Content
- Definition of disease
- Ascaris biology
- Fertility of parasites
- Ascariasis symptoms
- initial stage
- Intestinal stage
- Classification and stages of development of ascariasis
- Drug treatment
- Treatment with folk remedies
- Diet for ascariasis
- Features of treatment in pregnant women
- Video about ascariasis
Ascariasis provoked by worms of the nematode class - a common parasitic invasion, affecting adults and children with equal frequency. In adult patients, the disease develops with severe symptoms of allergic syndrome, systemic intoxication, and digestive disorders.
Definition of disease
Ascariasis is a parasitic pathology caused by round worms-nematodes. Sexually mature etiological agents form colonies in the intestinal lumen, migrating from the upper digestive tract in the form of larvae.
The disease is most common in regions with warm and humid climates. The period of maturation of ascaris takes 30-60 days before the first symptoms of parasitic invasion appear. Nematodes and their waste products affect the gastrointestinal tract, the respiratory system, and the urogenital apparatus.
Ascaris biology
White and yellow worms are large for members of their class. The adult reaches 15-35 cm in length. The main area of localization is the ileum and small intestine.
Ascariasis in adults, the symptoms are of a different nature, depending on the stage of the disease, the general state of the immune system, and the presence of concomitant pathologies. Females of nematode parasites reach a length of 40 cm, males - no more than 25 cm.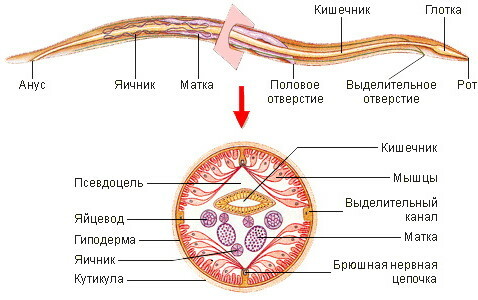
The worms have a yellowish-pink color, which, after death, changes to a white-matte shade. The lateral surfaces of the body of pathogens are equipped with excretory channels with glands. Through them, intoxication of the human body occurs.
Ascaris excretory canals are longitudinal thin depressions. At the head end of an adult, there are 3 spongy elements with jagged edges. They function as taste buds surrounding the mouth.
The peculiarity of this variety of nematodes is the absence of attachment organs. Parasites are in constant drift in the direction of food movement. To keep the roundworms in contact with the intestinal walls, causing obstruction and congestion.
The body thickness of the female pathogen is 3-6 mm, the male - 2-4 mm. The worms have a dense 10-layer epithelial coating with keratin-filled cuticles. Such structures play the role of a skeletal structure and protect the individual from the acidic environment of the gastrointestinal tract.
The bending of the roundworm's body is carried out due to the muscle cords. The nerve ganglia in the form of periopharyngeal ridges are responsible for the innervation of parasites. Roundworms reproduce sexually with abundant egg-laying.
Fertility of parasites
A mature female nematode lays up to 240,000 eggs daily. After the incubation period of helminthic invasion, the pathological symptoms increase rapidly. The size of an egg is no more than 0.106x0.05 mm.
This makes it difficult to detect them in feces during microscopic examination. The released roundworm eggs are highly resistant to unfavorable environmental factors.
The suitability for re-infection lasts for 12 years. Ascaris larvae can easily withstand long-term freezing.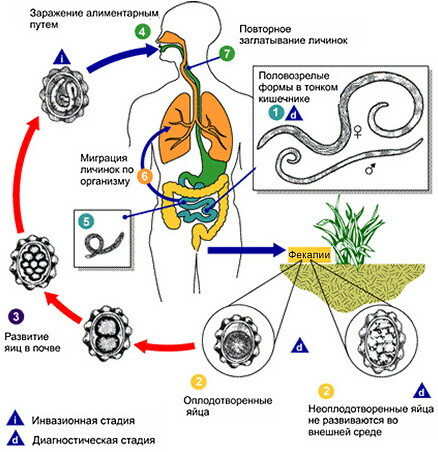
The death of eggs laid by nematodes and released with feces is caused by:
- gasoline;
- acetone;
- direct ultraviolet radiation;
- extremely high temperatures - open fire, boiling;
- alcohol-containing substances;
- quicklime.
Under favorable environmental conditions, nematode eggs mature outside the body in 15-17 days, acquiring pronounced invasive characteristics. The optimum temperature for the development of parasites is considered to be the range of + 12... + 36 ° С and the air humidity of at least 8%.
Ascariasis symptoms
The clinical manifestations of helminthic pathology are diverse.
The observed symptoms are determined by:
- the level of invasive parasitic load;
- the age of the patient;
- the state of the immune system;
- stage of the disease;
- concomitant pathological processes;
- individual physiological and biochemical factors.
Ascariasis is characterized by allergic reactions to protein compounds produced by parasites, infectious and toxic lesions of internal organs and the cerebral zone. There are signs of functional failure of the liver, kidneys, lungs.
Helminthic invasion may be asymptomatic for a long time. Anaphylactic syndrome occurs with a significant increase in the ascaris colony in the small and other parts of the intestinal tract. An allergic reaction is manifested by a vesicular or urticarial rash on the skin of the trunk, hands and feet.
Ascariasis in adults (symptoms of anaphylactic genesis include high-intensity itching) are often accompanied by typical infectious-toxic signs:
- subfebrile fever;
- general malaise;
- muscle weakness;
- excessive sweating;
- lymphadenopathy - an inflammatory lesion of the lymphatic plexus;
- drying out of the oral mucosa.

Hepatobiliary symptoms include an increase in the size of the liver, swelling of the spleen, pain of medium or low intensity in the hypochondrium of the right-sided localization.
Ascariasis in adult patients is often accompanied by local or systemic lymphadenopathic syndrome.
The condition is combined with:
- night sweats;
- a sharp loss of weight, provoked by a violation of digestive activity and infectious and toxic reasons;
- increased risk of infection with bacterial-viral agents of the upper respiratory system;
- hepatomegaly;
- splenomegaly.
With ascariasis, in the course of laboratory diagnostics, an increased activity of liver enzymes is detected. For helminthic invasion, bronchopulmonary symptoms are characteristic, which is often observed in patients with chronic respiratory pathologies.
This category of clinical manifestations includes eosinophilic pneumonia - inflammatory-allergic damage to organic tissues of the respiratory organ with the formation of unstable migratory infiltrates.
initial stage
The stage of progression of invasive pathology is alternatively called the migration phase. The duration of the initial stage is estimated at 6-8 weeks, which corresponds to the incubation period of ascaris.
The larvae enter the human body by the oral-fecal route. Typical ways of spreading through biological tissues are hematological and lymphatic. Roundworms inhabit the intestinal parts, lungs, liver, bronchial cavity.
This causes a corresponding symptom complex. In the initial (migratory) stage of helminthic invasion, moderate signs of Leffler's syndrome appear, which is a type of eosinophilic infiltration of the lungs.
The pathogenesis has benign clinical characteristics. At the initial stage of ascariasis, the symptomatic picture is blurred, nonspecific and mild. The increase in body temperature reaches 37.1-37.5.
There are signs of general malaise with low-intensity headaches. With massive helminthic invasion, the migratory phase of the parasitic disease is accompanied by cramps in the abdominal cavity and nausea, which indicate the onset of an infectious-toxic process.
A rare allergic rash with itching or without discomfort appears on the skin. Sometimes the symptomatic migration stage of the pathology can be determined by soft tissue edema and enlarged lymph nodes.
More often, the signs of the development of ascariasis in the initial stage are individual in nature and depend on the physiological characteristics of the organism. With the penetration of nematode larvae into the respiratory tract, a dry cough is added to the symptoms.
Shortness of breath and other signs of functional insufficiency of the respiratory system gradually appear. In chronic bronchopulmonary diseases, the cough is accompanied by a moist component.
The release of mucus exudate is caused by irritation of the goblet cells by pathogenic pathogens. Blood fragments are visible in the sputum of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis, bronchial asthma, COPD.
Breathing becomes whistling. Among the clinical manifestations of the initial stage of helminthic invasion in chronic bronchopulmonary pathologies, asthma-like conditions appear.
Ascariasis in adults has symptoms in the phase of migration of the pathogen larvae in the form of dry wheezing sounds during pulmonary respiration. For the secondary attachment of bacterial microflora, inflammatory signs are characteristic.
Intestinal stage
This phase of the parasitic disease is characterized by 2 clinical syndromes - gastrointestinal and asthenovegetative.
The period of development of helminthic invasion is accompanied by:
- suppression of appetite;
- morning sickness caused by the process of gastrointestinal intoxication;
- activation of the gag reflex;
- cutting pain in the epigastric cavity;
- diarrhea;
- difficulty defecating caused by intestinal obstruction;
- bloating;
- a sharp decrease in body weight.
The neurological symptomatology of the intestinal stage of the parasitic disease is due to the toxic effects of ascaris waste products on the central nervous system. Such clinical manifestations include decreased muscle tone, sleep disturbance, and increased anxiety.
In severe cases, with massive helminthic invasion, suppression of mental function, meningitis symptoms, epileptimorphic convulsive states are observed.
An acute infectious-toxic process is accompanied by:
- A mechanical hepatobiliary syndrome called jaundice and is caused by excess release of conjugated bilirubin into the intestinal lumen. The condition is determined by the icteric (yellowish) condition of the skin, mucous sclera, pain reactions in the right hypochondrium.
- Purulent cholangitis. Acute toxic inflammation of the bile ducts is combined with the release of necrotic exudate and dead particles of biological tissues into the urinary sediment.
- Multiple abscess foci in the liver. Cavities with clear boundaries are filled with purulent discharge caused by toxic damage to hepatocyte cells.
- Acute pancreatitis. The inflammatory process of parasitic genesis in the pancreas is provoked by foreign proteins secreted by roundworms. They trigger an acute immune response.
In the intestinal stage of helminthic invasion, clinical symptoms are possible in the form of inflammation of the appendix, peritonitis, mechanical obstruction of the respiratory canals. The latter is capable of provoking such a life-threatening condition as acute ascaris asphyxia.
The parasitic-invasive process is often complicated by intestinal obstruction, malabsorption and breakdown of food, metabolic disorders, and other concomitant symptoms. With the penetration of pathogens into the structure of the heart apparatus, symptoms of toxic damage to the myocardium arise.
Classification and stages of development of ascariasis
According to the type of course, the parasitic-infectious disease is divided into typical and atypical. The first is characterized by a clearly expressed clinical picture with specific symptoms.
Ascariasis of atypical form in adults proceeds without noticeable signs of intoxication. In some cases, there are inflammatory, allergic or digestive symptoms.
This type of disease is determined by methods of laboratory differential diagnosis. Protein substances characteristic of nematodes are fixed in a test sample of uric acid and hematological fluid.
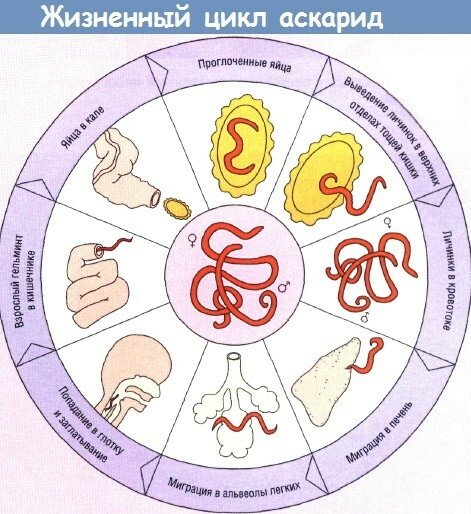
The larvae of worms are found in the feces during the coprogram. According to the phases of development, ascariasis is classified into the migration stage and intestinal.
The first is characterized by the distribution of colonized larvae:
- lumen and cavities of the gastrointestinal tract;
- respiratory tract;
- genitourinary system;
- hepatobiliary mechanism;
- heart apparatus.
The intestinal phase is distinguished by the generalized toxic effect of mature pathogens on the body. According to the severity of the course, helminthic invasion is divided into mild, moderate and complicated forms.
The stages of development of the disease include infection, spread, toxic effects of pathogens on organs and functional systems. The last phase is secondary penetration into the structure of the gastrointestinal tract from other colonized areas of the body.
This stage is considered chronic and difficult to treat. The progression of a parasitic disease begins with an invasive phase, during which the larvae of pathogens enter the body by the oral or fecal route.
Violation of basic personal hygiene requirements leads to infection. The larvae are introduced into the epithelial lining of the walls of the upper or lower parts of the digestive system, where there are optimal conditions for their development.
At the next stage, called migratory, eggs and mature individuals nestle into the systemic circulation and lymphatic channels.
Parasites pass sequentially:
- liver;
- bile ducts;
- right-sided heart;
- pulmonary cavity;
- genitourinary system.
Roundworms are deposited in each of the presented organic structures. Penetrating into the dental zone, nematodes are sent back to the stomach and intestines, again infecting the digestive system.
At this stage, intestinal obstruction occurs. Symptoms are expressed in a violation of digestive processes and absorption of nutrients, which pathogens use for their own growth and increase in the colony.
Drug treatment
Drug therapy involves a combination of symptomatic drugs with etiotropic drugs. The tactics of drug treatment are selected taking into account the localization of the ascaris colony, the stage and complexity of the course of the disease.
An infectious disease specialist takes into account the patient's tolerance to drugs, anamnesis, and the physiological state of the body. Effective antiparasitic drugs are presented in the table.
| Name | Standard dosage for adults | Pharmacological properties |
| Mebendazole | 100 mg 2 times a day at regular intervals. The duration of the course of treatment is 3-4 days. | Anthelmintic agent with a wide range of therapeutic effects. Violates the utilization of glucose by parasites, inhibits the synthesis of ATP - an important enzyme for the life of ascaris. |
| Mintezol | 50 mg / 1 kg of body weight 2 times a day for a week. | Antiparasitic drug of Slovenian production. Highly effective in the elimination of chronic ascariasis. Differs in low toxicity to the human body. |
| Decaris | Single dose 120-150 mg. | Levamisole-based anthelmintic drug. It affects the nematode nerve ganglia, causing depolarization of cell membranes and neuromuscular spasm in individuals, and disrupts the bioenergetic processes of pathogens. Effective for massive invasions. |
| Piperazine | 1 tablet 3 times a day, 1 hour after a meal. The duration of the course of treatment is 3 days. | It has a nerve-paralyzing effect on ascaris. Available in the form of tablets and solution for intramuscular injection. |
Ascariasis in adults, the symptoms of which depend on the stage of the disease and the massiveness of the invasion, is effectively eliminated by Albendazole, a drug with anthelmintic and antiprotozoal properties.
The presented antiparasitic drugs in the framework of complex therapy are combined with anti-inflammatory drugs on a non-steroidal basis, neurological drugs, antihistamines.
The intestinal stage of ascariasis is eliminated with tablets or injections containing levomizole, pyrantel. In the migration phase of helminthic invasion, drug therapy is carried out using thiabendazole or mebendazole.
Treatment with folk remedies
Alternative medicine recipes cannot be used as the main method for eliminating the infectious and parasitic process. Folk remedies can only serve as an addition to the prescribed drug therapy.
Pronounced anthelmintic activity is attributed to the following medicinal plants:
- common tansy;
- bitter wormwood;
- brittle buckthorn;
- elecampane;
- yarrow;
- cloves.
Such natural raw materials contain components that have a depressing effect on nematodes. Drinking decoctions are prepared from the plants presented above. Cloves are saturated with eugenol, a specific aromatic substance that creates unacceptable conditions for the development of ascaris.
Thujone, an etheric compound, which has a neuroparalytic effect on mature nematodes fixed in the small intestine, was found in the common tansy. A decoction of dried raw materials has antihelminthic and anti-lamblial properties.
Thujon destroys ascaris and accelerates the elimination of toxic waste products of parasites. Black walnut is considered an effective and widely used antiparasitic agent.
The medicinal properties of the plant are determined by the presence in its chemical formula of juglone, a natural naphthoquinone.
Such a decoction has the following properties unproven by official medicine:
- antibiotic;
- insecticidal;
- antiseptic;
- fungicidal;
- decongestants.
In the pharmacy, you can buy antiparasitic dry mixtures, liquid tinctures and decoctions, manufactured in the factory by well-known manufacturers of pharmaceutical products.
For the treatment of ascariasis, pharmacy chamomile, garlic or onion extract are used. In the treatment of helminthic invasion with folk remedies in adults, alcohol tinctures are used. To prepare such a liquid, chopped onions and 200 ml of vodka are required.
The tool is insisted for 10 days in a hermetically sealed container and take 2 tbsp. l. per day - in the morning and evening hours throughout the week. The antiparasitic efficacy of such a tincture has not been proven. Another homemade recipe involves using pumpkin seeds.
Vegetable raw materials in a volume of 500 g are cleaned, crushed in a blender to a powder state. The product is poured into boiling water, stirring slowly. Add 1 tsp to the resulting gruel. l. bee honey.
The tool is taken before breakfast for 1 tbsp. l. The clinical effectiveness of the prescription is questionable due to the lack of an evidence base. Folk remedies are not able to replace drug therapy and should be used only after consultation with an infectious disease specialist.
Diet for ascariasis
Until the complete elimination of the parasitic-infectious process and the restoration of the function of the body systems affected by nematodes, in parallel with drug therapy, medical nutrition is prescribed.
Ascariasis in adults (symptoms appear depending on the phase of the pathology, the extent of colonization of organic tissues and cavities by nematodes) requires exclusion from the diet:
- yeast baked goods;
- wheat bread;
- confectionery;
- meat and fish liquid dishes of high fat content;
- smoked meats;
- salty foods;
- cow's milk;
- millet porridge;
- pearl barley;
- pasta;
- legumes;
- vegetable fiber.
Such foods create a breeding ground for roundworm breeding and are used by parasites to generate energy. The therapeutic diet includes low-fat chicken broth, semolina and rice porridge without salt or sugar.
The diet for the infectious and parasitic process includes boiled roots, cauliflower, green fruits and berries. Bee and lime honey is useful for patients with ascariasis.
You should refuse carbonated drinks, black tea and coffee. Chocolate, marmalade, and other products with a high glucose content are completely excluded from the diet. They feed in small portions that do not create an excessive load on the gastrointestinal tract affected by roundworms.
Features of treatment in pregnant women
The period of bearing a child is characterized by hormonal changes against the background of suppressed immunity. A parasitic disease in pregnant women often has pronounced clinical symptoms.
In the migration phase, acute functional failure of internal organs is possible. Pulmonary infection has signs of respiratory pathology, which complicates the diagnosis and selection of adequate therapy tactics.
The clinical picture of the intestinal stage resembles classic gestational toxicosis. There are hypoxic and anemic conditions, vitamin starvation. They lead to intrauterine growth disorders.
Standard antiparasitic drugs with pronounced teratogenic activity are not suitable for the treatment of pregnant women. Toxic secretions of pathogens can provoke severe embryonic dysfunctions that cause fetal death or irreversible congenital malformations.
Complex therapy during gestation includes only drugs with an established safety profile for the mother and child. These products are designed on a natural plant basis. With massive helminthic invasion, the patient is hospitalized for the use of injectable drugs.
The subsequent correction of the intestinal microflora is performed with probiotics. To normalize the digestive function after ascariasis in pregnant women and other categories of adult patients, synthetic pancreatin is used. Proper treatment eliminates the symptoms of helminthic invasion and is safe for the fetus.
Video about ascariasis
Malysheva about roundworms:


