Content
- Why Staphylococcus Aureus bacteria are dangerous
- Risk factors for Staphylococcus aureus infection
- What analysis determines the presence of Staphylococcus aureus
- How to prepare for analysis
- Features of the diagnosis
- Microscopic method
- Cultural method
- How is the level of staphylococcus measured
- The rate of staphylococcus in a smear from the throat
- Reasons for detecting staphylococci in a smear from the pharynx
- Treatment of staphylococcus
- Local preparations
- Systemic medications
- Antibiotic sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus
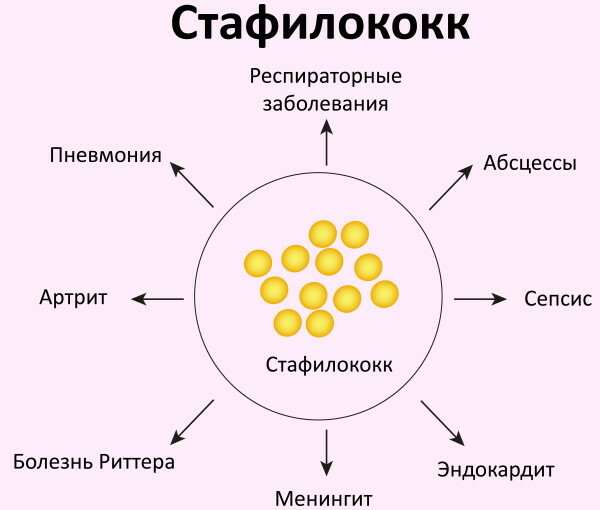
- What diseases does Staphylococcus aureus cause?
- Consequences of staphylococcal infection in the absence of treatment
- Endocarditis
- Meningitis
- Toxic shock syndrome
- Sepsis
- Video about staphylococcus aureus
Infection with staphylococci is currently considered a common cause of infectious diseases. Not all types of these bacteria, which are widespread in the environment, are especially dangerous to human health. The most aggressive microorganism is the subspecies Aureus (Staphylococcus aureus), called golden for its color.
Up to 40% of the healthy population are carriers of the microbe without even knowing it. The excess of the norm can be judged by the number of bacteria in a smear taken from the throat or other mucous membranes affected by the purulent-inflammatory process.
Why Staphylococcus Aureus bacteria are dangerous
Staphylococci belong to the family of spherical anaerobic bacteria that are responsible for many infectious diseases (pneumonia, meningitis, external and internal infections). The causative agent from the group of gram-positive cocci is found not only in the environment. Colonies of staphylococcus constantly inhabit the skin, populate the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and oropharynx.
As long as the level of human immunity does not fall below normal, microbes do not pose a particular threat. With the weakening of the immune defense, the population of staphylococci is rapidly increasing, they become pathogenic. Bacteria penetrate deep under the skin, and when they enter the blood, they provoke general intoxication of the tissues of internal organs, bones and joints.
Of all the varieties of staphylococci, groups are distinguished:
- Hemolytic. A microbe of this type causes purulent damage to the upper respiratory tract, which is difficult to cure.
- Golden. A microorganism that is resistant to most antibiotics affects the skin, mucous membranes, and the gastrointestinal tract.
- Epidermal. The penetration of the pathogen into the blood with weakened immunity occurs during the course of the surgical intervention.
-
Saprophytic. The bacterium is less dangerous, but its uncontrolled reproduction in the body causes general intoxication.
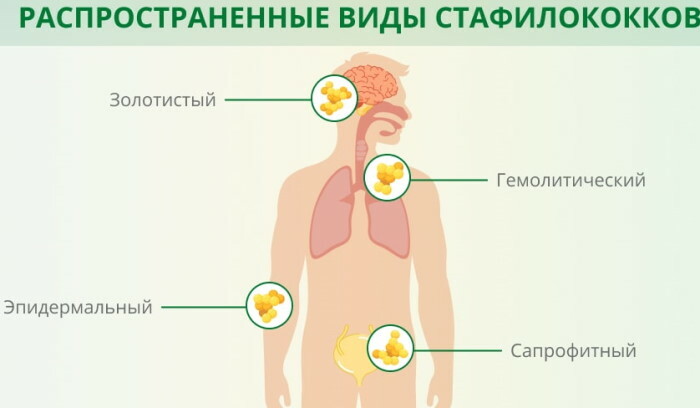
The most dangerous for humans is Staphylococcus aureus due to the extreme resistance of the microorganism that populates mainly the nasopharyngeal mucosa. Much less often, Staphylococcus aureus is found in a smear from the vagina and gastrointestinal tract. On the surface of the skin, populations of bacteria colonize the armpits and the groin area.
Factors of high pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus:
| Name | short info |
| High stability | S. aureus is not afraid of the action of many types of antiseptics, high temperatures and direct sunlight. Pathogens do not die from freezing, drying, boiling, they cannot be destroyed with hydrogen peroxide and alcohol solutions. |
| High vitality | The bacterium does not die from the action of a wide group of antibiotics due to the enzymes produced. Penicillinase and lidase protect the microbe during treatment with penicillins, help its penetration into the subcutaneous tissue. |
| High toxicity | The production of endotoxin by Aureus causes general intoxication, accompanied by purulent-inflammatory lesions. Under the influence of the toxin, the condition can be complicated by septic shock, abscesses, and dysfunction of the body systems. |
 An important point: immunity to the attack of Staphylococcus aureus is not produced. After recovery, a person who has recovered from the infection risks suffering from re-infection. Staphylococcus aureus is especially dangerous for infants in a maternity hospital, since the bacterium is a nosocomial infection.
An important point: immunity to the attack of Staphylococcus aureus is not produced. After recovery, a person who has recovered from the infection risks suffering from re-infection. Staphylococcus aureus is especially dangerous for infants in a maternity hospital, since the bacterium is a nosocomial infection.
Risk factors for Staphylococcus aureus infection
Staphylococcus aureus (the norm in a smear from the pharynx does not pose a threat to health) is always present as a representative of the normal microflora. As a result of the activation of the vital activity of bacteria for various reasons, their number is rapidly growing, provoking the development of a wide range of diseases.
The group of people at risk of S. Aureus, persons of the following categories fall:
- Patients suffering from inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity (caries), bronchopulmonary pathologies (emphysema, cystic fibrosis). Treatment of tumor processes, inflammation of the mucous membranes, skin, organs of the genitourinary system, burns and purulent wounds is often complicated by the activation of staphylococcus.
- In people with a weakened immune system, problems of endocrinology and the gastrointestinal tract, staphylococcus in the smear periodically exceeds the norm. The risk group also includes patients after surgery who have had serious illnesses and have been taking antibiotics for a long time.
- In the high-risk category there are AIDS patients, a group of injection drug users, as well as patients after implantation of foreign bodies (prostheses, catheters). Systemic administration of hormonal and antineoplastic agents, staying in a maternity hospital (mother and baby) are considered easy routes of infection with S. Aureus.
Medical personnel working with cultures of various microorganisms, in contact with solutions of biological fluids, samples of tissue structures, and infectious patients are at high risk.
What analysis determines the presence of Staphylococcus aureus
The most characteristic habitat of Staphylococcus aureus is the upper parts of the nasal passages and the respiratory tract. If the number of microbes is normal, they belong to conditionally pathogenic (permanent) flora, exceeding the boundary values turns Aureus into an aggressive pathogen that causes septic lesions.
In this case, the main symptoms of intoxication are rapidly developing:
- increase in temperature indicators;
- lack of desire to eat;
- signs of weakness and drowsiness.
Staphylococcus aureus (the norm in a smear from the throat is 10 to 3 degrees) is distinguished by the production of aggression enzymes and toxins, as well as a unique structure. Externally immobile bacteria have a regular spherical shape, the walls of the capsule of which become a protective barrier against phagocytosis. The cluster of cocci looks like a bunch of grapes, which explains their name - "spherical bunch".
Due to the similarity of the clinical picture of staphylococcal infection with other types of diseases (pharyngitis, tonsillitis, acute respiratory infections, tonsillitis) the doctor needs to identify the exact type of pathogen infectious process. Therefore, for the final diagnosis, a specific analysis is prescribed (throat swab), which will show the degree of insemination of the oral cavity with staphylococcus.
How to prepare for analysis
In order for the results of bacterial culture for staphylococcus to be reliable, it is important to properly prepare for taking material for a smear by fulfilling several prerequisites:
- A few days before the study, stop using drugs (solutions, ointments) based on antibiotics or antiseptics.
- If sputum is submitted, it is recommended to consume as much liquid as possible, preferably pure water, at least 12 hours before taking it.
- On the day of the smear, you cannot brush your teeth. You will have to give up food and drink, so as not to wash off the germs from the oral mucosa.

The obtained clinical material is inoculated on a nutrient medium. If S. Aureus, the growth of clusters up to a diameter of 4 mm is observed already after a day. It is in the nutrient solution that the cocci turn golden. This effect gave the name to the microbe, discovered in 1878 by the German microbiologist Robert Koch, who discovered the tubercle bacillus 4 years later.
Features of the diagnosis
Taking a smear from the oral mucosa is not accompanied by pain, the patient just needs to tilt his head back, opening his mouth wide.
To take the material, the laboratory assistant uses a cotton swab (sterile), with which he treats the mucous membrane of the throat, lightly pressing the tongue with a wooden spatula. The procedure is performed carefully so as not to provoke the appearance of an emetic urge. The study of the obtained material is carried out by two of the most informative methods - microscopic and cultural, which solve different diagnostic problems.
Microscopic method
The technology using a microscope allows you to examine microscopically small objects (staphylococci) to determine the external as well as internal signs of the pathogen according to the Gram method. The sample, placed on the glass, is treated with one of the aniline dyes. After washing off the dye fixed with iodine, the gram-positive cocci present in the solution are single, paired, or their clusters are colored blue.
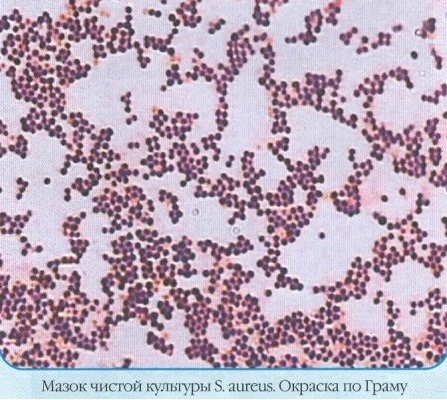
Staphylococcus aureus species found in selected material is not always a threatening fact. If the norm of microbes in the smear is not exceeded, S. Aureus is considered a member of a conditionally friendly microbiota taken from a patient's throat.
Microscopy with Gram staining of the test sample is a preliminary diagnostic method. The technique is used only to confirm the presence or absence of pathogen chains (globular cocci) in the test preparation. The result is ready in 3-5 days.
Cultural method
To accurately establish the degree of pathogenicity of Staphylococcus aureus, it is necessary to isolate a pure culture of bacteria. For this, the selected material is placed in a nutrient medium that simultaneously performs a differential diagnostic function.
Pathogenic Aureus has a good ability to cultivate on a variety of nutrient media. Basically, solutions are used on the basis of agar - mesopatamia, saline, blood, the temperature of which is not higher than 37 ° C, but also not lower than 30 ° C.
In the course of the study, it is important to take into account the appearance of possible deviations from the typical parameters of S. Aureus:
- loss of normal gram-positiveness under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, as well as lysozyme;
- the appearance of golden pigmentation does not always indicate the pathogenicity of the pathogen due to the widespread use of antibiotics.
If there are no symptoms of the disease, but Staphylococcus aureus is seeded in a throat swab, this is not a reason to prescribe antibiotics. However, the combination of symptoms with the results of the analysis already requires antibiotic therapy based on an antibiogram.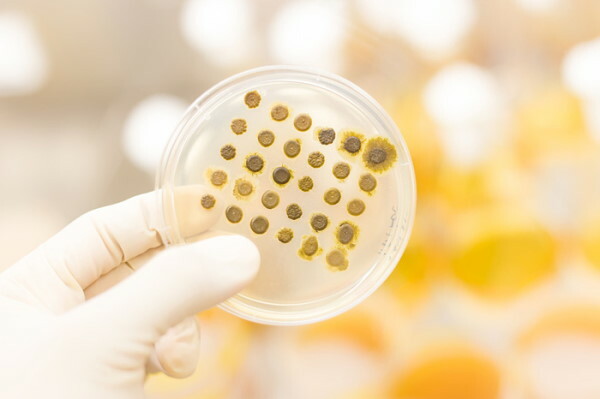
To obtain data on the sensitivity of the detected bacteria to a certain type of antibiotics, microbes spread over a solid nutrient medium and covered with a material impregnated with different types antibiotics. Those drugs that inhibit the growth of the culture will be most effective in eradicating the infectious agent. The result can be obtained in 7 days.
How is the level of staphylococcus measured
Deciphering the results of a smear test for Staphylococcus aureus may be as follows - the growth of bacteria absent (reference values) or the growth of pathogens detected (acute or asymptomatic carrier). A negative result indicates a low chance of contracting Staphylococcus aureus. The resulting value is displayed in units of CFU / ml, which corresponds to the number of units forming an S. Aureus, in a volume of one milliliter of medium.
The rate of staphylococcus in a smear from the throat
The normal value of the test result is not the same, depending on the environment from which the sample was taken (urine, feces, wound). When taking material from mucous membranes, the limit value of the norm should not be more than 104, exceeding the indicator is a sign of the disease. An increase in the indicator in the direction of increase is considered a pathology in which a calmly breathing patient seeds the surrounding space with pathogens of staphylococcal infection.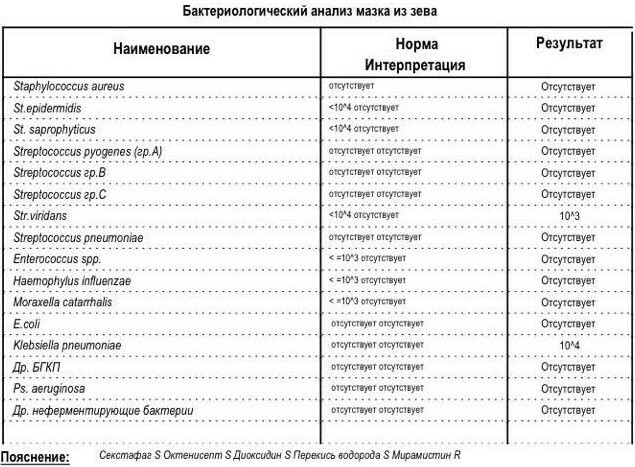
Staphylococcus Aureus (the norm in a smear from the pharynx is a sign of normal immune defense) is a very persistent microorganism that does not die on any environmental objects. The presence of bacteria on human skin rarely becomes the cause of the disease, but with a decrease in immunity, the process of reproduction of the microbe is activated, threatening the carrier with a wide variety of diseases.
Reasons for detecting staphylococci in a smear from the pharynx
A simple method of infection through direct contact or sneezing / coughing leads to the rapid spread of a microbe that is unpretentious to the conditions of the surrounding space. You can also get infected in everyday life after contact with an infected person or his personal belongings. Infection of newborns occurs from the mother during labor.
Overview of results by indicator:
| Number of bacteria | What does the indicator mean |
| 10 to the 2nd power | The result of testing sputum from the mouth and nasopharynx is considered a normal variant and does not require treatment. |
| 10 to 3 degrees | For the mucous membrane of the nose and mouth, this is the borderline value of the norm, but also a signal of the onset of the disease. |
| 10 to the 4th power | This variant of the indicator indicates the presence of chronic respiratory infections. |
| 10 to 5 power | The risk of developing complications of chronic pathologies of the respiratory type in the nasopharynx is increased. |
| 10 to 6 degrees | The result of the diagnosis of material from the nasopharynx informs about the development of the infectious process. |
Most often, the bacterium enters the body from the external environment through damage to the skin, and into the oropharynx from the nasal cavity. A favorable environment for injury or nasal mucosa contributes to the rapid multiplication of pathogens, leading to a rapid increase in their population. As a result, the blood becomes infected, which carries pathogens to different organs.
Treatment of staphylococcus
It is necessary to treat Staphylococcus aureus when the result is 104 CFU / ml, but only in the presence of negative manifestations of the infection. At 105 CFU / ml infection intensifies, signaling already quite intense symptoms, the fight against which will not be crowned with a positive result without prescribing antibiotic therapy.
Local preparations
The combination therapy of staphylococcal infection also includes the use of additional methods. In the course of local treatment, the inflamed mucous membrane of the oropharynx is treated with antiseptics (Chlorophyllipt solution).
To increase the immune defense, the administration of immunostimulants, an antistaphylococcal bacteriophage is prescribed for purulent processes. To correct immunity, it is important to connect B vitamins, as well as vitamin C, Levamisole tablets, Taktivin injections.
Systemic medications
In severe infectious pathology, a systemic intake of antibacterial drugs is prescribed.
These medications can be:
- Amoxicillin - an antibiotic (broad spectrum of action) inhibits the growth of bacteria;

- Cefazolin - cephalosporin reduces the strength of the cell walls of microorganisms;
- Vancomycin - changes the permeability of cell membranes, causing their destruction;
- Clarithromycin - inhibits the production of bacterial proteins at the cellular level;
- Clindamycin is a bacteriostatic that comes into contact with a certain type of ribosome.
Staphylococcus aureus (the norm in a throat swab is not a reason for prescribing antibiotics), acquiring properties of the pathogen (exceeding the norm in the analysis), becomes a threatening factor that is urgently needed treat. From the list of antibiotics active against Staphylococcus aureus, the doctor chooses a drug based on the antibiogram data.
Antibiotic sensitivity of Staphylococcus aureus
When composing an antibiotic therapy regimen, it is important to take into account that for many types of antibiotics S. Aureus has long been stable. Therefore, it is possible to quickly suppress the activity of pathogens by a combination of several medications. Resistance to antibiotics used to treat staphylococcal infections is due to the high ability of the bacteria to recombine and mutate.
Long-term use of penicillins led to the fact that pathogens stopped responding to treatment with these drugs, as well as methicillin. Currently, drugs of the macrolide and fluoroquinolone family are considered more effective against Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics help break down the protein walls of the bacteria. As a result, resistance to these types of antibacterial agents does not have time to develop.
What diseases does Staphylococcus aureus cause?
Infection with Staphylococcus aureus signals a variety of symptoms of many diseases. For example, pneumonia and tonsillitis of staphylococcal etiology, infection of the urinary tract, the development of ocular toxicoinfections, as well as articular pathologies. Inhabiting the tissues of internal organs, bacteria poison the blood of the carrier of the infection with the products of their vital activity, causing the spread of the inflammatory process.
Consequences of staphylococcal infection in the absence of treatment
The list of diseases due to infection with the Aureus microbe is regularly updated due to the ability of the bacteria to mutate. So, 1980 was the date of the appearance of a new disease called toxic shock, the culprit of the pathology was a new methicillin-resistant strain of Staphylococcus aureus. If the treatment of staphylococcal infection is not started in time, the situation for the patient may be complicated by a life-threatening condition.
Endocarditis
The reason for the development of infectious pathology is often bacterial, among the pathogens are staphylococci. The valve apparatus of the heart (endocardium), as well as the cell layer lining the cavity of the organ from the inside (endothelium), suffers from an infectious lesion.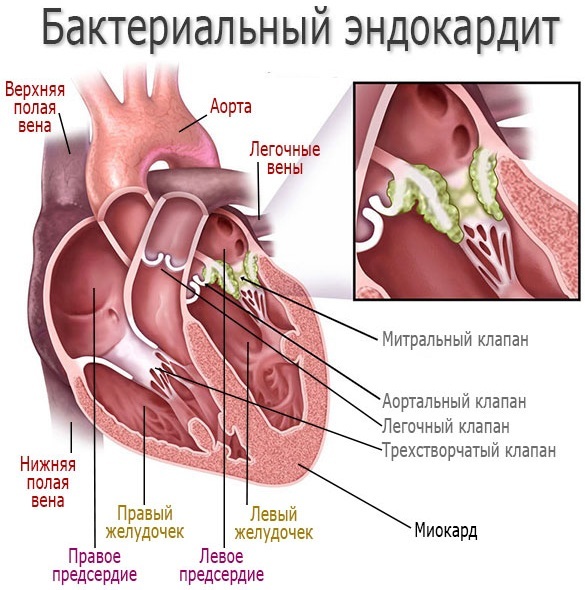
The routes of entry of microorganisms into the heart chambers are different, more often these are distant foci of infection, the installation of a central venous catheter, injection of drugs. Staphylococcal endocarditis is acute, without treatment it is fatal, even therapy does not exclude mortality in elderly patients. The mortality rate is up to 60%.
Meningitis
With staphylococcal meningitis, infectious inflammation spreads through the meninges, accompanied by a purulent process. The most frequent culprit of pathology is the bacterium Aureus, which penetrates into the structures of the brain against the background of the development of pneumonia, sinusitis, endocarditis. Usually staphylococcal meningitis is diagnosed in newborns, as well as in infants under the age of 3 months. If antibiotic therapy is started on time, the mortality rate does not exceed 30%.
Toxic shock syndrome
The pathological condition develops under the influence of exotoxins produced by Staphylococcus aureus. In the high-risk group, women with staphylococcal colonization of the vagina, persons with complicated inflammation after injury, burns.
S. Aureus, responds poorly to drug therapy, signaling bright symptoms of infection, as well as meningeal and acute respiratory symptoms, shock. In the case of a severe course of the disease, antibiotic therapy is supplemented with an infusion (intravenous) of immunoglobulins.
Sepsis
The cause of septic infection (sepsis) is the spread of bacteria along with their toxins to various organs and tissues with blood flow. In 50 percent of cases, it is Staphylococcus aureus that becomes the culprit of sepsis, as the most dangerous type of staphylococcal type infections. Severe pathology against the background of severe immunodeficiency manifests itself in two forms - septicemia (non-metastatic toxicosis) and septicopyemia (purulent form with metastasis).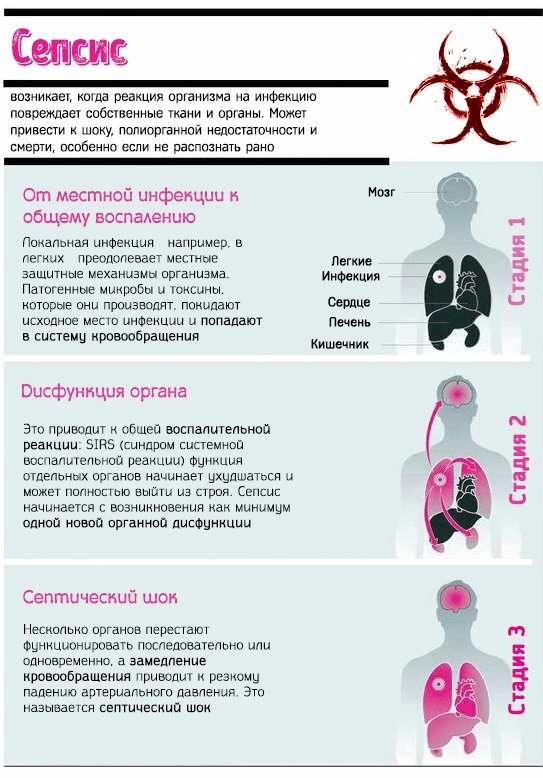
For infants (premature babies or those with weak immunity), this is a threat of death in most cases. In adult patients, mortality is much higher when antibiotics are selected without taking into account the results of the antibiogram.
According to doctors, it will not be possible to quickly cure staphylococcus aureus of the Aureus group. In the case of high indicators of the number of microbes in the smear material from the pharynx, the prescribed antibiotics should be taken for a long time, and not 7-10 days. Even the onset of positive dynamics cannot be a reason for stopping antibiotic therapy, since damaged S. Aureus are not devoid of the ability to metastasize.
Video about staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus: