Content
- Who is predisposed to developing schizophrenia?
- The first signs of disorder
- Obvious symptoms of schizophrenia
- Catatonic form
- Paranoid form
- Hebephrenic form
- Primitive (simple) form
- Diagnosis methods
- Clinical and anamnestic examination
- Analysis of mental status
- Assessment of external signs in a patient
- Analysis of symptoms of the "small circle"
- Analysis of the symptoms of the "big circle"
- Psychological tests to detect schizophrenia
- How to determine schizophrenia by instrumental and laboratory methods
- MRI
- Neurotest
- Neurophysiological test system
- Differentiating schizophrenia from somatic diseases
- Schizophrenia Symptom Videos
Differential diagnosis of schizophrenia is of key importance for reducing the frequency and severity of exacerbations, stopping attacks, prolonging remission in an incurable mental disorder. It is possible to determine the disease in a person using MRI, by external signs and behavioral tests.
Who is predisposed to developing schizophrenia?
The etiological factors of severe psychiatric syndrome, often accompanied by somatic symptoms, have not been established for certain. Schizophrenia is considered a multifactorial disorder.
The pathological process of changing consciousness occurs under the influence of a number of endogenous or exogenous factors of predisposition, presented in the table.
| Predisposition category | Characteristics and features |
| Genetic factor | It was found that with schizophrenia in close relatives, the risk of developing a mental disorder increases by 10-15%, which is 20 times more than the average population probability. |
| Perinatal complications | A predisposition to schizophrenia is observed in patients with intrauterine infection with cytomegalovirus, neurosyphilis, and toxoplasmosis. In women, after a burdened childbirth, the likelihood of developing a mental disorder increases. |
| Social conditions | Researchers note a stable correlation of the occurrence of schizophrenia with place of residence, strong emotional turmoil, and the level of financial well-being. Rural dwellers are less likely to be diagnosed with mental illness than urban dwellers. |
| Early psychological trauma | People who have been subjected to physical or sexual abuse, psychological pressure in childhood are predisposed to schizophrenia. Some experts are inclined to believe that the development of the disease depends on the style of upbringing, the characteristics of family relationships. |
| Harmful addictions | People suffering from chronic alcoholism, drug addicts and substance abusers are predisposed to schizophrenia. There are studies that indicate a clear connection between the onset of schizophrenia and the uncontrolled use of psychoactive substances. |
| Brain abnormalities | In patients with this psychiatric syndrome, changes in the hippocampus, temporal and frontal the proportion of the cerebral organ responsible for prudence, decision-making and logical thinking departments. |
 It is often possible to determine schizophrenia in a person by obvious external signs. Such changes are caused by metabolic and neurochemical reasons. There are hypotheses about the predisposition to psychiatric pathology of patients with impaired dopamine synthesis, dysfunction of the cholinergic system, and inhibiting the GABA mechanism.
It is often possible to determine schizophrenia in a person by obvious external signs. Such changes are caused by metabolic and neurochemical reasons. There are hypotheses about the predisposition to psychiatric pathology of patients with impaired dopamine synthesis, dysfunction of the cholinergic system, and inhibiting the GABA mechanism.
The first signs of disorder
The initial stage of the disease is distinguished by a polymorphism of the course, which makes it difficult to recognize and differential diagnosis. The early signs of a mental disorder vary by age and gender.
Schizophrenia is a complex and controversial psychiatric pathology. The disease in the initial phase is manifested by neurasthenic or depressive symptoms. The latter is typical for women.
Generally, among the typical first signs of a mental disorder, there are:
- a sharp change of interests;
- psychological lability;
- hysteria in women;
- short periods of lethargy in men;
- weakening of attention and inability to concentrate in adolescents;
- auditory hallucinations called "voices in the head";
- ragged speech;
- illogical thinking;
- irritability;
- causeless anxiety.
The initial symptoms of a progressive psychiatric syndrome are individual and multifaceted. Women neglect the rules of hygiene, lose sexual interest in members of the opposite sex.
In men, among the first signs of schizophrenia, loss of appetite and decreased physical activity are noted. Symptoms are nonspecific and are often purely behavioral in nature with no clinical manifestations. This makes the diagnosis very difficult.
Obvious symptoms of schizophrenia
With the development of the disease, the spectrum of psychosomatic manifestations expands, intensifies and deepens. Signs of autistic behavior are considered a clear symptom for children.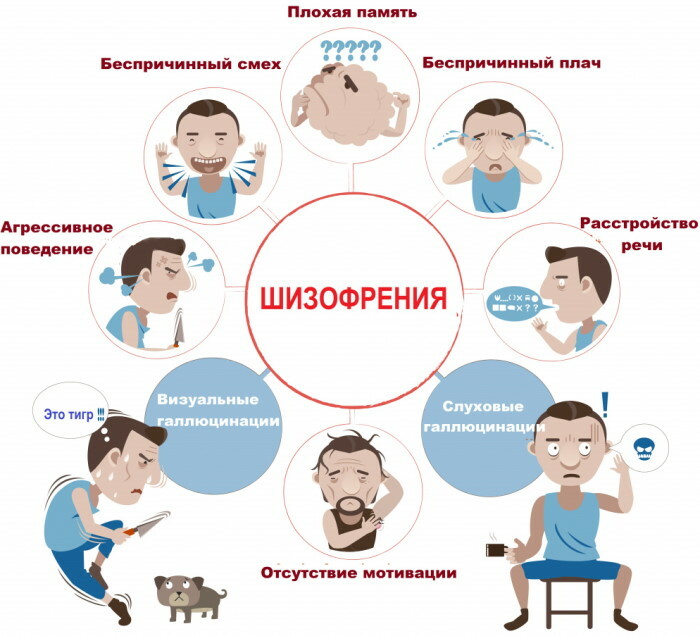
The manifestations of mental illness in adults are chaotic and varied. They depend on individual life experience, social environment, characteristics of family relations.
To facilitate the classification of symptomatic manifestations of schizophrenia, obvious signs are divided into:
- positive - hallucinations, delusional disorders, obsessive states;
- negative - emotional lability, the desire for social isolation, hypo- or hyperthymia (unmotivated spontaneous deterioration or improvement in mood, respectively);
- volitional disorders, manifested by pathological passivity and inability to make elementary decisions;
- violation of socially accepted behavioral norms without a clear awareness of their own actions.
The overt symptoms of schizophrenia are thought to be due to a dysfunction of neurotransmitter regulation in the brain. The obvious signs of the disease depend on the form of psychiatric pathology. Below are the typical symptoms for each of them.
Catatonic form
Specific physical conditions and behavioral nuances are considered characteristic signs of this type of mental disorder.
Among them:
- catalepsy - movement disorder, expressed in pathologically prolonged preservation of a given body position;
- mutism - lack of reaction to attempts by others to enter into verbal contact with the patient;
- senseless motor activity, manifested by monotonous claps, bouncing, head shaking, and other similar actions;
- thoughtless obedience to commands;
- periodic adoption of a rigid posture with tonic muscle tension, individual painful spasms, limited mobility.

It is possible to determine schizophrenia in a person by alternating periods of mutism and excessive psychomotor agitation, which is characteristic of catatonic pathology.
Paranoid form
In addition to the general symptomatology, delusional states of a specific nature are characteristic of this type of personality disorder. Their analysis and definition are used in differential diagnostics.
Delusional-obsessive states are manifested:
- persecution mania;
- outbursts of unmotivated jealousy;
- a change in the perception of household items;
- obsession with bodily transformations;
- assertion of one's own chosenness;
- associating your personality with other people, historical or literary characters.
In paranoid schizophrenia, auditory hallucinations have a commanding or threatening meaning. Deceptive gustatory and olfactory sensations are often present.
There are bodily sensations - the effects of unbearable pain, severe burning or tingling, not due to somatic reasons. Patients with paranoid schizophrenia are prone to elimination - self-harm, self-mutilation.
Hebephrenic form
To define such a mental disorder, clear diagnostic criteria are used, including general symptoms and at least one of the following specific signs:
- a state of emotional torpor of varying duration;
- inadequate psychomotor reactions to external stimuli;
- aimless and cyclical behavior;
- speech disorders;
- obvious violations of mental activity.

Delusional-obsessive states and hallucinations are not considered typical manifestations of hebephrenic disorder. However, these symptoms are often mild.
Primitive (simple) form
Identification of this type of psychiatric illness requires dynamic monitoring of neurophysiological parameters and long-term follow-up on an outpatient basis.
The approximate term of the latter is at least a year. Several psychiatric examinations are prescribed to make a definitive diagnosis.
Primitive schizophrenia is determined by the persistence of the following symptoms throughout the observation period:
- loss of interest in what is happening;
- social self-isolation;
- autistic behavior;
- taciturnity;
- gradual depletion of the vocabulary used;
- physical passivity;
- emotional lethargy.

In patients with a simple type of mental disorder, there is a deterioration in the activity of facial muscles. Such a diagnosis is made in the absence of hallucinations, delusional states, abnormal personal experiences.
There should not be a history of senile dementia or disorders of brain activity provoked by organic lesions of the cerebral regions, hemodynamic disorder.
Diagnosis methods
The psychiatrist conducts an initial interview with the patient, interviews relatives. Diagnostics includes clinical and anamnestic measures, pathopsychological testing, neurophysiological methods.
Instrumental and laboratory studies help to determine the disease. Schizophrenia often develops due to impaired connections in neural structures. Such pathological manifestations in combination with organic lesions of the brain in the examined person are detected by laboratory-hardware methods.
To assess the psycho-emotional state and mental status, specially designed scales with tests are used - Luscher, Carpenter, MMMI. Mental disorders are accompanied by macromorphological lesions of organic etiology, which are detected by MRI.
Clinical and anamnestic examination
Such diagnostic measures are aimed at identifying obvious and hidden signs of schizophrenia, clarifying the probable causes of pathology. Exogenous provoking factors, nervous overload, severe emotional experiences exacerbate the disease.
The task of the psychiatrist during clinical and anamnestic examination is to exclude or minimize the influence of such factors. Examination of the patient, conversations with relatives help to identify and record deviations in behavior for differential diagnosis.
Analysis of mental status
Such a survey can be shortened or detailed. The first option is used in patients with clear visual signs of schizophrenia. A detailed and detailed analysis of the mental status is necessary for a latent or simplest form of the disorder.
There is no standard diagnostic protocol for these patients. The applied method of analyzing the mental status is determined by the clinical objectives, the characteristics of upbringing and the degree of education of the subject.
The methods are used:
- Classification of objects. The method is considered the main one among the methods of psychological testing for suspected schizophrenia. It allows you to study the patient's ability to generalize, abstract thinking, consistent and logical inferences. In schizophrenia, these basic thought processes are impaired.
- Pictogram method. Experimental psychiatric test is used to study the patient's ability to mediate mental activity. The subject is asked to memorize a set of words or phrases. The technique is used to analyze the mental status of patients with a secondary education or higher.
- Concept comparison test. The method reveals cognitive impairments characteristic of schizophrenia. In the children's version, a special Wechsler test is used.
-
Rorschach spots. Visual test, during which the subject is shown 10 images of ink blots of different configurations. The patient talks about his emotional sensations and visual images. The analysis takes into account the answer and the speed of its issuance.

Analysis of mental status is of secondary importance, since the final diagnosis is established on the basis of characteristic clinical symptoms.
Assessment of external signs in a patient
It is often possible to determine schizophrenia in a person visually. With such a mental disorder, clear phenotypic manifestations are observed, expressed in abnormalities of physical development, structural features of the skull and body constitution.
External signs mark the neuroendocrine pathologies that provoked schizophrenia. In patients with asthenic constitution, there are no deep mimic wrinkles characteristic of such a morphology.
In schizophrenia, a sloping configuration of the frontal surface is noticeable. External signs include the paucity of facial expressions, a blurred or defocused look. Pupils often move quickly and erratically.
Schizophrenia is externally manifested by incoherent speech, aimless cyclical gestures, excessive motor expression. In some forms of the disease, it alternates with periods of vestibular inhibition.
Analysis of symptoms of the "small circle"
This category of specific signs of a mental disorder includes the use of unusual verbal constructions with no logical connection between phrases.
Such speech is combined with delayed psychoemotional reactions. When pronouncing his monologue incomprehensible to others, the patient looks at one point and does not notice what is happening around.
The diseased brain forms a kind of alternative reality. As schizophrenia develops with clear symptoms of the "small circle", the patient loses the cognitive skills and physical skills inherent in him previously.
Analysis of the symptoms of the "big circle"
These signs of mental disorder include auditory and visual hallucinations, mental echoes. The latter is expressed in the effect of retransmission of thoughts in the patient's head.
Delusional ideas, tactile sensations, obsessive states are considered to be the symptoms of the "big circle". The analysis of such signs is performed by a psychiatrist in order to differentiate the form of pathology and choose a method for stopping exacerbations.
Psychological tests to detect schizophrenia
A special express method has been developed to identify the deterioration of mental abilities, attentiveness, and memorization of elementary information inherent in schizophrenia.
Pathopsychological examination allows to detect and fix such changes. They use pictures, simple tasks for logical thinking, a set of questions developed by psychiatrists.
Such methods make it possible to determine the patient's ability to distinguish between illusions, to build associative rows. The complex of pathopsychological examination necessarily includes the Luscher color test.
How to determine schizophrenia by instrumental and laboratory methods
Assign an analysis of various biological materials of the patient's body to identify:
- neuroendocrine pathologies;
- inflammation;
- hormonal disorders;
- brain poisoning with salts of heavy metals;
- signs of alcoholic, drug or drug intoxication.
Laboratory and instrumental studies make it possible to identify the probable cause of a mental disorder, to select the composition of drug therapy, the optimal dosage of drugs.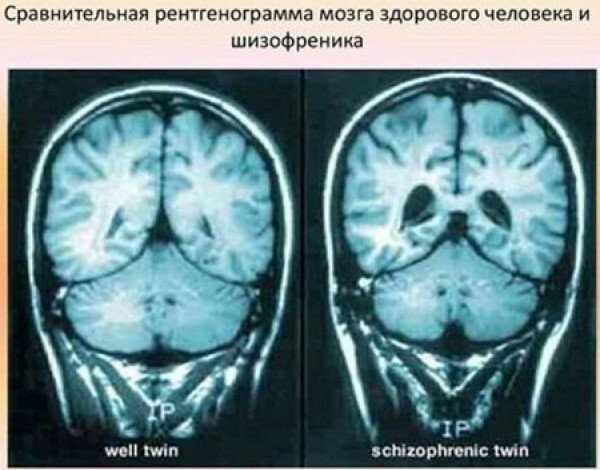
It is possible to determine schizophrenia in a person by means of biophysical (instrumental) diagnostics.
Apply for this:
- electroencephalography;
- method of calling electrochemical potentials;
- magnetic resonance imaging;
- ultrasound dopplerography.
Such examinations are completely safe, painless, and do not require preliminary preparation. They allow you to obtain reliable data on the functional state of the brain and the whole organism.
MRI
The tomograph creates a three-dimensional digital model of the cerebral zone with visualization of the internal structure. MRI detects characteristic schizophrenia structural anomalies, exclude:
- tumor processes;
- hematomas;
- swelling;
- cystic formations;
- damage to the vascular network;
- stroke.
Magnetic resonance imaging is used to detect a decrease in the volume of the brain substance inherent in a mental disorder.
Neurotest
Such a laboratory study is necessary to detect inflammatory markers in the blood. The concentration of specific proteins is directly proportional to the severity of the mental state.
Hematologic neurotest is used to confirm the diagnosis and assess the effectiveness of drug therapy. The technique determines the immunological parameters of the serum blood fraction associated with the functions of the cerebral organ and the parameters of cerebral hemodynamics.
Neurophysiological test system
The technique provides for the study of the patient's reactions to external stimuli - bright flashes of light, sound signals. Schizophrenia is determined by the speed of movement of the pupils, reflex responses of the nervous system.
NTS is used to confirm the diagnosis, to draw up a detailed clinical picture at the physiological level. Dysfunctions of nerve circuits are closely related to organic damage to the corresponding regulatory parts of the brain.
Differentiating schizophrenia from somatic diseases
Symptoms of a mental disorder resemble those of some neuroendocrine pathologies.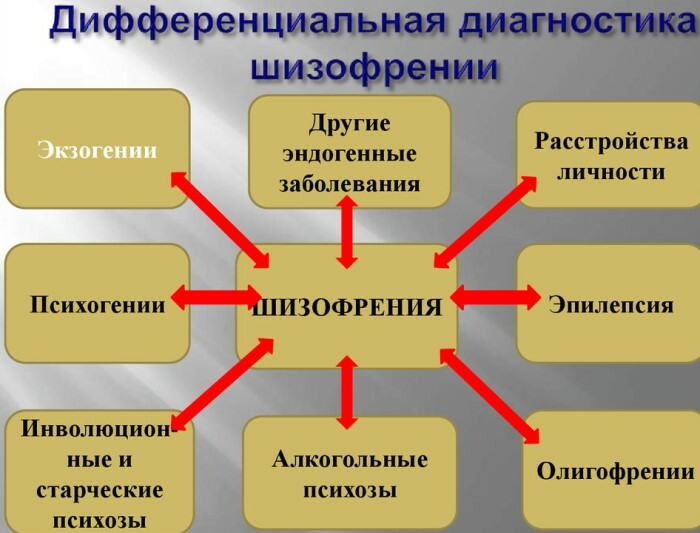
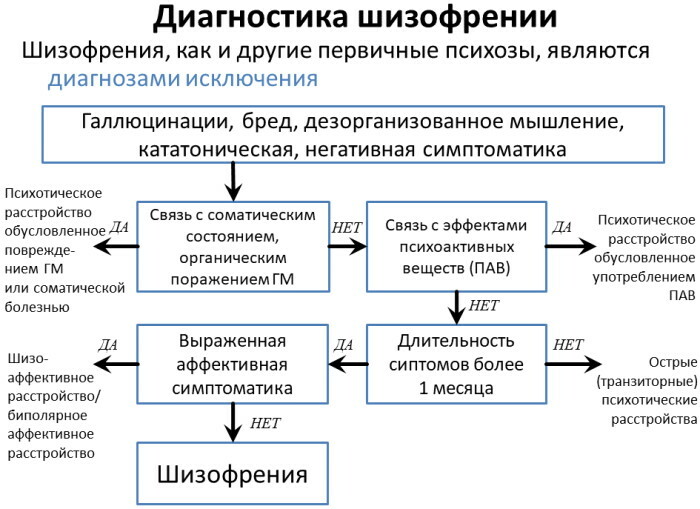
These include:
- hyper- or hypothyroidism;
- suppression of the functions of the parathyroid glands;
- disruption of the adrenal glands;
- diseases of the pituitary gland.
Clinical manifestations similar to schizophrenia are characteristic of autoimmune processes - systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis. Reminiscent of the pathological picture of mental disorder, neurodegeneration, senile dementia, some diseases of the cerebral vessels.
Differentiation of schizophrenia from somatic destructive processes is performed according to the presence in the examined person of a combination of clinical indicators with diagnostic criteria of the 1st and 2nd ranks. Unmistakably psychiatric illness can be identified by a stable combination of such signs.
Schizophrenia Symptom Videos
How to recognize schizophrenia: