Content
- Characteristics and properties
- The table is ok
- Symptoms of the rise and fall
- Reasons for promotion and demotion
- Indications for research
- How is it determined
- Decoding
- How to bounce back
- Arrhythmia
- Tachycardia
- Cirrhosis
- Vitamin K deficiency
- Polycethymia
- Thrombosis
- Video about INR analysis
INR (International Normalized Ratio) - an informative method for determining the rate of thrombus formation. The norms for women differ by age, the indicators are shown in the table. The INR assessment method is standardized.
Characteristics and properties
INR (the norm for women by age in the table is present in the article) - indicators of the rate of blood clotting. During the study, the concentration of prothrombin, a glycoprotein produced by liver cells (hepatocytes), is detected. Vitamin K is involved in the synthesis.
Most often, a low level of prothrombin is caused by a deficiency of this component that enters the body along with food. The activation of an inert protein is suitable with the participation of a clotting factor or external hemostasis. The INR test is a fairly qualitative test that allows you to determine the quantitative content of an inert protein in the blood.

Usually, a comprehensive study of PTT is carried out, determining the prothrombin time. This is an indicator that allows you to find out for what time period a person's blood coagulates. The INR is calculated in the laboratory by identifying the ratio of the PTV of an individual patient to the PTV-norm. The last value is a standard indicator that remains unchanged.
The table is ok
INR (the norm in women by age in the table is described below) allows you to determine the rate of blood clots.
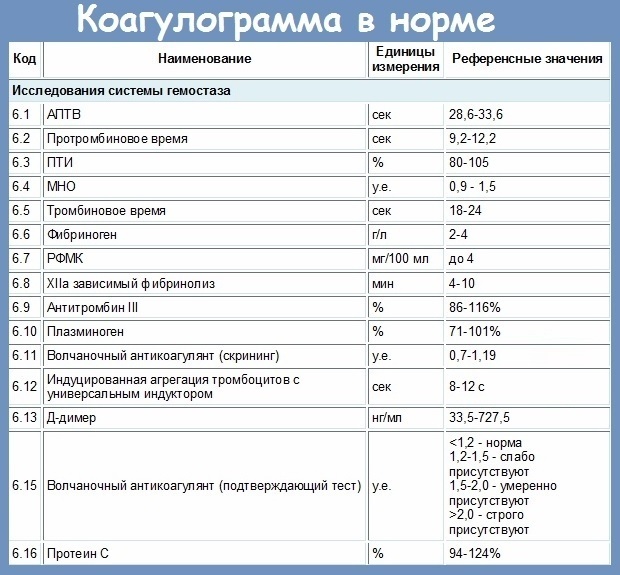
Indicators of a healthy patient:
| Age | The values |
| 25-35 years old | 0.8-0.9 g / l |
| 35-45 years old | 0.8-1 g / l |
| 45-55 years old | 0.9-1 g / l |
| 55-65 years old | 1-1.1 g / l |
| 65 years and more | 1.1-1.2 g / l |
Deviations from the norm (increased or decreased indicators) may indicate the development of diseases on the part of internal organs and systems.
Symptoms of the rise and fall
INR (the norm for women by age in the table allows you to identify possible deviations) is determined by the formula.
Symptoms of a decrease in prothrombin in the blood:
- insomnia / drowsiness;
- vibration or tinnitus;
- dizziness;
- deterioration in performance;
- migraine;
- bleeding from the gums;
- cartilage calcification;
- tendency to bruise, hematomas;
- stomach, menstrual, or intestinal bleeding.
Symptoms indicating an increase in prothrombin concentration:
- pressing, burning, constricting pain in the sternum that radiates to the jaw, neck, shoulder blades and shoulders;
- excessive sweating (especially at night);
- light-headedness;
- blanching of the skin;
- dyspnea;
- pain in the left hypochondrium;
- rapid weight loss;
- temperature jumps; weakness;
- tachycardia;
- moist cough.
Also, the concentration of prothrombin may increase slightly during pregnancy.
Reasons for promotion and demotion
The concentration of prothrombin decreases in the following diseases:
- Lack of vitamin K in women who are breastfeeding. In this case, the infant develops hemorrhagic diathesis. The main symptoms of pathology are the formation of peeling on the scalp, swelling, puffiness, redness of the integument, a small rash in the cheeks.
- Vitamin K deficiency during diet. In this case, the patient's performance decreases. The woman gets tired quickly, she has sleep disturbances, dizziness and general weakness.
- Hypofibrinogenemia. The pathology is accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of fibrinogen, an easily soluble protein responsible for the formation of a blood clot in case of violation of the integrity of the vessels. The disease can be acquired or congenital.
-
Hepatrombinemia. The disease is accompanied by blood clotting disorders. The pathological condition is characterized by a high risk of developing external and internal bleeding (including menorrhagia and hemarthrosis). The disease can be congenital.

Also, a decrease in the level of prothrombin in the blood can be caused by prolonged use of the following medicines:
- Heparin (salicylate);
- Oxyphenbutazone;
- Neomycin;
- Indomethacin;
- Thyroxine;
- Glucagon;
- Clofebrat;
- Phenilin.
Diseases characterized by an increase in protein concentration:
- The growth of malignant neoplasms. Oncological pathologies are manifested by dyspeptic disorders, bleeding (external internal), headache, dysfunction of the bladder and intestines, pain in joints, bones, general weakness, rapid fatigue, temperature fluctuations, sharp weight loss. Also, the growth of neoplasms of a malignant type may be indicated by a change in the shape, thickness, color and diameter of moles.
- Polycythemia. The chronic course of the disease is characterized by an accelerated production of erythrocytes by the bone marrow. At the initial stage, it may be asymptomatic. With polycythemia, there is a high risk of blood clots forming and blocking the vascular lumen.
- Myocardial infarction. The pathological condition is life-threatening. It occurs against the background of the death of myocardial cells (heart muscle). The main reason for development is oxygen starvation. The first sign of a heart attack is a sharp burning pain in the sternum, radiating to the back, shoulders or neck.
-
Thromboembolism. The disease is characterized by the formation of blood clots, which are able to migrate through the vessels, provoking a blockage of the lumen.

Also, an increase in the concentration of prothrombin is observed with the systematic use of barbiturates, corticosteroids and oral contraceptives.
Indications for research
INR (the norm for women by age in the table helps to quickly decipher the results of the analysis) requires an assessment of PTV. Any doctor can prescribe a laboratory test. Most often, the blood for the INR is donated by patients of therapists, hepatologists, obstetricians-gynecologists and cardiologists.
The main indications for the analysis are the following situations:
- profuse / scanty, long-term / short-term frequent nosebleeds, usually occurring for no reason and suddenly;
- the appearance of bruises of unknown etiology on different parts of the body;
- suspicion of thrombosis of arteries and veins;
- anemia (regardless of degree);
- suspicion of disseminated intravascular coagulation;
- tachycardia, bradycardia, angina of unexplained etiology;
- suspicion of heart and vascular disease;
- various pathologies of fetal development and pregnancy (including a history of spontaneous abortion);
- suspicion of liver disease (including cirrhosis);
- menstrual bleeding (profuse, prolonged, systematic).
An INR test can be prescribed for a woman whose close relatives suffer or have suffered from pathologies characterized by impaired blood clotting processes. Laboratory tests must be completed before surgery.
An INR blood test is prescribed before the selection of anticoagulants. People taking this type of drug are advised to donate biomaterial on a regular basis.
How is it determined
The method for determining the concentration of prothrombin was standardized in 1984. The patient in the laboratory takes blood from a vein (mainly peripheral). The collection is carried out with a sterile syringe. The biomaterial is placed in a test tube and a reagent acting as a citrate (preservative) is added to the container.
An additional component interrupts the binding of calcium ions with each other. Thanks to citrate, the blood clots more slowly. The laboratory assistant separates the cells (platelets, erythrocytes) from the plasma and examines only the serum. In order to neutralize citrate, plasma is mixed with calcium. The technician must time the clotting reactions. The PTV indicator must be divided by the PTV-norm value and multiplied by the MIC (the last two values are standardized).
Decoding
The results of a blood test for INR are deciphered by the attending physician. Previously, the specialist must collect an anamnesis of the patient's illness and find out from the patient what medications that affect the rate of blood clotting he is taking.
Decoding of indicators:
- 0,85-1,15. The blood clotting rate is normal. The patient has no diseases of the hematopoietic system. Coagulation is proceeding correctly.
- 1,85-2,9. Increased rates indicate the development of the following diseases: pulmonary thromboembolism, venous thrombosis, atrial fibrillation. Also, such values are observed in people who systematically take anticoagulants.
- 2,5-3,4. Such indicators are observed in patients after installing prostheses on the mitral valve.
- 3,5-4,5. Several times increased concentration of prothrombin indicates the development of pathologies of the heart and blood vessels (including myocardial infarction).
To confirm or deny the diagnosis, the attending physician usually prescribes a series of studies to obtain a complete clinical picture.
How to bounce back
INR is a standardized test. The norm in women by age is indicated in the table. If the deviations are caused by the development of diseases, then the patient is individually selected drug therapy. With oncological pathologies, surgical intervention can be prescribed.
Arrhythmia
Drugs that are part of drug therapy for arrhythmias:
-
Cordaron. The drug is marketed in the form of an infusion solution. The active ingredient is amiodarone hydrochloride. The drug has a pronounced antiarrhythmic effect. Due to the ability to block potassium and sodium channels, the drug is characterized by an alpha-adrenergic blocking and coronary-expanding effect. For arrhythmias, the solution is administered intravenously. The therapeutic norm is no more than 5 mg / kg once. The daily dose is 15 mg / kg. The drug form is mixed with a glucose solution (5%, 250 ml).
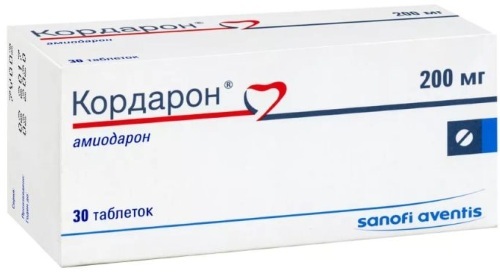
- Allapinin. The drug comes on sale in the form of tablets. The active ingredient is the substance of the same name (allapinin). A drug belonging to the category of antiarrhythmic drugs is able to block sodium channels and slow down intraventricular and atrioventricular conduction. Allapinin also has a sedative, analgesic, anticholinergic, coronary dilating and antispasmodic effect. The daily rate is 2 tablets (1 pc. once).
- Propanorm. Dosage form - solution for infusion The active ingredient is propafenone hydrochloride. The drug has a membrane stabilizing effect by blocking sodium and calcium channels. For arrhythmias, patients are injected no more than 2 mg / kg once. The daily dose is no more than 580 mg, which is equivalent to 160 ml of the drug. The dosage form is mixed with a glucose solution.
At the initial stage of development, arrhythmia can be cured with the help of traditional medicine. On the basis of medicinal plants, infusions and decoctions are prepared.
Effective remedies:
- Melissa. 15 g of dry pharmacy collection is poured into 600 ml of boiling water. The resulting mixture is infused in a thermos for 20-25 minutes, decanted and cooled. The infusion is taken 3 times a day, 50 ml.
- Rose hip. 15 g of fruits are poured with 500 ml of hot water. Insist means 60-70 minutes. and add 10 g of hawthorn fruit to it. The infusion is decanted and taken before breakfast daily, 50 ml.
- Calendula. 15 g flowers are poured with 500 ml of hot water, infused for 45-50 minutes. The infusion is decanted and taken 3 times a day, 50 ml.
It is necessary to prepare traditional medicine in accordance with the recipe. It is strictly forbidden to select medications on your own. All medicines that have an antiarrhythmic effect have a number of contraindications that only a doctor can identify.
Tachycardia
Most diseases of the cardiovascular system are treated with medication.
The following drugs may be included in the therapy:
-
Diltiazem. The composition of the drug contains a component of the same name in the form of a hydrochloride. The drug comes on sale in tablets. The active substance has a hypotensive, antianginal, antiarrhythmic effect. The principle of action of the drug is based on the ability to block annular channels. For tachycardia, adult patients should take 2 tablets per day (180 mg). With the permission of the attending physician, the therapeutic rate can be increased to 360 mg, which is equivalent to 4 tablets.
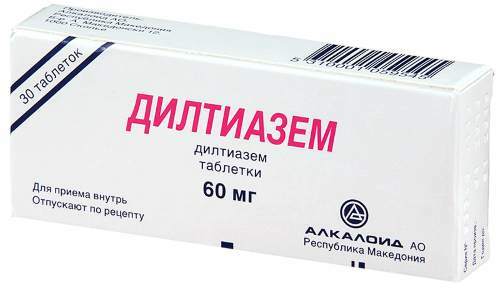
- Breviblock. The drug is marketed in the form of a solution for infusion administration. The active ingredient is esmolol in the form of hydrochloride. The drug has a membrane stabilizing, antihypertensive, antiarrhythmic, antianginal and sympathomimic effect. Esmolol blocks beta-adrenergic receptors. With tachycardia, patients are administered no more than 0.5 mg / kg. The course of application is selected individually. With the permission of the attending physician, the dose can be doubled with a positive result.
- Metoprolol. The drug form is tablets. The active ingredient is the substance of the same name in the form of succinate (tartrate). Selective beta-blocker has a membrane stabilizing, antiarrhythmic effect. Metoprolol is not a partial antagonist. For tachycardia and other cardiac arrhythmias, patients are prescribed 1 tablet per day. The course of application is 7-14 days.
Drug therapy can be combined with traditional medicine.
Infusions and decoctions are responsible for restoring heart rate based on:
- Hops and dill. Dill seeds, medicinal lemon balm, hop cones and valerian root (1 tbsp each) l.) Mix in a separate container. Pour the mixture with 500 ml of boiling water, mix thoroughly, pour into a thermos and remove to a warm place for 40-45 minutes. Express the ready-made infusion, take 100 ml 3 times a day for 14 days.
- Horsetail and hawthorn. Mix leaves of hawthorn (15 g), dry motherwort (15 g), horsetail (15 g) in a separate container and pour 500 ml of hot water. Steam the product for 12-15 minutes. Then the broth must be drained and removed to a warm place for 40-50 minutes. Take 50 ml 2-3 times a day. The course of treatment is 14-20 days.
Freshly squeezed juices from carrots, cranberries and chokeberries have also proven themselves good in the treatment of tachycardia. They must be mixed with warm boiled water in equal proportions before use.
Cirrhosis
With cirrhosis of the liver, patients are prescribed hepatoprotectors and antibiotics.
The most effective medicines:
-
Cefazolin. As part of a broad-spectrum antibiotic, there is a component of the same name, which acts as an active agent. Cefazolin is marketed in the form of a solution for intravenous and intramuscular injection. Patients suffering from cirrhosis are prescribed broad-spectrum antibiotics for complications caused by the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the body. The daily rate for adult patients varies between 4-6 g. The solution is administered intravenously or intramuscularly up to 3 times a day. The course of application is up to 10 days.
- Nutrilite Liver Active. With cirrhosis of the liver, it is important to provide the body with the necessary vitamins and minerals, therefore, biologically active additives should be included in the complex therapy. Nutrilite contains plant components (milk thistle, dandelion, malpighia), vitamins (thiamin, cyanocobalamin, niacin, riboflavin). The drug form is tablets. Dietary supplement helps to restore metabolic processes inside the biliary organ. Adult patients need to take 3 tablets per day. The course of treatment is 30 days.
- Essentiale Forte N. The drug belongs to the category of hepatoprotectors. It is marketed in capsule form. The active ingredient is EPL-phospholipid. Phosphatidylcholine restores the oxidative and metabolic functions of hepatocytes. With cirrhosis of the liver, take 2 capsules 2-3 times a day. The course of treatment is selected individually.
Traditional medicine helps to restore the integrity of liver cells.
A positive effect is exerted by:
- Freshly squeezed juices. Cucumbers, carrots, tomatoes are peeled, cut and squeezed out. Fresh juices must be consumed without diluting with water.
- Lemon based drinks. Citrus in combination with garlic has a cleansing effect. Lemon (4 pcs.), Garlic (2-3 heads), olive oil (200 ml) and honey (1 l) are mixed in a separate container. Chop the garlic and lemon, mix all the ingredients thoroughly until a homogeneous mass is obtained. You need to take the remedy daily for 1 tbsp. spoon 2-3 times a day. The finished mixture is stored in a plastic container in the refrigerator.
Acceleration of the processes of elimination of toxins from the bile ducts and liver contributes to the juice of black radish. It is better to mix it with natural honey (ratio 3: 1).
Vitamin K deficiency
With hypoavitaminosis, patients are shown parenteral administration of Fitomenadione, which has a hemostatic effect. If vitamin K is synthesized in an insufficient amount by the body, then its water-soluble analogue of synthetic origin is included in the composition of drug therapy. The therapeutic norm of Fitomenadione for adult patients is no more than 25 mg once. The course of treatment varies within 40-50 days.
Also, patients are shown a diet. The basis of the diet is made up of foods containing a large amount of vitamin K.
Experts recommend daily use:
- dairy products (including fatty cottage cheese);
- olive oil;
- broccoli;
- cauliflower, white cabbage;
- fresh nettle leaves;
- greens;
- avocado;
- banana;
- kiwi;
- wheat bran.
It is advisable to boil products from the list of permitted ones, sauté in vegetable oil or simmer. Milk and cottage cheese do not need to be heat treated.
Polycethymia
At the initial stage of the development of polycythemia, patients are prescribed bloodletting. The procedures minimize the risk of developing thrombosis. Exfusion is performed up to 3 times a week. The volume of emitted blood is not more than 500 ml.
The volume is replenished with riopolyglucin or saline solutions. Do not bleed more often 3 times a week. In this case, the risk of developing anemia is high. Exfusion can be replaced with erythrophoresis. The erythrocyte mass is extracted from the biological fluid, the composition of the plasma remains unchanged.
With the development of visceral and vascular complications, patients are prescribed drug therapy, which is based on cytostatics (Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Cisplatin). Medicines are prescribed in the absence of contraindications in patients. The dosage regimen, the regimen and the course of treatment should be selected on an individual basis. To thin the blood, acetylsalicylic acid and Heparin can also be included in the therapy.
Thrombosis
If a blood vessel is completely blocked by one or more clots, surgery is indicated for patients. At the initial stage of development, the disease can be cured with medication. Thrombolytics and anticoagulants should be included in the therapy. Low molecular weight Heparin is highly effective in thrombosis. Preparations containing this component require intravenous or subcutaneous administration in an individually selected dose.
The INR rate in women usually varies by age. The indicators obtained in the course of laboratory research are compared by experts with the data of standardized tables. This allows you to identify possible deviations from the norm and diagnose the patient.
Video about INR analysis
What should be the target INR value:
