Content
- Types
- Physiological (transistor)
- Pathological
- Pharmacological (medicinal)
- Stages and degrees
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Diagnostics
- Treatment methods
- Medications
- Operative treatment
- Radiation therapy
- Folk remedies
- Possible consequences and complications
- Video about hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia is a condition in which the systemic flow there is an increase in prolactin (lactogenic hormone or mammotropin) produced by the pituitary gland. The hormone causes the breast to grow and develop, and after the baby is born, it affects milk production. Women normally have small amounts of prolactin in their blood, levels of which are controlled by other hormones such as dopamine. In non-pregnant women, lactogenic hormone regulates the menstrual cycle.
Elevated mammotropin interferes with the normal production of other hormones such as estrogen and progesterone. This can change or stop ovulation and lead to irregular or missed periods. In some women, the increase in prolactin levels goes away without any symptoms.
Types
Hyperprolactinemia in women (symptoms and subsequent treatment are discussed with a specialist) has several well-known causes. Among them are gynecological diseases: adnexitis, endometriosis, uterine myoma. But by their nature, the main ones are physiological and pathological causes.
Physiological (transistor)
In this case, the increase in prolactin is associated with a natural increase in hormone production. Its increase is observed during sleep, after increased consumption of protein products, during intercourse, during pregnancy, lactation. Prolonged stress or the moment of taking venous blood for analysis also leads to jumps in the level of lactogenic hormone.
In the female body, an increase in prolactin is noted in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, since at this time it is responsible for preparing for pregnancy.
At the points listed above, an increase in the concentration of the hormone is a normal reaction of the body. Treatment for this condition is not required.
Pathological
Clinically, the increase in the level of the hormone against the background of the development of the disease is divided into tumor and non-tumor type.
A tumor - prolactinoma - forms in the pituitary gland, the part of the brain responsible for the production of mammotropin. At the same time, an increase in concentration by more than 2 thousand. units.
The non-tumor type is observed with a decrease in the functioning of the thyroid gland. Also, the level of prolactin increases with the development of renal failure, chest pathologies, liver cirrhosis or polycystic ovary syndrome.
Pharmacological (medicinal)
Hyperprolactinemia in women (symptoms help determine the degree of development of the process) is a common endocrinological condition that can be caused by pharmacological reasons. Some drugs increase serum prolactin levels. Typical antipsychotics often contribute to the development of drug-induced hyperprolactinemia. Among them, Risperidone stands out, which is most likely to increase the level of the hormone.
Other medications help to increase the production of mammotropin:
- antidepressants (Anafranil, Norpramine);
- antipsychotics (Haldol, Zyprexa);
- antihypertensive drugs (Isoptin);
- antitussives (Raglan, Primperan);
- H2-acid blockers (Tagamet);
- Estrogen 3.

Oral estrogen-containing contraceptives, psychotropic and narcotic drugs, antidepressants and antiemetic drugs work to increase prolactin.
Stages and degrees
Disease-induced hyperprolactinemia has:
- primary stage;
- secondary;
- iatrogenic.
The primary form is one of the main causes of female infertility. In this case, hyperprolactinemia manifests itself with micro- and macroadenomas or for no apparent reason (idiopathic). With endocrine or somatic diseases, a secondary stage of the disorder manifests itself. The iatrogenic form unfolds against the background of taking certain groups of drugs.
Symptoms and Signs
Hyperprolactinemia of the initial stage, when the level of prolactin begins to change, is difficult to miss, since there are no obvious signs.
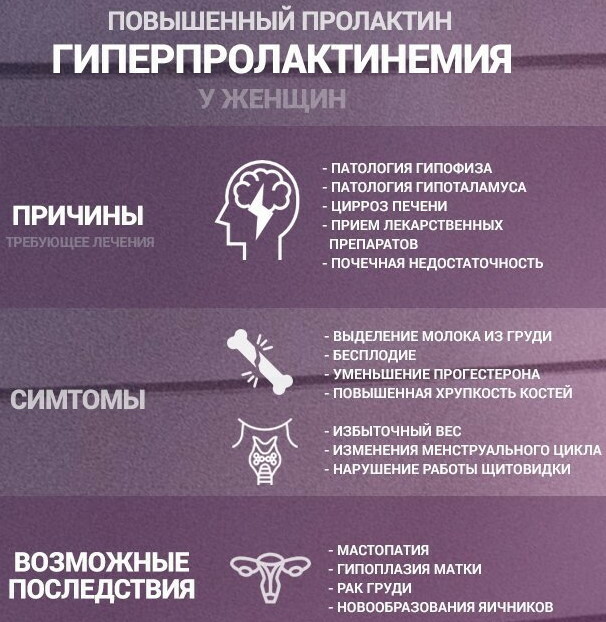
However, an increase in prolactin levels in women can affect the menstrual cycle and cause loss of libido and other general symptoms:
- development of psychoemotional disorders (depression, sleep disturbance, memory impairment, irritability);
- metabolic disorders in the form of an increase in lipid levels, the development of insulin resistance, obesity;
- reproductive disorders (decreased libido, infertility, milk production outside childbirth);
- changes in the nature of the menstrual cycle (anovulation, amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea);
- disorders of the endocrine system with symptoms of pituitary insufficiency, the development of diabetes insipidus, the appearance of adrenal insufficiency, deterioration of the thyroid gland;
- pain during intercourse;
- neurological pathologies, including decreased visual acuity, headaches, memory impairment.
Masculinization in women is also noted. The condition is characterized by an increase in hair growth, coarsening of the voice and an increase in the fat content of the skin.
Acne, osteoporosis, uterine endometrial hypoplasia, colostrum secretion and lengthening of the menstrual cycle are also signs of hyperprolatinemia.
Causes
Among the reasons that cause an increase in the level of prolactin, the main one is the appearance of a benign tumor of the pituitary gland, prolactinoma or adenoma.
Other reasons:
- Hypothyroidism (an underactive thyroid gland).
- Medications for depression, psychosis, and high blood pressure.
- Herbs including fenugreek, fennel seeds, red clover.
- Chest irritation (from surgical scars, shingles, or too tight a bra used for a long time).
- Stress, excessive or extreme exercise.
- Certain foods.
- Hypothyroidism, liver failure.
- Physical stress.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Sexual intercourse.
The above factors usually cause only a small, temporary increase in hormone production.
In rare cases, a head injury, accompanied by a violation of the structure of the pituitary stem or its complete separation, can lead to hyperprolactinemia. In this case, the supply of dopamine is disrupted, which leads to overproduction of mammotropin.
In about 1/3 of all cases of hyperprolactinemia in women, the cause is not found.
Diagnostics
Prolactin levels usually change within 24 hours. They do not match in the morning after getting up and in the evening. Normal values in non-pregnant women will be less than 25 ng / ml and in pregnant women between 80 and 400 ng / ml. It is important to discuss the results with your healthcare professional as "normal" levels may differ. Hyperprolactinemia in women (symptoms are not always obvious) requires a number of diagnostic measures. It is necessary to pass the examination in a medical institution under the supervision of a doctor.
Initially, venous blood is donated to determine the concentration of the hormone. An important step is the correct sampling of the biomaterial. Blood is taken on an empty stomach, in the morning, no later than 1 hour after getting up.
On the eve, one should refrain from taking alcoholic beverages, protein foods, and sexual intercourse. You should limit physical activity and do not visit baths and saunas before taking the test. If the patient smokes, the last cigarette should be smoked no earlier than 2 hours before taking the test. The cost of the analysis depends on the clinic and is 500-700 rubles. excluding the cost of blood sampling.
If the high level of the hormone is confirmed after 2-3 tests passed on different days, the results of other studies are additionally collected:
- Concentration of macroprolactin (1 thous. RUB 500);
- TSH, T4 to exclude hypothyroidism (400-600 rubles);
- ACTH to exclude adrenal insufficiency (800-1 thousand. rubles;
- somatomedin-S to exclude somatotropin (700-1 thous. rub.);
- insulin and C-peptide in case of obesity and for the detection of diabetes insipidus (400-600 rubles);
- HCG during pregnancy (350-500 rubles).
Studies of the pituitary gland using MRI and CT scanners are necessary to detect the tumor process. The cost of an MRI with contrast is $ 3-4 thousand. rub., CT - from 5 thousand. rub.
When confirming the diagnosis of macroprolactinoma, it is necessary to consult an ophthalmologist to determine the visual fields. You can get a consultation on the compulsory medical insurance policy in the clinic at the place of residence, or for a fee in a private medical institution. A neurosurgeon's consultation is required to check for symptoms of tumor compression.
Treatment methods
The goal of treatment is to normalize the level of lactogenic hormone. In the case of the development of hyperprolactinemia due to a concomitant disease, its symptoms are eliminated. When a diagnosis of prolactinoma is made, treatment is directed at regression and stabilization of the tumor.
Hyperprolactinemia in women (symptoms often include galactorrhea), developed while taking certain medications, is assessed by the degree of symptoms. If it is established that the drugs are the culprit for the increase in prolactin, then they are canceled.
All other forms of the disease are treated with medication. The main active ingredients are dopamine agonists, a neurotransmitter that causes hyperproduction of prolactin.
Medications
Most patients with small and enlarged prolactinomas are successfully treated with drugs that affect the effects of dopamine - dopaminergic drugs. They act as first-line therapies, normalize prolactin secretion and gonadal function, and contribute to significant tumor shrinkage.
The most common drugs are based on the active substance cabergoline. A third-generation agonist with a long-lasting and potent prolactin-lowering effect stimulates pituitary receptors, causing hormone suppression. It is produced in tablet form in a concentration of 500 mcg under the trade name Dostinex.
| Cabergoline | It is prescribed to be taken orally with meals. The initial dosage is 500 mcg per week or 2 doses per week of 250 mcg. Increasing the dosage is possible gradually with the addition of 1 tablet and stabilization of the effect within a month. Cabergoline is taken twice a week and has fewer side effects than bromocriptine. Typically, cabergoline reduces prolactin levels to normal levels faster than bromocriptine. Cabergoline can cause heart valve problems when taken in high doses, but these doses are not used in women trying to get pregnant. |
| Bromocriptine | Dopamine receptor agonist. The starting dose is 0.625-1.25 mg per day. Therapeutic dosage is in the range of 2.5-7.5 mg. The drug is not very convenient for patients, because it requires taking twice a day, and Cabergoline - 1-2 times a week. |
| Quinagolide | A selective dopamine receptor inhibitor is prescribed at a starting dosage of 25 mcg per day. Gradually, the concentration is increased every 3-5 days by 25 μg. The average daily therapeutic dose is within 75 mcg. The maximum allowable dosage is 300 mcg. |
| Aripiprazole | Antipsychotic drug - neuroleptic - due to agonistic activity against dopamine receptors leads to a decrease in prolactin. The dosage regimen is individual. The daily dose is 10-30 mg. |
| Reserpine | An antihypertensive drug that inhibits dopamine production. It is prescribed for oral administration in an individual dosage regimen. The maximum daily dose is 1 mg. |
| Sulpirides | An atypical antipsychotic drug that has an antidopaminergic effect. Reception is carried out in the morning to avoid an increase in the level of vigor. The maximum daily dosage is 1600 mg. |
| Cyclodinone | A phytopreparation based on the dry extract of the common barnacle fruit has a dopaminergic effect. Take 1 tablet once a day with 100-200 ml of water. The duration of treatment is at least 3 months. If it is necessary to continue treatment, a doctor's consultation is required. |
| Cariprazine | The therapeutic effect is due to a combination of dopamine and serotonin receptor agonism. It is used once a day at the same time, regardless of food intake. |
Not all women with hyperprolactinemia need medication. Women who do not produce estrogen in their bodies need therapy that either causes the body to produce estrogen or provides it with this hormone.
Treatment may not be necessary if no cause is found or if high prolactin levels are caused by a small tumor in the pituitary gland and the patient is still producing estrogen.
Dopamine agonist pharmacotherapy is the treatment of choice even in patients with macroprolactinomas. These agents are able to eliminate galactorrhea, promote menstruation and reverse hypogonadism. In many cases, they also reduce the size of the tumor.
Treatment for drug-induced hyperprolactinemia is only indicated for unpleasant symptoms, such as galactorrhea, or to reduce the risk of long-term side effects. In this case, estrogen supplementation may be required to prevent osteoporosis.
Operative treatment
Surgical resection of prolactinoma is one option for patients who refuse or do not respond to long-term pharmacological therapy. Surgical intervention is necessary for late diagnosis of macroprolactinoma. It has compression of the optic nerves and drug resistance, these reasons are an indication for surgery.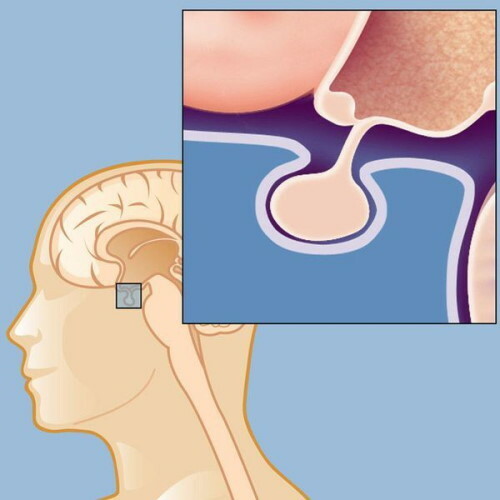
In what cases is surgical treatment indicated:
- an increase in the size of the tumor, despite drug treatment;
- apoplexy of the pituitary gland;
- compression of the optic chiasm;
- liquorrhea while taking dopamine agonists.
An MRI will be done from time to time to check the size of the tumor.
Radiation therapy
Radiation treatment is offered if the operation is unsuccessful or, for medical reasons, it is impossible for the patient to undergo surgery. Also, radiation therapy is used for aggressive or malignant forms of pituitary tumors.
Folk remedies
Home methods are used in cases of physiologically mediated hyperprolatinemia. In pathological conditions, the use of folk remedies is ineffective and irrational.
Phytotherapy is used to reduce prolactin:
- Tincture of common prutnik fruit is aged in 40% alcohol for 2 weeks. Tincture is taken 3 times a day for 1 tbsp. l. before meals.
- A steep sage infusion is taken regardless of food intake 2 times a day for ½ cup.

- The infusion of elecampane root is kept for 4-6 hours. Should be taken 25 ml 4 times a day.
Eating foods high in iodine, calcium and fiber leads to a decrease in prolactin. The diet should be diluted with kelp, seafood, dairy products, raw vegetables and fruits.
Possible consequences and complications
Lack of treatment for hyperprolactinemia leads to the development of severe disorders and complications. The most common one is the compression of the optic nerve by prolactinoma. Progressive osteoporosis, the transition of tumors to a malignant form are also often found among the consequences of lack of treatment.
The reproductive system also suffers. Prolonged abnormal production of prolactin increases the risk of developing uterine fibroids and other gynecological diseases. Menstrual irregularities, galactorrhea, loss of vaginal lubrication are complications of hyperprolatinemia.
Among the pathologies of the endocrine system, there are disruptions in the work of the adrenal glands and the thyroid gland. Breast engorgement, swelling, and tenderness are also associated with persistent elevated levels of prolactin.
A decrease in bone mineral density, the development of osteoporosis and osteopenia is manifested with prolonged hyperprolactinemia. Among autoimmune pathologies, the development of antiphospholipid syndrome is more common.
Currently, hyperprolactinemia is successfully diagnosed in the early stages and is treated with medication. Timely seeking medical help prevents possible complications and concomitant pathologies.
If the symptoms of hyperprolactinemia are not detected in time, the cause is not eliminated, then the consequences can be devastating for the normal functioning of all endocrine glands. In the future, this can lead to infertility in women, decreased vision up to blindness caused by a growing adenoma.
Video about hyperprolactinemia
Hyperprolactinemia syndrome: