Content
- Characteristic
- Functions and properties
- Anatomy and structure
- Possible diseases and pathologies
- Kienbeck-Prizer pathology
- Classification
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Tendinitis
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Classification
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Arthritis
- Classification
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Arthrosis
- Classification
- Symptoms and Signs
- Causes
- Treatment methods
- Wrist video
The wrist is part of the hand, which is located between the radius, ulna and metacarpal bones. Its structure contains 8 bones. Since the wrist is a very mobile part of the hand, it is often prone to injury. There are also a number of diseases characteristic of this particular part of the hand.
Characteristic
The wrist is part of the hand. This is the most mobile part of the limb, which helps to perform not only rough, but also precise work. This would not have been possible without the wrist, which connects the hand to the hand. The wrist begins to actively develop when the child is three years old. Due to it, the hand can make movements in different directions, hold the support.
Functions and properties
The bones of the wrist are small, movable structures that make it possible to manipulate the hand. This allows you to take and release objects, move them away, and bring them closer. If the brush is bent 90 degrees, it is used as a support. This is necessary for some sports, dances. Support is also required in everyday life.
The wrist helps to move the hand, hand in the right direction, affects the motor activity of the fingers, provides a sharp or smooth movement. At the same time, the wrist corrects movements in the vertical, horizontal plane.
The wrist joint is made up of three bones of the proximal row - with three faces, lunar and similar to a boat. But the main role is assigned to the radius. Rotation (including circular) of the hand occurs due to elastic cartilage. All other movements are associated with the mid-carpal joint, have an irregular shape.
Anatomy and structure
The wrist has a complex structure. The palmar part resembles a boat, it is concave inward. The back side is slightly convex, articular. The wrist is formed by eight small, irregularly shaped bones arranged in 2 rows. In comparison with other structures of the hand, the ray structure is absent.
The proximal row (closer to the forearm) forms a convex surface. The distal (located at the palm) connects to the previous row of joints.
The bones of the wrist, except for pisiform, have 6 surfaces. The anterior ones are slightly rough, with ligaments of the palm attached to them. The upper (proximal) ones participate in the formation of the central head, the lower (distal) ones form the glenoid fossa. The side bones are also articulated with each other.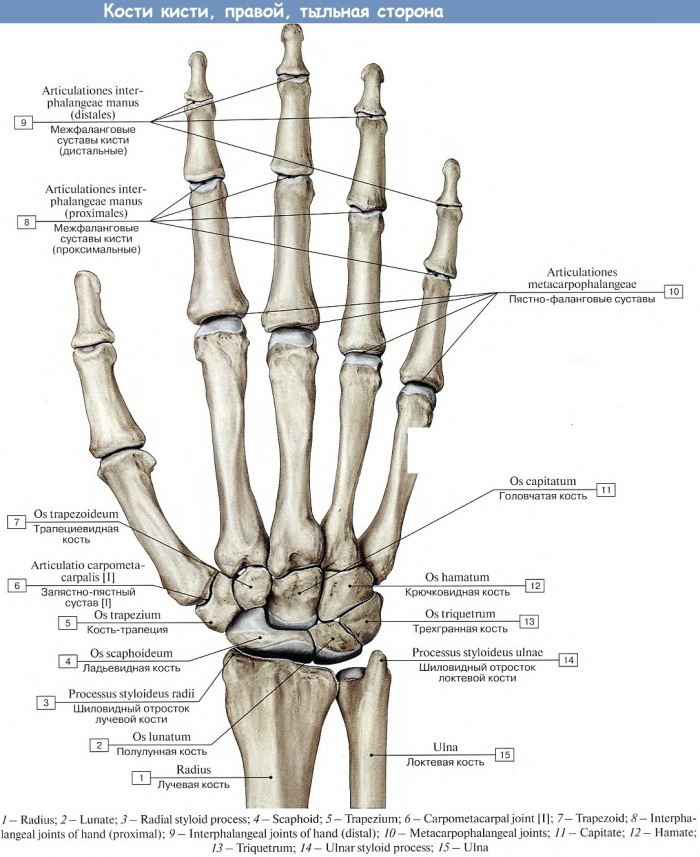
| Bone name | Short description |
| Scaphoid | It is located in the first row, with a concave surface at the palm, below it turns into a tubercle. Its back side is in the form of a narrow strip, connected to the radial side. The lower section is concave, next to the capitate, and above - with the crescent. |
| Crescent | Located next to the rook-shaped bone. Slightly convex from above, connected with the radial. There is a small surface for adhesion to the capitate and hook bones. |
| Triangular | Located in the 1st row of the wrist bones. Its upper part is convex. The lateral region is flat, connected to the lunate bone. The lower part of the triangular is slightly concave, connected to the hook-shaped, and from the side of the palm to the pea-shaped. |
| Trapezoid | It is located in the 2nd row of bones. On the upper side there is a small square for connecting with a bone in the form of a rook. At the bottom, the trapezoid is saddle-shaped. There she connects with the 1st metacarpal. On the medial side there are 2 concave surfaces, next to the trapezoidal and 2nd metacarpal. |
| Pea | It is small, located in the middle of the tendons. On the dorsum, the surface is flat where it meets the 3-sided bone. There is a small tubercle on the palmar side. |
| Hook-shaped | It is located near the capitate, completing the 2nd row. In front, on the hook-shaped - a developed, slightly curved process. The upper surface of the hook is located next to the lunate, capitate, 3-sided. On the distal site - the place of articulation with the 4th and 5th metacarpals. |
| Capitate | It is the largest of the 8 bones, with a spherical head. The rest is slightly thickened. It is located next to the hooked bone. The lateral region is slightly convex, next to the trapezius. The lower side of the capitate is connected to the 3rd metacarpal, and the lateral ones - to the second, fourth. |
| Trapezoidal | Located next to a bone of a similar name. The lower, saddle side is connected to the 2nd metacarpal. Above, the trapezoidal bone is concave, articulated with the scaphoid, capitate. |
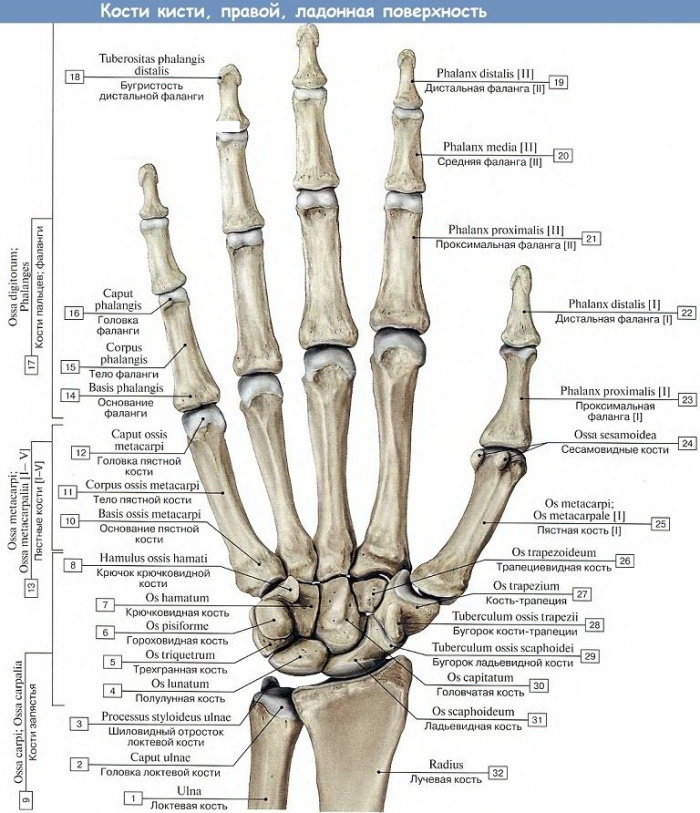
The wrist bones form a small groove at the base of the palm. Muscles and tendons pass through it, providing flexion of the fingers. The inner edge of the groove ends with hook-shaped and pea-shaped bones. They are well felt. The outer edge of the groove consists of two bones - polygonal and scaphoid.
The space between the bones is filled with nerve fibers, veins, ligaments. Inside the wrist is the cartilage and connective tissue. Many ligaments pass through it. The most important ones are those coming from the styloid processes. There is a retaining ligament between the tubercles of the bones. It runs along the groove, along with the median nerve, tendons.
The carpometacarpal joints form a distal row. All, except for the area of the thumb, are inactive, but with strong ligaments.
Almost all of them go from the capitate (central) - along the entire wrist:
- the dorsal ones connect the bones of the joint, prevent excessive displacement of the hand;
- palmar: the wrist holds the palm during extension, and the elbow-carpal strengthens the inner surface of the hand during extension;
- the ligaments between the bones almost motionlessly fix the bones of the first row;
- lateral (radial and ulnar) prevents excessive displacement of the hand, do not allow it to be strongly retracted inward.
The wrist is covered with thin skin. Each bone is covered with protective tissue. There is a large cartilage in the center of the junction. It is necessary for cushioning, brush rotation. Softens blows, protects bones from wear and tear. The extra cartilage ensures maximum joining of the wrist elements. In its depth, protected by soft tissues, there are nerve fibers.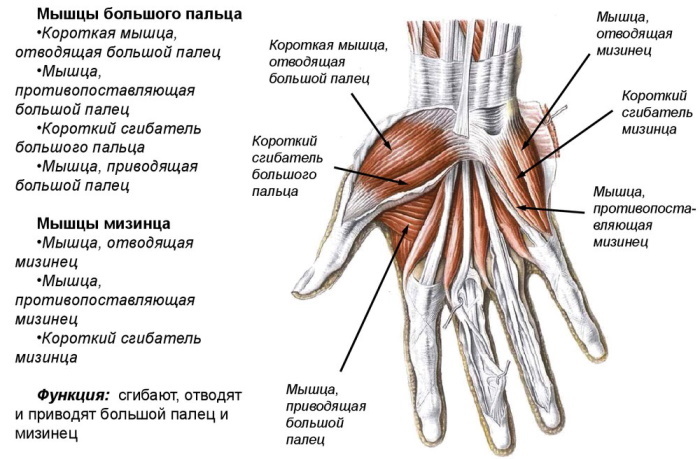
In the groove of the wrist canal, there are three main canals. They help separate nerves, veins, and tendons into separate bundles. This excludes their mechanical damage while driving. The ulnar is located deep, there is an artery, the main nerve, veins.
In the radial canal is the tendon of the corresponding muscle, the artery that feeds the thumb. The carpal tunnel contains 9 tendons that are necessary for flexion of the fingers, the median nerve, and the artery.
Possible diseases and pathologies
Malformations come to light by chance. More often it is the fusion of small bones, due to which the amplitude of rotation decreases. Even in utero, there may be underdevelopment of the joints (hypoplasia), aplasia (part of the bone fragments is missing), subluxation or dislocation. Malformations lead not only to limited movement, but also to excessive mobility.
When receiving heavy loads on the wrists, aching pulling pains sometimes occur in it. Sprained ligaments during sports can be the cause. Then more often treatment is not required, gradually they get used to heavy loads.
Pain in the wrist can also indicate serious disorders - hand injuries (cracks, fractures), dislocations, diseases. Of the soft tissue diseases, bursitis, stenosing ligamentitis, periarthrosis are more often diagnosed. Sometimes a hygroma (tumor) can grow from the bursa.
Kienbeck-Prizer pathology
The second name of the disease is osteonecrosis of the lunate bone. It plays an important role in the wrist, and damage to it disrupts hand movement. With the disease, the blood supply to the lunate bone is disrupted.
Classification
Fractures can be of several types, including those with displacement.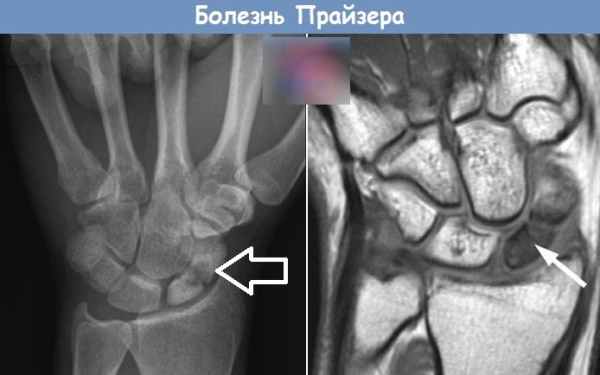
Major injuries include:
- Collis fracture. Usually occurs from falling on straightened arms. As a result, the radius bone breaks, and its fragments are displaced in the hand opposite to the palm. Therefore, this injury is called extensor. But bones heal quickly due to a good blood supply.
- Smith's fracture (otherwise - reverse Collis) is rare. This usually happens when a person falls on their back, when the blow hits the forearm. The fragments of the bone are displaced towards the palm. But they grow together quickly, the prognosis is favorable.
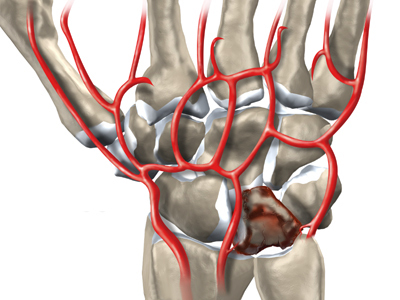 Also, a fracture is divided into open, in which the skin is damaged and there is a possibility of blood poisoning or shrapnel when several bones are broken. Injuries can be with or without longitudinal or transverse displacement (these are more common).
Also, a fracture is divided into open, in which the skin is damaged and there is a possibility of blood poisoning or shrapnel when several bones are broken. Injuries can be with or without longitudinal or transverse displacement (these are more common).
Symptoms and Signs
The disease is always accompanied by swelling, pain that increases with movement of the wrist and subsides when the hand is at rest. There is no discomfort on palpation. Hand movements are limited. Diagnosis is by radiography. As the disease progresses, small fractures occur, then the bones fall into fragments - until they are completely destroyed.
Causes
The development of the disease is provoked by regular heavy physical exertion. People who are busy with hard work are often susceptible to pathology. The cause may be domestic injuries, falls, congenital anomaly (shortened ulna). Displaced fractures can be caused by involuntary muscle contractions, impaired blood flow and outflow.
Treatment methods
In case of fractures, plaster is applied to the damaged area. Additionally, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed (for example, "Diclofenac", "Iuprofen"). At the same time, they eliminate tissue swelling.
Additionally, chondroprotectors are prescribed to strengthen bones and cartilage ("Chondroxide", "Artra"), calcified mineral supplements ("Calcium gluconate", "Calcimin"). After removing the plaster (if it is not there, then appoint immediately) an anesthetic and anti-inflammatory agent (for example, "Fastum-gel").
Drugs that restore blood flow are prescribed. Surgery is performed if the pathological changes progress, and the pain intensifies, despite drug therapy and physiotherapy. Then the damaged joint is fixed in the desired position. After the bones grow together, the mobility of the joint is restored. Or the affected area is replaced with a prosthesis.
Tendinitis
This is an inflammation of the tendons in the wrist. The disease can be triggered by stressful situations, trauma. More often, tendonitis is accompanied by a sprain. Complex treatment, using medicines, physiotherapy, folk recipes.
Symptoms and Signs
First, slight discomfort appears in the wrist, then acute pain in the tendons. Symptoms appear mainly during the period of active movement, during rest they decrease. In the affected area, the skin swells, turns red, and feels warmer than the rest of the epithelium. A crunch is heard when the wrist is bent. It is difficult for the patient to hold heavy objects.
Causes
It occurs due to the same type of movements, more often the peculiarity of the work becomes the cause. Other provoking factors can be bone growths, reactive arthritis, gout. Often, tendonitis appears against the background of prolonged physical exertion, sprains, and dislocations.
Often, tendonitis appears against the background of prolonged physical exertion, sprains, and dislocations.
Treatment methods
It is necessary to reduce the stress on the arm and keep it at rest until the pain passes. Compresses with ice are applied to the affected area. Additionally, the damaged area is fixed with special devices - splints, flexors, bandages.
Additionally, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. They reduce swelling, pain. If the disease is infectious, antibiotics are prescribed (selected individually).
Additionally, physiotherapy is carried out - treatment with a laser, ultrasound, shock wave method. In the chronic form of pathology, mud and paraffin applications are made. As soon as the acute stage passes, exercise therapy and massage are prescribed. Suppurative tendonitis is treated with surgery.
From the methods of traditional medicine, a healing infusion is used. Mix for 1 tsp. l. chopped ginger root and sassaparilla. Pour them with 250 ml of boiling water and insist for three hours. Then they are consumed in small portions throughout the day. Alternatively, you can eat 0.5 g of curcumin daily. Compresses with elecampane, clay, lavender extract help well.
Carpal tunnel syndrome
It belongs to the group of compression-ischemic neuropathies. In tunnel syndrome, nerve endings are compressed by bone and tendons. This can be due to anatomical features or due to other provoking factors.
Classification
This is a chronic disease that is accompanied by exacerbations and remissions.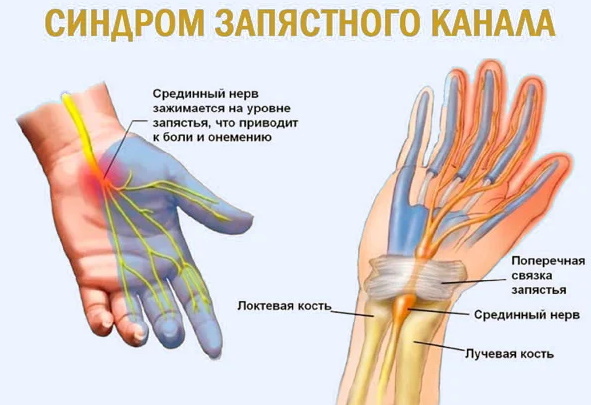
There are two types of tunnel syndrome:
- The primary does not depend on other pathological processes. More often, the cause is a strong and prolonged effect on the wrist, muscle strain.
- Secondary arises as a complication after another disease. For example, due to arthritis, arthrosis, connective tissue pathologies.
The symptoms of the disease are of varying severity. The onset of pathology is often diagnosed at the age of 30-45, and the peak occurs at 50-60 years.
Symptoms and Signs
The main signs are pain in the wrist, numbness of the hand, and impaired mobility of the fingers. There may be limb tremors, itching and tingling. The sensations disappear when you shake your hand. Then comes the stiffness of the joints, the symptoms intensify, complemented by a convulsion. It becomes difficult for the patient to lift heavy objects, open doors, and drive a car.
Causes
The most common cause is a pinched median nerve. This can happen during prolonged playing of musical instruments, working on a computer. Other reasons are endocrine disruptions, hormonal imbalances, pregnancy or menopause. There are many other provoking factors - hereditary predisposition, diseases, tumors.
Treatment methods
It is recommended to change the type of activity or temporarily eliminate the load on the brush. If this is not possible (for example, to refuse to work), then while using the computer, small rollers are placed under the arm. Periodically, you need to knead and shake the sore hand.
Additionally appoint:
- pain relievers (for example, "Nise", "Diclofenac" - 1 tablet per day, course - 5 days);
- muscle relaxants ("Midocalm", "Sirdalud");
- corticosteroids ("Diprospan", "Prednisolone");
- diuretics ("Furosemide");
- anesthetic ointments ("Fastum-gel");
- vitamin complexes;
- hondoprotectors (Alflutop, Rumalon).
Novocaine blockade is introduced into the place of compression. Surgical interventions are resorted to only as a last resort (endoscopic, open surgery).
Of the methods of physiotherapy, they are prescribed:
- shock wave therapy;
- electrophoresis;
- UHF;
- mud therapy;
- laser treatment;
- ultrasound;
- magnetotherapy.
The wrist can be treated with folk methods. For example, an ointment made from salt and mustard powder (200 g / 100 g). They are mixed with melted paraffin to a creamy mass. Lubricate the wrist 1-2 times a day, this helps relieve pain. To normalize blood circulation and eliminate numbness of the fingers, rub the sore spot with an infusion of fresh cucumber, ammonia, pepper.
You can make a burdock compress or use a wrestler root tincture. It improves blood circulation, relieves inflammation and pain. For tincture, take 100 g of crushed plant root, pour 1 liter of vodka, remove to a warm, dark place for three days. Then, 1-2 times a day, rub the wrist with tincture.
Arthritis
It is an inflammatory disease with limited mobility. Pathology develops rapidly. More often it becomes a consequence of another disease, less often it becomes independent. Without timely treatment, there is a risk of complete loss of wrist and hand mobility.
Classification
Arthritis is acute and chronic. There are 3 degrees of the disease. At first, aching pains, stiffness of movements appear after sleep. On the second, there are swelling around the joints, symptoms increase with load on the hand, and the range of motion decreases. On the third, the pain becomes very pronounced. The mobility of the joints is impaired, self-service is difficult.
Arthritis is divided into several types:
- rheumatoid;
- reactive, with joint inflammation;
- purulent infectious;
- gouty;
- infectious and allergic;
- psoriatic.
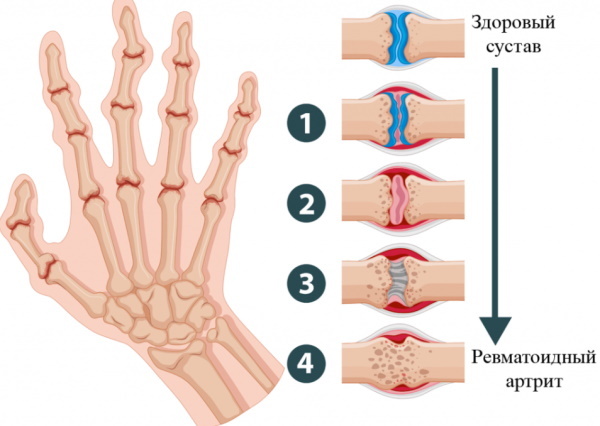 The disease gradually affects all joints of the wrist. In rheumatoid form, both hands are affected.
The disease gradually affects all joints of the wrist. In rheumatoid form, both hands are affected.
Symptoms and Signs
The main symptoms are pain in the wrist, swelling and inflammation of the tissues at the site of the lesion, limitation of hand movements. In the morning, there is a stiffness of the hand, with inaction, its numbness appears. Symptoms depend on the type of disease. Non-infectious arthritis is accompanied by aching pain and limited mobility, acute - severe edema, flushing of the skin. The pain becomes excruciating.
Causes
The cause can be internal and external factors - unhealthy diet, diseases, infections.
Arthritis appears as a result of hypothermia, trauma, immunological reactions. Infectious inflammation causes tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea. Against the background of bacterial lesions, the pathology becomes chronic. Acute inflammation causes purulent arthritis. Purulent-infectious often appears as a complication after measles, flu.
Treatment methods
Acute disease is treated with intra-articular injections. Corticosteroids ("Betamethasone", "Prednisolone") are used more often. They stop inflammation and pain. For bacterial arthritis, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed (for example, "Amoxiclav", "Ampicillin"). Pain syndrome is relieved with anti-inflammatory drugs (Diclofenac, Nimesulide).
Physiotherapy is prescribed only after the acute phase. They use magnetotherapy, current therapy, electrophoresis. Additionally, they do massage, therapeutic exercises. From folk methods, you can make compresses with cabbage juice. A warm woolen cloth is moistened in it and applied to the affected area. Cover with foil and insulate. The compress is kept for 4-6 hours, you can do it in the evening and leave it until the morning.
Additionally, you can drink herbal decoction. The crushed flowers of elderberry, chamomile and calendula are mixed. Add chopped willow bark and nettle leaves to them. All ingredients are taken in equal parts, pour 500 ml of water. Bring to a boil, filter and pour into a thermos. The broth is drunk in a glass before meals, 3-4 times a day.
Arthrosis
The disease is caused by degenerative changes leading to the destruction of joints and cartilage. Pathology rarely develops, but without timely treatment, the wrist is deformed, its mobility is lost, which complicates self-care.
Classification
Arthrosis is primary (the joint is deformed due to external causes) and secondary (it is caused by the disease). In the early stages of pathology, there are no symptoms.
The disease progresses slowly (sometimes over years), in stages:
- At first, the pain is weak, aching, more often after physical exertion. There may be slight swelling, deterioration of tissue condition, quiet crunch of joints.
- On the second, the cartilage is almost completely destroyed, which is accompanied by the appearance of bone growths, narrowing of the joint space. Osteophytes can even be felt. The cracking of the joints becomes more pronounced, and the pain becomes daily.
- A stiff wrist makes self-care very difficult. Ankylosis develops (immobility, fusion of the joint), the edges of the osteophytes are closed. The pain becomes constant.
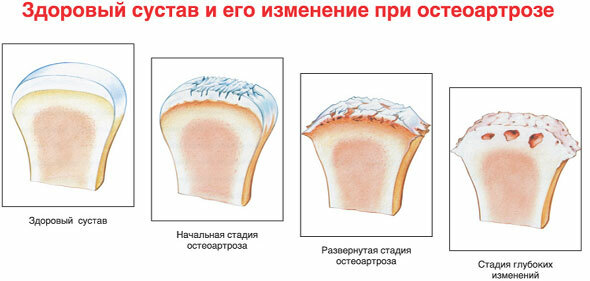
Muscles are less well developed around the affected joint. In the first stages, complex treatment of arthrosis is used, in the third - only surgical intervention.
Symptoms and Signs
First, there is discomfort in the wrist, a feeling of tightness, slight pain (mainly at rest). Then it gets worse - especially after physical exertion. Movement becomes difficult. Swelling is added in the area of the sore wrist, a crunch in the joints. When lifting weights, the pain intensifies, it is impossible to lean on the palm of your hand.
Causes
It mainly occurs due to injuries, hormonal imbalance, metabolic disorders.
Also, the reason may be:
- autoimmune diseases;
- heredity;
- psoriasis;
- hypothermia;
- tuberculosis;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- syphilis.
The risk of developing the disease increases if the work is associated with heavy excessive physical exertion (for example, for blacksmiths, loaders, construction workers).
Treatment methods
When stiffness of movements appears, warm-up and warming baths help. However, when the inflammatory process develops, Nise and Diclofenac are prescribed instead. Additionally, muscle relaxants, chondroprotectors, glucocorticosteroids are included in the therapy regimen. If the disease is of an infectious nature, then antibiotics are prescribed.
Broths and tincture of cinquefoil are taken orally or the joints are rubbed with means. Means are prepared from crushed plant roots. Take 100 g of raw materials, pour 1 liter of alcohol. Insist for 3 weeks, then take 1 tbsp daily. l., before meals. Before use, the tincture is mixed in a small amount of water.
For problems with the gastrointestinal tract, liver and pancreas, a decoction is prepared. To do this, take 50 g of crushed roots of the cinquefoil. Pour 250 ml of boiling water and keep for 15 minutes in a water bath. Then they insist for 2 hours, filter and take daily in several doses, 50 g each. The product should be drunk fresh every day.
The wrist plays an important role in the movement of the arm, hand. He has a complex structure, and any disease and injury can disrupt the mobility of the joints. Cancers in the wrist can also be diagnosed. Therefore, with the appearance of pain, swelling, redness, you cannot self-medicate, but you need to consult a doctor.
Wrist video
Anatomy of the bones of the hand: