Content
- General concept of plasticity. Plasticity of consciousness
- Under. Petrov
- According to S.Yu. Klyuchnikov
- Plasticity of thinking
- By Lorenzo Valla
- According to Norman Joyce
- According to Maxim Vlasov
- How to develop
- Emotional plasticity
- By Susan David
- According to N. A. Wedmesh
- Plasticity of behavior (temperament)
- According to V.A. Wagner
- According to Yu.I. Savchenkov
- According to D.A. Zhukov
- Video about plasticity in psychology
Plasticity - it is flexibility, variability, adaptability, malleability to various influences. This term is widely used in psychology to characterize various concepts: "plasticity of thinking", "emotional plasticity", "plasticity of behavior".
General concept of plasticity. Plasticity of consciousness
Plasticity in psychology is a person's increased ability to psychically adapt to the environment in the process of communication and professional activity.
Under. Petrov
Practicing psychologist and hypnoanalyst Dmitry Petrov believes that plasticity (flexibility) is more or less inherent in any human body. Thanks to this quality, the individual easily assimilates new experience and knowledge, replaces outdated beliefs and emotional reactions.
According to the psychologist, the "plastic person" subtly feels where his needs end and the obsessive the influence of society, which allows him to show a sense of intuition, paying attention to the signals of his body.
According to S.Yu. Klyuchnikov
Plasticity or flexibility of consciousness is, in the opinion of a practicing psychologist, psychotechnologist and coach Sergei Yuryevich Klyuchnikov, a person's ability to avoid unnecessary collisions, while maintaining their strength. Plasticity is also understood as an instant reaction, which makes it possible to predict a person's actions and respond to them in a timely manner.
Describing this concept in his book "The Success Factor" S.Yu. Klyuchnikov noted that "plasticity" is the ability of an individual's psyche at the right time to adapt to the prevailing circumstances.
Plastic consciousness with flexible perception is free from psychological complexes, clamps and psychoenergetic blocks that inhibit and restrict it. Such flexibility, according to a specialist, allows you to protect yourself from any psycho-emotional blows much better, rigid principles and attitudes.

A "plastic" person, according to S.Yu. Klyuchnikova, is able to:
- take the point of view of the opponent, admitting that “others are right in some way”;
- notice the nuances of the psychological atmosphere and take note of all the signals that it sends;
- give in to people in small things, while remaining true to yourself and your beliefs in the main thing.
The plasticity (flexibility) of the individual's psyche allows him to:
- Learn to get used to the image of another person, understand his condition and prevent the possible development of a conflict, anticipating possible ways to resolve it.
- Respond quickly to any changes.
- Overcome the limitations of your egocentric position by developing a sense of compassion for those who unknowingly try to be aggressive.
Plasticity of thinking
Plasticity in psychology is, according to American psychologist Norman Joyce, the ability of a person to find many solutions in cases when others see only 1 or 2. Due to plasticity, there is an operational reorganization of the events taking place, followed by their direction in the right direction.
The concept of "plasticity" in psychology is used to characterize the "plasticity of thinking", which defines this term as the ability to dynamically lay out and meaningfully transform the structural components of the current situation in a peculiarly posed goals.
By Lorenzo Valla
The plasticity of the mind, was first defined by the Italian humanist and Renaissance presbyter Lorenzo Valla as the ability find and use favorable opportunities, smooth out sharp corners in any relationship, without bringing them to a conflict situations.
The philosopher also identified 5 important conditions for the development of the plasticity of the mind:
- communication with educated people;
- literary abundance;
- comfortable spot;
- free time;
- peace of mind.
According to Norman Joyce
Plasticity (flexibility) of thinking in the modern concept is, according to the American psychoanalyst and author of the book "Plasticity of the Brain" Norman Joyce, the ability of an individual to adapt and adapt to changing circumstances, with the help of his creativity and ability to think out of the box.
The flexibility of thinking was also defined by the Russian specialist and psychologist Maxim Vlasov, as the ability of an individual to "survive" using any, including non-standard methods, showing flexibility and the ability to abandon standard actions and views.
According to Maxim Vlasov
According to Maxim Vlasov, "plasticity of thinking" is a need that allows a person, in some cases, to preserve his life and achieve success in professional activity. The flexibility of the mind will allow a person to avoid deadlock situations, and if he gets into them, it will give an opportunity consider the problem from different angles, determining the maximum possible number of ways to resolve Problems.
Plasticity of thinking (cognitive flexibility) is not an innate, but an acquired quality that occurs when teaching a person vital skills and artificially creating situations that allow him to apply received knowledge.
The opposite concept of mental plasticity is mental rigidity associated with the inability of the brain to respond quickly to non-standard situations. The plasticity of a person's thinking allows him to quickly adapt to changes in the environment, see possible alternatives in behavior and easily switch from one type of activity to another.
Rigidity of thinking is characterized by a routine (traditional) way of acting, the inability to change attitudes and consider the problem from different points of view.
How to develop
Despite the fact that, according to scientists, cognitive flexibility is formed in a person up to the age of 20, under the influence of genetic and mental characteristics of the personality, family behavior patterns, temperament and life experience, there are a number of modern techniques that allow a person to develop cognitive flexibility in a more mature age:
| Exercise type | Method characteristics |
| "Brainstorm" | The technique is based on the subconscious creation of a crisis situation by a person and the search for the maximum number of ways to overcome it. Such an exercise allows you to expand your thinking, using it to include in the scope of your concepts new things that a person usually does not think about, because of his own unwillingness.
|
| "Improvisation" | The ability to improvise allows not only to develop plasticity, but also to learn how to approach any situation from the creative side. The purpose of this exercise is in a person's attempt to go beyond the "usual" framework of solving a problem, to feel a sense of freedom and to look for new, non-trivial ways out of the situation. |
| "Development of intuition" | Feelings in many cases are able to tell a person a way to overcome a problem that has arisen, which is why an individual it is necessary to develop the ability to listen to them, while not prioritizing them over the mental activities. |
| "Thinking process" | It consists in teaching an individual the methods and principles of solving various kinds of problems, by means of:
|
Also, in order to develop the plasticity of thinking in a person, according to experts, it is necessary:
- constantly strive for something new, without getting hung up on the existing circle of communication and field of activity;
- learn a lot of information;
- learn to adapt to emerging life situations;
- set yourself "ambitious" goals and try to achieve them;
- learn to play and pacify your negative emotions.
Emotional plasticity
Plasticity in psychology is the ability of a person to be aware of his emotions, not limiting himself to passive experience, but also use their mobility, flexibility and variability to choose the most optimal and adequate option response.
By Susan David
American psychologist and business coach Susan David in her book of the same name says that emotional plasticity (flexibility) does not imply a rigid change in emotions and attitudes. Its mechanism is built on the individual's ability to relax, stop worrying about every moment that happens or did not happen, and begin to perceive the events that are happening through the prism of awareness.
Under awareness, the author understands the conscious choice of a person of his emotional reactions, which easy to accomplish when moving your perception of reality from the past or future to the present moment. So, according to the psychologist, having included his responsibility and realizing the possibility of choosing his response to the stimuli sent nervous system, a person learns himself to choose the options for a possible response, both severe and destructive, and light or relaxed.
The concept of "emotional plasticity" comes from neuroscience (neuronal plasticity) and is associated with the ability of neurons to "connect" with each other, learning to perform the functions of dead cells.
Thus, thanks to emotional plasticity, according to psychologist Susan Davis, a person learns not to fix attention. on negative emotions and fears that cause stress and inhibit the development of vital functions, and learns to overcome stressful stages.
For each of them, the individual chooses his own solution: to leave his paths and reactions unchanged, or to try to overcome fear and focus on finding new solutions. Heavy emotions and experiences, according to Susan Davis, are not ignored, but simply excluded from perception, allowing the individual to notice and appreciate the dynamics of positive movement.
The development of emotional plasticity, according to a specialist, also allows a person not to panic. when change occurs, allowing yourself to trust feelings and intuition that help you realize and accept situation.
According to N. A. Wedmesh
According to a practical psychologist, speaker of the Medical and Psychological Center "PsychoMed" N.A. Vedmesh, the right choice of one or another emotional reaction is embedded in the mechanism of the brain and is available to every person, since in accordance with its structure, the stimulus, issued in response to it and the reaction connects a certain period of "silence", at the moment of which the organism chooses exactly how to should be enrolled.
By bringing their actions and reactions to automatism, people often lose sight of this gap, and its use allows one to see other, possible ways of solving the current situation.
The use of the gap between the stimulus and the reactions is, according to the expert, a reflection of the emotional plasticity that allows you to develop many talents and learn to "correctly" respond to non-standard situations.
Well-developed emotional plasticity allows a person to cope with low self-esteem, as well as to avoid the development of severe depressive states associated with emotional experiences about the possible development of future events. The danger of such a state, according to Dr. Vedmesh N.A., is that negative experiences are capable of bring a person to the development of a hypertensive crisis, while the significance of a future event is strong overpriced.
According to the specialist, emotional plasticity will make it possible to timely realize the meaninglessness of one's soul feelings, prevent the development of depression and allow you to start working on finding more productive solutions Problems.
According to the expert, it is not worthwhile to equate emotional plasticity with the desire to experience only positive emotions, since her task is not to focus on problems, but to realize and let go of negative emotions that interfere with the search for a way out of the prevailing situations.
In the professional field of activity, emotional plasticity becomes an invaluable quality that allows you to cope with stress, tension and any, even non-standard tasks. For the successful fulfillment of his professional duties, a person needs to foresee the possibility of the future of certain difficulties, but abandon unnecessary expectations and plans, opening up to emerging choices when changing situations.
Plasticity of behavior (temperament)
Plasticity in psychology is the ability of an individual to change his behavior depending on the emerging life situations.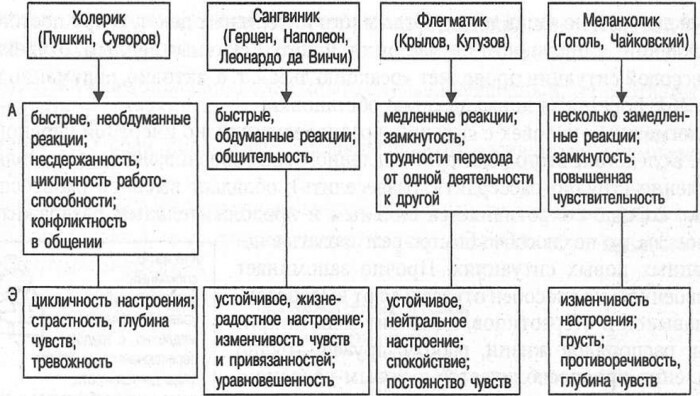
"Behavioral plasticity" is a concept that came to psychology from zoology and characterizes the possibility of a living being (including humans) adapting to changing environmental conditions (both external and internal) to adjust their behavior to the changed circumstances.
According to V.A. Wagner
Russian biologist and psychologist V.A. Wagner in his work "Biological Foundations of Comparative Psychology" defined the instinctive behavior of living beings as a variable a value that can change under the influence of external environmental influences, while species-typical behavioral frameworks remain in living beings, unchanged. This plasticity developed gradually in the course of evolution, under the influence of natural selection.
In modern psychology, there are 2 types of behavioral plasticity:
| Exogenous plasticity | Associated with a change in the behavioral phenotype (observed behavior) under the influence of an external stimulus, experience or environment. |
| Endogenous plasticity | Includes a change in behavior due to internal changes in the body (genotype, menstruation). |
These categories are also subdivided into:
- Contextual plasticity associated with the initiation of non-hormonal and hormonal mechanisms in the body that change behavior in response to external changes.
- Developing (dynamic) plasticity associated with behavioral change due to previously acquired experience.
According to Yu.I. Savchenkov
According to Doctor of Psychology, Honorary Professor of KrasSMU Yuri Ivanovich Savchenkov, behavioral plasticity plays of great importance for the adaptation of a person in the world around him, adjusting his behavior to gradually changing conditions life. Due to the short adaptation period to changed circumstances, plasticity allows you to quickly change the model of behavior in accordance with new requirements.
The plasticity of a person also allows him to deal with several things at the same time, which, according to the Russian writer and psychologist, Zhukov Dmitry Anatolyevich, is more inherent in women, than men, because they are better than men to cope with teaching work, which requires the simultaneous execution of 3 tasks at once: giving lectures, monitoring the audience and studying it reactions.
In contrast to women, men, according to the specialist, have a more inherent rigidity of behavior that prevents them quickly and painlessly adjust to circumstances, and forcing to firmly defend your point vision.
The concept of rigidity in psychology is the opposite of plasticity (flexibility), a term that defines inertia, slowness in adaptation to new conditions of life. If a plastic person quickly rebuilds his behavior when circumstances change, a rigid individual with with great difficulty changes his line of behavior, trying to fit his usual actions into the changed conditions life.
Plasticity of behavior, according to the doctor of psychology Savchenkov Yu.I., is most characteristic of this type of temperament as a sanguine person. While rigidity is inherent in choleric, phlegmatic and melancholic personality types.
According to D.A. Zhukov
The most striking example of the plasticity of behavior, according to the psychologist D.A. Zhukov, is the "Stockholm Syndrome", forcing a hostage, adjusting your behavior to external circumstances, to feel friendly feelings for the invader, and in some cases, to switch to him side.
Plasticity in psychology is a property of thinking, emotional perception and behavior, manifested in a person's ability to quickly adapt and adapt to emerging circumstances.
Not congenital, but acquired under the influence of hard work, self-development or changes in external (internal) circumstances quality allows a person not to get hung up on the situation and negative emotions, but to look for all kinds of, even non-standard ways of solving it.
Video about plasticity in psychology
The plasticity of the psyche: