansion and mineralization of bones, and an increase in muscle mass.
What happens during anabolism?
Anabolism is a set of metabolic processes in biology in which the synthesis of complex molecules is activated by the energy released as a result of catabolism. Complex large molecules are produced in a systematic process from small and simple precursor molecules.
For example, an anabolic response can begin with relatively simple precursor molecules (previously created by catabolic reactions) and end up with fairly complex foods such as sugar, certain lipids, or even DNA, which has an extremely complex physical structure.
The increased complexity of foods derived from anabolic reactions also means they have more energy than their simple counterparts.
Anabolic reactions are divergent processes. This means that from a relatively small number of precursor molecules, a wide range of end products are created by synthesis. Anabolic processes are responsible for cell differentiation and increase in body size. These processes are attributed to bone mineralization and an increase in muscle mass.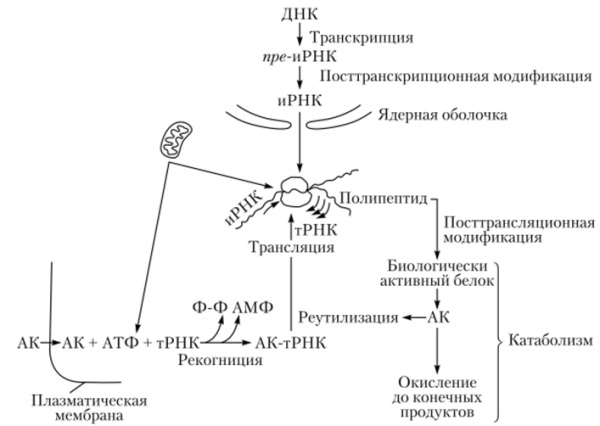
The biosynthesis process produces:
- peptides;
- proteins;
- polysaccharides;
- lipids;
- nucleic acids.
The listed molecules include all materials of living cells: membranes and chromosomes, as well as specialized products of certain cell types, such as enzymes, antibodies, hormones, and neurotransmitters.
Stages of anabolism
In molecular biology, there are 3 stages of anabolism, these are:
- Creation of progenitor cells: monosaccharides, nucleotides, amino acids, isoprenes.
- Conversion of precursors into reactive forms using energy from ATP (a substance that supplies energy for most biochemical reactions in the cell).
- Creation of complex molecules from precursors: polysaccharides, nucleic acids, proteins, lipids.
Examples of anabolic processes
With anabolism, the processes of synthesis of monosaccharides, nucleic, amine, fatty acids, ATP occur. The nutrients that enter the body are the building blocks for making the body's own proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
Protein synthesis
The construction of proteins by living cells occurs through synthesis.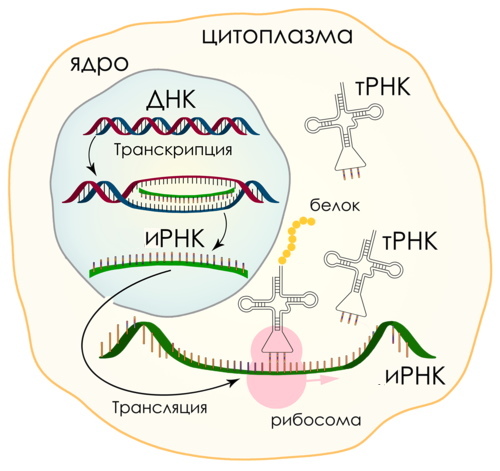
The active process involves:
- enzymes and ribosomes;
- RNA or ribonucleic acids;
- DNA or deoxyribonucleic acid.
The complex process takes place in 2 stages. In the first, called transcription, DNA molecules transmit in their nucleus the genetic instructions of mRNA (informational ribonucleic acid).
After processing, the information is transferred to the ribosome, rRNA, in the cytoplasm.
At the second stage, called translation, rRNA reads information, forms a bond between amino acids, forming a polypeptide bond. After the polypeptide chain is synthesized, it undergoes additional processing to form the finished protein. Briefly, the process occurs according to the following scheme: DNA → RNA → protein.
Examples of proteins:
| Fibrous | Collagen, keratin, myosin, tubulin, elastin |
| Globular | Albumin, gamma globulin, protein inhibitor, serum albumin |
| Membrane | Estrogen receptor, muscarinic acetylcholine receptor, potassium channel, transferases |
Proteins are the building blocks of cellular structures. They carry oxygen, build tissue, copy DNA for the next generation.
DNA synthesis
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the genetic material of a living organism. DNA synthesis takes place in the nucleus of the cell before its division and refers to the anabolic process.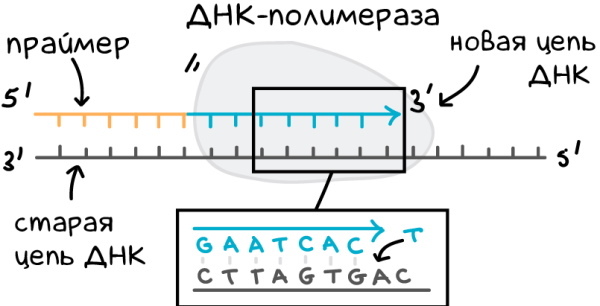
It involves unpacking double strands of DNA, attaching new nucleotides, each of which contains ½ part of the old DNA strand. Thus, the reproduction of the genome of the organism is ensured in cells, which are divided in the course of their vital activity.
Bone and muscle growth
Bone Mineralization - A Typical Example of Anabolism. During the process, mineral crystals are deposited in an organized manner on the organic extracellular matrix.
Bone is formed from a specific type of cell, osteoclasts. Osteoblasts, another type of cell, mineralize bone. During mineralization, osteoblasts produce calcium phosphate crystals. These structures are embedded in the bone, making it strong and solid. As a result of biosynthesis, muscle fibers grow through the accumulation of energy.
Synthesis of carbohydrates
Carbohydrates provide the body with energy, especially from glucose, a simple sugar found in many staple foods. Carbohydrates contain both soluble and insoluble elements. The insoluble part, fiber, promotes regular bowel movements, regulates blood glucose consumption, and helps flush excess cholesterol from the body.
As a direct source of energy, glucose is broken down during cellular respiration, resulting in the formation of ATP, the energy unit of the cell. Biological macromolecules are large molecules that are essential for life and are made up of smaller organic molecules.
One of the main classes of biological macromolecules are carbohydrates, which are divided into three subtypes: monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. Carbohydrates provide the body with energy, especially from glucose, a simple sugar that is a component of starch and an ingredient in many staple foods.
Formation of glucose
The breakdown and synthesis of glucose is the most important process in the human body. Glucose provides essential substrates for aerobic and anaerobic metabolism. Glucose metabolism is mainly controlled by the hormones insulin and glucagon. The former is released for anabolic metabolism when glucose is broken down and converted into storage forms (eg glycogen, fat).
Glycogen synthesis
Glycogen is an additional source of glucose and acts as a reserve battery for the body, providing a quick source of glucose when needed, and providing a place to store excess glucose when the concentration of the substance in the blood rises. The liver and skeletal muscle are the main sites in the body where glycogen is found.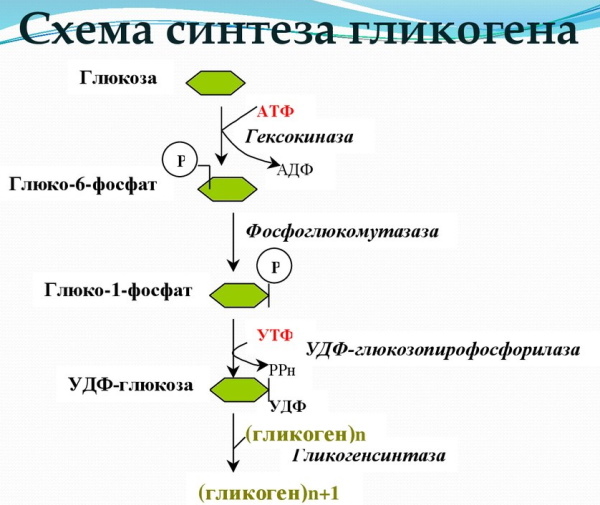
Glycogenogenesis is the process of anabolic synthesis of glycogen. Glucose molecules are phosphorylated and added to glycogen chains for storage.
Synthesis of nucleotides and fatty acids
Nucleotides are large monomers that the cell produces, and their synthesis involves many steps and a lot of energy. The biosynthesis of nucleotides is under strict regulatory control of the cell. Organisms must only produce the right amount of each base.
If too much is produced, energy is wasted; if too little, DNA replication and cellular metabolism stop.
Lipogenesis, the synthesis of fatty acids and their reaction to glycerol with the formation of triacylglycerols, occurs mainly in the liver. At the same time, dietary carbohydrates are the main source of carbon. Fatty acid synthesis is the most important anabolic pathway for most organisms.
In addition to being the main constituent of membranes, fatty acids are also important energy storage molecules. Fatty acyl CoA derivatives are used in various protein modifications at the final stage of translation. Fatty acid biosynthesis is important for cell growth, differentiation and homeostasis.
How can you influence the rate of anabolism?
Anabolism - in biology, as a molecular science, it is considered a set of chemical transformations of substances, including testosterone, estrogen and growth hormone.
It is difficult to maintain an anabolic state all the time, but there are many ways to enhance the process by increasing the production of these chemicals:
- It is good to rest at night.
- Stick to proper nutrition. This includes a balanced diet filled with all the vitamins, nutrients, and minerals needed to build and maintain mass.

- Focus on high-intensity exercise with short rest periods. It has been proven that lunges, pull-ups, squats and other complex multi-joint exercises performed at high intensity with short breaks between sets, increase growth hormone, testosterone and IGF-1, chemicals that play a role in anabolism.
- Take a protein shake after training, which should contain carbohydrates in addition to proteins.
- Minimize or completely eliminate smoking and alcohol. Alcohol can dramatically lower levels of testosterone, growth hormone, and other chemicals involved in protein synthesis.
- Find constructive ways to reduce or cope with stress. Excessive stress triggers the production of cortisol, which lowers testosterone and growth hormone levels.
What is the connection between sleep and anabolism?
Adequate sleep not only helps the body to rest, but also puts it into a state of anabolism. During the first hour of sleep, the level of growth hormone (growth hormone) rises in the body, which contributes to a faster metabolism of proteins. Research shows that poor sleep and insomnia contribute to catabolism.
The influence of sports nutrition on the process of anabolism
Sports nutrition is aimed at improving performance, endurance, increasing muscle mass or reducing body fat. The synergistic effect of the combination of essential amino acids and carbohydrates maximizes the anabolic response of resistance training.
Clinical studies in recent years have shown that essential amino acids can produce significant anabolic effects by increasing protein synthesis and net nitrogen balance. The most effective period of taking post-workout supplements in the form of sports nutrition is called the "anabolic window of opportunity."
This time covers the first 30-40 minutes after training. The combination of carbohydrates and amino acids taken at this time stimulates the body to quickly restore lost muscle tissue, strength, endurance.
Anabolic steroid
Anabolic steroids are a general term for a number of drugs that are used to accelerate muscle building. They induce a positive nitrogen balance and thus create a metabolic situation that promotes muscle building.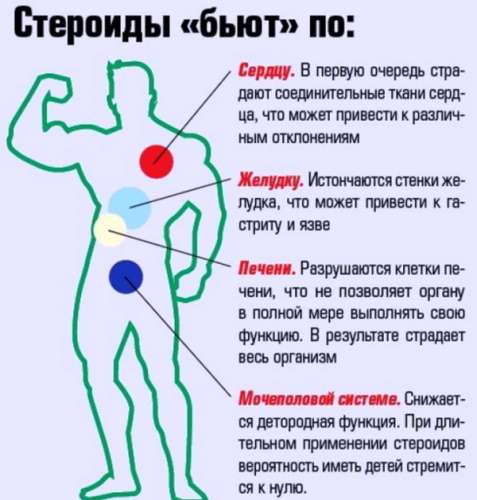
The best way is to regulate the body's own protein synthesis, which significantly speeds up muscle building. But body weight can be increased by consuming synthetic anabolic steroids.
Steroids have negative properties, they can affect the structure of the heart, blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and the liver.
None of the biological forms of energy - anabolism or catabolism - are completely good or bad. But to achieve energy balance, a person needs both forms of metabolism.
Metabolism videos
Metabolism - growth and metabolism:



