Content
- What is syphilis
- Reasons for development
- Possible localization of rashes on the face
- Syphilis on the face in the primary period of the disease
- Syphilis on the face during the secondary period of the disease, what a rash looks like
- Papular syphilis
- Seborrheic papular syphilide
- Acneform (acne-like) syphilide
- Pustular syphilis
- Herpetiform syphilide
- Impetiginous syphilide
- Syphilis on the face in the tertiary period of the disease
- Gum on the face
- Tuberous syphilis of the face
- Serping (creeping) syphilis
- Syphilis of the nose
- With early congenital syphilis
- With late congenital syphilis
- In the primary period
- In the secondary period
- In the tertiary period
- Syphilis on the lips
- Congenital
- In the primary period
- In the secondary period
- In the tertiary period
- Symptoms of syphilis on the scalp
- Video about syphilis on the face
Syphilis on the face manifests itself as local purulent abscesses on the surface of the cheeks, nose, lips, epithelial tissues located in the circumference of the oral cavity. The inflammatory formations caused by this disease are provoked by a pathogenic microorganism - treponema pale. Photos of patients with syphilis show how a bacterial infection gradually destroys skin cells, provoking the development of deep and non-healing ulcers.
What is syphilis
Syphilis is a chronic infectious disease that affects the mucous membranes of all parts of the body, destroys the internal organs, cells of the central and peripheral nervous system, affects the bone, connective, muscle tissue of the musculoskeletal apparatus. Treponema pallidum, which is the causative agent of syphilis, is a sexually transmitted infection. The disease progresses gradually as the population of bacterial microorganisms increases.
There are the following routes of transmission of syphilis:
- sexual intercourse without the use of barrier contraception;
- during blood transfusion;
- injection of drugs or drugs with a syringe, which was previously used by a patient with syphilis;
- in the process of dental treatment and surgery;
- infection from an infected mother of a newborn baby (congenital type of disease);
- sharing the same toothbrush.
The most common route of transmission of syphilis is through unprotected sex. Despite this, in medical practice, there are cases of domestic infection with this disease. For example, pale treponema can get on dishes, cutlery, towels, linen. If a healthy person has wounds, abrasions on the skin, they come into contact with the infected surface of surrounding objects, then there is a high probability of domestic infection with syphilis.
Currently, there are no scientifically proven facts that pale treponema is transmitted through the urine and sweat of an infected person. The causative agent of syphilis is found in the saliva of an infected person if there are characteristic rashes, open ulcers in his oral cavity.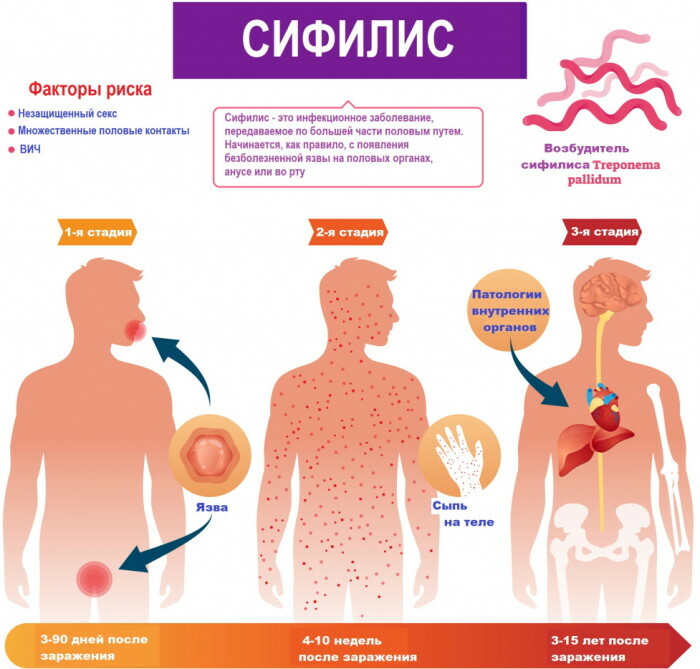
Treponema pallidum is highly infectious. This microorganism can enter the body of a newborn baby through the milk of a mother who became infected after the birth of the baby.
Reasons for development
Photos of syphilis in different areas of the face can be seen on the information stand near the venereologist's office. This disease develops as a result of infection of a healthy person with pale treponema. The foci of the inflammatory process on the surface of the lips, in the circumference of the oral cavity, on the cheeks arise due to primary infection with syphilis, or as a result of the total spread of pathogenic bacteria throughout all tissues organism.
In the first case, purulent and ulcerative formations appear on those areas of the face that have been in contact with the source of infection. For example, during oral sex without using barrier contraception.
In the second case, the cause of syphilis on the face is the total spread of pale treponema throughout the infected person's body. At this stage of development of syphilis, ulcerative formations may appear not only on the surface of the facial disc, but also on other parts of the body.
Possible localization of rashes on the face
The table below lists the main areas of the face, on the surface of which syphilitic rash is most often localized.
| Localization of rashes | Distinctive features of syphilitic rash |
| Lips | The rash that occurs on this part of the face looks like purulent abscesses of medium size. The foci of the inflammatory process are localized on the surface of the upper, lower lip, or are located in the corners of the oral cavity. This manifestation of syphilis is considered the most dangerous, since the infected one contributes to the spread venereal infection, using cutlery, common utensils, cups, cosmetics and towels. |
| Cheeks | The manifestation of syphilis on the cheeks can be easily confused with allergic or atopic dermatitis. On the patient's face, there are foci of inflammation, a red or pink rash without signs of suppuration. In this case, infection with pale treponema through touching the infected cheek is impossible. |
| Nose | Syphilitic chancre on the nose looks like a dense inflammatory formation. As the disease progresses, the destruction of epithelial tissues occurs. The result of the pathological process is the formation of a non-healing ulcer, which covers a significant area of the nose. |
Syphilis on the face (a photo of this disease displays the entire danger of an infectious process) can begin with a small purulent abscess or sore. Weakening of immunity, an increase in the numerical population of pale treponema in infected tissues leads to the growth of wound formation. The main danger of this disease is that its pathogen can penetrate into the deep layers of the skin, muscle fibers and bones of the face.
Syphilis on the face in the primary period of the disease
Primary syphilis on the face is characterized by the following clinical manifestations:
- the formation of a dense chancre, which is hard to the touch (formed in the zone of penetration of pale treponema into the epithelial tissues of the face);
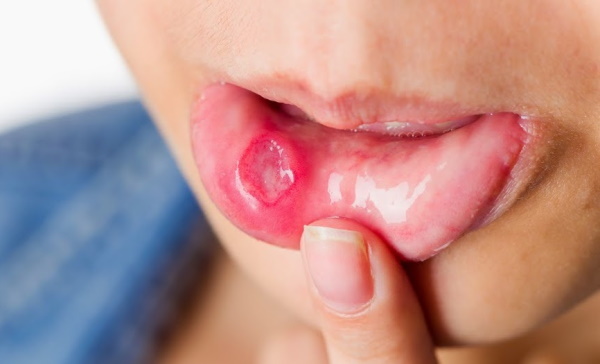
- the appearance of a painless rounded ulcer;
- the syphilitic wound has a smooth bottom and edges of the correct shape;
- the ulcer has signs of increasing inflammation, but there is no discharge of blood or ichor;
- the wound formation is not soldered to the circumferential tissues of the face;
- as the disease progresses, there is an increase in the syphilitic wound in diameter, as well as its growth into the deeper layers of the epithelium.
At the end of the stage of primary syphilis, pronounced swelling of the tissues appears around the resulting ulcer. There may be a characteristic redness of the skin of the face around the syphilitic ulcer.
Syphilis on the face during the secondary period of the disease, what a rash looks like
Syphilis on the face (a photo of this disease confirms the localization of syphilitic wounds on the surface of the lips and in the area corners of the mouth) is manifested by a small rash of red or pink color, which covers a large area cheeks.
Papular syphilis
The appearance of papular syphilis occurs in patients with secondary recurrent syphilis. The inflammatory mass on the face has an opal hue with a characteristic ham rim. A syphilitic papule is localized in the corner of the mouth on the left or right side. In appearance, it resembles a jam.

In most cases, papular syphilis is accompanied by additional symptoms in the form of rashes of the oral mucosa.
Seborrheic papular syphilide
The development of seborrheic syphilide is manifested by the formation of multiple red papules, which merge into one continuous plaque with signs of an inflammatory process. Extraneous neoplasms do not cause pain, do not bleed and do not emit purulent exudate. As syphilis progresses, seborrheic syphilis can spread from the cheeks to the epithelial tissues of adjacent facial areas.
Acneform (acne-like) syphilide
Acneform syphilis is manifested by single or multiple rashes in the form of follicular papules. At the apex of the inflammatory mass, there is a pustule with a diameter of 2 to 3 mm. With acne syphilis, the entire rash has a regular conical shape.
Syphilitic neoplasms secrete purulent exudate, which dries quickly, forming a layer of crust from a yellow to brownish tint. After rejection of the surface layer of the papule, pigmented scars are visible at its apex. In terms of clinical manifestations, acneform syphilide resembles acne, but with a much lesser severity of the inflammatory process.
Pustular syphilis
Pustular syphilis is characterized by the following distinctive features:
- the oral mucosa has no signs of infection;
- on the surface of the red border of the lips, a non-healing ulcer is formed, which for a long period of time remains the same size without growing to the sides and deep into the epithelial tissues;
- the bottom of the syphilitic pustule has a perfectly smooth or pitted bottom.
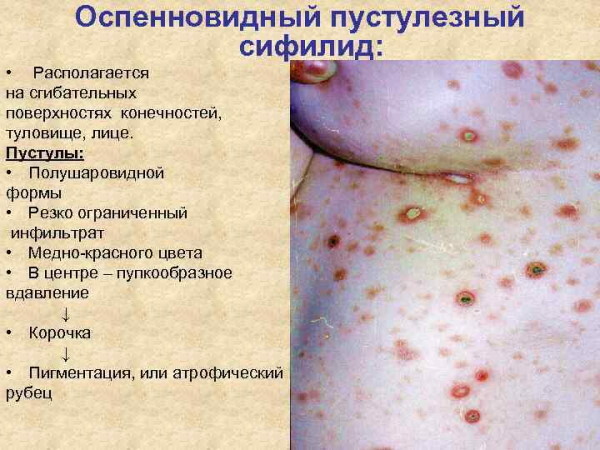
The diagnosis of pustular syphilis is considered a difficult task even for experienced venereologists. In this case, secondary syphilis on the face can manifest itself only with the above symptoms. The final diagnosis is made on the basis of the results of serological reactions that determine the bacterial invasion of treponema pallidum.
Herpetiform syphilide
A distinctive feature of syphilis herpetiformis is the focal appearance of red papules, which cause swelling of the epithelial tissues of the face. In terms of clinical manifestations, this symptomatology of secondary syphilis resembles a rash caused by a herpes infection. Timely venous blood serological test confirms the fact of infection with treponema pale.
Impetiginous syphilide
Impetiginous syphilis has the following morphological features:
- a bacterial rash appears as a papule;
- the cycle of development of syphilitic education lasts from 3 to 5 days;
- after a specified period of time, a yellowish superficial crust forms in the center of the papule.
A severe course of secondary syphilis may be accompanied by a complicated form of impetiginous syphilis. In this case, multiple papules spread over the entire surface of the cheeks, forming extensive plaques with signs of sluggish inflammation.
Syphilis on the face in the tertiary period of the disease
Syphilis on the face, a photo of which resembles a herpetic rash, manifests itself as inflammatory symptoms of varying severity. In the tertiary period of the development of this disease, numerous signs of destructive lesions of internal organs, walls of blood vessels, brain tissue and peripheral nerves. The skin of the face is destroyed by deep and extensive ulcers that are difficult to treat with medication.
Gum on the face
In the tertiary period of syphilis, gums are formed on the patient's face, which have the appearance of a deep ulcer of an irregular shape. From a syphilitic wound of this type, ichor and lymphatic fluid are secreted. As the tissues dry, a yellowish crust with a brown tint is formed on the surface of the gum. After the ulcer heals, deep scars remain on the patient's face. The gum contains the highest concentration of pale treponema.
Tuberous syphilis of the face
In patients with tertiary syphilis with manifestation of tubercular syphilis of the face, the following symptoms are present:
- on certain areas of the face, dense formations in the form of tubercles are formed;
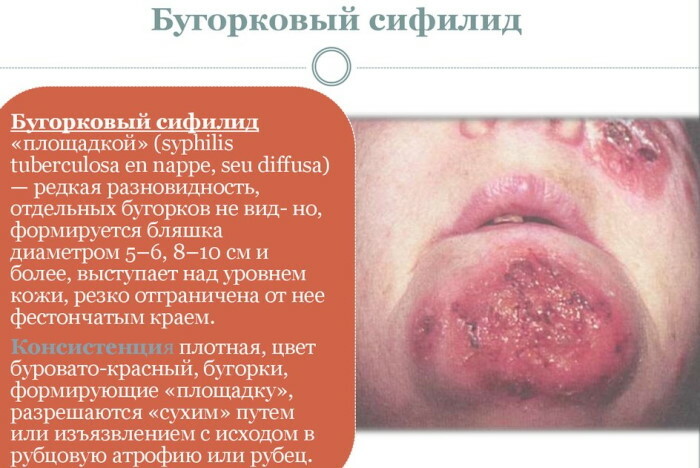
- new nodes appear slowly;
- syphilitic bumps are bluish or reddish;
- have dimensions of about 5 mm in diameter, and can also rise above the general level of the face up to 3 mm.
The final stage of development of tubercular syphilis of the face is ulceration of the nodular formations. At the site of tissue seals, gums of different sizes appear. Serous exudate follows from ulcerative formations.
Serping (creeping) syphilis
Serping syphilis is manifested by multiple recurrent rashes that look like dense formations. A fresh rash coexists with old facial redness. Creeping syphilis covers the cheek area, localized on the surface of the chin, in the area of the triangle of the nose. A serpentine rash with syphilis can spread over the entire surface of the face, as well as cover the scalp.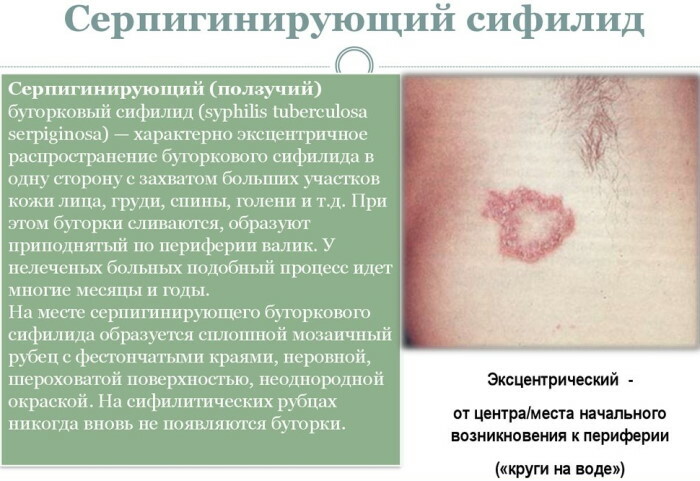
Separate syphilitic seals of this type, after ripening, transform into small ulcers, from which the ichor is released.
Syphilis of the nose
Syphilis on the face, a photo of which resembles an acute form of acne, affects the epithelial tissues of the nose. The development of the disease begins with the formation of a dense chancre of a bluish or reddish color.
With early congenital syphilis
Signs of early congenital syphilis appear in the first 3 months. after the birth of a child infected with treponema pale. An infected infant has persistent nasal congestion. Purulent contents or blood mixed with mucus are periodically released from the nasal canals. The child does not have full nasal breathing.
With late congenital syphilis
More serious damage to the nose caused by late congenital syphilis occurs in children aged 2 years and older.
A sick child has the following symptoms:
- a gummy ulcer forms on the nose;
- the process of slow destruction of the nasal septum starts;
- the pathological process involves the hard palate and tissue of the periosteum.
Violation of the anatomical structure of the nose leads to the development of concomitant complications. On the frontal and parietal regions of the child's skull, signs of deformational changes appear in the form of tubercles and eminences.
In the primary period
Syphilic lesions of the nose in the primary period of the development of this disease is considered a rarity. The destruction of the tissues of this organ of the respiratory system is possible in cases where an infectious infection of its mucous membrane occurs with non-sterile medical instruments, contaminated with a finger.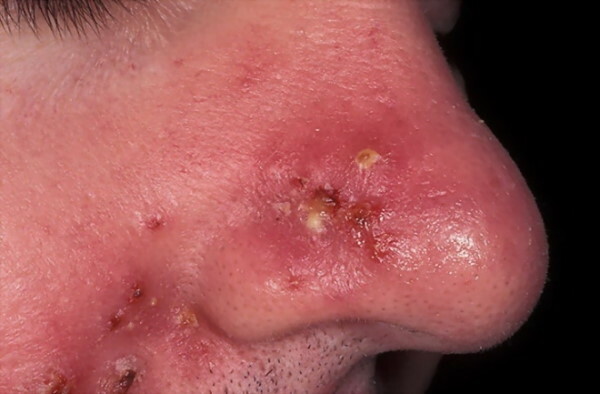
In this case, the patient has the following symptoms:
- a dense chancre forms at the tip of the nose, which transforms into an ulcer;
- submandibular lymph nodes swell;
- nose is stuffed up all the time;
- an ulcer on the tip of the nose gives off a bloody exudate.
In the initial period of development of syphilis, the appearance of a hard chancre inside the infected nasal canal is not excluded. In such a situation, the surface of the nose remains without visual signs of bacterial destruction.
In the secondary period
In the secondary period of the development of syphilis, the following additional symptoms are added to the ulcerative lesion of the nose:
- multiple papules appear in the nasal passages, and the mucous membrane is affected by an erythematous rash;
- nasal congestion alternates with a runny nose, which is difficult to get rid of with drugs;
- red papules are located at the entrance to the nasal canals;
- the surface of the papular rash is covered with a yellowish crust and cracks.
Chronic inflammation inside the nasal canals leads to rapid detachment of the ciliated epithelium with further formation of erosion. Eczema can join this pathological process.
In the tertiary period
According to medical statistics, tertiary nasal syphilis occurs 2-3 times more often than its primary and secondary syphilitic lesions.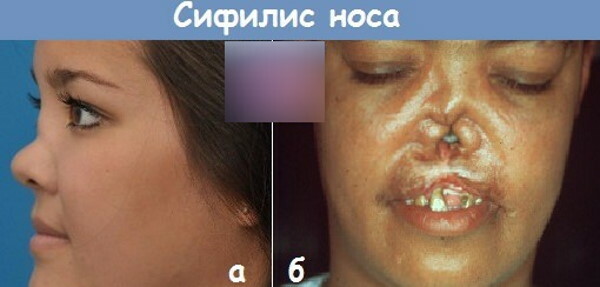
In this case, the patient has the following symptoms of the disease:
- gum or open ulcers with oozing infiltrate form on the surface of the nose;
- non-healing wounds affect epithelial tissues, the mucous membrane of the nasal canals and the periosteum;
- the septum of the nose is damaged;
- the patient's nose acquires a saddle shape.
The advanced stages of tertiary syphilis lead to the complete ulcerative decomposition of the soft tissues of the nose, its septum, periosteum and bone. During rhinoscopy, a through hole is found connecting the entrance to the nasal canals, as well as the patient's oral cavity. Tertiary syphilis of the nose is dangerous because of the high probability of the spread of the infectious process to the cranial cavity.
Syphilis on the lips
Syphilitic lesion of the face is manifested by rashes on the surface of the lips. The severity of this symptom depends on the stage of the venereal disease.
Congenital
Congenital syphilis of the lips is diagnosed in the first 3 months. after the birth of the child.
The patient has the following symptoms:
- multiple rashes around the mouth and on the border of the lips;
- papules are red or coppery;
- the submandibular lymph nodes are edematous.
In the absence of adequate drug treatment, the disease progresses slowly with the formation of new syphilitic ulcers.
In the primary period
Primary syphilis of the lips is manifested by the formation of a hard chancre, which looks like a round compaction of epithelial tissues. 1-2 weeks after infection with syphilis, an ulcer opens at the site of this nodule, from which a blood fluid is periodically released. A thin yellow or reddish crust forms on top of a syphilitic wound on the upper or lower lip, and then it dries up and cracks.
In the secondary period
A distinctive feature of secondary syphilis of the lips is the addition of itching of epithelial tissues and the appearance of a syphilitic rash. Rashes on the upper and lower lip appear after the healing of the ulcerative chancre.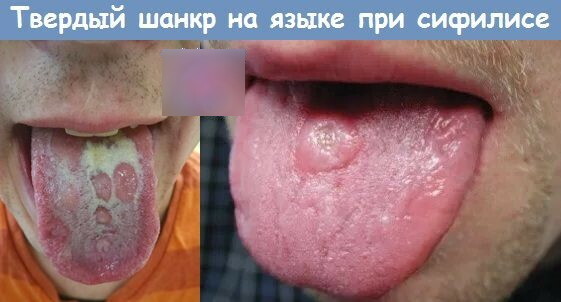
The secondary syphilitic rash is reddish-brown in color. In appearance, these rashes resemble the manifestation of other dermatological diseases. Secondary syphilitic rash disappears after 2-6 weeks, even in those clinical cases when a person is not being treated with drugs.
In the tertiary period
Tertiary syphilis develops 3-5 years after infection with treponema pale. At this stage of the disease, signs of lip infection are extremely rare.
If tertiary syphilis still spreads to this part of the patient's face, then the following symptoms are diagnosed:
- syphilitic gums and tubercles are formed only on one or on two lips at once;
- seals of epithelial tissue dissolve, forming painful ulcerations;
- the pathological process spreads from the surface of the lips to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, affects the hard palate, uvula.
During the examination of patients with signs of tertiary syphilis of the lips, the venereologist conducts differential diagnostics for tuberculosis infection and tissue damage by a malignant tumor.
Symptoms of syphilis on the scalp
Diffuse baldness is diagnosed in 15-20% of patients with syphilis. Loss of scalp occurs in lesions. First, a patient with syphilis loses hair in the back of the head and temples. Then baldness covers all areas of the head. This symptom appears after 3-6 months. after infection with pale treponema.
With the beginning of antibiotic therapy, the process of gradual restoration of the previous hairline is started. The appearance of this symptom indicates that the drug treatment is successful. A distinctive feature of syphilitic lesions of the scalp is that this part of the body does not itch, is not affected by gums, ulcers, and there is no peeling of the skin.
Syphilis on the face appears within 2-3 weeks after infection with treponema pallidum. One of the first symptoms of this disease is the formation of a hard chancre. This is a thickening of epithelial tissue that looks like a pea or cherry pit. After 1-2 weeks, the skin covering the chancre is ulcerated.
A non-healing wound forms on the surface of the lips or nose of the patient, from which the ichor is released. Syphilis on the cheeks is manifested by a multiple rash of a red or copper hue, and by its external signs it resembles acne. Photos of syphilitic lesions of the face confirm the danger of this disease, as well as the severity of the infectious process.
Video about syphilis on the face
Symptoms of syphilis on the face: