Content
- What is blood sugar and why is it needed?
- Norms of indicators by age, time of the test
- How blood sugar levels are determined
- Why does the sugar indicator "jump"?
- Insulin deficiency
- Insulin resistance
- Hereditary predisposition
- What does a stable sugar level 21-21.9 mean, the reasons for the increase in indicators
- How does the rise in blood sugar to 21 feel?
- Polyuria
- Polydipsia
- Polyphagia
- Rapid weight loss
- Itching
- Muscle weakness
- Inflammation of the skin
- Deterioration of vision
- Why is a sugar level over 21 dangerous?
- What to do if your sugar level is above 21
- Drugs
- Diet food
- Sugar substitutes
- Can sugar levels be stabilized permanently?
- Video about high blood sugar
Sugar is an integral part of the biochemical composition of the blood. This substance ensures the stability of energy metabolism, nourishes the tissues of internal organs, brain cells, and takes part in the implementation of the functions of the musculoskeletal system. Blood sugar is regulated by the hormone insulin, which is produced by the pancreas.
Normally, in a healthy person, the concentration of sugar on an empty stomach after fasting for 8 hours should not exceed 5.5 mmol per 1 liter of capillary blood. An increase in this level indicates the first signs of diabetes. Blood sugar, which is in the range of 21 mmol / l, causes the onset of a severe form of hyperglycemia with the further development of a precomatose state.
What is blood sugar and why is it needed?
Sugar in the blood is glucose, which is formed after the metabolic breakdown of sucrose in the organs of the digestive system. Being in the gastrointestinal tract, this substance is rapidly absorbed into the systemic circulation, and then spreads to all cells and tissues of the body. Glucose provides over half of all human food energy needs.
The functional purpose of sugar lies in its following properties and effects on the body:
- ensures the stability of metabolic processes;
- saturates the cells of all parts of the body with vital energy;
- takes part in most of the intracellular chemical reactions associated with the oxidation process;
- is a structural basis in the composition of cell membranes;
- accumulates in liver tissues as a reserve reserve of fast energy;
- participates in the thermal regulation of the general body temperature.
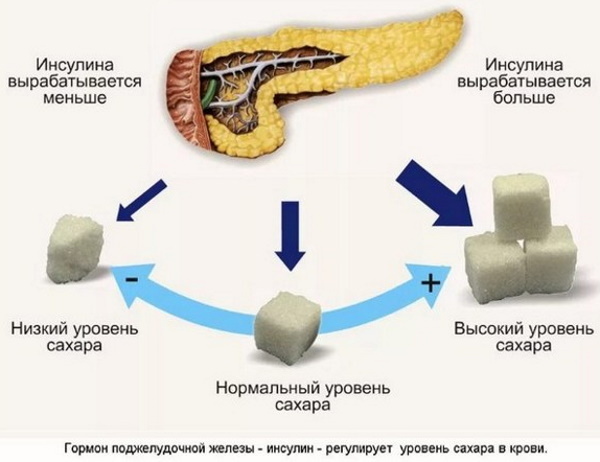
Sugar in the blood, which is within the normal range, ensures the stable operation of all parts of the human body. An increase in glucose to a level of 21 mmol / l causes severe symptoms in the form of confusion, acute metabolic disorders.
Norms of indicators by age, time of the test
The blood sugar concentration rate is the same for adults of all ages. Testing for glucose is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach after 8-14 hours of fasting. Normally, the composition of the patient's capillary blood sugar should not be more than 5.5 mmol / l. If, according to the results of laboratory research, 6.1 mmol / l of glucose is immediately detected in a person, then he is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus.
This analysis is performed in a biochemical laboratory using special reagents, or the same strips are used for express testing using a special electronic device - glucometer. The glucose test results are known after 2-3 minutes. after capillary blood collection.
How blood sugar levels are determined
Blood sugar 21 mmol / l is an indicator that indicates a serious condition of the patient. The table below describes the main methods by which the level of glucose in the composition of venous and capillary blood is determined.
| Method for determination of glucose | Critical indicator |
| Capillary blood examination | To perform this analysis, capillary blood collected from the bundles of the ring finger is used. A result of 6.1 mmol / L is considered critical, and also indicates a violation of carbohydrate metabolism. The study is performed in the morning on an empty stomach. The patient's last meal should take place the night before. The day before donating blood, it is not recommended to overeat, consume large amounts of sweet or fatty foods. |
| Venous blood analysis | In the process of examining venous blood, the sugar level is also determined. In a healthy person who has no signs of metabolic disorders, this indicator is not more than 6.0 mmol / l. If there are results of 7.0 mmol / l, the patient is given a preliminary diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. To perform this study, 2-3 ml of venous blood is sufficient. |
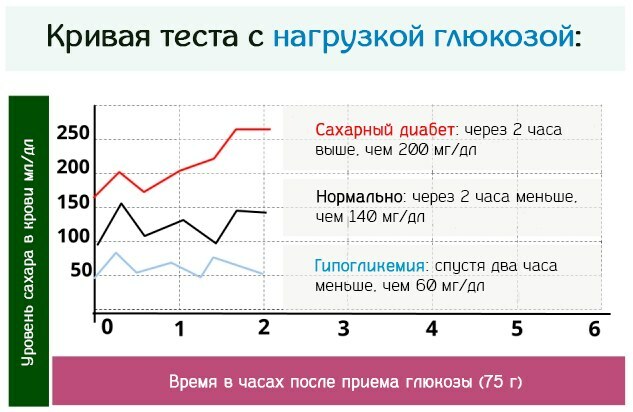
| Glucose tolerance test | The glucose tolerance test measures blood sugar levels by applying additional stress to the pancreatic tissue. The principle of this technique is that a person donates capillary blood for a standard analysis of sugar levels. After 5 minutes. after taking biological samples, the patient drinks 1 glass of water at room temperature, in which 75 g of granulated sugar is dissolved. After 1 hour, the glucose level is measured again. A result of less than 7.8 mmol / L is considered the norm. Upon receipt of indicators in the range from 7.8 to 11.0 mmol / l, the patient is enrolled in the risk group for the possible development of diabetes due to impaired glucose tolerance. The test result over 11.0 mmol / l confirms the presence of already acquired diabetes mellitus. |
| Clinical analysis of urine | Normally, no sugar crystals should be found in the urine. The appearance of glucose in the urine indicates a violation of carbohydrate metabolism. Patients with a similar urinalysis result are diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. |
In combination with the above laboratory tests, the patient's general condition is assessed. People with high sugar levels have an insatiable feeling of thirst, increased dryness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, decreased visual acuity, and rapid weight loss. A persistent odor of acetone from the mouth is also one of the signs of a high concentration of glucose in the systemic circulation.
Why does the sugar indicator "jump"?
Blood sugar 21 mmol / l is diagnosed in patients with diabetes mellitus who do not take hypoglycemic drugs. An unstable concentration of glucose in the blood indicates a malfunction of the pancreas. There are 3 main factors that cause your blood sugar to rise periodically.
Insulin deficiency
The tissues of the pancreas are responsible for the synthesis of the hormone insulin, which is involved in the metabolic process of converting glucose to the level of dietary energy. A systemic deficiency of this substance leads to a sudden or gradual increase in blood sugar.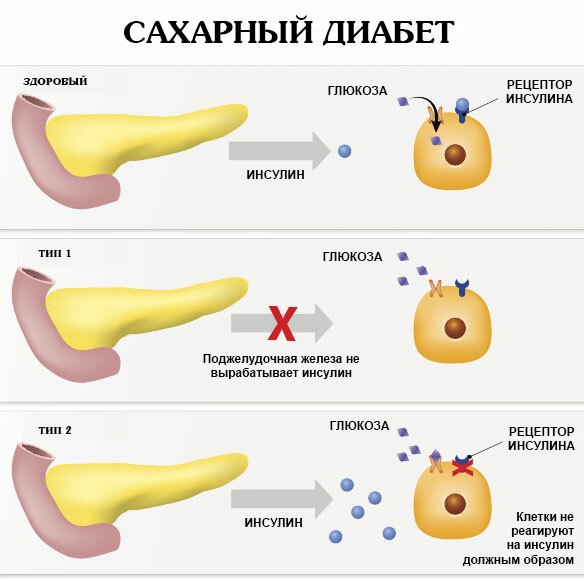
Lack of insulin can be caused by local damage to the cells of the pancreas due to chronic alcoholism, malnutrition, hereditary predisposition. Patients with unstable blood glucose levels require regular hormone replacement therapy in the form of injections of insulin.
Insulin resistance
Periodic increases and decreases in blood sugar can be caused by an acquired or congenital disruption of the physiological interaction between cells of certain tissues and insulin. In this case, the patient's pancreas produces the optimal amount endocrine hormone, but there is no effective relationship between insulin receptors and organelles of cells.
Hereditary predisposition
It has been scientifically proven that the propensity for high blood sugar levels is passed on to offspring along with genetic information. According to medical statistics, if type 1 diabetes is diagnosed in at least one of the parents, then there is a 10% chance of transmitting this pathology to the child. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is inherited in 80% of cases.
What does a stable sugar level 21-21.9 mean, the reasons for the increase in indicators
Blood sugar 21 mmol / l is a pathological sign that means the development of severe diabetes. Such glucose levels indicate progressive hyperglycemia. In this case, significant harm is caused to the internal organs of the patient, blood vessels, the tubular structure of the kidneys are damaged, and the work of the organ of vision is disrupted. The concentration of glucose in the range of 21-21.9 mmol / l is dangerous for the risk of diabetic coma.
The persistence of such high levels of sugar in the circulatory system can be caused by the following reasons:
- non-observance of dietary norms in the presence of already diagnosed diabetes mellitus;
- refusal to take hypoglycemic drugs;
- incorrectly selected insulin dosage;
- development of pancreatic insufficiency.
An increase in glucose to a concentration of 21-21.9 mmol / l is possible in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus who have not previously been tested for blood sugar levels, but at the same time had a violation of carbohydrate exchange. In this case, the signs of diabetes are determined suddenly after a sharp deterioration in the general well-being of the patient.
How does the rise in blood sugar to 21 feel?
Blood sugar 21 mmol / L is determined by the results of the analysis of capillary or venous blood. 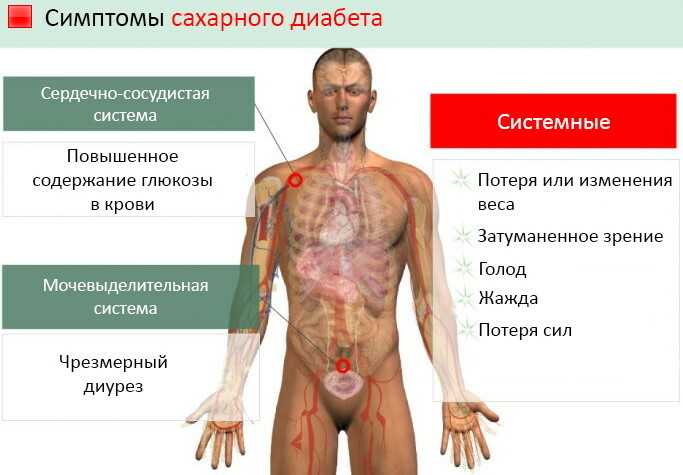 A person with such high glucose levels has a complex of pathological symptoms.
A person with such high glucose levels has a complex of pathological symptoms.
Polyuria
The state of polyuria is the frequent flow of urine that is caused by a sharp increase in osmotic pressure due to excess glucose concentration. Normally, sugar in urine should be completely absent. The interval between the next urge to urinate can be 15-20 minutes. At night, the flow of urine becomes even more active.
Polydipsia
Polydipsia is a feeling of constant thirst that cannot be satisfied with frequent and abundant drinking. The patient feels increased dryness of the oral mucosa. Water that is consumed due to intense thirst is almost immediately excreted by the kidneys during urination. The loss of a large amount of fluid causes an increase in osmotic pressure in the general bloodstream.
Polyphagia
People with a blood sugar level of 21 mmol / L are constantly hungry. The occurrence of this symptom is associated with a systemic violation of metabolic processes in the body. Due to the lack of a sufficient amount of insulin, cells of internal organs and muscle tissues lose their ability to process and absorb glucose.
The body tries to compensate for the energy deficit by consuming large amounts of food. Frequent, high-calorie and plentiful nutrition does not cause a feeling of satiety, but only provokes a further increase in blood sugar.
Rapid weight loss
The rapid loss of muscle and adipose tissue is due to the loss of glucose from the general metabolism. A person with a sugar level of 21 mmol / L continues to eat large amounts of food, experiences severe hunger, and continues to lose weight. The appearance of this effect is due to the fact that the patient's body starts the process of catabolism of protein and lipid compounds in order to obtain a sufficient amount of energy.
Itching
The itching sensation extends to the oral mucosa and epithelial tissues of the body. In this case, the patient may completely lack signs of irritation and redness of the skin.
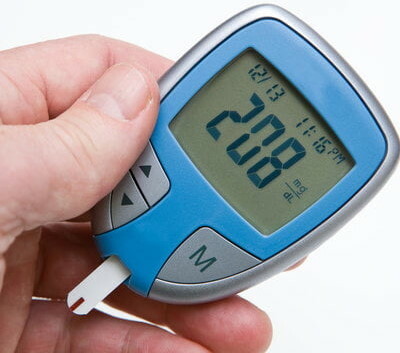
The itching sensation increases in proportion to the next rise in blood sugar.
Muscle weakness
Excessive concentration of glucose in the blood triggers the mechanism of damage to the nervous system. The innervation of muscle tissues is impaired, which is manifested by a feeling of general physical weakness in the upper and lower extremities.
Inflammation of the skin
Even minor damage to epithelial tissues is accompanied by acute inflammation, secretion of ichor and prolonged cell regeneration. The intake of antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs does not improve the dynamics of the healing of wound areas of the body.
Deterioration of vision
Patients with diabetes mellitus, whose blood glucose level is kept within 21 mmol / l, complain of a periodic decrease in visual acuity. The occurrence of such sensations is due to the fact that sugar microcrystals damage the structure of the eyeball, and also disrupt the functions of the optic nerve.
Why is a sugar level over 21 dangerous?
Prolonged maintenance of blood sugar levels above 21 mmol / l is dangerous for the development of the following severe complications:
- the occurrence of diabetic ketoacidosis, when the products of metabolism of fats and proteins accumulate in the blood, causing general intoxication of the whole body;
- hyperosmolar coma, which occurs due to severe dehydration (a prerequisite for the onset of this complication is an insatiable feeling of thirst and frequent urination);
- damage to capillaries and walls of large blood vessels;
- lactic acid coma, which occurs due to the accumulation of excess lactic acid in the blood (people are at risk over 50 years old who have concomitant diseases in the form of renal, hepatic failure, pathologies of the heart and blood vessels);
- acidosis with further development of the collapse of the cardiovascular system;
- a decrease in blood pressure indicators to critical indicators (the patient loses consciousness, or is in a state of apathy, prostration);
- diabetic retinopathy, the manifestation of which is the destruction of the retina of the eyeball;
- increased fragility of blood vessels with a simultaneous violation of their permeability to general blood flow;
- focal lesion of peripheral nerves;
- loss of pain and temperature sensitivity;
- multiple hemorrhages in the fundus, impairing the function of vision;
- diabetic nephropathy, which leads to the destruction of the tubular structure of the kidneys (patients with this the disease eventually face a severe complication in the form of chronic renal failure);
- arthropathy with destruction of the structure of the joints of the upper and lower extremities, the appearance of pain, crunching, a decrease in the volume of synovial fluid;
- clouding of the lens and the development of cataracts of the eye;
- the formation of purulent-necrotic ulcers localized on the fingers and feet of the lower extremities (this complication is caused by damage to peripheral nerves, blood vessels, soft tissues, and the consequence of this pathology is amputation);
- pathological changes in the psychoemotional state, which are expressed by deep depressions, a sharp change in mood;
- the occurrence of anxiety disorder;
- dysfunction of the muscles responsible for chewing and swallowing food.
The main danger of maintaining sugar levels above 21 mmol / L is the high risk of hyperglycemic coma. In this case, against the background of the above complications, the patient loses consciousness, the work of the central nervous system partially stops. To eliminate the pathological signs of hyperglycemia, a diabetic needs emergency medical care with the introduction of hypoglycemic drugs. Otherwise, death may occur.
What to do if your sugar level is above 21
People with a blood sugar level higher than 21 mmol / l should undergo complex treatment in a hospital of the endocrinology department.
Drugs
Patients with a blood sugar level of 21 mmol / L are prescribed an injection of insulin. The dosage of the pancreatic hormone is selected individually by an endocrinologist.
The following diabetic medications are also used to maintain a stable blood sugar level:
- Siofor;
- Metfogamma;
- Diaglizide;
- Diabetone;
- Diaformin;
- Metformin.
The above drugs help to reduce too high blood sugar levels, and also restore the patient's normal well-being. These medicines are taken during a continuous therapeutic course. The dosage and duration of treatment are determined by the doctor.
Diet food
People with high blood sugar should minimize their intake of the following foods:
- butter;
- fatty meats;
- granulated sugar;
- smoked meats;
- jam;
- chocolate candies;
- fatty fish;
- pumpkin and sunflower seeds;
- honey;
- sausages;
- ice cream;
- biscuits and other confectionery products containing sugar, excess fat;
- sweet carbonated drinks;
- sour cream with a high concentration of milk fat;
- mayonnaise and other sauces, which contain preservatives, chemical additives, starch.
 For patients with high blood sugar, alcoholic beverages are strictly prohibited. and all foods that put additional stress on the pancreatic tissue and liver.
For patients with high blood sugar, alcoholic beverages are strictly prohibited. and all foods that put additional stress on the pancreatic tissue and liver.
Sugar substitutes
Patients with diabetes who have stopped consuming sugar are advised to use the following substitute drugs for this product:
- Huxol;
- Stevia extract in powder form;
- Erythritol "Melon sugar";
- Sucrasite;
- Milford;
- SoloSvit.
These drugs are available in the form of white round tablets, which are thrown into an already prepared dish or drink. In terms of taste, they are identical to granulated sugar, but do not cause an increase in glucose.
Can sugar levels be stabilized permanently?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease of the endocrine system. Modern medicine has not yet found working methods that would completely normalize glucose levels in patients with this disease.
High sugar levels can be effectively controlled with hypoglycemic drugs, as well as by adhering to dietary norms. In this case, the prognosis for life with diabetes is favorable. Subject to all the rules of treatment, restrictions on the use of food rich in sugar, carbohydrates, the patient remains able to work, and also avoids the development of severe complications.
Sugar is a biochemical substance that the human body needs as a source of food energy. In healthy people who do not have pancreatic diseases, the normal capillary blood glucose level is no more than 5.5 mmol / L. Exceeding these indicators indicates the manifestation of the first signs of diabetes mellitus.
Glucose, which is in the range of 21 mmol / L, causes a precomatose state. The patient experiences dizziness, dry mouth, intense thirst and hunger. Such high blood sugar levels cause severe complications in the form of a diabetic foot, lesions of the nervous system, kidneys and the organ of vision.
Video about high blood sugar
Malysheva about high sugar, but not diabetes:
