The term "dysthymia"( dysthymic disorder, chronic or minor depression) has received its modern name relatively recently, although the state itself has been repeatedly described in detail in Russian fairy tales( the image of Princess Nesmeyana), as well as in classical literature.
The term "dysthymia"( dysthymic disorder, chronic or minor depression) has received its modern name relatively recently, although the state itself has been repeatedly described in detail in Russian fairy tales( the image of Princess Nesmeyana), as well as in classical literature.
Lightweight and accurate pen. Pushkin once wrote: "... similar to English spleen, in short: the Russian spleen," having previously blamed psychiatrists: "An ailment whose cause it would be long ago to find. ..".For in the year 1831, when "Eugene Onegin" saw the light, the cause of dysthymia as a variant of depression was not yet established. As there were no versions about the causes of the depression itself.
Contents
- In terms of terminology
- In the thirds of the terminology
- About cyclotymia
- Who falls in the risk group
- Do not want to, can not do it
- Classification and features of the
- clinic About the concomitant disorders
- Diagnostic criteria and evaluation methods
- Therapy methods
- About the effects of dysthymia and dysthymia
- wait, suffer and not cry under the moon
- In the thirds of the terminology
In the thorns of the terminology
The term itself was proposed by psychiatrist Robert Spitzer - not subject to English spleen by an American - and introduced toas the nomenclatural unit in the third edition of the 1987 Diagnostic and Statical Manual of Mental Disorders( DSM-III).
Spitzer, the father of the modern systematics of mental disorders, cited this term to replace the outdated concept of "neurotic depression" and nothing explaining psychiatry, which, moreover, was considered part of neurasthenia.
In this day the actual DSM-V dysthymia is already directly marked by the category: permanent depressive disorder. In ICD-10, the disease corresponds to the code F34.1.
Why is dysthymia called small depression? Because unlike the present depression, called large, manifestations of the disease are less significant and noticeable. Born with dysthymia, even accustomed to consider dysthymnost an inherent feature of his character and personality.

About cyclothymia
But in addition to the big depression there is also such a thing as cyclothymia. Is there a significant difference between these two psychiatric terms?
Cyclotemia reflects the "circling" twin episodes-phases of an affective disorder with mood swings from indistinct depression to hypertension, and these phases are usually separated by periods of mental health.
Dysthymia, the main criteria of which is moderate severity of symptoms for a minimum of two years, is only one of the facets of the "polyhedron" of depression.
It is worth turning the dysthymic disorder slightly in the direction of alternating episodes of depression with phases of excessively elevated mood and this is already manic-depressive psychosis, when viewed from a different angle( the same background, but the amplitude of mood swings is less), cyclothymia occurs.
About recurrent depressive disorder, thought occurs with episodic attacks of significant depression, not accompanied by episodes of violent activity against the background of a major mood. And only a long, almost constantly reduced mood in combination with signs of asthenia or characterological features indicate a distemper of behavior.

Who falls into the risk group
Despite many years of research and research on dysthymia, so far not so much has been established, as psychiatric science and  would like to practice.
would like to practice.
It is for certain established only that in the genesis of the disease the role of the neurotransmitter serotonin is archived. This is either a variant of its deficiency, or inhibition( cessation or sudden deceleration) of the transfer of a given chemical agent, leading to the onset of a depressive disorder.
Presumptive etiological factors are availability:
- external causes of the category of chronic obscheomatic pathology, metabolic disorders due to imbalance and inadequacy of nutrition, chronic stress effects, as well as the absence in the daily routine of such a thing as rest;
- personality characteristics and individuality of the structure of the nervous system due to genetics;
- causes psychological reasons, such as the costs of upbringing in the form of excessive severity of the father or mother, or the loss of one or both parents in childhood, being in social isolation or in a closed children's institution.
It would not be desirable, it is not possible, it is not done
The general or common symptomatology of a dysthymia keeps within a classical fairy-tale image of princess Nesmeyany:
- unreasonable tearing;
- the desire for solitude;
- taciturnity;
- constant mourning is a feeling of hopeless despair, experienced in the present time, coupled with a constant analysis of past mistakes and dull pessimism in looking at the future;
- uncertainty about own capabilities due to low self-esteem;
- a sense of inability to fulfill basic requirements and norms of everyday life;
- difficulty concentrating;
- low daily activity due to chronic energy deficiency;
- night insomnia;
- lack of pleasure from sex and craving for others, considered pleasurable for everyone, classes( anhedonia).
 Dysthymic type of personality is the walking image of exhaustion, exhaustion, chronic fatigue, almost physically palpable weakness. It is always the pose of a drooping plant, lacking in strength and energy.
Dysthymic type of personality is the walking image of exhaustion, exhaustion, chronic fatigue, almost physically palpable weakness. It is always the pose of a drooping plant, lacking in strength and energy.
In cases of rare communication, in view of their gloominess, apathy, grumbling, irritability, anguish and tediousness, they make an impression on the interlocutors of incorrigible hardened pessimists who regard current life difficulties as natural phenomena that should not even be attempted to overcome or counter them.
Classification and features of the
Clinic Emerging most often in childhood or adolescence and more common among women, the dysthymic disorder can be of two kinds:
- somatized( catesthetic);
- characterological( characterogenic).
If the first species is a variant of the course of the disease with predominantly somatic-asthenic vegetative manifestations, then in the second, the pessimistic-hypochondriacal personality warehouse predominates.
Somatized dysthymia is characterized by complaints of persistent loss of strength, accompanied by severe palpitation, dyspnea without significant physical exertion and at rest, frequent crying, intermittent sleep, constipation and intestinal discomfort, trembling in the hands and their cooling, sweating and similar vegetative disorders.
In the mood, the predominant symptom is the irrationality anxiety that provokes the development of a feeling of anguish, depression and depression, accompanied by somatic sensations of burning and "icy cold" in the chest and heart area.
With the progression of the state to the forefront, asthenic indicators come out with further aggravation of anomalies in bodily sensations; in the mental sphere, the ideas of hopelessness and despair become dominant; in another version, scrupulous self-examination of one's own health with the inevitable outcome in cardio- or carcinophobia.
Characteristic( characterological) dysthymia inherent features inherent in the constitutional-depressive personality structure, namely susceptibility:
- anhedonia;

- "melancholy";
- pessimism( as if innate);
- from the whole volume of thoughts there is a predominance of meditations about the meaninglessness of one's own existence;
- expecting from the future exclusively problems and sorrows;
- remorse about the part in the past "fatal", "irreparable" mistakes, in fact - imaginary;
- of excessive sensitivity to the most insignificant criticism and other insignificant negative factors-irritants, which provoke thoughts of a suicidal orientation.
The chronic state of apathy forms the "loser complex", which becomes the "ideological headquarters" of the depressed-decadent worldview, the expression of which is gloomy silence or taciturnity, constant discontent with others, capable of alienating even the closest and most devoted people from the sick person.
Patients with dysthymia are characterized by their inability to manifest initiatives and to long-term volitional acts, extreme indecision and suspiciousness. Doing any kind of work causes not interest, but only dislike and quick fatigue, and mental activity, despite highly developed intellect, leads to extreme fatigue due to the colossal strain of thinking abilities.
Oppression is also manifested in outwardly traces of inhibition in movements and facial expressions: mournfully lowered corners of the mouth, slowness of seemingly meditative gait, stinginess of gestures.
For all its repulsive nature, patients do not consider themselves to be such, and when pointing to signs of a mental disorder arrogantly declare their own meanness of the pointer.
About concomitant disorders
In addition to dysthymia, the patient may also suffer from a parallel existing nervous pathology of an organic or other nature:
- alcoholic or narcotic;
- is somatogenic.
These can be disorders:
- conversion;
- anxious-depressive( with frequent panic attacks, generalized anxiety states).
Diagnostic criteria and assessment methods
 In the diagnosis of dysthymia, the criteria approved by the IBC of the 10th revision and DSM-5, largely overlapping and described above, should be used.
In the diagnosis of dysthymia, the criteria approved by the IBC of the 10th revision and DSM-5, largely overlapping and described above, should be used.
Difficulty in diagnosis is a feature of the disease, because a painful condition can occur not only in young, but also in middle age, and even in involutionary.
Complicates the case and the patient's conviction that he does not have a psychopathology that began with childhood, but there are only individual traits that explain everything, so he simply does not come to ask for help from a specialist doctor.
The presence of concomitant disorders, veiling dysthymic disorder, also serves as an obstacle to its detection.
Purely clinically chronic depression differs from similar forms of the disease by the lack of action, simultaneously disabling not only the mental and psychic spheres of life, but also the motor, as in the case of major depression.
In the differential diagnosis, the following disorders are cut off:
- major depressive disorder;
- cyclothymia;
- episodes of mania;
- schizophrenia;
- is a delusional disorder;
- hypothyroidism and other hormonal dysfunctions;
- depression as a result of abuse of alcohol-containing beverages, narcotic or psychotropic drugs, including drugs.

Not only methods of clinical psychiatry, but also instrumental and laboratory methods of investigation are able to help diagnose:
- MRI( CT) of the brain;
- EEG;
- study of cerebral vessels;
- blood glucose test and similar methods.
Methods of therapy
For successful treatment of dysthymia, it is not enough just to differentiate it from similar pathology - it is necessary, based on the severity of the disease, to outline the range of drugs needed for drug therapy, and also to think about the application of the most promising areas of psychotherapy.
The application of psychotherapeutic methods allows the patient to see not only the whole depth, but at the same time the ephemerality of the sensations experienced, to see the deepest foundations of their existence, and not just to pronounce habitually-unconsciously, that everything is supposedly the will of God. The patient must understand: and mine - too!
Of the specific techniques, the appointment is acceptable:
- relaxation therapy;
- cognitive therapy( personal, then group);
- hypnotherapy;
- ergo and art therapy with elements of psychoanalysis.
It is mandatory to use the method of psychoeducation - enlightenment for the family members of the patient, explaining the nature of the disease with the possibility of healing from it by applying joint efforts with the patient.
But one development of techniques of positive interpersonal communication is not always enough to increase self-esteem and develop self-confidence on the spot of gloomy self-confident estrangement. In case of "aging" of the process, drug therapy can not be dispensed with.

The main category of treatment for minor depression are antidepressants with different mechanisms of action:
- TCAs( tricyclics);
- SSRIs( selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors).
 Representatives of the first category are classic Melipramine( Imipramine), Amitriptyline and Anafranil( otherwise Clomipramine), prescribed in doses adequate to the severity of the condition.
Representatives of the first category are classic Melipramine( Imipramine), Amitriptyline and Anafranil( otherwise Clomipramine), prescribed in doses adequate to the severity of the condition.
The direction of SSRIs is presented by fluoxetine, citalopram, excitalopram, dapoxetine, zymeline, and others.
Psychopharmacotherapy also offers the use of OIMAO-A( reversible MAO type A inhibitors) equivalent in terms of the strength of TCAs exposed by the drug Moclobemide( Auroxom).Its effect allows us to solve two problems at once: to normalize the mood and to correct the negative manifestations of somatovegetatics in somatisated dysthymia.
The pharmacotherapy of characterological depression is usually a combination of moderate doses of antidepressants with neuroleptics, which 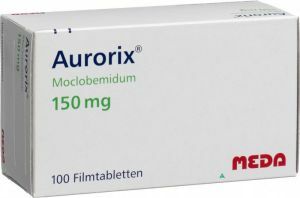 allow you to adjust behavior. It is used Neuleptil or preference is given to the antipsychotics of prolonged action: Haloperidol, Fluansoxol-Depot.
allow you to adjust behavior. It is used Neuleptil or preference is given to the antipsychotics of prolonged action: Haloperidol, Fluansoxol-Depot.
The patient and his immediate circle should be informed that the drugs begin to function after 2-3 weeks from the start of treatment, as well as the need for strict adherence to the regimen and the frequency of medication. For the onset of the effect of treatment, a period of six to nine months is necessary.
It is also important to notify caregivers that antidepressants are not canceled immediately, but with a decrease in dose for 2-3 weeks, which is accompanied by the possibility of light side effects.
Only with the proper implementation of all the recommendations of a psychiatrist can eliminate symptoms of disease manifestations that are relatively easy to treat, reduce the risk of relapse and return the patient to a full life in society.
On the consequences of dysthymia and dysthymia
First of all, the emergence of consequences and complications is due to the period of the disease and the non-recognition of the patient's presence of a mental pathology.
When the disease lasts for more than three years and the onset of the development of violations up to 21 years, the danger of deeper forms of depression( the risk of developing a major depressive disorder) actually increases with the complication of the picture of the condition and the deepening of the patient's social self-isolation.
For limiting the mental and physical capabilities of a person who suffers from a disease a person makes significant restrictions to his life: he has to give up cultural and simply mass events, change work, break off relations with his spouse or with a loved one.
In order not to wait, not to suffer and not to cry under the moon
 Prevention of dysthymic disorders should begin from childhood, and if there are peculiarities and strangeness of behavior, always consult a doctor. A timely disorder of the psyche is amenable to a more rapid correction than a neglected one.
Prevention of dysthymic disorders should begin from childhood, and if there are peculiarities and strangeness of behavior, always consult a doctor. A timely disorder of the psyche is amenable to a more rapid correction than a neglected one.
As for the family, the notorious "holding in the gloves" usually ends with a mutual dislike between parents and children.
And only the full existence of all its members, without harassment, but without connivance with children, can grow into mutual respect and the true friendship of all its generations. And then children will grow up healthy adults.