Content
- What is parthenogenesis
- The biological significance of parthenogenesis
- Classification of types and mechanisms of parthenogenesis
- Automictic
- Sex of offspring
- Optional
- Obligate
- The prevalence of the phenomenon
- Induced parthenogenesis
- Parthenogenesis in humans
- Research
- Parthenogenesis and human diseases
- Is the birth of a parthenogenetic child possible?
- Examples of the phenomenon
- Video about parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis is a form of asexual reproduction living organisms, which provides for the growth and physical development of embryos without preliminary fertilization of eggs. This type of cell division occurs in water fleas, ticks, aphids, honey bees, nematodes, amphibians, and fish.
What is parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis is the result of the evolutionary development of the animal and plant world. This type of asexual reproduction is based on the reproduction of offspring exclusively by maternal individuals. The development of new embryos occurs from the mother's egg, which has not been in contact with male reproductive cells.
Parthenogenesis ensures the survival and preservation of the species diversity of invertebrates, animals and plants, which are in conditions of natural isolation, do not have the physiological possibility of mating with males of their species.
The principle of parthenogenesis is based on the formation of a full-fledged egg at the end of the meiotic stage. In this case, the maternal germ cells are haploid, and also contain 2 times fewer chromosomes.
At the same time, individuals of the haploid type have a diploid number of chromosomes, all or only half of the alleles of the mother. The offspring that subsequently inherited the entire amount of maternal genetic material by parthenogenesis are considered to be full clones. Parthenogenetic individuals with half the alleles are half-slopes.
A distinctive feature of parthenogenesis is that the formation of full clones occurs without the use of meiosis. The offspring that have developed on the basis of meiosis of the maternal genetic material receive only a small part of the hereditary alleles.
In this case, at the stage of asexual reproduction, the process of DNA crossing is started with the creation of several variations of the final result of division. Parthenogenetic offspring reproduce on the basis of several systems of asexual reproduction.
In the process of reproduction of a certain species of animals or insects using parthenogenesis, the system for identifying the sex of XY or XO operates. Females usually have 2 X chromosomes. Animals that use the ZW type sex determination system contain 2 Z-chromosomes (exclusively of the male type), or 2 W-chromosomes (in most cases, they are not viable). Parthenogenetic offspring may have one Z and one W chromosome.
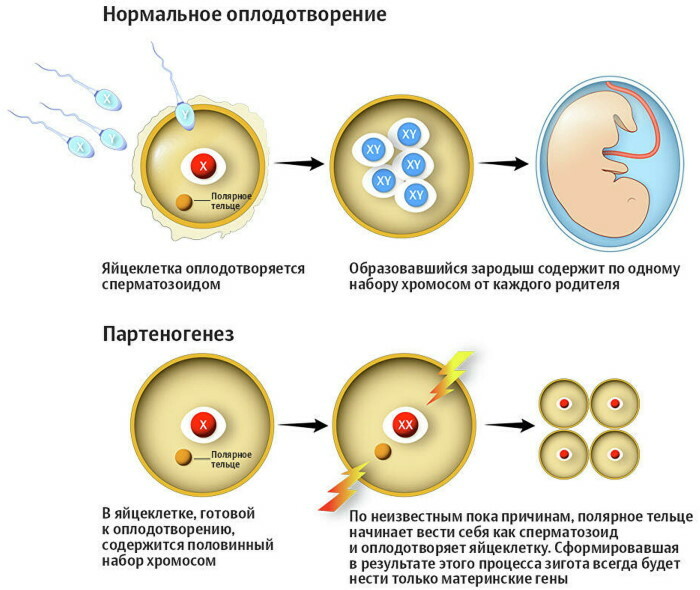
In the process of parthenogenesis, it is possible to reproduce exclusively males or females. Asexual reproduction, as a result of which only females are born, is called the biological term calves. Reproduction of only males is referred to as the arrhenotoka process.
In this case, only males are born from mothers' eggs that have not been fertilized by sperm. Egg cells that have passed the stage of fusion with male reproductive cells allow the reproduction of females. A similar principle of parthenogenesis can be observed in honey bees.
The biological significance of parthenogenesis
Parthenogenesis is asexual reproduction, which has the following biological significance for the entire biosystem of the globe:
- preserves a variety of different species of animals, invertebrates and plants;
- allows reproduction of offspring exclusively to females without involving the genetic material of males;
- eliminates the factor of sudden interruption of the natural reproduction process;
- ensures the stable transfer of genetic material from the mother to subsequent generations;
- regulates the balance of the numerical ratio of males and females of a certain species.
The main advantage of parthenogenesis is that this type of reproduction guarantees the survival of a particular species of animals, plants or insects, even in the absence of males.
Classification of types and mechanisms of parthenogenesis
Reproduction of offspring through parthenogenesis can be carried out without the use of meiosis.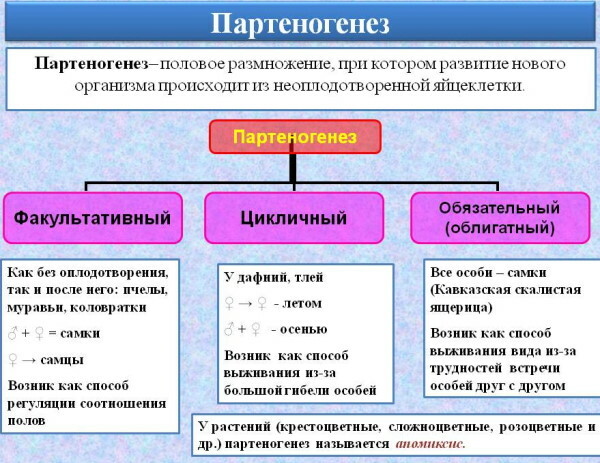
In this case, the mechanism of mitotic oogenesis is triggered, which involves the passage of the following biological stages:
- Mature eggs from the mother are produced by mitotic division.
- On the basis of the female's sex cells, the embryo develops.
- The offspring is born, reproduced through parthenogenesis using mitotic oogenesis.
Parthenogenetic individuals that have developed as a result of the division of the mother's egg, inherit the entire amount of genetic material, and are also considered full clones. A similar breeding option is typical for aphids and several other invertebrate species.
Mayosis-based parthenogenesis is a more complex mechanism for asexual reproduction of offspring. In this case, the offspring inherits only part of the mother's genetic material. DNA crossing involves the transfer of hereditary information from the female to the embryo, but with different variations.
The offspring born according to the principle of parthenogenesis, but with the use of meiosis, are considered half-slopes of the mother. The disadvantage of this division mechanism is that most males born in this manner remain haploid. For example, male ants.
Automictic
Parthenogenesis is asexual reproduction that encompasses several mechanisms of reproductive activity of living organisms at once. An automictic is one of the ways of transferring genetic material to a female without the participation of male germ cells.
In this case, diplodia is restored on the basis of chromosome doubling, but without preliminary cell division before the onset of meiosis, as well as after its completion. This reproductive mechanism is called the endomitotic cycle. A similar result is achieved after fusion of 2 blastomeres.
Automictic provides for the possibility of restoring ploidy due to the subsequent fusion of meiotic products. The chromosomes of the maternal individual are not separated in the process of restorative meiosis, and the formed nuclei can merge with the mother's germ cells at a certain stage of their biological development.
This reproductive mechanism of asexual reproduction has been compared to the self-fertilization procedure. Subsequently, a viable offspring is born autotomy, which inherits only part, or the full amount of genetic information from the mother.
The genetic component of the offspring is significantly influenced by the stage of endomitosis. For example, if the fusion of the mother's germ cells occurs before the onset of meiosis, then the embryos receive more than 50% of hereditary information.
At the same time, the principle of heterozygosity is preserved. A similar result of reproductive division is associated with the separation of homologous chromosomes in anaphase I. Retention of heterozygosity is completely absent in cases when crossing over occurs under conditions of central fusion.
Sex of offspring
Reproduction through parthenogenesis leads to the birth of complete or partial clones of the mother. In this regard, the sex of the offspring is females with identical external characteristics and body functions.
The exception is the aphids, the reproduction of which involves the simultaneous birth of males and females, which are full clones of the mother. In this case, the only difference is that only one X chromosome is missing in male aphids.
When meiosis is involved in the reproduction of offspring, the sex of the offspring directly depends on the type of apomixis. In those individuals that genetically use the XY gender identification system, only females are born, and their genome contains 2 X chromosomes.
Living organisms that use the ZW sex determination system during reproduction have offspring with the ZW or ZZ genotype. In the first case, a female is born, and in the second, a male. Individuals with the WW genotype are not viable.
Offspring with a set of ZW chromosomes are born by endoreplication of the maternal genetic material before the stage of meiosis, or by central fusion. The emergence of new individuals with the ZZ and WW genotypes is possible only in the case of terminal fusion, as well as the process of endomitosis inside the egg cell.
In nature, there are individuals of the animal world, the reproduction of which involves the birth of exclusively females. For example, in a whip-tailed lizard. These are obligate parthenogens of the polyploid type, which never give birth to males.
Most hymenoptera insects have a complex mechanism of parthenogenetic reproduction. For example, in honey bees, a numerical increase in the population is possible only if the queen of the colony lays fertilized eggs in the combs. To do this, she must mate with several representatives of males - drones.
From fertilized eggs, female bees are born, which are working bees responsible for building, raising and caring for young offspring, bringing nectar and pollen. If the queen bee lays an unfertilized egg, then a male honey bee - a drone - will be born from it.
Optional
Parthenogenesis is asexual reproduction that is characteristic of most insects and invertebrates with a high level of social organization. The facultative type of parthenogenetic division is very rare in the wild. This type of asexual reproduction provides for the female's ability to reproduce future offspring simultaneously sexually and asexually.
The mechanism of facultative parthenogenesis is triggered in critical situations. For example, when, in the conditions of its natural habitat, the mother cannot find a male capable of reproducing healthy offspring.
Facultative parthenogenesis is periodically recorded among the following types of living organisms:
- sharks;
- Komodo dragons;
- poultry for agricultural purposes;
- snakes.
In the process of facultative parthenogenesis, the mother lays an egg with a living embryo, the emergence of which occurred without preliminary fertilization with the sperm of the male. Sharks immediately give birth to living viable offspring. Most genetic scientists adhere to the version that the birth of young individuals in animals that initially reproduce sexually is a meiotic error.
Obligate
Obligate parthenogenesis is a reproductive mechanism that provides for completely asexual reproduction of living individuals. This method of reproduction of offspring is considered the result of a long evolution.
For example, for salamanders and geckos, obligate parthenogenesis is the only reproduction mechanism. There are scientifically documented cases where the transition from sexual to completely asexual reproduction, arose on the basis of mutations among a large number of maternal individuals of one population species.
Today in the wild there are about 80 species of reptiles, 1 species of snakes, amphibians and fish for which males are no longer an integral part of the reproductive mechanism. With obligate parthenogenesis, the female is able to independently reproduce a full-fledged egg cell with a full set of genetic material.
In this case, for the birth of offspring, the mother does not need the sperm of the male. The disadvantage of obligate parthenogenesis is the lack of biological diversity. All subsequent generations are born full clones of the mother. The absence of the male genetic material excludes the possibility of correcting the genome damaged by mutation or hereditary diseases.
The prevalence of the phenomenon
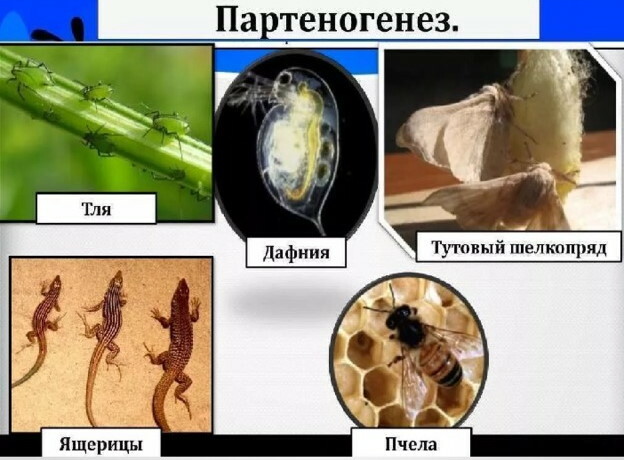
Parthenogenesis is asexual reproduction that occurs among animals, invertebrates, plants, and insects. Sexually mature maternal individuals reproduce offspring through the parthenogenetic reproductive mechanism only under the conditions of their natural habitat. Reliance on this mode of reproduction is an advantage for most invasive species, since eliminates the need to find a sexual partner for fertilization and further reproduction offspring.
In the wild, parthenogenetic reproduction is an integral part of the reproductive mechanism in representatives of the following species:
- daphnia;
- nematodes;
- aphid;
- rotifers.
Among vertebrates, the principle of parthenogenesis is strictly adhered to by lizards, some species of amphibians, snakes, and birds. Asexual reproduction occurs periodically in sharks. Reptiles are characterized by the emergence of various forms of hybridogenesis, as well as gynogenesis.
Induced parthenogenesis
Induced parthenogenesis is stimulated asexual reproduction using the genetic material of the mother. This reproductive mechanism is triggered as a result of exposure to one or several external stimuli factors.  Induced parthenogenesis is widely used in laboratory conditions in the process of scientific experiments to obtain viable offspring through asexual reproduction of living organisms.
Induced parthenogenesis is widely used in laboratory conditions in the process of scientific experiments to obtain viable offspring through asexual reproduction of living organisms.
Parthenogenesis in humans
Under normal living conditions, parthenogenesis of the human body is impossible.
There are several scientifically confirmed facts of the birth of children with signs of a partial parthenogenetic factor. In 1995 g. a case of the birth of a boy with signs of parthenogenetic development was recorded. In the leukocytes and epithelial cells of the child's skin, the genetic information from his father was completely absent.
This phenomenon is explained by the influence of the following factors:
- at the stage of embryonic development, the unfertilized egg cell began to divide independently within the woman's reproductive system;
- after sexual intercourse, not all of the cellular material of the egg was fertilized with sperm;
- in relation to unfertilized cells, the process of duplication of maternal DNA has started;
- there was an erroneous increase in the numerical number of chromosomes to 46 pieces.
A similar parthenogenetic phenomenon in humans led to the fact that unfertilized cells blocked the further development of individual tissues of the body. The egg cell material, which was fertilized by sperm, provided the further formation of the child's body.
A boy with partial parthenogenetic development had the following pathologies:
- asymmetry of the face caused by the disproportionality of its individual parts;
- cognitive impairment and learning disabilities;
- absence of the paternal genome in the structure of leukocytes and skin cells.
The internal organs of the child, as well as other life support systems of the body, worked without disturbances. Despite the preservation of the general health of the body, the result of partial parthenogenesis in humans was genetic anomalies of its development.
Research
The table below describes scientific studies that are devoted to the study of cases of parthenogenetic development in humans.
| Scientists | The essence of research and scientific theories |
| Helen Sperway | Helen Sperway is a geneticist with a specialization in reproductive biology. In 1955, according to the results of laboratory studies, she made a report in which she admitted the possibility of a "virgin birth" of a person according to the principle of parthenogenesis. Theoretical information provided by H. Sperway, formed the basis for further experiments. |
| Hwang Woo-Suk | In 2004, the South Korean scientist geneticist Hwang Woo-Sok, for the first time in a biological laboratory, bred human embryos that were obtained as a result of parthenogenesis. |
| Isigaru Matchaki | University of Tokyo scientist I. Matchaki in 2019, developed 7 successful stem cell lines of the human body, which were obtained as a result of parthenogenetic division. |
 Scientific research shows that in fact the birth of a parthenogenetic person is possible, but with various genetic abnormalities. Laboratory experiments in this direction are limited to the removal of stem cells obtained on the basis of a woman's genetic material.
Scientific research shows that in fact the birth of a parthenogenetic person is possible, but with various genetic abnormalities. Laboratory experiments in this direction are limited to the removal of stem cells obtained on the basis of a woman's genetic material.
Parthenogenesis and human diseases
The intrauterine development of a person with partial parthenogenesis can lead to various genetic abnormalities. It is impossible to predict the occurrence of congenital diseases in the body. Most often, the result of parthenogenetic birth are defects in appearance, dysfunctional disorders of the central nervous system. Depending on the quality of the mother's genetic material, the manifestation of hereditary diseases with various symptoms is possible.
Is the birth of a parthenogenetic child possible?
In medical practice, there are occasional cases of the birth of parthenogenetic children, the formation of which occurred from one activated oocyte. In general, there are more than a dozen such anomalies of intrauterine development.
In all cases, without exception, parthenogenetic children had congenital genetic pathologies. There is no scientifically proven data that from a woman's egg cell without preliminary fertilization sperm, a healthy child was born without signs of disturbances in the work of internal organs and systems life support of the body.
Examples of the phenomenon
In some species of animals, plants, insects and invertebrates, full or partial reproduction by parthenogenesis is part of their reproductive mechanism. For a person, such a way of procreation is considered an anomaly that occurs at the stage of conceiving a child.
An example of parthenogenetic development is children with congenital pathologies of the body that arise due to the duplication of hereditary information of the mother, as well as the partial absence of the genome on the paternal lines. The consequence of the parthenogenetic development of children is the asymmetry of individual parts of the body, skin diseases, and defects of internal organs.
Parthenogenesis is one of the forms of asexual reproduction that is present in sharks, aphids, honey bees, wasps, and most lizards of various species. A distinctive feature of parthenogenetic development is the formation of an embryo based on the genetic material of the mother.
Moreover, in the process of conception, the use of male spermatozoa is not required. In medical practice, there are no scientifically confirmed data on the existence of completely healthy children, the birth of which occurred with partial parthenogenesis.
Video about parthenogenesis
Does the Immaculate Conception exist? Parthenogenesis: