Content
- What is fatty liver disease (steatosis)?
- Causes of development and risk factors
- Forms and symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Laboratory research
- Ultrasound
- Elastometry
- Treatment
- Drugs
- Surgery
- Treatment with folk remedies
- Diet
- Possible consequences, forecast
- Video about fatty liver disease
The liver takes an active part in the metabolism of fats. In this organ, they are broken down, which promotes the release of energy. But for some reason, this process can be disrupted, liver cells begin to accumulate fats, and fatty degeneration develops.
Pathology most often occurs in people over 40, but can be diagnosed at a young age. The danger is that the disease does not manifest itself for a long time, and only with a serious damage to the organ does a person begin to feel discomfort.
What is fatty liver disease (steatosis)?
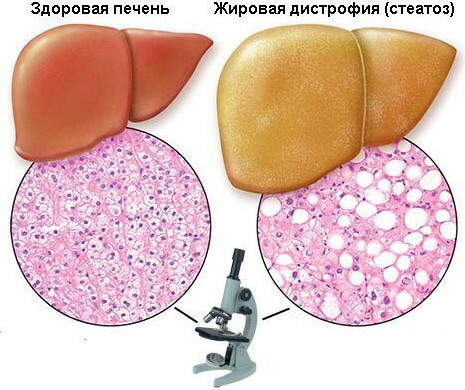
Fatty liver disease is called a pathology that is characterized by excessive accumulation of fat in its tissues. Normally, the cells of the organ contain a small amount of fat (no more than 10% of the mass of the liver), the disease develops when the process of its utilization is disrupted.
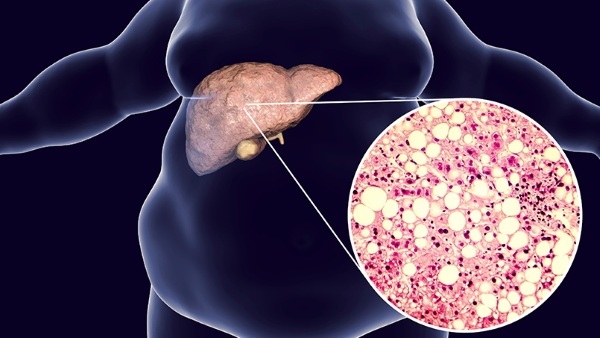
There are many reasons for this condition; people with obesity, diabetes mellitus, and impaired metabolism are at risk. Also, the likelihood of developing the disease depends on age, genetic factors, sex of a person (men are more likely to suffer).
Causes of development and risk factors
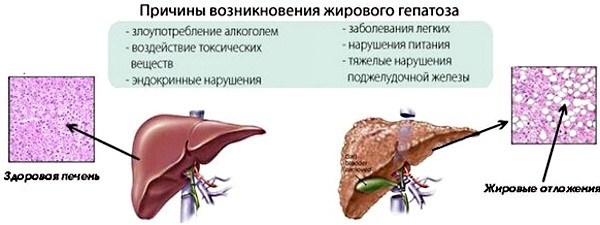
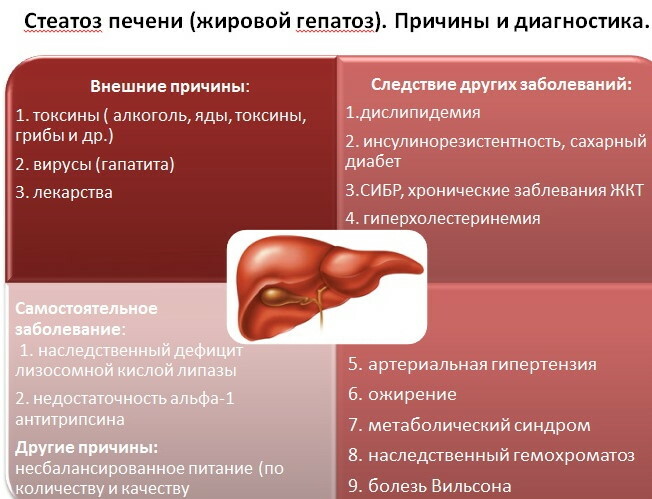
Fatty degeneration of the liver (the causes of the pathology are quite diverse) can develop as a consequence:
- alcohol abuse. Under the influence of alcohol, hepatocytes (the main cells of the organ) are damaged, which increases the likelihood of developing the disease. The number and duration of alcohol intake affect the severity of morphological changes. Without proper treatment, the development of liver cirrhosis is possible;
- taking medications. Toxic to the organ are hormonal drugs, antibacterial, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- diabetes mellitus. With insufficient sensitivity of cells to insulin and excess sugar content, it increases concentration of free fatty acids in the blood, which contributes to the enhancement of triglyceride synthesis and deposition fat in the liver;
- obesity. Overweight people often have metabolic disorders, which increases the likelihood of developing pathology;
- pathologies associated with metabolic disorders. Some diseases, which are characterized by metabolic disorders, can cause fatty degeneration of the liver (thyrotoxicosis, hypothyroidism, gastrointestinal tract pathologies with impaired absorption);
- errors in nutrition. Trans fats, simple carbohydrates in excess amount disrupt fat metabolism, provoke the development of the disease. At risk are people leading a sedentary lifestyle;
- hereditary enzymopathies. This is a group of diseases characterized by a lack of enzymes involved in the metabolism of fats.
The risk of developing the disease increases with:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- fasting, fast weight loss diets, vegetarianism;
- protein deficiency in the diet;
- severe viral infections;
- small bowel resection;
- parenteral nutrition;
- the presence of fistulas in the intestine;
- dysfunction of the pancreas;
- poisoning with hepatotoxic poisons.
Forms and symptoms
The disease can be alcoholic (triggered by alcohol intake). In the liver, about 80% of toxins are neutralized. It is this body that is responsible for converting ethanol into acetaldehyde. Alcohol abuse provokes the accumulation of ethanol breakdown products in hepatocytes. This leads to disruption of the synthesis and utilization of lipids, their accumulation in the parenchyma.
Alcoholic steatosis is manifested by rapid fatigue, heaviness in the stomach after eating, pain in the right side, and nausea. The non-alcoholic form of the disease has a similar clinical course, but develops under the influence of other factors.
Depending on the degree of damage, fatty degeneration is divided into:
- focal - characterized by the presence of single fatty deposits. They arise inside cells. Without treatment, the destruction of hepatocytes occurs with the release of their contents into the intercellular space;
- diffuse - the entire organ is affected. It is considered the most severe form of the disease. The size of the liver is enlarged, its functions are impaired, and liver failure develops.
Fatty degeneration of the liver, the causes of which are associated with a congenital metabolic disorder, is called primary. The secondary form of the disease is a consequence of other pathologies.
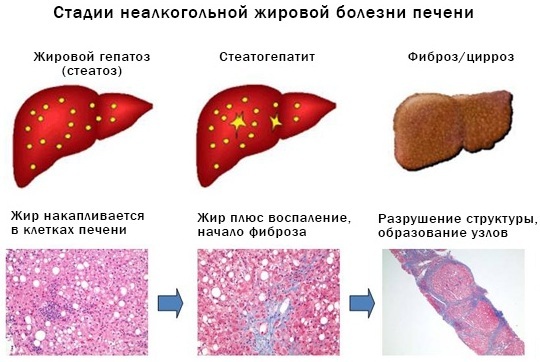
In addition, there are several stages of the disease:
- I - steatosis. The initial stage, characterized by the accumulation of fat in the cells of the organ, is reversible;
- II - steatohepatitis. At this stage, inflammation processes are activated;
- III - fibrosis. Replacement of hepatocytes with connective tissue occurs. May progress to cirrhosis or liver cancer.
 Fatty degeneration of the liver (the causes of the disease can be determined during a thorough diagnosis) is most often an accidental finding during ultrasound due to an asymptomatic course. In most cases, specific symptoms indicating the development of pathology are absent in patients. Signs by which one can suspect liver damage usually occur in the later stages.
Fatty degeneration of the liver (the causes of the disease can be determined during a thorough diagnosis) is most often an accidental finding during ultrasound due to an asymptomatic course. In most cases, specific symptoms indicating the development of pathology are absent in patients. Signs by which one can suspect liver damage usually occur in the later stages.
The patient suffers from:
- heaviness in the right hypochondrium;
- aching pains of low intensity;
- increased fatigue;
- weakness;
- dyspeptic disorders;
- sleep disorders.
An advanced disease, up to cirrhosis, manifests itself:
- itchy skin;
- nausea;
- yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes;
- an increase in the abdomen in volume;
- bleeding;
- impaired cognitive functions.
Diagnostics
For an accurate diagnosis, you must contact a gastroenterologist. The doctor will analyze the patient's complaints, collect anamnesis, clarify the presence of other pathologies, and find out whether the person is taking alcohol or drugs.
You will also need a physical examination. At the same time, the color and condition of the skin, mucous membranes are assessed, the size of the liver is determined by palpation, and the body mass index is calculated. After that, the doctor will recommend laboratory and instrumental studies.
Laboratory research
First of all, a general blood test is performed. This allows you to identify possible anemia, to detect signs of the inflammatory process. A biochemical blood test in patients with fatty degeneration will show an increase in the level of special proteins that are involved in metabolic processes (ALT, AST). Also, blood sugar and cholesterol levels may be overestimated.
An analysis is also carried out for antibodies to viral hepatitis, cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, rubella, and markers of autoimmune organ damage are determined. To rule out hypothyroidism, thyroid hormone levels are assessed.
Ultrasound
An ultrasound examination helps to assess the size of the liver, its structure, and detect lesions. 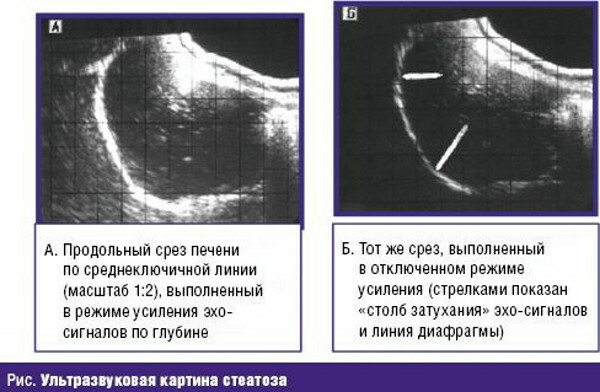 You should first prepare the intestines, giving up the use of dairy for several days products, carbonated drinks, black bread, fresh vegetables and fruits, alcohol in order to reduce gas formation. If necessary, an additional biopsy is recommended to assess the degree of organ damage.
You should first prepare the intestines, giving up the use of dairy for several days products, carbonated drinks, black bread, fresh vegetables and fruits, alcohol in order to reduce gas formation. If necessary, an additional biopsy is recommended to assess the degree of organ damage.
Elastometry
Elastometry is a non-invasive method for examining the structure of the liver. Allows you to determine the elasticity of organ tissues using ultrasound. In terms of information content, the technique is not inferior to biopsy, it is used to assess the degree of fibrosis.
Treatment
Fatty liver disease (the causes of the disease affect the tactics of treatment) requires, first of all, a change in lifestyle. The patient must change his eating habits, increase the level of physical activity. Due to physical activity, insulin sensitivity increases, and fatty tissue of internal organs decreases.
Exercise should be done at least 4 times a week. The lesson should be 30 minutes long. At least 30 min is recommended. walk in the fresh air a day. Yoga, swimming, body flex are useful.
Weight loss is very important for obese people. Losing even 5% of body weight significantly improves the condition of the affected organ. However, you need to lose weight correctly. It is optimal to lose no more than 500 g of weight per week. Dramatic weight loss causes massive breakdown of fats, while free fatty acids enter the liver more actively, which can exacerbate the disease.
It is also necessary to exclude or reduce the influence of negative factors that contributed to the development of pathology. For example, patients with alcohol dependence should see a narcologist. If the disease has arisen against the background of diabetes mellitus, additional consultation with an endocrinologist will be required.
Drugs
After the transition of the disease to the stage of steatohepatitis and with a high risk of developing fibrosis, drug treatment is prescribed.
It aims to:
- reducing the degree of organ damage;
- normalization of metabolic processes;
- correction of concomitant pathologies;
- prevention of fibrosis;
- normalization of intestinal microflora.
Drugs for the treatment of steatosis:
| Group | Name | Properties |
| Hepatoprotectors |
|
They protect liver cells from the negative effects of various factors, help to strengthen cell walls, and stimulate the regeneration of hepatocytes. |
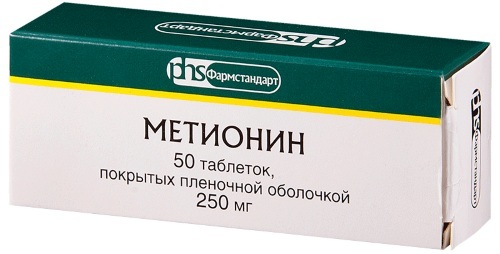
| Sulfoamino acids |
|
They improve the processing of fats, promote an increase in the activity of hepatocytes, and prevent further destruction of organ tissues. |
| Sugar-lowering |
|
Normalizes glucose levels. |
| Lipid-lowering | Rosuvastatin | Allows you to normalize cholesterol levels, preventing vascular damage. |
| Antioxidants | Mexidol | They prevent the destruction of cells under the influence of oxidative processes. |
| Vitamins |
|
Replenish the deficiency of substances necessary for the body, normalize metabolism, promote the elimination of toxic substances. |
 Also, drugs are used that reduce the influence of provoking factors and allow you to lose weight. Medicines are selected on an individual basis, taking into account the degree of liver damage, the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Also, drugs are used that reduce the influence of provoking factors and allow you to lose weight. Medicines are selected on an individual basis, taking into account the degree of liver damage, the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Surgery
At the last stage, when the body is not able to fully function, surgical intervention may be recommended. Organ transplantation is associated with great risks, in addition, patients have to wait a long time for surgery due to a shortage of donor organs. Therefore, the operation is performed only in extreme cases.
Treatment with folk remedies
As an auxiliary method, you can use traditional medicine. To improve blood flow in the liver, corn silk, calendula, dandelion roots in the form of a decoction are used. Bran (2 tbsp) helps to reduce body fat. l. per day).
It is also useful to use:
- infusion of milk thistle roots. 1 tbsp. l. raw materials are poured into 1 tbsp. boiling water, insist for 20 minutes. and are taken several times a day. Plant seed powder can be used. It is taken 3-4 times a day for 1 tsp. l .;

- infusion with dried fruits. Washed dried fruits (1 tbsp.) Are combined with oats (3 tbsp. l.), pour boiling water (1.5 l) and let it brew for 3 hours. The drink is filtered and drunk during the day;
- rosehip infusion. Fruits (50 g) are poured with boiling water (0.5 l), insisted for 10 hours. Take 200 ml 3 times a day;
- lemon infusion. Thoroughly wash 3 lemons, cut into small pieces with a peel, pour boiling water (3 tbsp.), Let it brew for 10 hours. Drink 2 times a day, 350 ml;
- oat infusion. Birch leaves (50 g) and oats (300 g) are poured with boiling water (3.5 l), insisted for a day. Take 50 ml before meals;
- broth of sorrel. Plant roots (1 tbsp. l.) is poured with water (1.5 tbsp.), boiled for 7 minutes, then insisted for 3 tsp. Take 1 tbsp. l. funds 3 times a day;
- green tea. The drink has medicinal properties, thanks to its use, the amount of fat that is in the liver is blocked, and the functions of the organ are improved. Tea is drunk during the day (2-3 cups), the drink can also be taken to prevent disease;
- apple cider vinegar. 1 tbsp. l. the funds are dissolved in 1 tbsp. warm water, if desired, you can add honey. Take a drink before meals 2 times a day for 2 months;
- pumpkin honey. The pumpkin is thoroughly washed, the top is cut off, the seeds are removed. The resulting cavity is filled with honey, covered with a cut off top. Sent to a dark place for 2 weeks. After that, the liquid is poured into a convenient container and sent to the refrigerator.
Herbal preparations are also effective.
You can take:
- calendula - 2 tbsp. l .;
- goldenrod - 2 tbsp. l .;
- celandine - 1 tbsp. l .;
- elecampane - 2 tbsp. l .;
- Leuzea root - 4 tbsp. l.
Or:
- elecampane - 4 tbsp. l .;
- gentian - 4 tbsp. l .;
- calamus - 3 tbsp. l .;
- mint - 4 tbsp. l .;
- birch buds - 2 tbsp. l .;
- motherwort - 2 tbsp. l .;
- dandelion root - 2 tbsp l .;
- wheatgrass - 2 tbsp. l.
The components are mixed, 2 tbsp is selected. l. collection, pour 1 liter. boiling water and kept on low heat for 10 minutes. Pouring the finished product into a thermos, let it brew for another 12 hours. You need to take the broth for at least 3-4 months for 0.5 tbsp. in a day. Then the therapy is interrupted for 14 days and the course is repeated.
Herbal remedies can last for years. Simultaneous use of medicines is also allowed. The positive effect will be noticeable within a month, but to obtain a lasting result, therapy must be long-term and systematic.
Diet
Fatty degeneration of the liver, the causes of which are associated with inaccuracies in nutrition, requires adherence to a diet. If fatty foods are not excluded from the menu, then even drug therapy may be ineffective.
Diet goals:
- facilitate the work of the liver;
- normalize lipid metabolism;
- control the level of glycemia;
- restore the work of the digestive system as a whole.

The patient should:
- eat at least 6 times a day. This normalizes the outflow of bile, allows you to activate metabolic processes;
- drink about 2 liters of liquid per day. It can be still mineral water, compote, green tea. Drinking plenty of water reduces the intoxication of the body;
- refuse to take alcoholic beverages;
- give preference to protein foods;
- eat foods in boiled, baked, stewed form. Food prepared in this way is easy to digest and does not overload the liver. Dishes should be warm.
Prohibited use:
- fatty foods;
- sweets high in carbohydrates;
- rich broths;
- legumes;
- mushrooms;
- onions and garlic;
- fatty meat and fish;
- canned foods;
- semi-finished products;
- offal;
- carbonated drinks;
- coffee;
- smoked meats.
The patient's diet should contain foods high in fiber. They provide a feeling of fullness for a long time, avoid overeating.
It is also useful to use:
- cereal soups;
- pasta;
- cottage cheese casseroles;
- vegetable stews;
- puddings;
- low fat dairy products;
- porridge (oatmeal, buckwheat);
- lean meat and fish;
- stale bread;
- honey;
- pumpkins, carrots, potatoes, zucchini.
Possible consequences, forecast
The prognosis of the disease is relatively favorable. Most often, it is enough to eliminate the cause of the pathology in order to restore the normal functioning of the liver. The patients' ability to work remains. It is imperative to follow the doctor's recommendations, correct dietary habits, increase physical activity, and eliminate alcohol consumption.
Without proper treatment, the disease will gradually progress, while the risk of developing:
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- hepatitis A. The disease in a neglected state ends with inflammation of the organ. At the same time, the patient's immunity decreases, the balance of hormones is disturbed, signs of intoxication appear;
- fibrosis. Scars are formed, the liver is completely disrupted;
- cirrhosis. Organ tissues are destroyed, liver failure develops;
- small cell cancer. It is the most severe complication, but rarely develops. The disease is practically incurable.
Even after a complete cure, it is necessary to monitor the state of the organ throughout life, do not forget about preventive measures. It is important to control body weight, glucose and cholesterol levels, proper nutrition, and regular exercise. Medication should be taken only on the recommendation of a specialist. In some cases, hepatoprotectors are prescribed to a patient who has had a disease for the purpose of prophylaxis.
Fatty degeneration of the liver in most cases is completely reversible. An important condition for recovery is the elimination of the causes that provoked the pathological process. Timely diagnosis and adequate therapy will help avoid inflammation and the development of fibrosis. It should be remembered that the disease may be asymptomatic, therefore it is important to timely undergo preventive examinations, especially in the presence of risk factors such as obesity, sugar diabetes.
Video about fatty liver disease
Malysheva about liver steatosis: