Content
- Definition
- Various approaches and theories
- Personal integrity
- Integrity of perception
- Integrity-ego
- In a transpersonal approach
- In gestalt theory
- Gestalt therapy videos
Integrity is a state in which consciousness and unconsciousness are in mutual and harmonious agreement. In psychology, the idea of integrity is directly related to the union of two conflicting opposites. In his theory, K. Jung defined it as the goal or purpose of human life, corresponding to health and at the same time representing the potential and abilities of a person.
The process of interaction with the environment or other people can interfere or, on the contrary, contributes to the appearance integrity, and in some cases the thirst for its appearance can turn into an escape from the psychological conflict.
Definition
Integrity in psychology is a concept that implies the internal unity of an object, the interconnectedness and interdependence of its parts. Describing the structure of the human psyche, Z. Freud singled out the "conscious self", sexuality and narcissism as the main components that give integrity to the psyche.
The Swiss psychoanalyst and psychologist Carl Jung defined the concept of the term "Self", which occupies a central part in his theory, as the subject of the integrity of the human psyche. "Self", according to Jung, predetermines all human activity aimed at achieving the integrity and unity of its constituent parts. Continuing psychoanalysis, Z. Freud, his student described the self as a central, holistic archetype, including not only conscious, but also unconscious mental being.
The self is viewed by Jung as the center of the whole subject, covering both the conscious and unconscious spheres of his psyche. Selfhood manifests itself in a variety of personified forms: animals, human, godlike, and also impersonal: in the form of lakes, mountains, trees.
Self (wholeness) in Jung's theory is a container for all conflicting disparate elements of the psyche and assumes that subsequently he will acquire integrity or will be perceived as a whole.
In his work, K. Jung defines selfhood as an unconscious "image of a life goal", a person's realization of his integrity and individuality, at will or against it.
In the theory of F. Nietzsche integrity is humanity, manifesting itself through difference, while the individual was considered in his theory as an infinite and highest value.

In the Dictionary of Biomedical Ethics, the concept of "integrity" is a bioethics principle put forward by European scientists to designate a concept that provides both physical and mental identity of the person herself yourself.
Responsible for personal identity, she should not be manipulated or destroyed and is directly related to the individual's life path, as a way of reflecting the most important life events. Doctor of Biological Sciences Arsanausova A.Yu. notes that some medical interventions contribute to the violation of integrity.
Knowing this, the specialist notes that during their implementation it is necessary to protect the psychophysical integrity, to minimize its possible damage by introducing ethical and legal frameworks governing medical and surgical interventions aimed at changing the genetic structure the individual. According to the expert, all legal norms regarding transplantation should also be changed.
Author of the "Dictionary of Practical Psychologist" Golovin Yu.S. defines integrity as a principle of perception, consisting in the ability of any object perceive any object or spatial situation as a whole, even if its individual parts are currently hidden from review
Various approaches and theories
Integrity in psychology is a general concept given in the dictionary of psychological terms and implying autonomy, internal the consistency and at the same time the independence of an object or phenomenon from the influence of other surrounding phenomena of the external environment ("Dictionary of psychological terms ").
Depending on the object in psychology, there are:
Personal integrity
Integrity in psychology is, in relation to the personality, the connection of its parts, which creates a strong and harmonious foundation. Giving such a definition of personality integrity, the popular psychologist and author of many scientific works N.I. Kozlov talks about external, or general integrity of the person, meaning the harmonious unity of her bodily, mental and spiritual and moral life.
The integrity of the personality presupposes the correspondence of a person's inner life with his outer activities. For example, a true believer Christian will not be able to serve in the army, since he will be forced to violate the commandments regarding the refusal to kill and harm human health. The implementation of such actions, contrary to his inner convictions, can violate his integrity and lead to serious mental anguish.
In psychology, it is customary to understand the internal integrity of the personality as the ability of a person in critical situations to remain true to his life position and holistic orientation. Such a person should be open to people and at the same time be in harmony with his inner world, and, if necessary, openly declare his convictions.
Whole person, in the interpretation of N.I. Kozlova is an individual with a stable value system and worldview, possessing confidence in the correctness of the thoughts and actions he has chosen, and ready to be responsible for all he has done actions. A striking example of a holistic personality, according to psychologists, is Jesus Christ.
Psychologist and head of the Baikal Instructor School of TCTC, author of many articles Chursina T.M. notes that psychological integrity personality in its structure resembles an "inner core", manifested in a high level of satisfaction with life and the joy of existence person.
According to the specialist, such a person is very pleasant in communication, prone to optimism, creation and support of the positive aspirations of other people. The holistic person is rational in his decisions and acts on the basis of the best intentions, but at the same time he is able to stubbornly resist the destructive actions of others.
The antipode of a holistic personality in psychology is the concept of a “fragmentary personality”, the internal elements of which are in constant conflict with each other and do not strive for common interaction.
According to the psychologist N. AND. Kozlov, psychological integrity is not inherent in a person genetically, but is formed under the influence of the immediate environment and external influence.
Ways to form personality integrity:
| Forming method | Characteristics of an integral personality |
| Power model | According to N.I. Kozlov, is based on the rigidity of beliefs and the ability to defend these beliefs in direct and open conflict. Such a model of integrity, according to psychologists, is more characteristic of men and is inherent in people with a certain level of development, in whose beliefs there is a high morality and concept spirituality. A striking example of such a personality is the English utopian Thomas More, who died on the scaffold. |
| Model of inner harmony of personality | It is based on internal flexibility and harmony and consists in the internal and external interaction of a person with his environment. For such a person, according to psychologists, it is typical:
Such a model of the formation of personality integrity is to a large extent inherent in women, manifesting itself, according to N.I. Kozlova, soft voice intonations, external kindness and the ability to quickly adapt to changing living conditions (an example of such a personality is Mother Teresa Calcutta). |
Integrity of perception
Integrity in psychology is a person's ability to perceive, based on the person's ability to perceive any object or objective situation. as an integral system even if some of its parts cannot be seen at a certain moment (for example, the inside of a subject).
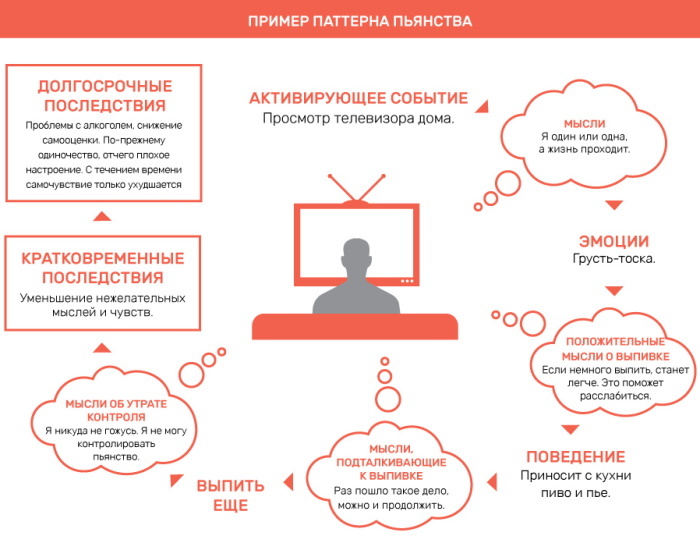
First reflected in Gestalt psychology by German scientists M. Wertheimer and W. Koehler understood the problem as the integrity of perception - the initial property of the brain, regulated by the laws of the subconscious.
Soviet psychologists understood the integrity of perception as a part of the psychological integrity inherent in the person who perceives the object. In this case, the image that arises in his mind and reflects the existing reality is the totality of all its components, regardless of their presence at a certain moment.
The degree of formation of the distinctness of the image at the moment of perception of the object is based on the anticipation of its actually imperceptible parts. An example of the integrity of perception can be a person who observed only the head and shoulders of a passer-by, but thanks to the integrity of his consciousness, he perfectly represents the position of the arms, torso and body, as well as the gait passerby.
Integrity-ego
Integrity-ego is in psychology the commonality of a person's ideas about himself, which allows him to feel his own uniqueness.
NS. Erickson in his "Theory of personality development" covering the entire living space of the individual (from infancy to old age) notes that the ego ("I") of the child is gradually formed under the influence of historical conditions, changing social prescriptions, cultural aspects and systems values.
"I" (ego) in Erickson's theory is an autonomous system that interacts with reality through perception, thinking, attention and memory. In this way, a person interacting with the environment in the process of his development gradually becomes more competent in the ideas about his own essence.
Integrity-ego is a characteristic that enables a person to feel his uniqueness, helps to fight against despair that occurs with aging and described by him as an opportunity to gain wisdom (“integrity-ego before despair "). In accordance with the Development Theory, at the final stage, after going through identity crises, a person conducts a “review my life ", while experiencing either satisfaction from what has been achieved, or despair and pain for previously committed errors.
Soviet and Russian psychologist and publicist N.I. Kozlov understood by "ego integrity" (ego-identity) feeling-sensation that arises in a person when realizing the continuity of his "I" at different stages of life. Ego identity, also, according to the scientist, is the main factor responsible for the formation of personal maturity.
Z. Freud considered the integrity of the ego as an intermediate part between the id and the superego, which is responsible for the connection and balance of a person with the outside world around him. In the task of the ego, according to Z. Freud includes the need to achieve a balance and the search for a compromise between the primitive motives of the individual, morality and existing reality.
It was followed by defining the integrity-ego as a necessary part for the formation of the structure of the personality.
Gail Sheehy defined the ego-integrity stage of development of the "second adulthood", which begins at the age of (65-85 +).
In a transpersonal approach
The transpersonal approach in psychology defines integrity - as a harmonious fusion of physical, emotional, mental and spiritual aspects of well-being, as well as social responsibility. A characteristic difference between the methodology and other psychological approaches is the inclusion, in addition to others, of a spiritual component.
The basis of the content of transpersonal psychology is life experience that allows you to cope with spiritual personality problems through mythical, archetypal, personality or transpersonal components.
TO. Jung was one of the first to appreciate the value of the transpersonal psychological approach as a way to free a person from pathological mental suffering.
Later, representatives of transpersonal psychology (S. Grof, K. Wilber, T. McKenna) subjected the theory of K. Jung criticized him, believing that the very concept of self is harmful, because it misleads a person about its nature.
The founders of the transpersonal approach represent the world around them as an integral structure, with the simultaneous presence in it of many in parallel and simultaneously existing realities that have an equal ontological status and do not have clear ones among themselves, previously invented by psychologists, borders.
Introduced by Z. Freud, K. Jung and E. Erickson recognized the "concept of I" and "theories of personality" according to the transpersonal psychological approach as harmful, as misleading a person regarding his true nature.
The world is interpreted here as an integral arena of action "over the world" forces, aimed at self-knowledge, and a person is understood not as a subject of activity, but as a temporary form that takes on a certain "spirit". The experience and experiences of an individual person are understood only as fragments of the experience of this "spirit".
In gestalt theory
Founded by F. Perlsom Gestalt therapy takes as its basis a holistic approach to the study of a person, with all his mental, bodily, spiritual and social aspects. Specialists working in this direction help people to realize what is happening to them at this very moment. processes, thereby teaching them to take responsibility for all events occurring in life, as well as possible change.
Perls himself defined "gestalt" as a single whole, which, when destroyed, manifests itself in a multitude of fragments. The form created by him invariably strives for unity, and in its absence, it leads a person to an unfinished, pressing situation.
According to Perls, people themselves can hide numerous unfinished gestalts, which are easy enough to overcome after careful study and elaboration. A huge advantage of Gestalt therapy is the ability not to try to penetrate the unconscious part, but to consider the problems that are on the surface.
Integrity in Gestalt therapy is directly related to the individual, viewed solely as whole. a being, without artificial division into bodily and mental, violating a person's understanding of his inner peace. Integrity here is based on the interaction of the individual with the surrounding space, being in contact with him and exerting a certain influence on him.
The concept of "integrity" in psychology is closely related to the study of personality, its psychological, social and spiritual aspects. Leading its origin from the introduced by K. Jung's term "self", the principle of integrity is intended to reflect the structure of the human personality, the integrity of its perception, is one of the foundations Erickson's "Theory of Human Development", and is also used as the basis for the development of Gestalt psychology and the transpersonal approach to studying human consciousness.
Gestalt therapy videos
Gestalt psychology: