1 Reasons for passing the
test Indications for the passage of ultrasound:
- inflammatory, infectious, functional or oncological diseases;
- abdominal pain;
- tumor, cyst, kidney stones or gallbladder;
- trauma( consequences are not always accompanied by pain);
- violation of urinary outflow;
- causeless increase in temperature;
- occurrence of gravity in the stomach, nausea, bitterness in the mouth;
- strengthening of gas generation.
Do you have gastritis?
GALINA SAVINA: "How easy is it to cure gastritis at home for 1 month. A proven method - write down a recipe. ..!"Read more & gt; & gt;
We recommend that you read
- What you can eat before the ultrasound of the abdominal cavity
- Causes of fluid in the abdominal cavity
- What shows CT of the abdominal cavity
- Effective agent for gastritis and stomach ulcer
Patients should be prepared for ultrasound. Preparatory activities depend on what organs will be examined by a specialist. Before the examination of the kidneys it is necessary:
- to refuse to eat for 8-12 hours before the procedure;
- drink 1.5 liters of fluid for 1 hour before the examination.
Before examining the gallbladder, liver, pancreas or spleen, specialists recommend:
- refuse to eat for 8-12 hours before the procedure;
- to choose on the eve of a light supper( vegetables, chicken breast, low-fat fish).
Before examining the abdominal aorta, it is sufficient not to eat for 8-12 hours. The patient should notify the doctor if several days before the examination the following procedures were performed:
- X-ray with contrast.
- Irrigoscopy of the digestive tract.
- Colonoscopy.
- Gastroscopy.
In this case, the study will need to be postponed for several days.
2 Preparing for the
Study. Wounds and bandages in the area under study and a large amount of adipose tissue can be an impediment to ultrasound. Within 3 days before the examination it is desirable to follow a diet. It is allowed to eat:
- soft-boiled eggs( not more than 1 per day);
- cereal cereals;
- cheeses with reduced fat content;
- fish or low-fat meat( cooked steamed, boiled, baked without butter).

From the diet it is necessary to exclude apples, cabbage, carbonated drinks( including beer), milk, white bread, corn, chewing gum, sweet. Take food every 3-4 hours 4-5 r / day in small portions. If difficulty digestion, shows the reception of funds from flatulence( the drug is prescribed by a doctor).
If the ultrasound of the abdominal cavity in a child is shown, the conditions for preparation are as follows:
- for children under 1 year of age, you must stop drinking and skip 1 meal before the procedure;
- children aged 1-3 years should stop drinking for 1 hour and from eating 4 hours before the examination;
- children older than 3 years will need to refrain from drinking for 1 hour and from eating 6-8 hours before ultrasound.
-
 IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
IMPORTANT TO KNOW! Gastritis? Ulcer? To have a stomach ulcer not turned into cancer, drink a glass. ..Read the article & gt; & gt;
3 How does the procedure work?
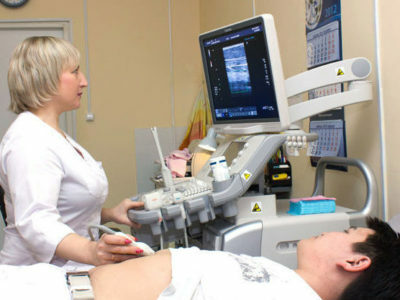
Patients after the information on the training are interested in what is included in the ultrasound, how ultrasound acts on the body. The ultrasound machine emits high-frequency sound pulses, which are delivered to the sensor. Due to this, the monitor receives 2 or 3-dimensional images of the organs being examined.
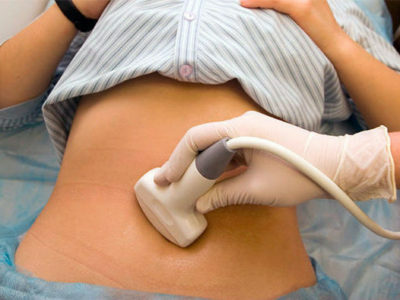
The procedure is painless and does not harm the body. The patient undresses to the waist, lies on his back, on his side or on his stomach( depends on which body is to be inspected).The doctor applies a special gel on the surface of the skin to ensure penetration of ultrasound into the tissues.
Sometimes you need to hold your breath for a few seconds( the expert will say when).The duration of the procedure is 20-60 minutes( all the time it is necessary to lie still, so that the image quality is high), it can be carried out at any time of the day.
4 What can I see during the diagnosis?
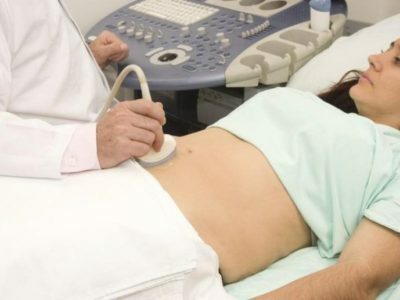
The gallbladder and bile ducts are the organ in which bile is stored and stored, which is necessary for the breakdown of the fat of the food that enters the body. Ultrasonography of the gallbladder and bile ducts allows to detect cholecystitis in acute or chronic form, pathology of organ development, empyema( suppuration of the wall of the bladder) and the presence of stones.
The ventral aorta is the largest artery in the human body. Ultrasound can detect an aneurysm and its stratification( upon detection, an additional tomography of the abdominal cavity organs will be required).
-
 Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
Gastroenterologist. IMPORTANT: "I beg you, if you began to worry about abdominal pain, heartburn, nausea, do not in any way do gases. .."Read more & gt; & gt;
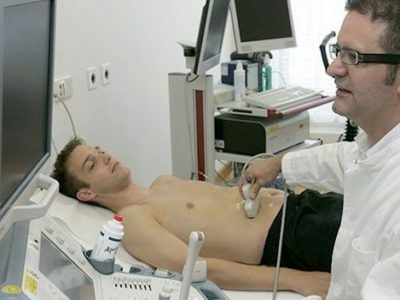
The liver is the largest gland that stores backup carbohydrates, destroys toxins and synthesizes proteins. Using ultrasound, parasitic cysts, organ structure changes, fibrosis, tumors and other changes accompanied by liver damage can be detected. To get more detailed information about the functioning of the body, the proteinogram, liver tests and coagulogram allow.
The spleen is an organ that grows in the presence of infections and helps to fight them. On ultrasound, you can find an increase in the spleen.
The pancreas is an organ that synthesizes enzymes for digesting food and insulin. Ultrasound helps to identify cysts, pancreatitis in acute form, pancreatic necrosis, abscesses, tumors, gland damage in cytomegaly, toxoplasmosis, herpes or parotitis.
Stomach and 12-colon - hollow organs, the thickness of which allows to determine ultrasound examination and to suspect duodenoiditis or gastritis. For the diagnosis is required fibrogastroskopiya and X-rays.
Kidney: a kidney examination is carried out separately, and its cost is an order of magnitude higher. Before research in the urinary bladder should accumulate urine.
ADVICE FROM THE MAIN GASTROENTEROLOGIST
Korotov SV: "I can recommend only one remedy for the rapid treatment of Ulcer and Gastritis, which is now recommended by the Ministry of Health. .." Read testimonials & gt; & gt;
5 Decoding of the results
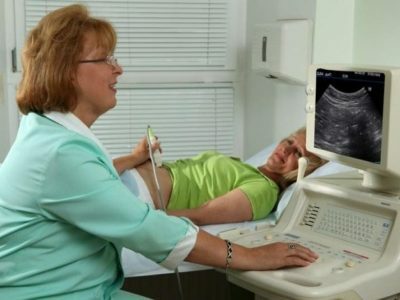
After the procedure, the doctor fills in a special form that indicates the moments related to the organ under examination:
- Liver: when decoding the ultrasound, the doctor takes into account the size of the lobes, contours, capsule differentiation, the presence or absence of focal lesions. If the diagnosis is "fatty hepatosis," then the doctor reveals an enlarged echo cavity of the organ. The edge of the liver is rounded. If cirrhosis, then the portal and splenic veins are enlarged. The contours of the organ are uneven. At the same time, ascites takes place. With a stagnant phenomenon in the liver, the following pattern is observed: an enlarged liver size, rounded edges, an enlarged hollow vein.
- Gallbladder: Normally the shape of the body is cylindrical or pear-shaped. The volume is 30-70 cm3.Wall thickness up to 4 mm. In the norm in the lumen there are no educations. The presence of stones or tumors is indicated by the acoustic shadow from the formations. Taking into account this characteristic, the doctor deciphers the types of stones. By their bias, the doctor can determine the nature of education( benign or malignant).In acute cholecystitis, the doctor notes thickened organ walls, but the size of the gallbladder is normal. In the presence of fluid around the body, local peritonitis is diagnosed. In this case, an urgent operation is indicated. A similar sign is also evident in chronic cholecystitis. But the contour of the organ is clear and dense.
- Bile ducts: Normally the diameter of the common bile duct is 6-8 mm. Intrahepatic ducts are not dilated. Normally, ultrasound of the pancreas has no additional formations. If the echolality of the gland is reduced, then acute pancreatitis is developed. The enlargement of the gland indicates the course of chronic pancreatitis or oncology. In the first case, the ductal duct is also enlarged, and with iron cancer there is an uneven contour, the surface of the liver is pressed inward, the lower hollow vein or aorta is displaced( squashed).
- Spleen: normal vein of the organ is in the gates. If the ultrasound shows an enlarged size of the organ, then the pathology of the blood or liver is developed. If there is a tight tissue, you need to treat a spleen infarction. With the help of this study, the doctor can see the rupture of the organ, which is provoked by a trauma or injury.
- Hollow organs: ultrasound images indicate the symptoms of the affected organ, the presence in the lumen of the intestine of a deposited liquid. If the kidneys were simultaneously examined, then the description of this organ is included in the conclusion of the ultrasound.
6 Additional methods
Additional diagnostic methods are used when examining some internal organs. If the lymph nodes are normal, then their ultrasound "does not see."Otherwise, the infection in the abdominal cavity or a tumor. In the latter case, such formations may increase( because of the presence of cancer cells in the hematopoietic system).In conclusion, the doctor indicates that the echoes are similar. Simultaneously with ultrasound, ultrasound can be performed( with suspected pathology of celiac vessels).In this case, the doctor evaluates the anatomy and blood circulation characteristics in these vessels.
Abdominal aorta - diagnosis is carried out with frequent fainting, headaches, repeated strokes, pain in the legs. If ultrasound is performed on modern equipment, then duplex angioscanning( evaluation of blood circulation in the veins) is simultaneously shown. With the help of the latest examination, a physician can detect abnormal blood spills, assess the localization of blood flow, its extent and severity. On the resulting colored two-dimensional image red indicates the movement of blood to the sensor, and blue - from the sensor. Taking into account the intensity of these colors, the expert draws a conclusion about the rate of blood flow in any part of the aorta.
The patient receives a doctor's report within a few hours or days after the procedure( depending on the workload of the specialist and the quality of service in the clinic).
Without medical education, it is impossible to draw conclusions about the condition of the organ in the picture.
Along with the conclusion, the doctor can give the patient a video recording of the study on the disk. If an ultrasound was previously performed and the patient has its results or record, it is necessary to bring them to the doctor in charge for examination.
- 1 Reasons to undergo
- 2 examination Preparation for
- 3 How does the procedure work?
- 4 What can be seen during the diagnosis?
- 5 Decoding results
- 6 Additional methods
At least once a year, doctors advise to undergo ultrasound of the abdominal cavity, which is part of a comprehensive examination for suspected internal diseases and retroperitoneal space.