Content
- Stages and degrees
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- When to see a doctor
- Treatment methods
- Medications
- Traditional methods
- Other methods
- Possible complications
- Video about cervical vertebra fracture
Vertebral column fractures stand out in a special group of spinal injuries. It is characterized by a severe course, damage to important nerve centers, and sometimes partial or complete loss of motor function.
Often it is damage to the cervical vertebra that leads to such consequences as permanent disability. In other words, they lead to disability. At the same time, many patients belong to the group of young, active people. Therefore, their rehabilitation potential with timely treatment is quite high.
Stages and degrees
Fractures and injuries in the cervical spine do not proceed in stages. But with a fracture of the 2nd cervical vertebra, depending on the clinic and biomechanical features, three degrees are distinguished.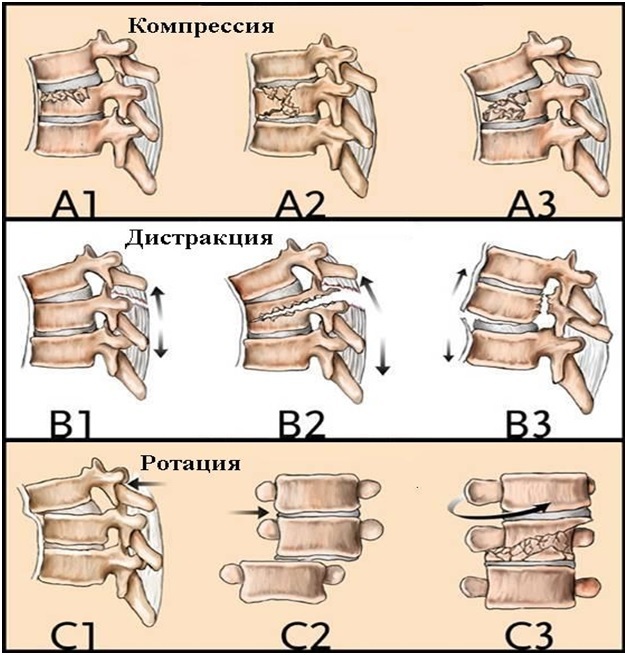
| Stage | Symptoms |
| 1 | At the initial stage, there is no displacement. The patient is worried about discomfort in the neck, limitation of its movements. |
| 2 | When diagnosing grade 2, an anterior displacement is detected. Signs of spinal cord compression include paresis, paralysis, and loss of consciousness. |
| 3 | A pronounced displacement can be detected already at the third stage. Usually it is a fractured fracture with many fragments. |
Symptoms
Fractures of the cervical vertebrae are different from each other. After all, there are 7 vertebrae in the cervical spine. The five lower ones have approximately the same structure. There is a body, an arch, various processes. Cartilaginous plates are located between the vertebrae, which provide mobility in the neck due to the joints. Ligaments and muscle mass are also involved in the formation of the musculoskeletal system of the neck.
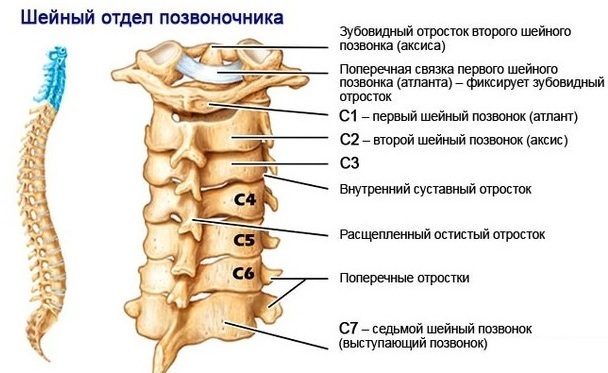
With fractures of the lower cervical vertebrae, the symptoms are almost the same. The mechanism of injury is usually flexion. That is, the injury is caused by strong flexion. Extension fractures are less common.
Fracture of the cervical vertebra (the consequences depend on the location of the injury) manifests itself primarily in pain. It is usually limited to the fracture area. That is, the pain is localized, not common.
When you try to examine the affected area with your fingers, soreness is found. If it increases when pressure on the spinous process is reproduced, an unstable fracture should be considered.
The pain itself can cause limitation of movement. It could be stiffness. The patient spares himself, therefore, in order not to cause pain again, he limits the turns of the head, neck, and flexion. The muscles of the neck (back group) are tense. They are in a state of reflex spasm.
If the fracture in its mechanism is not compressive, but fragmented, comminuted, then it is more likely that neurological symptoms will join due to damage to the spinal cord. The same situation is possible with simultaneous dislocation and fracture. Neurological disorders can be different.
Usually this is a violation of all types of sensitivity. With more serious injuries, the motor sphere is disturbed up to paralysis of all 4 limbs (tetraplegia). Situations with a loss of control over the processes of defecation and urination are not uncommon.
Fracture of the atlas, or 1 cervical vertebra, occurs with forceful blows, as well as in the case of excessive flexion in the cervical spine. The pain syndrome is more diffuse. It spreads from the fracture to the occiput, sometimes even to the parietal region.
The pain is not "dagger", not shooting, but rather aching. At the moment of impact, it is more pronounced, then “dulls”. The patient cannot keep his head in the usual physiological position, and therefore holds it with his hands. At the same time, he speaks of a loss of sensitivity. Soft tissues are also not sensitive, including to the doctor's palpation.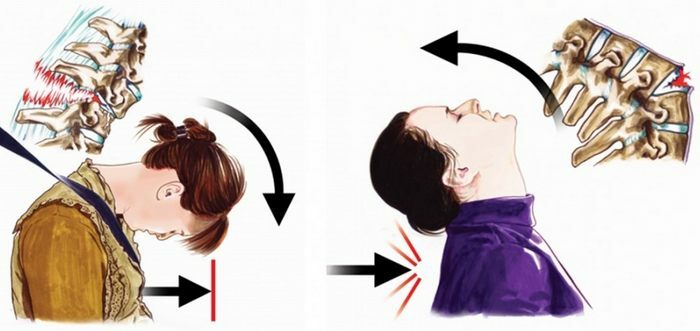
When the upper four vertebrae of the neck are affected, it causes damage to the motor sphere in all 4 limbs. Sensitivity is impaired. This applies to all its types. At the same time, the patient may experience pain in the neck or occipital region.
Pathways from the cranial nerves are damaged. Therefore, there are such manifestations as impaired swallowing, phonation. Double vision occurs. The neurologist detects nystagmus. In response to light, the reaction of the pupils decreases. Strobism (squint) is sometimes seen. On the part of the cardiovascular system, there is a slowdown in the heart rate up to bradycardia.
Diagnostics
First of all, you need a doctor's examination, anamnesis collection. This is important in the formulation of a preliminary diagnosis and the formation of a working hypothesis in order to further draw up a survey plan.
The traumatologist gently palpates the neck area to determine the area of soreness, muscle spasm, and possible manifestations of mixing. All types of sensitivity are determined. It is necessary to investigate the motor sphere, pathological reflexes. These simple techniques allow you to timely identify or exclude the spinal cord.
Radiography determines the presence of a fracture, displacement, dislocation. It is performed in two projections. To exclude damage to the brain, spinal cord, computed tomography is shown. In case of doubt, an additional MRI is prescribed.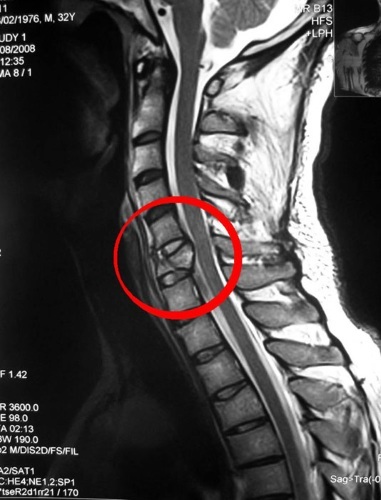
If there is a suspicion of a violation of the integrity of the peripheral nerve trunks, the patient is consulted by a neurologist or neurosurgeon. If necessary, electromyography is prescribed. It is this method that will make it possible to make a final conclusion about whether this or that nerve is affected.
Echo-encephalography is indicated for severe headaches. A search is underway for a dysfunction of the brain, the presence of pathological cerebral electrical activity, or a violation of outflow through the veins or arteries of the neck, brain.
When to see a doctor
Fracture of the cervical vertebra (the consequences can be extremely serious), even only if it is suspected, requires immediate intervention, therefore, for any injury to the neck, head, you should soon contact either an ambulance or a clinic for a surgeon, traumatologist in emergency room.
This is especially true for situations accompanied by the following patient complaints:
- headache;
- stiffness and pain when moving the neck;
- inability to hold the neck without the help of hands;
- loss of sensitivity;
- weakness in the lower, upper limbs;
- visual impairment;
- difficulty speaking;
- fecal and urinary incontinence.
Even if the injury happened 2-3 days ago, it is never too late to seek help from a doctor.
Treatment methods
The management of neck fractures depends on many factors. The main ones are the presence of complications and displacement of fragments. Conservative treatment or surgery is provided.
In the framework of emergency care, the introduction of a strong analgesic is provided. For example, Ketorolac. Ideal when it is possible to give a mask with nitrous oxide and oxygen. A Scheinz collar is put on the neck.
The transportation is carried out by several participants. Better if it is 5 people. One of them slightly unbends the spine of the injured person, while holding his chin. A second participant holds the ankle area. The next one holds the hips and shoulder girdle. As a result, the spine is gently extended.
Medications
Medical treatment provides adequate pain relief. At the time of injury, the pain can be so severe that it can cause a vascular reaction, up to shock. Therefore, first use any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent.
It can be Ketorol, Diclofenac, Ortofen. The preferred route of administration is injection (into the muscle). If NSAIDs are ineffective, switch to Tramadol or other narcotic analgesics.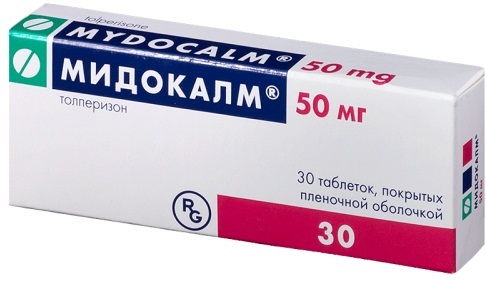
If a spasm of the posterior muscle group of the neck is palpable, muscle relaxants are used. They are also appointed before dislocation management. Mydocalm injections are effective. Pay attention to blood pressure, as this group of medications can cause hypotension.
Traditional methods
Doctors treat alternative methods of treating fractures with great skepticism and mistrust. The only thing you can trust in traditional medicine is how to replenish the lack of calcium, which will help speed up the healing of the fracture and the formation of callus.
Shilajit helps to consolidate the fragments faster. Another proven and safe way is to eat ground eggshells.
Other methods
Conservative treatment is considered the only tactic that is preferable in the absence of splinters, fragmentation, impairment of the integrity and function of the spinal cord.
It involves the following methods of therapy:
- Reduction of the vertebrae is used in rare cases. This is considered a dangerous procedure, as there may be consequences in the form of spinal cord injury. It is carried out by a traumatologist, the essence lies in a strong overextension of the cervical spine.

- Fixation with a Scheinz collar is indicated if there are no fragments and the fracture is not fragmented. The bottom line is to create the most favorable conditions for the fusion of fragments and cracks. This can be achieved by maximum immobilization at the site of injury. Terms vary from 6 to 9 weeks. After such treatment, rehabilitation is necessary, including physical therapy classes, since hypotrophy and hypotension of the neck muscles can begin to form. And this creates the prerequisites for the formation of hernias, the rapid development and progression of chondrosis.
- Skeletal traction attempts to achieve alignment of fragments with minor displacements. It is performed in a hospital setting, under periodic X-ray control; if necessary, you may need to consult a neurosurgeon. The traction is carried out under the patient's own weight. A special arch is fixed behind the ears, which is fixed on the other side at the head end of the bed. The latter should be raised. A weight up to 9 kg is suspended from the arc. There are special formulas for calculating the weight of goods. On average, the stretching time can reach 4 months. But with positive dynamics on the X-ray, they go to the stage of fixation either with a Scheinz collar or with a rigid plaster half-collar. It is recommended to wear it for up to 8 weeks. At all stages of treatment, it is assumed that the complexes of medical gymnastics are performed.
- Another option for traction involves the use of a special glisson loop. It is drawn in the form of a wire around the face and fixed to the chin area. The head end of the bed is raised. For this reason, traction is carried out due to the gravity of the patient's own weight. The timing is approximately the same as in the previous method.
- Rollers and pillows are used depending on the mechanism of injury. In the case of pronounced overextension, a roller is placed under the neck. If the fracture is due to excessive flexion, they are placed in the waters of the scapula or shoulders.
- Surgical intervention is performed for non-consolidating fractures, the presence of fragments. Fracture-dislocations are indications for surgical treatment. It is these types of injuries that are dangerous for spinal cord injury. Tears of nerve trunks, damage to vascular structures, muscles, ligaments can bring a fracture to a group of complicated ones. Therefore, they are also treated with surgery.
- Physiotherapy.
- Physiotherapeutic methods of influence.
A fracture of the cervical spine is accompanied by damage to blood vessels: veins and arteries. The vertebrae are very close to them. During the operation, the consequences are eliminated: bleeding by suturing the vessels, and the integrity of the nerve trunks is also restored.
This is done by a traumatologist or neurosurgeon. Then they move on to bone structures, tendons, muscles. Immobilization is required after surgery. Fixation with a Scheinz collar is carried out for about 8 weeks.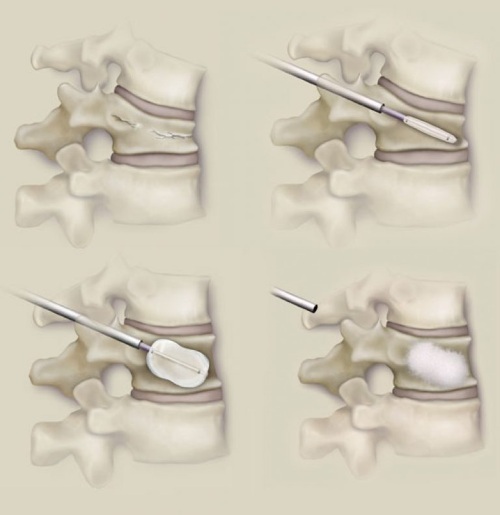
Sparing surgical interventions can be considered vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Fragment fixation is carried out with metal structures or autologous bone. Liquid bone cement is sometimes used to fill the defects in the vertebrae. After fixation, you need a Scheinz collar or a plaster corset.
Rehabilitation includes classes with a trainer or physician in physiotherapy exercises, physiotherapy. Diet recommendations are followed. For faster healing of fractures, it is necessary to eat foods rich in calcium and phosphorus.
These are fish of different varieties, milk, dairy products. The preferred way of cooking is steaming or boiling. The diet should include fruits and vegetables, preferably fresh.
In addition to diet, the level of calcium in the blood can only increase its intake in the composition of dietary supplements, tablet preparations. In the first case, the product must be certified and sold through the pharmacy chain. The course of admission is up to 2 months.
Physiotherapy is indicated both after fixation and at the stages of immobilization. This is important to create the conditions for a quick recovery. It is necessary to develop the functions of the hands, feet, forearms, and muscles of the shoulder girdle. Despite the pain, you need to perform sets of exercises. But only under the supervision of a doctor or exercise therapy instructors.
Possible complications
Fracture of the cervical vertebra (the consequences depend on the severity of the injury) is accompanied by damage to various structures. The most serious and dangerous consequences relate to the contents of the spinal canal, namely the spinal cord. This can be compression, which is manifested by a violation of sensitivity.
The larger the volume of the lesion, the more pronounced the dysfunction in the sensitive area. Movement disorders are not uncommon. It can be paresis or complete paralysis. There are paralysis of only the upper or only the lower extremities (paraparesis) or paralysis of the extremities on the right, on the left (hemiparesis).
In case of spinal cord ruptures, there is a risk of impaired respiratory and circulatory function. The situation becomes critical and requires treatment in the intensive care unit in neurosurgery.
Fracture of the cervical vertebra (the consequences relate to infection) occurs according to different mechanisms. Injuries that caused a fracture of the cervical vertebra are simultaneously accompanied by hematomas and bruises, sometimes wounds. Hemorrhages are often infected, so they are complicated by abscesses. The same applies to possible infection of open wounds.
Fractures of the cervical spine are dangerous and not always favorable in terms of prognosis injuries. The vertebrae have a complex structure, therefore, in case of injuries, the consequences can affect the nerve trunks, blood vessels. At a young age, with adequate treatment, the fracture heals, and the lost functions, as a rule, are restored. With injuries to older people, the prognosis is much worse.
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Video about cervical vertebra fracture
About cervical vertebrae injuries: