Content
- Acute bronchitis
- Signs of obstructive respiratory disease
- Asthmatic bronchitis
- Chronical bronchitis
- Allergic bronchitis
- Smoker's bronchitis
- Tracheal bronchitis
- Bronchitis without cough
- No temperature
- Videos about bronchitis
Acute, obstructive, or chronic bronchitis called diffuse (penetrating) inflammation of the epithelium of the lower respiratory system. Signs depend on the form of the disease. In adults, the pathological process can proceed without hyperthermia or with a slight increase in body temperature.
Acute bronchitis
Diffuse inflammation of high intensity affects only the mucous membrane of the respiratory cavity or extends to the entire thickness of the smooth muscle walls. The defeat of the bronchial tree is primary or develops as a complication of systemic pathology.
Signs of bronchitis in an adult without fever occur on the background of allergic reactions, smoking, asthma. The symptomatic picture differs depending on the etiological factor and pathogenetic characteristics of the disease.
Inflammatory damage to the mucous membrane of the walls of the bronchial tree disrupts the secretory function goblet cells, motor activity of the ciliary epithelium, natural cleaning of the respiratory space.
The acute form of bronchitis is caused by respiratory infections of a viral or bacterial nature. Depending on the etiological factor of dysfunction, the symptomatic picture differs.
Typical provocateurs of chronic bronchitis in adults are presented in the table:
| Causative agent | Typical signs of an infectious process |
| Parainfluenza | An RNA-containing viral strain that causes prodromal syndrome, sore throat, severe cough, febrile hyperthermia. |
| Respiratory syncytial infection | The pathological process in the bronchial tree is provoked by metapneumoviral agents. Depending on the degree of involvement of the respiratory tract, signs of infection include nasal pharyngitis, bronchiolitis, serous-mucous discharge, dry cough. |
| Adenovirus | The symptomatic picture of the lesion combines rhinopharyngitis with tonsillitis and pharyngoconjunctival fever. Signs of gastrointestinal disorders, diarrheal syndrome, muscle and joint pain develop. |
| Measles | The pathological process is characterized by a combination of catarrhal symptoms with a specific exanthema - a type of skin rash. There is a combination of catal signs with intoxication symptoms. The clinical picture of acute bronchitis is complemented by headaches, sleep disturbances, and chills. |
The aggravated course of diffuse inflammation of the epithelium of the bronchial tree is caused by entero- and rhinoviruses, mycoplasmic infections. The pathological process in adults is provoked by mixed flora and chlamydia.
Each cause has its own set of local signs and generalized symptoms. The clinical picture depends on the involvement of other organs.
An aggravated pathological process often affects:
- nasopharyngeal cavity;
- tonsils;
- trachea;
- pulmonary alveoli.
Viral lesions provoke the activation of opportunistic microflora and the attachment of pathogenic bacteria, which expands and aggravates the observed symptoms.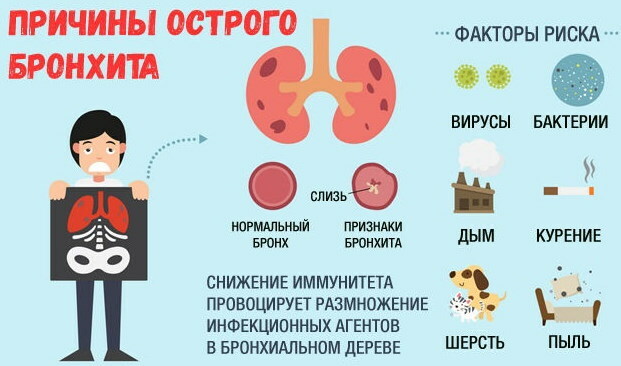
There are infiltration changes in the morphological structure of the mucous membrane. For acute lesions of the upper layer of the bronchial walls, hyperemic manifestations are characteristic, the formation of edema obstructing breathing.
Signs of obstructive respiratory disease
The pathological process proceeds with an increased spasm of the respiratory cavity and a pronounced inhibition of the ventilation function of the lungs. The aggravated form of obstructive bronchitis is provoked by various infectious agents. The risk group includes patients with autoimmune diseases, difficult and harmful working conditions, smokers.
Obstructive bronchitis has the following set of clinical signs:
- Infectious toxicosis.
- Dyspeptic disorders.
- General weakness.
- Increased cough syndrome at night.
- Participation in the respiratory activity of auxiliary muscle groups - cervical, abdominal, shoulder.
- Whistling or wheezing sounds when breathing.
Recurrent obstructive bronchitis is more common in men than women. The secondary form of pathology is common among patients with a congenital tendency to anaphylaxis, with weakened immune defenses, and frequent incidence of ARVI.
Signs of bronchitis in an adult without fever are due to bad habits or a pathogenetic factor. The basis of the clinical picture is the periodic attacks of dry cough.
Asthmatic bronchitis
The disease is considered multifactorial. Respiratory syndrome is anaphylactic, infectious, or autoimmune. The asthmatic form proceeds with a predominant lesion of medium and large organic structures.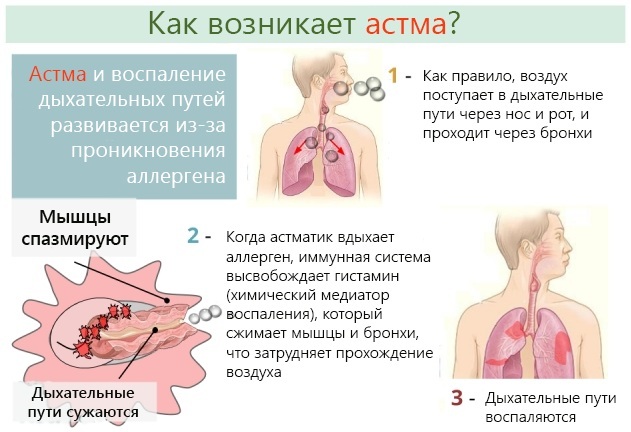
Typical signs include:
- paroxysmal cough;
- forced breathing difficulties;
- expiratory dyspnea;
- release of serous-mucous exudate;
- elimination effect with the cessation of seizures without the influence of a provoking factor.
Secondary asthmatic bronchitis often accompanies hay fever - a complex of seasonal anaphylactic reactions. The disease is a symptom of allergic diathesis due to congenital factors and constitutional physiological characteristics.
For each variant of the pathological process, different clinical signs are observed, combining bronchitis symptoms and manifestations of disorders in the work of other functional systems.
Respiratory failure often accompanies neurodermatitis. With such a pathology, skin rashes with itching are added to the clinical picture of asthmatic bronchitis.
The disease can be accompanied by neurological symptoms and autonomic signs in the form of:
- increased irritability;
- psychoemotional lability;
- general lethargy;
- excessive sweating.
Asthmatic bronchitis often occurs without fever. During periods of exacerbation, congestion in the sinuses, sore throat, and deterioration in the perception of odors are observed.
Chronical bronchitis
In adults, respiratory pathology flows into a sluggish form after repeated acute diffuse-inflammatory process in the bronchial tree.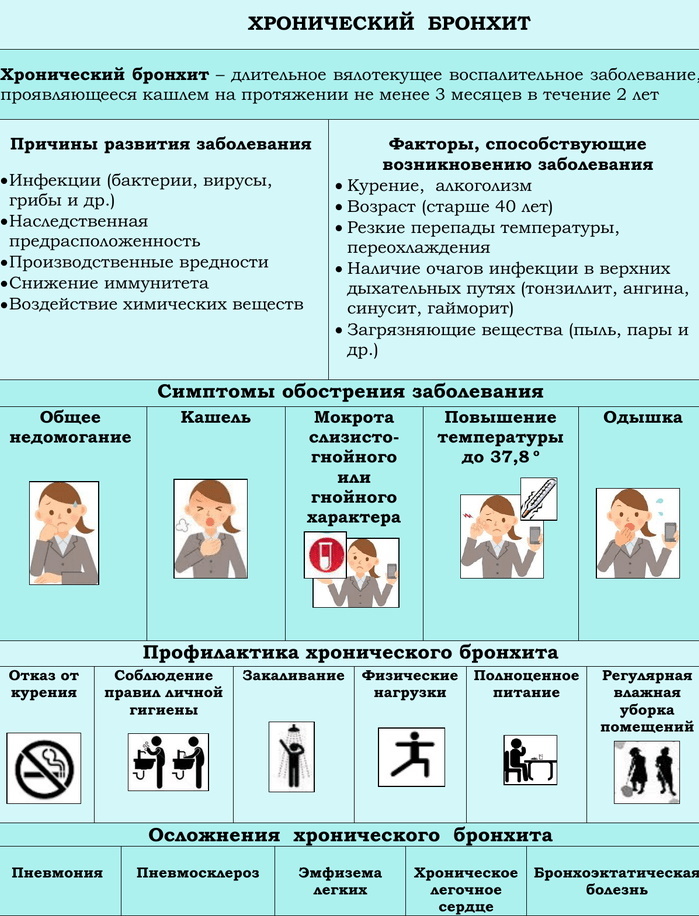
Irritation of the ciliary epithelium of the walls of the respiratory cavity causes regular exposure:
- cigarette smoke;
- fine particles;
- exhaust gases;
- coal, silicate or other dust;
- vapors of chemically aggressive substances;
- pet hair;
- flowering products.
In the stage of chronicity, bronchitis passes with the uncontrolled intake of certain medications.
Signs of a pathological process are determined by:
- disease activity - exacerbation or remission;
- the nature of the course - with or without obstructive lesion;
- the development of complications - catarrhal, autonomic, neurological;
- pathogenetic factors - allergic, hereditary, associated with bad habits, working conditions or the specifics of professional activity.
The symptomatology of chronic diffuse inflammation of the mucous membranes of the walls of the bronchial tree is based on a prolonged cough syndrome. It passes with the release of mucus secretion or is dry in nature.
The disease is activated by unfavorable factors - damp and cold weather, contact with allergens of plant or animal origin, smoking. Chronic bronchitis goes into remission during the warm and dry seasons.
As the disease progresses, new signs are added in the form:
- shortness of breath with the least physical exertion;
- pathologically rapid fatigability;
- discharge of purulent exudate;
- frequent bouts of harsh cough;
- periodic general malaise and loss of strength;
- night sweats;
- cardiac arrhythmias.
Systematic bronchospasm indicates the development of an obstructive process in the respiratory space. The disease is characterized by suppression of local and systemic immunity, which creates favorable conditions for the development of pathogenic microflora.
Allergic bronchitis
This form of respiratory pathology has its own and unusual for other types of diffuse-inflammatory lesions of the epithelium of the respiratory cavity, a set of typical symptoms.
Bronchitis of anaphylactic genesis in adults often proceeds without an increase in body temperature. The set of signs depends on individual immune responses to contact with an allergenic substance.
Common provocateurs of exacerbations:
- food products;
- pollen of plants;
- detergents;
- any chemical compounds of an organic or synthetic nature that provoke the release of histamine into the blood.
Inhalation, enteral, infectious causes of allergic bronchitis have different symptoms. The main symptom of diffuse inflammation of the respiratory epithelium is considered to be paroxysmal cough syndrome with the release of a small volume of viscous and turbid exudate.
Attacks with the same frequency are repeated during sleep and during periods of wakefulness. Contact with an inflammatory trigger increases symptoms. Often, before a cough paroxysm, there is a tickling in the larynx, indicating the allergic nature of the respiratory disorder.
The symptoms of the disease, depending on the provoking cause, resemble obstructive or other form of pathology. Whistling or wheezing sounds are observed when coughing.
For progressive tissue hypoxia caused by impaired pulmonary ventilation, spontaneous dyspnea is characteristic. A distinctive feature of allergic bronchitis is moderate intoxication.
Cephalalgia grows, appetite suppression is felt. Body temperature is often fixed within normal limits. Respiratory signs are combined with neurological symptoms, skin rash in the form of large blisters, intense itching.
With the penetration of the allergen into the digestive tract, the clinical picture is complemented by pain in the epigastric zone, gastrointestinal spasms, and nausea. Disorders of defecation are observed.
Smoker's bronchitis
Diffuse inflammation of the mucous membrane of the respiratory cavity is caused by the irritating effect of tobacco combustion products. The leading sign of the pathological process is considered to be a productive cough of long duration and often recurring paroxysms.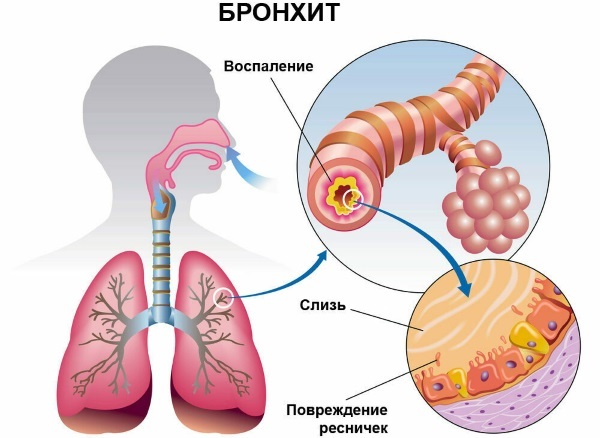
This form of bronchitis is characterized by slow, progressive development with an increase in clinical symptoms. After 10-15 years of daily smoking of 10 or more cigarettes, regular coughing attacks occur, accompanied by the release of mucus secretions.
Strengthening paroxysms provoke respiratory infections, hypothermia. The pathology is characterized by expiratory respiratory failure in combination with obstructive syndrome.
In the early phase of the development of a smoker's bronchitis, such symptoms are observed only during periods of exacerbation or under the influence of concomitant factors. The attachment of pathogenic microflora changes the color of the sputum, adds purulent-bloody fragments to it.
Tracheal bronchitis
The diffuse inflammatory process involves the respiratory tube of the cartilaginous structure. The trachea is lined with epithelial cover, therefore it is characterized by increased vulnerability. The severity of the course and the complex of symptoms are closely related to the form of the disease.
Typical signs of tracheobronchitis:
- dry or moist cough;
- acute pain in the chest area;
- an increase in body temperature up to 38 ° C and more;
- prostration;
- decreased muscle tone;
- difficulty breathing;
- tachycardia;
- profuse sweating.
Depending on the etiological factor, an allergic, infectious-septic or combined form of respiratory pathology is distinguished. Acute tracheal bronchitis is most often caused by viral pathogens.
The disease occurs against the background of seasonal flu, develops independently and in isolation, or accompanies a systemic pathological process and is of a secondary nature.
Signs of bronchitis in an adult without fever indicate an allergic origin or persistent the influence of a provoking factor - constant overwork, weakened immunity, unfavorable climate.
Separate etiological varieties include purulent pathology, occupational disease and atrophic. The latter morphological type is characterized by structural rearrangement of the integumentary epithelium with degeneration and thinning of the mucous membrane.
Among the signs of an atypical form of tracheal bronchitis are painful sensations with a deep breath, episodes of hemoptysis, irritative cough. In the primary inflammatory-diffuse process, the symptoms are exacerbated against the background of the progression of respiratory pathology.
Bronchitis without cough
This course of the disease is called atypical. Cough is the leading symptom of all other forms of bronchitis. The syndrome serves as a protective reaction that allows you to clear the respiratory space from foreign matters, exudate, infectious agents.
In some cases, in the initial phase of the inflammatory-diffuse process, cough is not observed, but other characteristic symptoms of damage to the bronchial tree are present.
This situation is characteristic of bronchiolitis, in which pathological changes affect only small branches of the respiratory canals. There are no cough receptors in the bronchioles.
The accumulation of mucus secretions in them makes it difficult to breathe and is fraught with complications. Chronic bronchitis often proceeds without coughing. In the remission stage, other typical symptoms persist - shortness of breath, sweating, fatigue.
Bronchitis, not accompanied by cough syndrome, causes oxygen deprivation and hypoxic tissue internal organs, which leads to dangerous consequences of cardiological, nephrological and hepatobiliary character.
No temperature
Symptom-free in adults is due to low immune status, allergic causes, or smoking. Such forms of pathology and asthmatic bronchitis are not accompanied by hyperthermia.
The temperature indicator remains normal in the initial phase of the development of the diffuse-inflammatory process in the epithelium of the respiratory cavity, with an atypical course of the disease.
Pathology is manifested by other characteristic signs - shortness of breath, profuse sweating, coughing. The likelihood of hyperthermia depends on the clinical form of the disease and the individual physiological characteristics of the organism.
Often, body temperature does not rise in patients with a combination of obstructive bronchitis and a weakened immune system that does not respond appropriately to stimuli.
The acute phase of a chronic inflammatory-diffuse process, an allergic form, respiratory failure provoked by smoking often proceeds without hyperthermia.
The absence of a symptom makes it difficult to diagnose and is a common cause of delayed seeking medical attention. As a result, the pathological process goes into an advanced stage and is difficult to stop.
Patients with congenital allergic predisposition and heavy smokers are advised to pay increased attention to the first signs of inflammatory-diffuse lesions of the respiratory cavity. In adults with bronchitis, there is a morning cough without fever and cyanosis, signaling oxygen starvation.
Videos about bronchitis
Bronchitis. How to distinguish it from a normal cough:
