Content
- What is the endometrium and its functions
- What happens to the endometrium during menopause, menopause
- Phases of menopause in women
- How the endometrium changes during menopause
- Norms of endometrial thickness at different phases of menopause
- How the thickness of the endometrium is determined
- Why does the endometrium grow during menopause?
- What does a thickened endometrium in menopause mean?
- Forms of endometrial hyperplasia
- Simple hyperplasia
- Complex hyperplasia
- How to cure hyperplasia
- What does the heterogeneous endometrium in menopause say and what to do about it?
- How does endometrial thickness affect the likelihood of menopausal discharge?
- Video about the thickness of the endometrium during menopause
During menopause, the endometrium of the uterus and all other organs of the female reproductive system undergo physiological changes. As the body naturally ages, the level of sex hormones decreases, metabolic processes slow down, and the risk of developing gynecological diseases increases.
Normal with the onset of menopause
endometrial layer of the uterus gradually becomes thinner, its main function of ensuring the stable development of the embryo in the early stages of pregnancy is lost.What is the endometrium and its functions
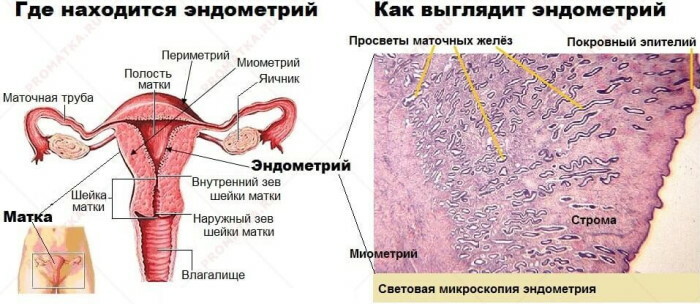
The endometrium is the inner lining of the uterus, which is evenly distributed over the entire surface of its walls. Physiologically, the endometrial layer of the female genital organ is classified into functional and basal tissue type. In the first case, the inner lining of the uterus is temporary.
The functional endometrium develops within 1 to 2 weeks and is then rejected by the body during the next menstrual period. In this case, the basal layer begins to recover immediately after the end of menstruation. Normally, the endometrium of the uterus has the same thickness, and its thinning indicates the imminent onset of menopause, or it indicates an imbalance in female sex hormones.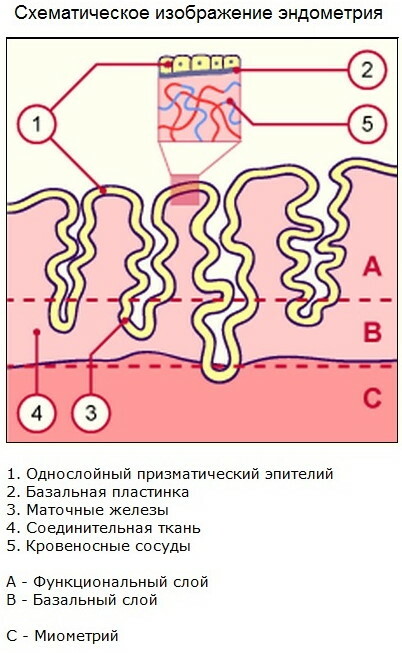
The following functions of the endometrium are distinguished:
- forms the inner lining of the uterus;
- changes its thickness depending on the level of sex hormones in the woman's blood, as well as the phase of the menstrual cycle (at the beginning of menstruation, the endometrial layer is thin, and as they are completed, it becomes thicker fabrics);
- takes part in preparing the female body for the ovulation phase and further fertilization;
- responsible for the reliable attachment of the egg to the walls of the uterus after successful conception;
- triggers the mechanism of partial detachment of endometrial tissues to remove an unfertilized egg (fragments of dead and damaged cells are removed from the female body during menstruation).
Maintaining stable endometrial functions ensures the health of all organs of the female reproductive system. Pathological growth or premature thinning of the inner layer of the uterus causes the development of concomitant diseases of the genital area, as well as infertility.
What happens to the endometrium during menopause, menopause
The endometrium during menopause, the rate of which depends on the woman's age, gradually becomes thinner. During the period of cessation of menstruation, processes for the development of the endometrial layer of the uterus are suspended. This is a physiological process that is regulated by the level of female sex hormones.
As the concentration of estrogen and progesterone decreases, the functional activity of the reproductive organs withers. Further growth of the endometrium of the uterus despite the onset of menopause and menopause indicates hormonal disorders in the female the body, and is also a harbinger of gynecological diseases in the form of endometritis, polyposis, tumor neoplasms, endometriosis.
Phases of menopause in women
The climacteric period is a certain period of time during which there is physiological transition of the female reproductive system from puberty to termination reproductive function.
In most cases, menopause occurs in women aged 45 to 60 years. During this time, menstruation gradually stops, the secretory activity of the ovaries decreases. It is believed that the development of menopause is the result of the natural aging of the female body.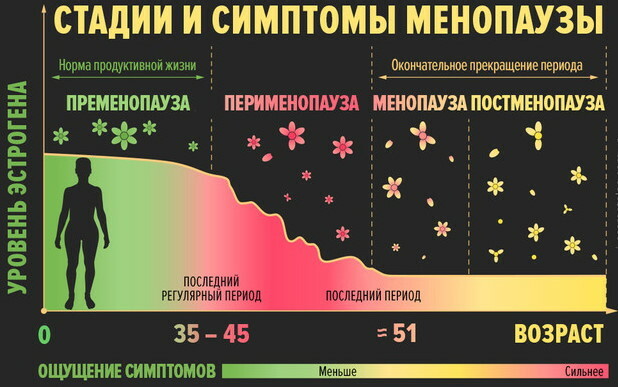
The table below describes the main phases of menopause in women:
| Phases of menopause | Distinctive features of physiological periods |
| Premenopause | In women who have reached the age of 40, the period of premenopause begins. At this stage of natural changes in the body, periodic cases of cardiopathy, the appearance of rare or, on the contrary, too frequent menstruation are recorded. The most dangerous symptom of premenopause is dysfunctional uterine bleeding. The severity of the signs of premenopause depends on the general hormonal background of the woman, the presence or absence of chronic diseases of internal organs, hereditary predisposition and the type of activity. The average duration of this climacteric phase is 2 to 10 years. |
| Menopause | Menopause is the next phase of the climacteric period. This state of the female body is characterized by the appearance of the last menstruation, which arose as a result of the secretory activity of the ovaries. The exact date of the beginning of this climacteric phase is set individually after 1 year after the last menstruation. During menopause, there is a sharp change in the level of female sex hormones in the direction of their rapid decline. In this regard, a woman experiences general malaise, physical weakness, and disturbances in the functioning of the nervous and cardiovascular systems. At this stage of menopause, the risk of developing gynecological diseases increases. The average period of menopause is 12 months. |
| Postmenopause | The postmenopausal period lasts for 6-8 years. All this time, a woman with varying severity may experience the following symptoms of unsatisfactory health:
The above symptoms are typical for the early postmenopausal period. As the female body adapts to a new hormonal background with a lower concentration of estrogen, unpleasant symptoms are smoothed out. |
 At the final stages of the climacteric period, the appearance of pathological symptoms associated with dysfunction of the internal genital organs is possible. These include dryness of the vaginal mucosa, pain during sexual intercourse, increased fragility of hair and nail plates.
At the final stages of the climacteric period, the appearance of pathological symptoms associated with dysfunction of the internal genital organs is possible. These include dryness of the vaginal mucosa, pain during sexual intercourse, increased fragility of hair and nail plates.
As old age approaches, the climacteric phase of postmenopause is aggravated by diseases heart and blood vessels, dementia, bone osteoporosis and arthritic lesions joints.
How the endometrium changes during menopause
The endometrium during menopause, the rate of which varies under the influence of female sex hormones, thins in proportion to the decrease in estrogen levels. Natural extinction of the secretory activity of the ovaries leads to a drop in the concentration of female sex hormones. This leads to a gradual decrease in the size of the endometrium with its transition to a state of hypoplasia and complete atrophy. The presence of such changes is a normal reaction of the female body to the state of menopause.
Norms of endometrial thickness at different phases of menopause
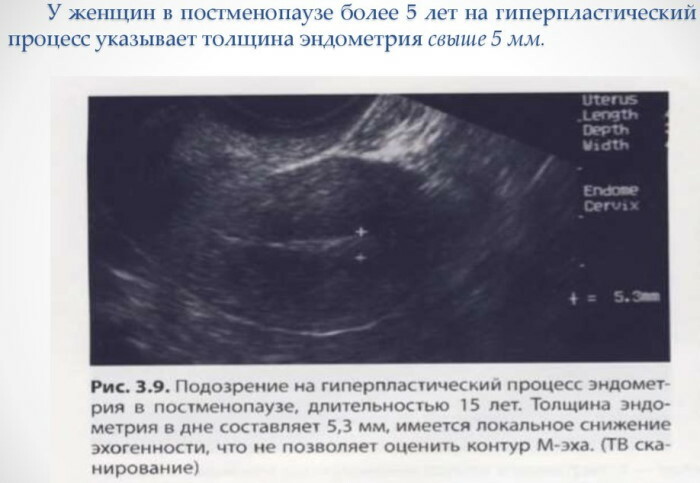
The parameters of the endometrial layer of the uterus are individual for each woman. During menopause, the normal is the inner shell of the genital organ, the thickness of which does not exceed 5 mm. 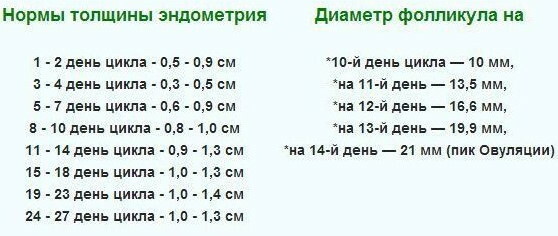 The absence of menstruation and the presence of an endometrium thicker than this indicator is the reason for visiting gynecologist with a comprehensive examination of the reproductive system and blood donation to the genital level hormones.
The absence of menstruation and the presence of an endometrium thicker than this indicator is the reason for visiting gynecologist with a comprehensive examination of the reproductive system and blood donation to the genital level hormones.
How the thickness of the endometrium is determined
The endometrium during menopause, the rate of which depends on the level of female sex hormones, changes with the natural aging of the body. To determine the thickness of the inner layer of the uterus, a comprehensive examination of the female reproductive system is carried out. At the preliminary stage of diagnosis, a standard gynecological examination is performed.
The doctor assesses the size and shape of the uterus, records visual changes in the tissue structure of the genital organ, checks the thickness of the endometrial layer. If there is a suspicion of premature thinning or excessive thickening of the inner lining of the uterus, instrumental research methods are prescribed.
The table below describes the main diagnostic methods that are used by gynecologists to determine the thickness of the endometrium as accurately as possible.
| Method for measuring the inner layer of the uterus | Diagnostic characteristics |
| Ultrasound | An ultrasound of the uterus allows you to determine and also study the thickness, density and structure of the endometrial layer. With this examination method, premature thinning or overgrowth of endometrial tissue can be diagnosed. The average cost of an ultrasound of the uterus is 1600 rubles. |
| Hysteroscopy | In the process of this diagnosis, a special probe is introduced into the woman's uterine cavity, which transmits a digital video image of the inner layer of the uterus to a computer monitor. This examination method is considered one of the most informative and objective in determining the thickness of the endometrium of the uterus. Also, hysteroscopy makes it possible to detect the possible presence of malignant tumors and polyps. The price of this study is 7700 rubles. |
In the process of measuring the inner layer of the uterus, auxiliary diagnostic methods are used in the form of blood tests for the level of progesterone and estrogen. In the event of an imbalance in female sex hormones, an appropriate decision is made on the use of substitution therapy drugs.
Why does the endometrium grow during menopause?
The active development of the endometrium during menopause is a pathological sign. At this stage, the thickness of the inner layer of the uterus should not be more than 5 mm. An increase in this indicator to the level of 6-7 mm requires a more detailed examination of the female body in order to determine the causes of hyperplasia as quickly as possible.
During menopause, the concentration of estrogen in the blood gradually decreases. A change in the hormonal background leads to a decrease in the size of the uterus and a gradual atrophy of its mucous layer. With the onset of menopause, hormonal disruptions may occur, which provoke abnormal activity of the tissues of the reproductive system.
Further growth of the endometrium after menopause and menopause is caused by the following negative factors:
- congenital or acquired diseases of the pituitary gland;
- pathological form of obesity (scientifically proven that fat cells are a potential source of estrogen);
- taking hormonal contraceptives;
- diseases of the tissues of the pancreas;
- autoimmune disorders;
- the consequences of a diagnostic examination of the uterus, which included curettage of its inner layer;
- imbalance of sex hormones with a decrease in progesterone concentration and an increase in estrogen levels;
- hereditary anomalies, when similar symptoms were noted in close female relatives;
- long-term therapy with drugs based on synthetic hormones;
- frequent abortions that injure the inner layer of the uterus.
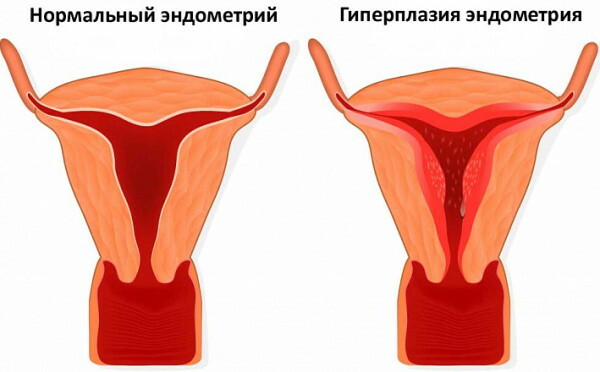
Exposure to the above factors contributes to the abnormal growth of the endometrium after menopause. To normalize the functions of the female reproductive system, it is required to eliminate the main cause that disrupts the hormonal balance of estrogen and progesterone.
What does a thickened endometrium in menopause mean?
The presence of a thickened endometrium during menopause indicates an imbalance in female sex hormones. In this case, we can talk about an increased level of estrogen, the concentration of which is higher than the norm for a woman of the corresponding age. This is a pathological sign that requires additional examination.
In women over 50, thickening of the endometrium during menopause is often caused by extraneous neoplasms in the structure of the ovaries. Benign and cancerous tumors localized in this part of the body disrupt the functioning of the organs of the reproductive system, provoke the effect of hyperfunction.
Forms of endometrial hyperplasia
According to morphological features, endometrial hyperplasia is a simultaneous thickening of the glandular tissue of the uterus and stroma. During menopause, this process is considered pathological, and is also classified into 2 main forms.
Simple hyperplasia
The cellular structure of the endometrium of the uterus does not change its quality characteristics. The growth of the inner layer of the genital organ proceeds with moderate dynamics, but at the same moment there are signs of an increase in the numerical amount of glandular tissue. Simple hyperplasia almost never causes dangerous consequences for the female body.
The risk of malignant neoplasms provoked by endometrial hyperplasia is at the level of 2%. Timely start of treatment allows you to restore the balance of female sex hormones, as well as prevent further growth of the endometrium.
Complex hyperplasia
The presence of a complex form of hyperplasia increases the likelihood of severe complications for the female reproductive system. With the pathological proliferation of the endometrium, a change in the cellular structure of tissues occurs. 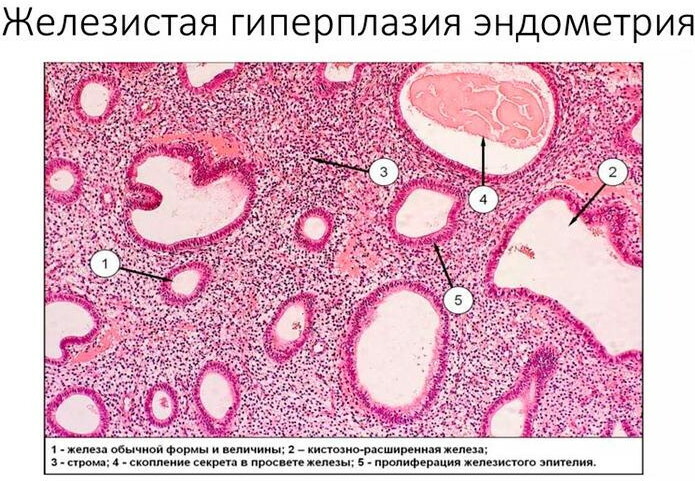 In this case, the risk of developing malignant neoplasms in the walls of the uterus is 20%. Complex hyperplasia has different dynamics of progression, and is also capable of causing local inflammation of the endometrial layer.
In this case, the risk of developing malignant neoplasms in the walls of the uterus is 20%. Complex hyperplasia has different dynamics of progression, and is also capable of causing local inflammation of the endometrial layer.
How to cure hyperplasia
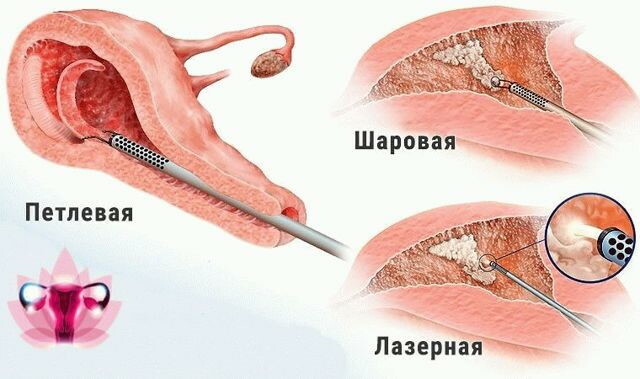
The endometrium during menopause, the rate of which changes depending on the age of the woman, should gradually become thin with the further onset of atrophy. Hyperplasia of the inner layer of the uterus during the period of cessation of menstruation requires surgical treatment. The most effective and common method of therapy in the presence of this pathology is endometrial ablation.
Surgery to remove the inner layer of the uterus is performed as follows:
- The woman is admitted to the hospital of the surgical or gynecological department.
- The doctor injects the patient with general or epidural anesthesia.
- In a sterile operating room, the doctor, using surgical instruments, removes the thickened layer of the endometrium from the uterine cavity.
- Upon completion of the surgical procedure, the patient is transferred to the general therapy ward.
- For the next 2-4 hours, the woman should be monitored by medical personnel for the timely prevention of complications.
In the absence of signs of uterine bleeding, attacks of spasmodic pain in the lower abdomen, the patient on the same day can independently leave the walls of the gynecological department. The actual ablation operation itself lasts from 20 to 45 minutes. depending on the complexity of the clinical case.
Preparing for the endometrial ablation procedure requires adherence to the following rules:
- stop taking medications that thin the blood;
- stop smoking 24 hours before the operation;
- refrain from drinking fluids and eating food on the day of ablation;
- on the eve of surgery, have dinner with light foods with a minimum amount of protein and fatty foods.
 The recovery period after ablation lasts from 1 to 2 weeks. During this time, it is not recommended to take a hot bath, have sex, or go to the bathhouse. During the first 3 days after surgical removal of the endometrium, bleeding may appear from the vagina.
The recovery period after ablation lasts from 1 to 2 weeks. During this time, it is not recommended to take a hot bath, have sex, or go to the bathhouse. During the first 3 days after surgical removal of the endometrium, bleeding may appear from the vagina.
Pads should be used as personal hygiene products, and the use of tampons is temporarily prohibited. 2-3 weeks after the ablation, the attending gynecologist appoints the woman a second examination with an ultrasound scan to monitor the development of the inner layer of the uterus.
What does the heterogeneous endometrium in menopause say and what to do about it?
The appearance of signs of a heterogeneous endometrium during menopause is a symptom of complex hyperplasia. Foci of abnormal growth of the inner layer of the uterus indicate destructive changes in its cellular structure. Similar symptoms indicate polyposis formations, as well as other benign tumors that grow in the walls of the uterus at the base of the endometrium.
With a heterogeneous distribution of the tissues of the inner lining of the uterus, the risk of developing malignant neoplasms increases. The growth rate of these tumors directly depends on the level of estrogen in the woman's blood, since they have hormone-sensitive receptors.
How does endometrial thickness affect the likelihood of menopausal discharge?
During menopause, hyperplasia of the endometrial layer of the uterus provokes atypical conditions of the female reproductive system, which is already at the stage of wilting. In a similar situation, a woman may have specific mucous discharge with a rich brown or brown tint.
This condition of the uterus can manifest itself with the following additional symptoms:
- active hair growth in those parts of the body where they were previously absent;
- coarsening of the voice;
- discharge of blood during sexual intercourse;
- pallor of the skin;
- decreased performance;
- physical weakness;
- dizziness;
- discomfort in the lower abdomen.
The appearance of these signs is associated with an increase in the concentration of estrogens in the blood and pathological thickening of the endometrial layer of the uterus. To minimize the risk of bleeding during menopause and menopause, it is necessary to control the size of the inner lining of the genital organ.
The norm for the thickness of the endometrium during menopause in women is no more than 5 mm. Thickening of the inner layer of the uterus to the level of 6-7 mm is an alarming sign of hormonal disorders. As the female reproductive system naturally withers, the concentration of estrogen in the blood decreases, the size of the uterus decreases with further endometrial atrophy.
With the onset of menopause, the growth of the inner layer of the genital organ completely stops. Thickening of the endometrium during this period of life indicates an imbalance of female sex hormones, as well as the development of gynecological diseases in the form of endometriosis, polyposis, endometritis. Similar symptoms are caused by tumor neoplasms, which are localized in the ovaries and the walls of the uterus.
Video about the thickness of the endometrium during menopause
Malysheva about endometrial hyperplasia after menopause:



