Content
- What are cocci and their varieties
- When men are prescribed a smear analysis, preparation for the study, an algorithm for taking material
- Norms of indicators in a smear from the urethra
- Reasons for detecting cocci in a smear in men and the accompanying symptoms
- Streptococci
- Diplococci
- Tetracocci
- Sarcinas
- Staphylococci
- Factors that accompany the development of cocobacillary flora
- Do you need additional examinations to make a diagnosis?
- How to treat cocci in a smear?
- Antibiotics
- Medicines that strengthen the body's immune functions
- Antihistamines
- Hygiene and decoction
- Features of the treatment of the established reasons for the increase in cocci with a poor test result
- With sexually transmitted diseases
- In case of disruption of the endocrine organs
- For allergies
- When taking antibiotics
- Possible complications
- Video about cocci in a smear
Cocci are present on mucous membranes any person. With a small amount, their presence in the urogenital tract is not dangerous. However, if in a smear from the urethra in men the number of such bacteria exceeds the norm, and, moreover, an obviously pathogenic flora is detected, then we are talking about an infectious and inflammatory process.
What are cocci and their varieties
Based on their shape, bacteria are classified as rod-shaped - these are bacilli, spiral-shaped - spirochetes, and globular - cocci. In fact, cocci have more shape options: they can be spherical, oval or absolutely round.
Within their class, cocci differ in the structures they form after cell division. Some form pairs, others line up in chains, and others combine into clusters resembling bunches of grapes. Unlike bacilli, cocci do not have flagella for movement and are mostly motionless.
Cocci in a smear in a man are well defined under a microscope due to their characteristic shape and structures. To differentiate cocci by cell wall components, the Gram staining method is used: due to structural features of gram-positive bacteria retain purple aniline dye, gram-negative - no.
The separation of bacteria, and, in particular, the coccal flora according to Gram is of clinical importance. The difference in cellular structure determines their different response to certain antibacterial drugs. Gram-negative microorganisms have an additional outer membrane, which makes them more protected from external influences. For this reason, they are more resistant to antibodies and antibiotics than their gram-positive counterparts.
Most of the cocci that inhabit the mucous membrane of the urogenital tract belong to the gram-positive flora:
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- enterococci;
- peptococcus;
- peptostreptococcus.
These are opportunistic microorganisms. On a healthy mucosa, their number does not exceed 3-4% of all normal microflora. Under unfavorable circumstances, they begin to multiply vigorously, displacing the beneficial flora (bifidobacteria, lactobacilli), which leads to inflammation.
Examples of gram-negative cocci:
- gonococcus;
- veylonella.
Gonococci are pathogenic bacteria that cause infections. Veilonella is classified as a conditionally pathogenic flora.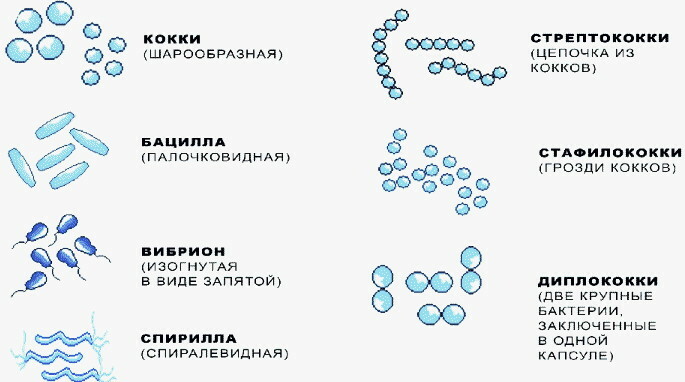
Like other types of bacteria, cocci are divided into aerobes and anaerobes. Aerobic cocci need oxygen to breathe and grow. Anaerobic sugars ferment - and thus receive energy for existence. Facultative anaerobic organisms can live with or without oxygen.
The table shows the division of cocci by morphological and physiological characteristics.
| Type and individual representatives | Gram differentiation | Cell shape and structure after division | Breath type |
| Streptococci. (S. pyogenes, S. pneumoniae) |
+ | Spherical, oval, or lanceolate cells. They form chains of various lengths, in which there can be from 2 to several dozen cells. Peptostreptococci have a similar organization. |
Facultative anaerobes |
| Staphylococci (S. Aureus, S. Epidermidis) |
+ | Are spherical. Form irregular clusters that resemble a bunch of grapes. In a smear, they can occur in the form of single (micrococci) and paired cells. |
Facultative anaerobes |
| Diplococci (Bacteria of the genus Neisseria, Enterococcus faecalis) |
— | In brush strokes, they look like coffee beans paired together. | Neisseria - aerobes Enterococci - facultative anaerobes |
| Tetracocci (Micrococcus luteus, Aerococcus urinae) | + | Round bacteria that form tetrads, that is, assemblies of four microorganisms. | Aerobes |
| Sarcinas (Sarcina ventriculi) | + | When dividing, they are organized into shapes resembling "bales". The structure includes at least 8 cells. | Anaerobes |
| Monococci, or micrococci (Veillonella) | Depends on the type of bacteria | Single cells that separate from each other after the formation of new cells. A single arrangement is simultaneously found in staphylococci, diplococci and tetracocci. | Aerobes or anaerobes |
When men are prescribed a smear analysis, preparation for the study, an algorithm for taking material
A referral for analysis is issued by a therapist, urologist or dermatovenerologist.
The reason for the appointment may be the following circumstances:
- symptoms of an inflammatory disease of the genitourinary sphere;
- preventive examination by a urologist;
- monitoring the state of microflora after prolonged antibiotic therapy;
- suspicion of a sexually transmitted infection (STI);
- infertility.
The study makes it possible to assess the composition of the microflora of the urethra and identify some pathogenic microorganisms. The method used is microscopy. The subject of the study is a smear applied to a glass slide.
To obtain a reliable result, you should:
- Refrain from sexual intercourse for 2 days before the procedure.
- On the eve of taking a smear, washing the glans of the penis should be carried out without the use of detergents.
- Exclude the installation of drugs into the urethra.
- Try not to urinate 3 hours before the procedure, so as not to wash off the biomaterial from the urethra.
A smear on flora from the urethra is taken by a laboratory assistant using a special sterile probe. The collected material is applied to a glass slide, dried and stained. The biomaterial is examined using a light or electron microscope.
Norms of indicators in a smear from the urethra
The urologic smear result form usually contains the following information:
- the nature and amount of microflora (Gram (+ or -) cocci, sticks, coccobacillary flora and diplococci);
- the presence of leukocytes, mucus, key cells and squamous epithelium;
- the presence of fungi, gonococcus and Trichomonas.
Variations are possible in the indicators.
Cocci in a smear in men are normally defined as "single" in the field of view. When a variety of gram-positive and gram-negative microbes are detected in the analyzes, a record is made about the detection of gram-variable or polymorphic flora.
Yeast-like fungi, gonococci and Trichomonas are absent in a normal smear.
Detection of mycelium and yeast spores indicates candidiasis; the presence of "mobile" bacteria - for trichomoniasis. Gram-negative diplococci with intracellular location are identified as possible causative agents of gonorrhea - bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
In a smear of a healthy man, the number of epithelial cells is single. An increase in their number to 10 in the field of view is called "moderate"; up to 20 is denoted by the word "a lot"; more than 25 - "abundant". If epithelial cells have an altered shape and size, there are many of them - an inflammatory process is suspected.
Key cells are epithelial cells, on the surface of which cocci are located. Their presence in the smear is characteristic of local dysbiosis.
The presence of mucus in a normal smear: not detectable or "scarce".
In the study, attention is paid to the blood cells. Normally, in a male smear, leukocytes do not exceed 5 units per field of view. An increase in their number indicates an inflammatory or infectious process: more than 4 units of leukocytes in the field of view indicate urethritis, more than 10 - about gonorrheal infection.
When decoding, the following violations of the norm are also taken into account:
- The combination of an increased number of lymphocytes and the presence of epithelial cells is a diagnostic sign of chronic urethritis.
- Damage to the mucosa is indicated by an increase in the number of leukocytes, erythrocytes and epithelial cells. The cause may be ulceration or trauma to the urethra, including caused by loose sand or small calculi with crystalluria, as well as neoplasms.
- "Small rods" arranged in an orderly manner on the cells of the epithelium are most likely gardnerella.
- Intracellular gram-negative diplococci, plus an increase in leukocytes with a small amount of normal flora, are likely to indicate gonorrheal lesions.
Reasons for detecting cocci in a smear in men and the accompanying symptoms
Coccal flora can exist in the male urogenital tract without causing any abnormalities. But under appropriate conditions, for example, with a weakening of immunity, these bacteria begin to multiply intensively, and become visible in a smear from the urethra.
A nonspecific bacterial infection with a high titer of coccal flora is often accompanied by a specific one - gonococcal or Trichomonas.
The reason for the appearance of a large amount of banal microflora in the urethra may be sexual contact with a woman suffering from inflammatory diseases with a high level of bacterial contamination of the vagina (erosion of the cervix, vulvovaginitis). In some cases, microbes are brought into the urethra with blood flow from various foci of inflammation that are located in other organs.
The pathological growth of the coccal flora in the genitourinary tract is accompanied by a number of symptoms:
- burning and pain during urination;
- genital itching;
- soreness in the lower abdomen;
- discharge from the urethra.
Even before the appearance of local symptoms, a person feels weakness, fatigue, and increased sweating. Temperature rise is possible.
Streptococci
Colonization by streptococci of the mucous membrane of the urogenital tract in men causes bacterial forms of urethritis and prostatitis. With urethritis, the walls of the urethra are affected, with prostatitis, the tissues of the prostate gland.
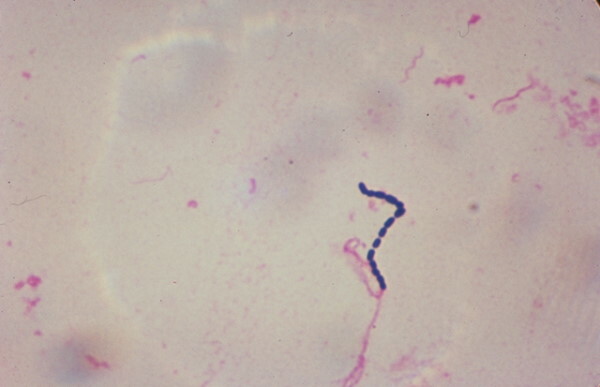
Urethritis, in turn, can be complicated by balanoposthitis. The disease is characterized by purulent discharge from the opening of the foreskin, itching and burning in the area of the glans penis. The inguinal lymph nodes are enlarged.
When high pressure in the urethra (for example, with sexual arousal) forces infected urine to move along the vas deferens to the epididymis, its inflammation develops - epidymitis. The man complains of pain in the testicular area.
Diplococci
Gram-negative diplococci that can be found in a smear are gonococci. They parasitize the mucous membranes lined with columnar epithelium and cause gonorrheal infection. Most often, gonorrhea manifests itself in the form of urethritis with discharge from the urethra: at first scanty, then abundant, purulent, yellowish-green in color.
Enterococci, in particular Enterococcus faecalis, are found in the form of pairs in the smear. Inhabiting the intestines, it behaves like a symbiotic microorganism. When colonizing the urinary tract, fecal enterococcus becomes one of the causative agents of inflammatory diseases. Enterococci account for up to 7% of all cases of prostatitis.
Tetracocci
Such a representative of tetracocci as Aerococcus urinae is associated with infections of the urogenital tract. The bacterium has the ability to aggregate platelets. When the infection spreads, it causes endocarditis in elderly patients.
Sarcinas
Clusters of cocci in the form of "bales" are characteristic of the skin and large intestine. 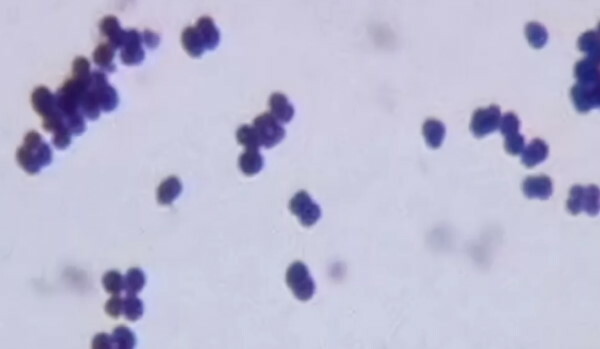 Cocci-sarcins are mainly saprophytes, that is, non-pathogenic microorganisms, and do not cause diseases in humans.
Cocci-sarcins are mainly saprophytes, that is, non-pathogenic microorganisms, and do not cause diseases in humans.
Staphylococci
An increased number of staphylococci in the urinary tract causes cystitis, urethritis and balanoposthitis.
Staphylococcus epidermidis is a common inhabitant of the skin and mucous membranes. The microbe produces substances that inhibit the growth of pathogenic flora. When his own growth gets out of control, he himself becomes the cause of purulent-inflammatory diseases.
Factors that accompany the development of cocobacillary flora
Coccobacillus include bacteria, which in their structure occupy an intermediate position between bacilli and cocci. In a smear from the urethra, it can be chlamydia and gardnerella. The presence of abundant coccobacillary flora indicates the possibility of chlamydia or gardnerellosis.
The main route of infection with chlamydia is sexual, and during sexual contact, only 1 person out of 4 becomes infected. The likelihood increases with frequent changes in sexual partners. Another way of transmission of infection is contact-household: a bath, the use of common hygiene products. Chlamydia is often associated with gonorrheal infection.
Gardnerella are conditionally pathogenic bacteria that are present in the body of any person and are activated under favorable conditions for him.
The impetus for the reproduction of gardnerell can be:
- a drop in immunity as a result of past diseases - influenza, SARS and other infections;
- taking antibiotics of a wide spectrum of action, hormonal drugs, cytostatics.
- flaws in personal hygiene.
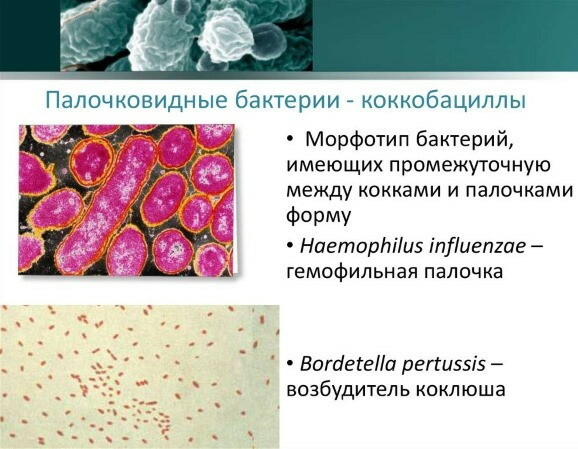
When detecting coccobacilli in a smear, additional tests are required to clarify all pathogens.
Do you need additional examinations to make a diagnosis?
Cocci in a smear in men indicate the presence of inflammation and only partially give an idea of a possible causative agent of infection. For its full identification, PCR diagnostics is used, which allows you to determine the pathogenic agent in the urethral discharge by its DNA.
They also use a cultural research method - bacterial inoculation. It not only makes it possible to see the "portrait" of the pathogen, but also determines its sensitivity to the antibiotic.
Additional research may be needed to clarify the site of inflammation. In addition to the urethra, the pathological process is often localized in the testes, seminal vesicles, or the prostate gland.
The result of a urological smear is assessed taking into account additional data - clinical, instrumental and laboratory. Urinalysis and ultrasound of the genitourinary system are informative for the diagnosis.
How to treat cocci in a smear?
If the cocci in the smear do not exceed "single" values, treatment is not required. Otherwise, it is necessary to suppress the excessive growth of pathogenic bacteria. For this, antibiotic therapy is carried out in combination with local treatment and measures to increase immunity.
Antibiotics
A feature of urogenital infections is the association of infectious agents, that is, a combination of 3-5 pathogens.
Therefore, the main component of therapy is antibacterial drugs of a wide spectrum of action, which make it possible to simultaneously act on different types of flora:
- tetracyclines (doxycycline);
- macrolides (Azithromycin, Roxithromycin, Josamycin);
- fluoroquinolones (Ciprofloxacin);
- cephalosporins (ceftriaxone);
- Rifampicin;
- Clindamycin.
Various dosage forms and their combinations are used: injections, tablets, ointments. The therapy is carried out under the supervision of clinical and laboratory examinations.
Despite the "universality" of broad-spectrum antibiotics, they still differ in the degree of effectiveness of the impact on a particular pathogen. So, Clindamycin reduces the number of cocci well, but the causative agent of gonorrhea is resistant to this antibiotic. Enterococci, on the other hand, have protection against certain aminoglycosides and beta-lactam antibiotics (cephalosporins and penicillins).
Coccal flora is the main cause of nonspecific urethritis. The drugs of choice in this case are macrolides and tetracyclines. Fluoroquinolone drugs are also used. Penicillins and sulfa drugs are not used, since the main causative agents of urethritis caused by opportunistic flora are not sensitive to them.
Medicines that strengthen the body's immune functions
For chronic forms of infection, taking medications that strengthen the immune system can help. They enhance the effect of antibiotic therapy and shorten the duration of treatment.
To maintain the strength of the body, take:
- Vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Herbal immunomodulators (Immunal and other echinacea preparations).
- Interferon inducers.
In the presence of concomitant autoimmune diseases, stimulation of the immune system is undesirable.
Antihistamines
Drugs of this series are used in the treatment of allergic urethritis. The disease develops in people with a tendency to hypersensitivity reactions. The external manifestations of the disease resemble bacterial urethritis. Correct diagnosis of the etiology of the disease is important, since the use of antibiotics can only worsen the condition.
Microscopy of a smear from the urethra reveals a large number of eosinophils, which indicate the allergic nature of the process. In addition, mucus, granulocytes are detected, but bacteria in the smear are not detected.
Treatment is reduced to the elimination of the allergen and the injection of antihistamines.
Hygiene and decoction
Smegma, which accumulates in the cavity of the preputial sac of the glans penis, is an excellent breeding ground for bacteria. Therefore, it is important to monitor compliance with the rules of personal hygiene: take a shower regularly, rinsing the head and foreskin.
With balanoposthitis and urethritis, local therapy is indicated in the form of applying antibacterial ointments and solutions. In the presence of abundant discharge from the urethra, it is recommended to rinse it with a solution of ethacridine lactate and furacilin, instill collargol.
Prescribe douching with decoctions of chamomile, celandine or calendula.
Features of the treatment of the established reasons for the increase in cocci with a poor test result
In various conditions of the body and concomitant diseases, the treatment of coccal infection has its own characteristics.
With sexually transmitted diseases
Cocci in a smear in men indicate the presence of a bacterial infection. Quite often, non-specific flora accompanies STIs.
So, gonococci activate conditionally pathogenic flora (streptococci and staphylococci) and create a breeding ground for concomitant infections - Trichomonas, mycoplasma, chlamydia and gardnerella. In this case, appropriate antibacterial treatment is selected. The choice of drugs and their combinations depends on the type of infectious agent.
In the treatment of gonorrhea, cephalosporins are used in combination with Doxycycline for 7 days with uncomplicated infection.
For the treatment of trichomoniasis, antiprotozoal agents are used, that is, drugs that can kill protozoa: Metronidazole, Tinidazole, Tiberal. Antibiotics are used in the presence of a concomitant genital infection.
Chlamydia requires 2-3 weeks of antibiotic therapy. Macrolides are used for treatment, since only this type of antibiotic is able to penetrate into the cell - the habitat of chlamydia. These drugs include Erythromycin, Roxithromycin, and Azithromycin. The "new generation" macrolides - Spiramycin and Josamycin - have the same mechanism of action as Erythromycin, but are safer and have better bioavailability. During treatment, limit the use of dairy products.
For the treatment of gardnerellosis, Doxycycline is used in combination with antiprotozoal drugs. The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks. It is important to complete the treatment, otherwise the disease may take a latent form and manifest itself in a few years.
The therapy is performed with both partners.
During treatment, you have to put up with a number of restrictions: alcohol and sex life are prohibited. Until complete recovery, you can not swim in the pool.
In case of disruption of the endocrine organs
Endocrine pathologies may be accompanied by an imbalance in the microflora of the mucous membranes of the genitourinary tract. So, nonspecific balanoposthitis in many cases serves as an indicator of diabetes mellitus. In this case, the appointment of drugs to lower blood glucose levels is required.
When choosing antibiotics for oral administration, the presence of sugars in the composition of excipients is taken into account. Autoimmune thyroiditis and type 1 diabetes mellitus require caution when using immunity-enhancing agents.
For allergies
In most cases, in the treatment of coccal infection, it is impossible to do without antibacterial drugs. In this case, antibiotics quite often cause hypersensitivity reactions. If allergic symptoms are limited to skin rashes, antihistamines compatible with them are taken in parallel with the antibiotic. In severe forms of an allergic reaction, immediate withdrawal of the antibiotic is required.
Before starting antibiotic therapy, it is recommended to conduct a sensitivity test to the prescribed drug in people prone to allergic reactions. As a sample, the antibiotic is injected subcutaneously in liquid form or a small amount is applied to the injection site. Then they look at the reaction of the skin.
When taking antibiotics
Before treatment, it is advisable to conduct an analysis of the sensitivity of the flora to an antibiotic and, with its help, select the most effective drug in a suitable dosage. In addition, if it is necessary to simultaneously take antibacterial drugs for the treatment of other infections, the peculiarities of the interaction of antibiotics are taken into account.
To prevent the infection from becoming chronic, you should adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen. In no case should you stop taking the medicine immediately after the disappearance of clinical symptoms.
Possible complications
With inadequate therapy or an untreated inflammatory process, symptoms may subside, but they reappear with a decrease in immunity or in the presence of provoking factors. Urogenital coccal infection eventually spreads to adjacent organs and affects the prostate gland and testicles.
A protracted course of the disease leads to cicatricial changes in the epididymis and inflammation of the seminal vesicles, which threatens infertility. Chronic urethritis leads to narrowing of the urethra, kidney and bladder disease.
The coccal flora found in the smear serves as a signal that further examination is necessary. Correct diagnosis and timely treatment will avoid adverse consequences for men's health.
Video about cocci in a smear
Cocci in a smear: