Content
- What curves does the human spine have in the norm?
- Causes and symptoms of lordosis and kyphosis
- The degree of curvature of the spine
- Pathological kyphosis of the thoracic region
- Pathological lordosis of the cervical spine
- Pathological lordosis of the lumbar spine
- Differences between lordosis and kyphosis
- How to determine the type of curvature
- Physiological examination
- Instrumental diagnostics
- How to treat kyphosis and lordosis of the spine
- Physiotherapy. Exercise complexes
- Proper nutrition. Sample menu for a week
- Massage. Execution techniques
- Physiotherapy
- Wearing orthopedic corsets
- Is it possible to cure lordosis and kyphosis of the spine
- Forecasts
- Video about kyphosis
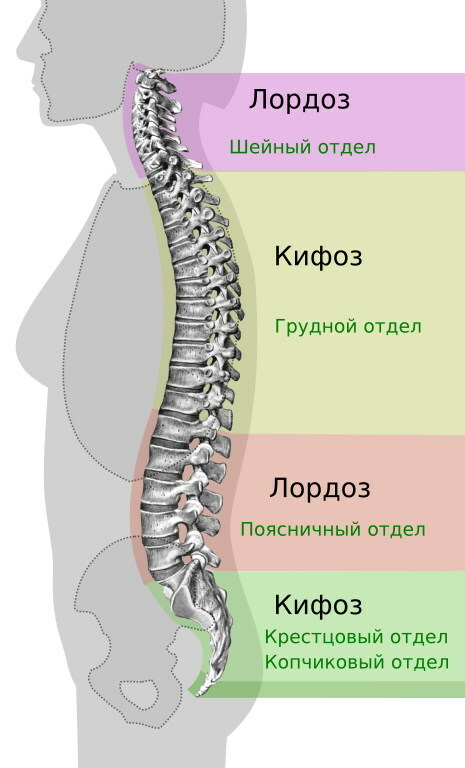
When viewed from the back, the spine appears to be vertically straight - from the neck to the coccyx. Looking at the spine from the side, you can see that it resembles a soft S-shape. Normally it has bends, called lordosis and kyphosis.
What curves does the human spine have in the norm?
Normally, the cervical and lumbar spine is slightly curved inward. This is due to the fact that the intervertebral discs in these two areas are thicker in the front than in the back, which causes this part of the spine to bend forward, this is called normal lordosis.
On the other hand, the thoracic and sacral spine is usually curved backward, which is normal kyphosis. A healthy spine has a smooth s-shaped curve when viewed from the side and straight when viewed from the front.
The four natural curves of the spine are:
- thoracic kyphosis;
- sacral kyphosis;
- cervical lordosis;
- lumbar lordosis.
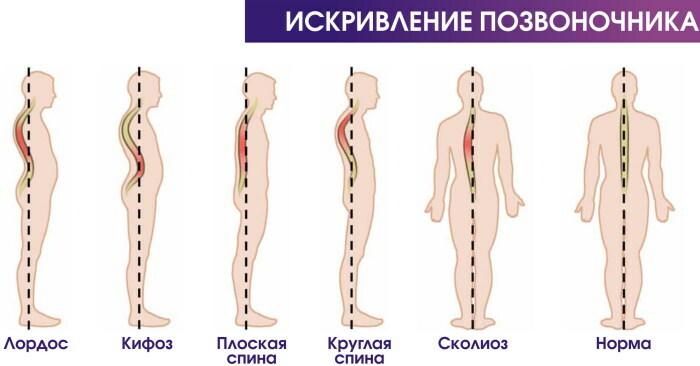 The 4 curves of the spine work together to provide mobility and support for the entire skeleton. The curvature of the cervical lordosis is found in the upper part of the spine, from the neck to the shoulder blades. Normally, the curvature of this part ranges from 20 to 40˚. Lumbar lordosis is in the lower back, and a 40 to 60 ˚ curvature is normal.
The 4 curves of the spine work together to provide mobility and support for the entire skeleton. The curvature of the cervical lordosis is found in the upper part of the spine, from the neck to the shoulder blades. Normally, the curvature of this part ranges from 20 to 40˚. Lumbar lordosis is in the lower back, and a 40 to 60 ˚ curvature is normal.
Thoracic kyphosis is the portion of the spine behind the breast that promotes erectness and balance. The normal curvature of this part is 20 to 40˚. Lordosis and kyphosis of the spine serves to distribute the mechanical stress that occurs when the body is at rest and during movement.
Causes and symptoms of lordosis and kyphosis
Pathological lordosis is associated with poor posture, overweight, injuries, operations, neuromuscular diseases:
- The human lumbar region is supported by the abdominal muscles. Children with weak abdominal muscles have a higher risk of developing hyperlordosis.
- The extra weight on the abdomen puts stress on the lower back and forces it to stretch forward, increasing the risk of pathological lordosis.
- Any injury to the spine weakens the spine and causes curvature of the vertebrae.
- Certain types of surgery, including selective dorsal rhizotomy (a minimally invasive procedure performed to reduce spasticity in the legs), can lead to lordosis.
- Children with hip dysplasia may develop lordosis.
The individual bones of the vertebrae usually look like stacked cylinders in a column. With kyphosis, the vertebrae become wedge-shaped.
This is due to various reasons:
- Compression fracture any part of the axial skeleton can cause curvature, although minor fractures usually do not cause any noticeable symptoms.
- Osteoporosis. The metabolic state leads to the fact that the bones become fragile, which further contributes to the curvature of the spine.
-
Disk degeneration. The soft, rounded discs, which act as cushions between the vertebrae, can dry out and contract, resulting in a curvature of the axial skeleton.
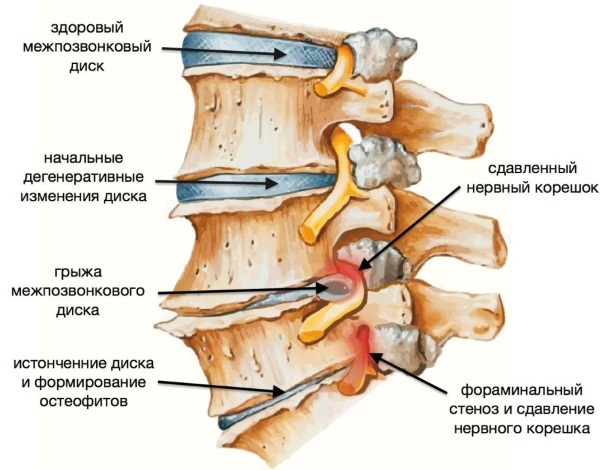
- Growth bursts. Scheuermann's kyphosis usually begins during growth and continues until puberty.
- Birth defects. Bones of the spine that do not develop properly before birth can lead to kyphosis.
- Children's syndromes. These include round back syndrome, which occurs during adolescence, Marfan syndrome, a genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue of the body.
- Cancer. A tumor in the spinal cord can weaken the vertebrae and contribute to the development of a spine prone to compression fractures. Chemo and radiation therapy also contribute to the development of kyphosis.
Risk factors for kyphosis include age and genetics:
- After 40 years, the curvature of the spine increases. After 60 years, 20 to 40% of people suffer from kyphosis. In women, the syndrome progresses faster.
- If there are family members with kyphosis in the family, the person is more likely to get the syndrome. One report published in 2017 in a medical journal found that up to 54% of cases of kyphosis in older adults were due to genetics.
Symptoms of excessive kyphosis:
- A visible hump in the upper back, especially when bending forward.
- Rounded shoulders.
- Back pain and stiffness.
- Constant feeling of tiredness.
- Labored breathing.
- Muscle stiffness.
Excessive symptoms of lordosis:
- Normal pose: bulging forward of the abdomen, and the hips back.
- Rupture in the lower back in the supine position.
- Pain and weakness in the back and legs.
- Numbness and tingling in the lower extremities.
The degree of thoracic kyphosis and lumbar lordosis depends on the relationship between the spine, hips, and pelvis. The angle that determines this value is called the fall of the pelvis. Because this constituent is unique, there is no normal value for lumbar lordosis.
The degree of curvature of the spine
Lordosis and kyphosis of the spine are rarely classified, but the normal physiological definition in the thoracic region is 15 to 30˚ bend.
The classification exists only for pathological kyphosis of the thoracic region and its gradation is very symbolic (many medical institutions do not adhere to it):
- Grade I - the curvature arc is 30-40˚.
- Degree II - 41-50˚.
- Degree III - 51-70˚.
- Grade IV - over 70˚.
Kyphosis and lordosis are of different subtypes.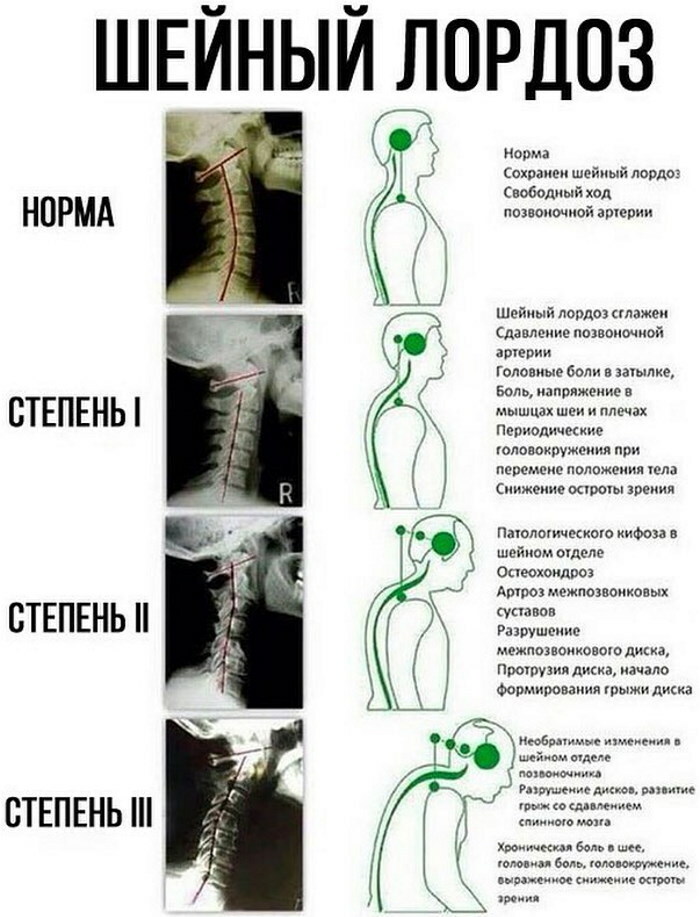
Types of kyphosis:
- Postural kyphosis. This is the result of poor posture and stoop. The diagnosis is typical of adolescents and affects girls more than boys. Rarely causes problems other than mild discomfort and a slightly rounded spine.
- Scheuermann's kyphosis. In this type, the vertebrae are wedge-shaped rather than rectangular. It is more common in boys and can be painful, especially with physical activity or after prolonged standing or sitting.
- Congenital kyphosis. It gets worse as the child grows. Children with this condition may have additional birth defects that affect the heart and kidneys.
There are different types of excessive lordosis:
- Postural lordosis is caused by overweight and weak muscles in the back and abdomen.
- Congenital lordosis is a defect that causes deformation of the connecting links of the spine.
- Traumatic lordosis is observed in children who have received a sports injury, when falling from a height or after a car accident.
Whatever the cause of congenital or traumatic lordosis, the vertebrae can slip forward over time and pinch the nerves in the spine, causing pain, numbness, weakness, or dysfunction in the legs.
Lordosis and kyphosis of the spine in excessive curvature can be painful conditions. They affect different parts of the vertebrae.
Pathological kyphosis of the thoracic region
Thoracic kyphosis develops at any age and affects both men and women. Depending on the underlying causes, the symptoms of kyphosis can vary from mild to severe. The most common symptom is poor posture, along with an emerging bump in the back, which can increase over time. In rare cases, this leads to neurological symptoms when the spinal cord is compressed.
Pathological lordosis of the cervical spine
Cervical lordosis at any axial load reduces the pressure on the spine. The statics of this bend is often violated. Instability is characteristic of degenerative pathologies of the neck and cervical spine in general. The main reason considered for instability of the cervical spine is osteochondrosis.
Disorders of the spine also occur due to dislocation and subluxation.
Pathological lordosis of the lumbar spine
It manifests itself as a large lumbar arch in the lower back. Along with this, a bulging belly, protruding buttocks and flat feet can be noted. The main reason for the development of increased lumbar lordosis is hereditary. Being overweight, especially during pregnancy, can also put pressure on your back.
When an increase in lumbar lordosis becomes chronic, the muscles involved in posture change. The abdominal muscles are no longer involved in keeping the body upright. The back muscles of the thigh are weakened and shortened. The pelvic floor muscles also shorten and harden, which increases the excess concavity. The muscles in the lower back harden and remain in an irregular shape.
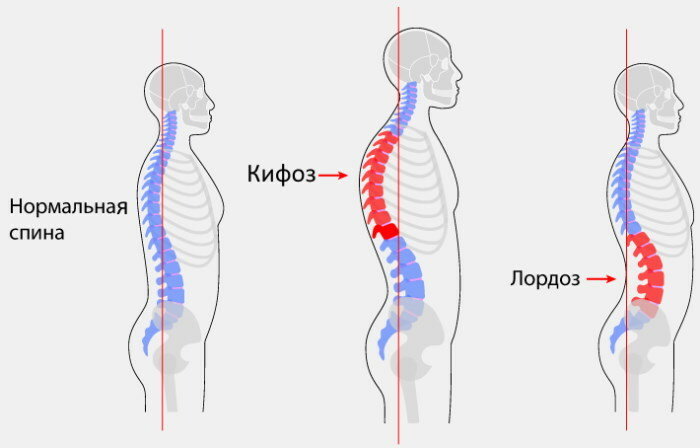
Differences between lordosis and kyphosis
Lordosis, as well as kyphosis of the spine, are terms that are used to refer to certain diseases in the area of the main part of the axial skeleton of a person.
| Lordosis | Excessive bending of the spinal column inward (antonym of kyphosis) | Although lordosis primarily affects the lumbar region, it also occurs in the neck area. |
| Kyphosis | Curvature in the upper spine, directed by the bulge back. | There are two types of abnormal kyphosis: one caused by poor posture and one that is structural kyphosis. Abnormal kyphosis is more common in the thoracic or thoracolumbar regions, but can also affect the neck. |
 Spinal problems and abnormal curvatures can develop due to osteoporosis, degenerating discs, trauma, certain cancer treatments, obesity, genetics, and a host of other causes.
Spinal problems and abnormal curvatures can develop due to osteoporosis, degenerating discs, trauma, certain cancer treatments, obesity, genetics, and a host of other causes.
How to determine the type of curvature
Lordosis is a postural deformity associated with the spine in which the lumbar spine is flexed from the front more than usual. In lordosis, the abdomen protrudes forward, the ribcage is flat, and the shoulders are extended outward and outward.
In kyphosis, excessive outward bending of the spine is seen, and the syndrome causes deformities such as hump. People with excessive kyphosis have a large forward bend or round back syndrome.
Physiological examination
Diagnostics include family and personal medical history, physical examination of the spine, imaging, and neurological examination.
- A physical examination evaluates the curvature, balance, and range of motion of the spine.
- For children, the Adams Forward Bend Test is performed. This test helps the doctor see the tilt of the spine and the degree of deformity or curvature of the axial skeleton.
Instrumental diagnostics
Examination with mechanical devices:
- X-rays show the curvature of the spine and help the doctor determine the curvature.
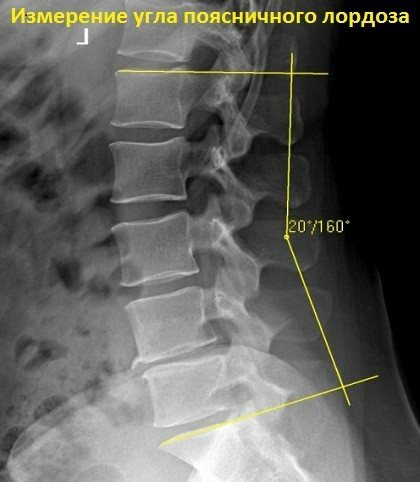
- A CT scan provides detailed images of pathological areas of the spine.
- An MRI is done if the doctor suspects another condition, such as a spinal tumor or changes caused by an infection.
Adults who develop kyphosis or lordosis will need additional testing to determine the underlying causes, including a blood test for the presence of infections and scans of bone density to assess bone strength and diagnose conditions that cause weakened bones, such as osteoporosis.
How to treat kyphosis and lordosis of the spine
Treatment options for kyphosis include:
- Lifestyle changes. Maintaining a healthy weight helps prevent pain and relieves some symptoms.
- Pain relievers such as Acetaminophen (Tylenol), Ibuprofen, Naproxen.
- Calcium and vitamin D supplements to slow the progression of kyphosis.
- Spine brace. A doctor prescribes it to relieve pain, shoe liners or insoles can also reduce back pain.
- Physiotherapy and exercise.
- Fusion surgery. During the operation, 2 or more affected vertebrae are connected and thus the degree of curvature is reduced, and nerve pinching is prevented. The method is used in severe cases.
Treatment options for lordosis include pain relievers, physical therapy, weight loss, spinal cord fixation, and surgery:
- Pain relievers: Tylenol, Ibuprofen, Motrin.
- Physiotherapy strengthens muscle strength, improves flexibility, and increases range of motion in the spine and lower back.
- Reducing weight reduces stress on weak abdominal muscles.
- Stretching exercises increase the flexibility of the spine.
- Wearing corsets and other devices reduces stress on the spine.
- Surgery to correct lordosis is considered if the nerves or spine are damaged.
When lordosis is the result of arthrosis, hip coxarthrosis, or a neuromuscular disorder, the underlying disease must be treated.
Physiotherapy. Exercise complexes
Physiotherapy or supervised exercise by a trainer who specializes in these types of conditions is recommended.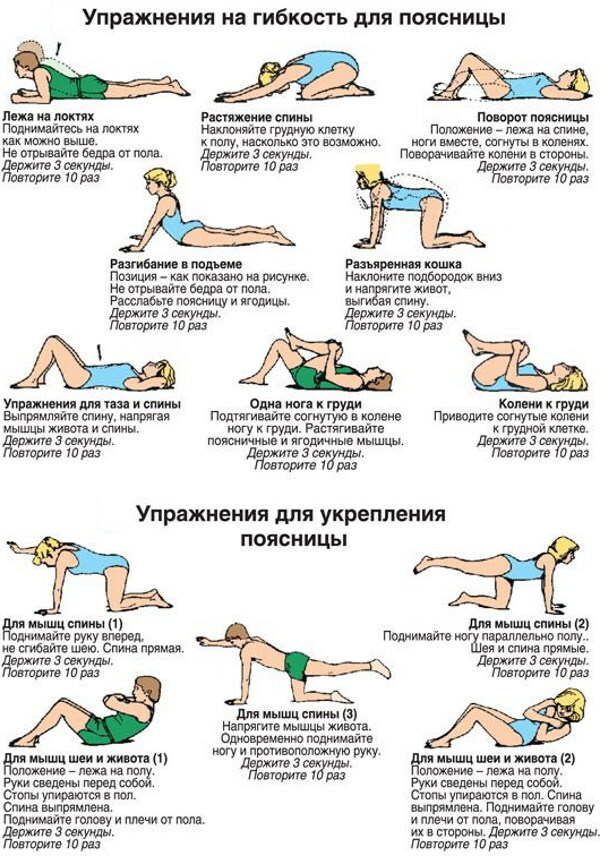
Exercises for kyphosis:
- Back deflection. In a standing position, the arms and toe of one leg are pulled back. The back is deflected. The leg is placed in its original position. The exercise is repeated with the other leg. Repeat the exercise 7-10 times.
- Half-bridge. The legs are bent at the knees while lying on the back. The pelvis is lifted and held in this position for a few seconds. It is done 5-8 times.
- Leaning on both legs and arms, squatting is done (pose on all fours). The right arm and left leg are extended. The position is delayed for a few seconds. Return to the starting position, then the exercise is repeated, but at the same time the leg and arm change.
Exercises for lordosis:
- Lying on your back, raise your legs in a bent position. Repeat the exercise 8-10 times.
- Lying on your back, sit down without using your hands.
- Lying on your back, take turns raising and lowering your legs, resting your hands on the floor.
- Do the previous exercise, but without support on your hands.
- Lean against the gymnastic wall. Holding the crossbar with your hands, bend your legs in the hip joint.
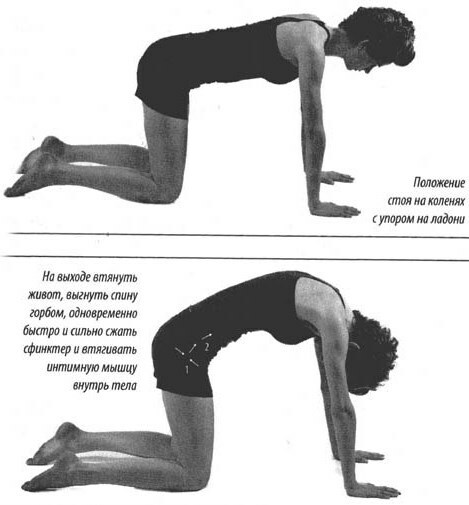
Cat Pose Exercise:
- Get on your knees, spreading them shoulder-width apart, toes bent.
- Arms under the armpits, face directed forward.
- Exhale and slowly bend the spine up, Hold this position for 10-15 seconds.
- Inhale and relax your spine and stomach. Hold this position for 10-15 seconds.
- Return the spine to a neutral position.
Cat-Cow Pose:
- Lie on your back, bend your knees, put your feet on the floor, at a distance of about 25 cm from the buttocks.
- Stretch your arms out to the sides at shoulder level.
- Take a deep breath and let your shoulders relax.
- Pull your shoulders down and back without arching your back, and hold this position during the exercise.
- Perform a light Kegel exercise - squeeze the pelvic floor, as if you want to stop urination.
- Pull your mid-belly towards your lower back without moving your hips.
- Do the Kegel exercise by pulling in your stomach, and repeat this while breathing normally.
If any exercise causes pain or worsens symptoms, it should be stopped.
Proper nutrition. Sample menu for a week
Lordosis and kyphosis of the spine, like other diseases, such as osteochondrosis, require a special diet: low-calorie, with sufficient protein and fluid.
You should eat fractionally, in small portions:
| Day of week | Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | Snack | Dinner |
| Monday | Hard boiled egg, 2 pcs. Hard cheese, cottage cheese or oatmeal with butter, green tea. | Yogurt, juice, or fresh fruit. | Fresh vegetable salad, borscht, sea fish dish. | Fruit jelly or fresh fruit. | Boiled fish, cottage cheese casserole, black tea, vegetables. |
| Tuesday | Cottage cheese casserole green tea without sugar. |
Any fruit | Pumpkin soup, buckwheat porridge, beef cutlets, steam, rosehip fruit drink. | Fruit salad | Fillet of lean sea fish with rice garnish, vegetable salad of carrots, cucumbers, herbal tea. |
| Wednesday | 2 egg omelet, green tea | Orange | Fish soup from sea low-fat fish, rice garnish on the water, vegetable salad, seasoned with vegetable oil (tomatoes, cucumber, green onions) dried fruit compote. | Fruit jelly | Pasta with vegetables, Fruit juice. |
| Thursday | Oatmeal porridge with fruit or molasses, green tea. | Fruit salad (apple, kiwi, banana) with yoghurt dressing. | Chicken fillet meatball soup, brown rice, berry fruit drink. |
Baked apple with cottage cheese, honey and nuts. | Potato casserole, fresh or dried fruit compote. |
| Friday | Broccoli casserole, green tea | Low-fat cheese with bran bread | Mushroom puree soup, sea fish fillet (tilapia) baked in foil, prune and dried apricot compote. | Fruit juice from orange + grapefruit | Chicken soufflé with rice, spinach, fruit jelly, berry juice, a handful of almonds. |
| Saturday | Lazy dumplings seasoned with molasses, milk | Fruit jelly | Beef broth soup, steamed turkey fillet cutlets, dried fruit compote. | A handful of almonds | Vegetable salad (radish, Chinese cabbage, cucumber, flaxseed, sunflower oil), buckwheat with fish in a pot, berry juice. |
| Sunday | Muesli with berries, bran bread with cheese, a glass of cocoa without sugar. | Grapefruit and a handful of hazelnuts. | Chicken and vegetable puree soup, vinaigrette without pickled cucumber, steamed chicken fillet with rice, dried fruit compote. | Soy milk, a piece of bran bread. | Fillet of sea fish with sweet potato and spinach puree, cottage cheese with cinnamon, cranberry juice. |
Before going to bed, you can drink a glass of fermented baked milk or use the following products:
- a glass of whey;
- a cup of low-fat yogurt;
- a glass of kefir;
- eat a portion of low-fat cottage cheese with sour cream and raisins.
Massage. Execution techniques
The purpose of the massage is to increase the tone of weakened muscles, relax tense muscle groups. Actions are performed without sudden movements, smoothly, gently. Pain may be present.
- In chest lordosis, massage begins with stroking the back. The concave side is massaged first, and then the convex side. Further, with massage movements, the muscles of the chest are relaxed, and the muscles of the abdomen are massaged (rubbed) in order to strengthen.
- When lordosis of the lumbar spine is massaged by stroking the back, and then using the techniques of "squeezing". In this case, the mechanical effect extends not only to the skin, but also to the superficial layer of muscles, subcutaneous tissue. Squeezing promotes the outflow of blood from the vessels and their rapid filling.
Physiotherapy
Lordosis and kyphosis of the spine, in addition to the main treatment, involves the appointment of physiotherapy. The use of shock wave therapy is often practiced. During the session, an acoustic wave with a frequency of 18-23 Hz affects the body. Good results are observed after 2-3 months of treatment.
Other physiotherapy treatments:
- Magnetic laser therapy. Combines laser radiation with a magnetic field.
- Electrophoresis of drugs.
- Transcutaneous electrical stimulation.
- Galvanization.
A deep cell massage is performed during ultrasound therapy.
Wearing orthopedic corsets
Lumbosacral braces are medical equipment, also called back braces, that are generally recommended for people with severe lordosis. They are worn to support the lower back and at the same time reduce its curvature.
Is it possible to cure lordosis and kyphosis of the spine
Usually, a person with mild lordosis does not need treatment, but physical therapy or medication may help if the curvature is causing pain. Severe lordosis will require surgery.
In case of successful treatment, mild kyphosis is corrected. Most patients with postural kyphosis achieve good results — correcting the curve to the normal range — by teaching correct posture and performing specific exercises. Severe kyphosis can cause deformity, pain, and breathing problems, but surgery can correct the situation.
Forecasts
In most cases, back pain responds to therapy and goes away after treatment.
Teens with Scheuermann's disease tend to do well even if they need surgery. Often, the disease stops as soon as they stop growing. If the kyphosis is caused by degenerative joint disease or multiple compression fractures, surgery is needed to correct the defect and reduce pain.
If left untreated, kyphosis can cause any of the following conditions:
- decreased lung capacity;
- nervous system symptoms including weakness or paralysis of the legs;
- back deformity.
The prognosis for lumbar lordosis depends on how severe the symptoms are and what the underlying cause is. For example, mild lordosis in children can be cured over time without active therapy, while severe lordosis may require surgery.
Kyphosis and lordosis are different curvatures of the spine. With excessive kyphosis, the spine arches forward, rounding the upper back. With excessive lordosis, the spine bends backward, causing the torso to swing. Both conditions can be painful, and treatment will depend on the cause and severity.
Video about kyphosis
Malysheva about kyphosis: