The human visual apparatus, together with auxiliary structures, ensures the clarity and quality of perception of the surrounding reality. The eyelids have a function protection of the eyeball from irritating factors and injuries, and the size of the lower eyelid is much smaller than the area of the upper one.
However, this fact does not diminish the importance of the protective mechanism of the lower fold of the skin, which has a unique structure, and under adverse conditions suffers from certain diseases.
Record content:
-
1 Where is the lower eyelid
- 1.1 Structure
-
2 Diseases
- 2.1 Symptoms of defeat
- 2.2 Inverted eyelid
- 2.3 The danger of meibomite
- 3 Why does the eyelid twitch
-
4 Treatment methods
- 4.1 Medicines
- 4.2 Compresses
- 4.3 Folk remedies
- 4.4 Lifestyle
- 5 Eyelid video
Where is the lower eyelid
The functioning of the eye is guaranteed by the complex anatomical structure of the apparatus, and the upper and lower eyelids provide the vulnerable eye membrane with reliable protection against various threats.
Outside, both eyelids (palpebral grooves) are skin folds extending from the outer corner of the eye to the lateral surface of the nose. Only a large fold of the upper eyelid is located above the orbit, under the eyebrow line, and a small strip of skin of the lower eyelid frames the eye vault from below, connecting with the skin surface of the cheek.
The lower eyelid, by analogy with the upper one, has a saturated blood supply, realized through the branches carotid artery (external and internal), and the work of the muscular apparatus is controlled by an extensive network nerves. The process of venous outflow is distributed along the orbit and veins of the face, the oculomotor, facial, trigeminal nerves are responsible for the work of the nervous regulation of the eyelids.
Structure
When the upper and lower eye strips are connected, a gap is formed. Its appearance is the result of the presence of a system of ligaments that provide a strong fixation of the edges and walls of the orbit using a cartilaginous mechanism.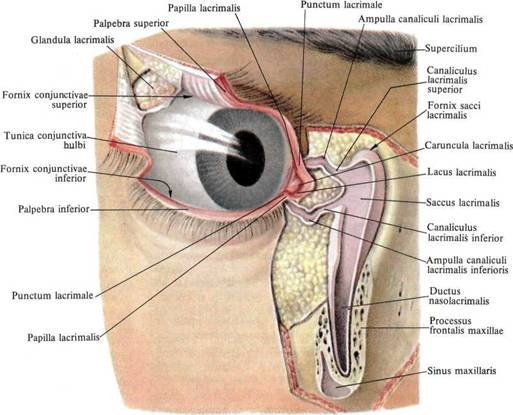
The skin layer of both palpebral grooves is no more than 1 mm thick; histologically, both eyelids differ in similar parameters. If we turn to the anatomy of the skin fold of the lower eyelid, then it consists of two types of layers.
| Formation name | Layer characteristics |
| Outer layer | The bottom plate is crowned with a strip of ciliary hairs, which also protects the organ of vision. The layer is a combined structure consisting of a thin area of skin and a large number of muscles that contribute to the mobility of the lower eyelid. Due to the thinness of the outer skin of the furrow, it is very sensitive to injury and the effects of eye diseases. This is manifested by rapidly emerging edema, hemorrhages, subcutaneous signs of emphysema. |
| The inner layer | The layer is located under the outer skin, it is the inner mucous membrane, which is in direct contact with the surface of the eyeball. This layer is represented by subcutaneous tissue saturated with important muscles. The extensive muscular apparatus provides a reflex of closing and opening the eyelids, the function of blinking or closing the eyes, as well as the functioning of the regulatory mechanism for the distribution of the light flux. |
The lower eyelid is a structure closely related in structure to the anatomy of the midface. Therefore, the transformation of facial structures is able to change the appearance of the fold, framing the organ of vision from below.
The inner frame of the lower eyelid plate consists of cartilaginous tissue with sebaceous glands (meibomian) located in it. In the deep layer of the eye septa, there is a dense cartilaginous structure in the form of a strip of collagen tissue.
Its purpose is to maintain the shape of the eyelid and the strength of its tissues. It is the collagen substance that is the location of more than 20 meibomian glands, which provide the production of fatty secretions for the smooth closure of skin folds.
From the inside, the cartilaginous area is tightly connected to the conjunctiva, which is a mucous membrane that produces lacrimal secretions. A viscous liquid is necessary to evenly moisturize the eyeball so that the eyelids can glide smoothly over it.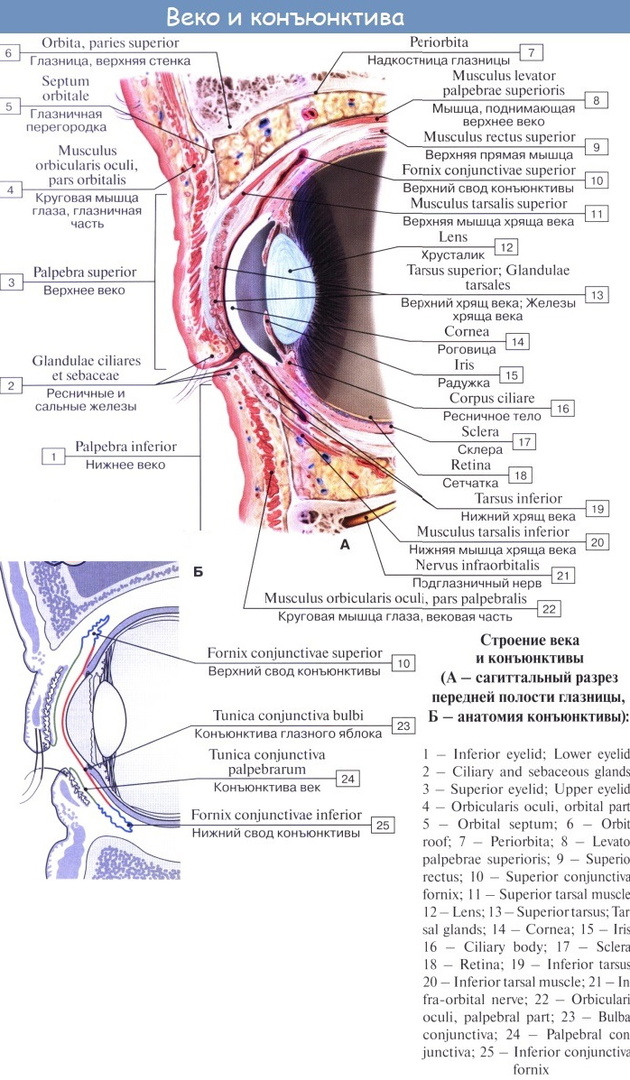
The cartilaginous layer of the lower eyelid consists of four circular muscle elements:
- the palpebral muscle circle is responsible for the function of closing the furrows and blinking, helps the even distribution of the tear fluid;
- the joint work of the palpebral muscle group with the orbital element forms the reflex ability to tightly close the eyes;
- the circle of the lacrimal muscles consists of fibers that envelop the surface of the lacrimal sac, which creates the possibility of outflow of the lacrimal fluid;
- the bulbs of the roots of the eyelashes and the exits of the meibomian glands are braided by the fibers of the ciliary muscle, thanks to their contractions, portions of the secretion are released.
The levator muscle in the thickness of the lower eyelid, unlike the upper one, is absent, and the cartilage is a dense collagen substance. The semilunar form of the cartilage is identical on both eyelids, but the semicircle is much smaller on the lower part.
The front surface of its cartilage is covered with a layer of fatty tissue, the connection between them is weak. The back is tightly linked to the mucous layer of the conjunctiva. Its layer is penetrated by the glands of the lacrimal secretion necessary for the stability of the tear film, which reliably protects and moisturizes the cornea.
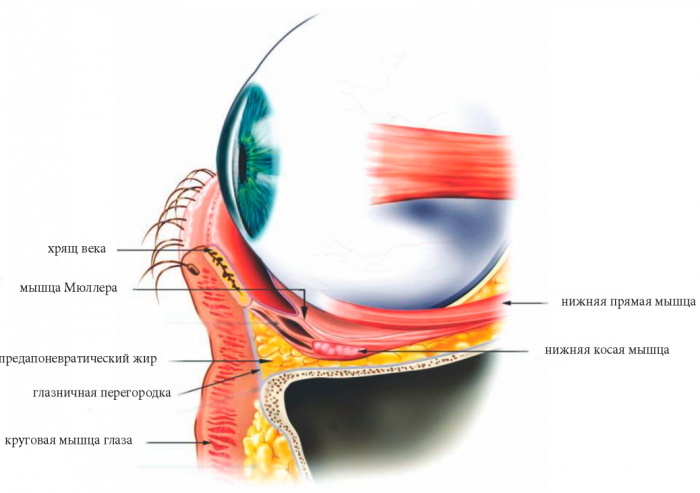
The state of constant humidity helps to remove foreign bodies from the surface of the eyeball. In addition, due to the lower auxiliary apparatus, moisture is distributed inside the lacrimal canal between the two eye sacs - the conjunctival and the lacrimal.
Diseases
The lower eyelid can be pulled down, this property is provided by the operation of the mechanism of the eye muscle, although it is poorly developed. However, the state of balance can be disturbed due to the development of pathological changes that can affect the layers of the lower palpebral groove.
Symptoms of defeat
The manifestations of diseases depend on the type of disorders, but external symptoms are clearly visible, and in both eyelids:
- the condition of edema is not always associated with an ophthalmic diagnosis (for example, kidney disease);
- sensations of itching and pain along with reddened skin are clear signs of an inflammatory process;
- the appearance of a local thickening of a thin strip of tissue that protects the eye requires urgent identification of the cause;
- the unusual appearance of the skin furrow at the base of the eye often indicates the onset of nervous disorders.
Pathological changes affecting the lower eyelid may be accompanied by a febrile condition, eyelid non-closure syndrome, which threatens to dry out the conjunctiva.
The main reasons for the development of diseases of the eye-protecting barrier include:
- pathological activity of skin mites due to weakening of the immune system;
- various types of allergic reactions (seasonal, medicinal, food);
- infection of the body with viruses and microbes, the action of chemical reagents;
- disorders of the cardiovascular and endocrine nature, hormonal imbalance.
At the slightest discrepancy in the external parameters of the lower eyelid, you should immediately seek the help of an ophthalmologist. Only a specialist is able to determine the type of eye disease that caused the dangerous symptoms. Among the most common pathologies of the palpebral sulcus are the following conditions.
Inverted eyelid
The inverted position of the fold leads to a violation of the physiological protection of the mucous membrane of the organ. The anomaly can occur due to age-related weakening of the facial muscles, trauma or burns of the eyeball, the appearance of a neoplasm. The progress of the destructive process leads to the exposure of the mucous membrane, causing the conjunctiva to dry out along with the stratum corneum.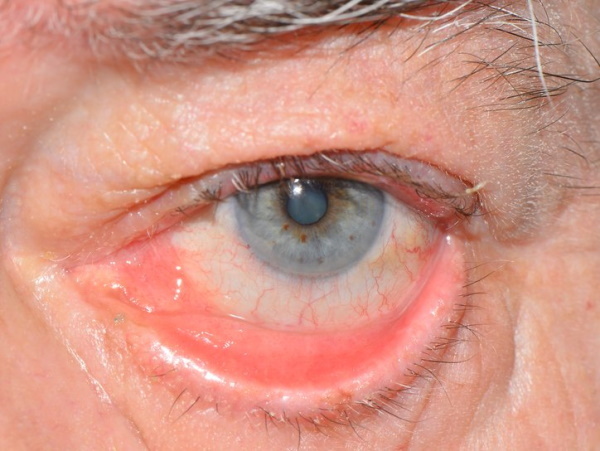
In addition, the palpebral fissure does not fully close, which is also observed with a volvulus of the lower eyelid. In both cases, the patient suffers from constant lacrimation, but with volvulus, the cause of lacrimation is irritation of the mucous membranes by the inward eyelashes.
The danger of meibomite
The lower eyelid is the location of the cartilaginous glands. The inflammatory process can affect the meibomian glands due to clogging of the sebaceous ducts. The main cause of the pathology is the colonization of tissue structures by pyogenic microbes, most often staphylococci.
The course of meibomite can be acute, then the process is accompanied by vivid symptoms of pain, signs of redness and swelling. The chronic form of ophthalmia is recognized by the thickening of the lower eyelid plate.
A characteristic symptom of the chronic course of the disease is the formation of a cystic formation in the thickness of the gland, in medicine it is called chalazion. Outwardly, the cyst resembles a traditional barley in the upper eyelid, but before choosing a method of treatment, the doctor must determine the nature of the structure of the chalazion.
Why does the eyelid twitch
Involuntary twitching of the muscle tissues of the left or right gas is considered a fairly common problem, regardless of age.
In medical practice, the phenomenon is denoted by the term "myokymia", and due to its characteristic manifestation, the syndrome is called a nervous tic. The upper eyelid often suffers from twitching, this is due to the larger area surrounding the eye of the upper strip, more saturated with nerve endings.
If myokymia appeared in the lower eyelid, then the main causes of the anomaly include a weakening of the immune function systems and the influence of hereditary predisposition, as well as susceptibility to high neuro-emotional loads.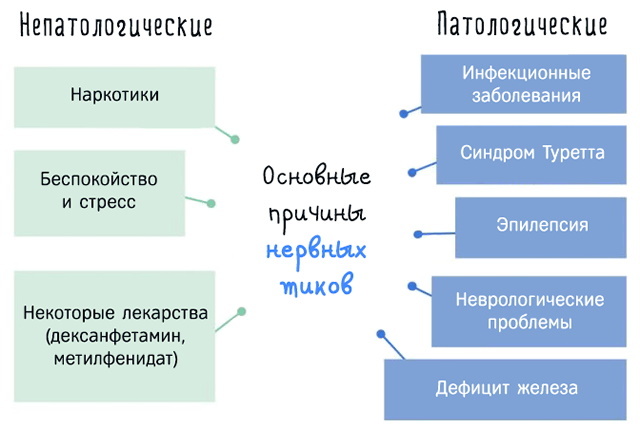
Other reasons include the following provoking factors:
| Problems | Details |
| Excessive eye fatigue | Exposure to increased loads due to reading in transport, poor lighting, prolonged work at the monitor. Eye fatigue provokes concentration on small and barely noticeable details, preventing the muscles from relaxing. |
| Wrong way of life | Abuse of coffee, energy drinks, alcohol causes a strong mental strain. Lack of sleep and vitamins affects the state of the nervous system, which leads to the appearance of nervous disorders. |
| Presence of diseases | Ophthalmic pathologies (conjunctivitis, blepharitis, convulsive spasm on one side of the face) are accompanied by muscle damage. Eye twitching syndrome is preceded by swelling and redness of the lower sulcus. |
| Cerebral circulation problems | The cause of a nervous tic can be ischemia, signs of atherosclerosis or vascular thrombosis, trauma to brain structures. Myokymia of the lower eyelid accompanies the tumor process or neuralgia of the facial nerve. |
Due to mechanical injury to one of the palpebral grooves, the muscle network is damaged, which is manifested by twitching of the lower or upper part of the eye. The appearance of an eye defect is preceded by swelling and redness of the eyelid, a feeling of sand in the eye.
Treatment methods
An ophthalmologist treats suspicious changes in the surface of the eyelids. To clarify the diagnosis and select the appropriate technique, the patient is prescribed an additional examination of the organs of vision. Based on the results of the diagnosis, the doctor draws up a scheme of therapeutic measures with the selection of an individual dosage and type of medication.
The lower eyelid is a mechanism that, paired with the upper skin strip, protects the easily wounded anterior membrane of the eye. Therefore, the problem of an everted eyelid is solved by removing the defect surgically. The operation is also necessary with frequent relapses of the chronic form of meibomite for excision of the hardened capsule of the chalazion.
In the case of pulsation of the lower eyelid, caused by neuroses and stress, therapy with sedatives is prescribed. Various types of ophthalmia, which caused twitching at the base of the eye, are treated according to traditional regimens, recommending the saturation of the patient's body with vitamins. Problems with cerebral circulation and the consequences of trauma require long-term medication courses.
Medicines
The choice of specific types of drugs depends on the factor that provoked the disease of the lower eyelid.
The action of the drugs is aimed at eliminating the cause of the abnormal condition: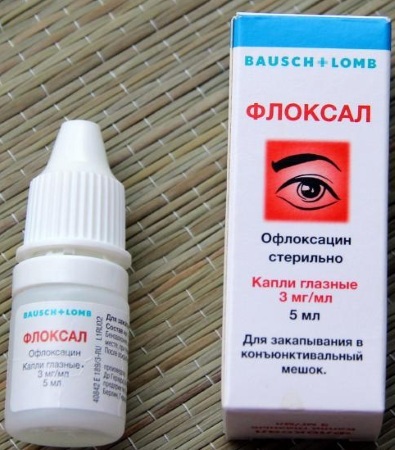
- Diseases of an infectious and bacterial nature are treated with eye drops based on antibacterial compounds. The type of antibiotic in the solution is selected individually. Floxal eye drops are recognized as the most popular; their composition acts destructively against most types of bacterial agents.
- The inflammatory process on the surface of the lower eyelid or in its thickness is blocked with the help of hormonal ointments. The most effective hormonal agent is considered to be an ointment with dexamethasone, followed by hydrocortisone ointment.
In severe conditions, therapy is carried out with combined drugs - an antibiotic plus a hormonal substance. Moreover, it can be not only ointments, but also drops. To eliminate purulent exudate, disinfectant solutions (Chlorhexidine, Furacilini, Miramistin) are used.
Compresses
Self-medication of ophthalmic diseases is unacceptable, such actions can impair vision, have unpredictable consequences.
In the initial phase of inflammation, compresses with decoctions of anti-inflammatory herbs (calendula, chamomile, sage) will bring relief. A tea bag steamed with boiling water can be applied to the affected eye, but only after it has cooled down to a comfortable temperature.
Important. The procedure for applying compresses is not relevant for every type of eye pathology, therefore it is better to consult a doctor about its necessity. The compresses themselves should not be hot, and they should not be kept for long.
Folk remedies
Despite the harmlessness of home treatment, its nuances should also be discussed with a doctor.
To quickly get rid of the twitching of the lower eyelid, traditional therapy can be enhanced using folk remedies:
- soothing teas made from collections of medicinal herbs - valerian, motherwort, lemon balm;

- lotions with honey infusion on a pulsating eyelid, after 20 minutes the lotion is removed by washing the eye with chamomile infusion;
- a decoction is prepared from rosehip berries, its saturation with vitamin C has a general strengthening effect.
For any eye problems, not only the help of vitamin drinks is needed to strengthen the immune system. It is important to give up bad habits and long loads on the organs of vision, as well as enrich the diet with healthy products.
Lifestyle
For patients undergoing treatment for myokymia, as well as other problems with the lower eyelid, ophthalmologists are advised to reconsider their lifestyle. Twitching eyelid syndrome is the result of instability of the nervous system caused by frequent stress, regular lack of sleep, and strong psycho-emotional shocks.
To avoid relapses, it is important to stick to your daily routine, avoid overwork, avoid drinking high-dose beverages, and not drink too much coffee.
Eyelid video
The structure and function of the eyelids:


