Content
- What is luteinizing hormone responsible for in women
- How is LH produced in the body, in what volume
- LH norms in women by age, health status
- LH to FSH ratio
- How to determine the level of LH, what tests to take
- Preparing for a blood test for LH hormone
- Decoding indicators
- Signs and reasons for lowering the level
- Symptoms and causes of elevated LH
- How to get hormone levels back to normal?
- How to raise
- How to downgrade
- What are the consequences if the hormone level does not correspond to the norm?
- Luteinizing Hormone Video
Luteinizing hormone (LH, lutotropin) - one of the key coordinators of the ovulation process. The woman's ability to conceive directly depends on whether its concentration in the blood is normal. An analysis to determine the level of LH is carried out to diagnose infertility and assess the functional state of the reproductive system.
What is luteinizing hormone responsible for in women
Appointment of luteinizing hormone in the body: participation in the regulation of the activity of the sex glands, both in men and women. In men, LH activates the secretion of testosterone in the testes. If we talk about the beautiful half of humanity, then its main function is to force a ripe egg to leave the ovary and cause ovulation.
The mechanism of formation and release of LH into the blood in women is cyclical, since it is associated with the menstrual cycle.
Eggs (oocytes) are regularly produced in the ovaries of a woman of childbearing age. The process takes place every 28 days. Each time, oocytes go through several stages of maturation. Inside the ovary, the egg cell is surrounded by a follicle - there it matures and acquires the properties that it needs to meet with the sperm and support the future embryo. Luteinizing hormone affects the connective tissues of the follicle membrane, stimulating the maturation of the female reproductive cell.
A sharp release of lutotropin occurs in the middle of the cycle: by about 13-14 days, its concentration increases. The so-called "ovulatory peak" sets in. The walls of the follicle rupture, and a full-fledged egg is released into the fallopian tube, where fertilization may await it.
LH concentration decreases after ovulation. The luteal phase begins, during which the stroma of the ruptured follicle is transformed into a corpus luteum. The transformation takes place under the influence of the same luteinizing hormone (luteus - from lat. "yellow").
Luteinizing hormone (the norm in women is determined by the cyclical nature of its secretion) is also responsible for the hormonal ovarian function, stimulating the formation in the follicle and in the corpus luteum of progesterone and pregnenolone - precursors estrogen. Progesterone affects the endometrium of the uterus, preparing it for the possible implantation of the ovum. For 2 weeks, LH maintains the corpus luteum.
A properly conducted process requires a sequence of the following steps:
- The gradual increase in LH in the follicular (follicular) phase of the cycle.
- Its sharp rise and peak concentration before ovulation.
- The formation of a corpus luteum and a decrease in LH in the luteal phase of the cycle.
Violation of the synthesis of lutotropin and the cyclicity of its secretion leads to problems in the reproductive sphere. Thus, the absence of an "ovulatory peak" in combination with the normal development of follicles leads to anovulation. With a small amount of the hormone, ovulation can occur, but the result will be functional insufficiency of the corpus luteum.
How is LH produced in the body, in what volume
The secretion and release of luteinizing hormone is a well-coordinated process of interaction between the pituitary gland, hypothalamus and ovaries. It starts in the cells of the pituitary gland, a small gland located at the base of the brain. In total, 6 hormones are produced in the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland, one way or another affecting the organs of internal secretion. Two of them - LH and FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone) - are gonadotropic, that is, they affect the sex glands (gonads).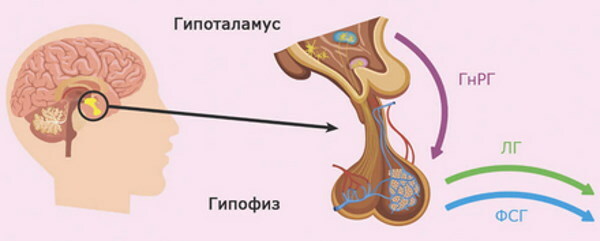
Formed in the pituitary gland, LH is released into the bloodstream and, together with the blood flow, reaches the cells of the tissues of the gonads.
The role of the main regulator of LH synthesis by the pituitary gland and its entry into the blood is performed by a hypothalamic neurohormone called "luliberin". It is the so-called LH releasing factor.
Other gonadal hormones also affect LH production. So, the introduction of estrogens or progesterone from the outside stimulates the release of LH into the blood and a rapid increase in its level. Long-term exposure to these hormones in combination with testosterone suppresses LH production.
In terms of chemical structure, it is a complex protein, a glycoprotein.
Luteinizing hormone production in the body begins before birth. In an embryo at the age of 2 months, LH synthesis in the pituitary gland is already detected. Reaching maximum values in the fetus by the 30th week of pregnancy, it decreases just before childbirth.
In different age periods, the production and excretion of LH changes. A child, regardless of gender, has a small amount. During puberty in girls, the concentration increases to 8-10 U / l. This level is also typical for adult men.
In women of childbearing age, the concentration of the hormone changes in accordance with the phases of the menstrual cycle. The smallest values are typical for the follicular and luteal phases: from 5 to 20 U / L. The largest - in the pre-ovulatory period, when the concentration of LH in the blood can reach 180 U / L.
With the onset of menopause, the synthesis and release of LH loses its cyclical nature. At the same time, the LH level is quite high and corresponds to the pre-ovulatory peak.
LH norms in women by age, health status
Luteinizing hormone has different normal values. When determining them, they come from age, from the phase of the menstrual cycle. A woman's LH level may fluctuate daily. Taking certain medications and the presence of comorbidities also make adjustments in the quantification of LH.
In general, low levels of the norm are characteristic of childhood and the period of bearing a child. High LH values are observed in menopausal women. In women of reproductive age, the values are average, while a sharp increase in LH concentration during the ovulatory peak is considered physiological.
In girls under 9 years of age, the level of luteinizing hormone does not exceed 1.3 U / L. In adolescence, the activity of sex hormones begins to increase, including LH.
The table shows the stages of puberty (I-V), which correspond to the external signs of puberty (growth of pubic hair and development of the mammary glands). The classification was adopted according to the scale of James Tanner, British pediatrician.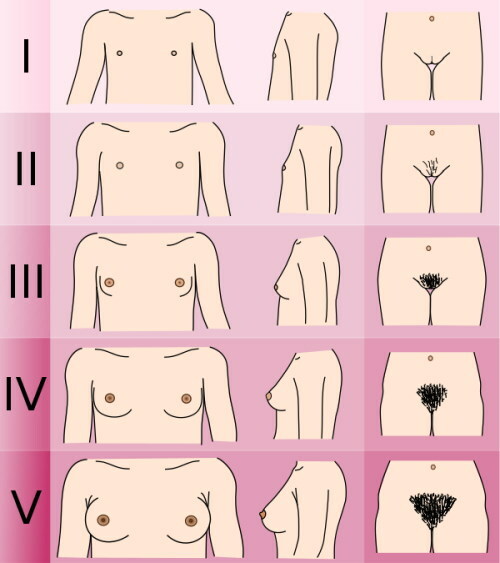
| Stage | Signs | LH values (U / L) |
| I (prepubertal) | Only the nipple is enlarged; no pubic hair. | 0,7—2,0 |
| II | Areoles are enlarged; the breasts are slightly indurated. Sparse, straight, slightly pigmented hair on the labia. | 0,4—11 |
| III | Areola enlargement without noticeable contours; the beginning of the growth of the mammary glands. Hair throughout the pubis is pigmented, coarser. | Also |
| IV | The areola and nipple protrude over the breast. Adult hair; extend to the medial surface of the thighs. | 0,9—13 |
| V | The mammary glands have an adult outline. Only the nipple protrudes. Hair grows in a triangle, which is typical for adults. | 1,1—19 |
The norms given in the tables are approximate, and an independent diagnosis of them is impossible. The concentration of the hormone is indicated in U / L. The following designations may appear in test forms: mU / ml, mIU / ml, or IU / L (where "U" is a unit and "IU" is an international unit). All indicators are the same and do not need to be recalculated.
Normal values may differ depending on the method used in the diagnostic laboratory. The current values of the limits of the norm are indicated on the analysis form in the corresponding column.
Luteinizing hormone is the norm in women over 18 years old, corresponding to the phases of the menstrual cycle:
| Phase | LH values (U / L) |
| Follicular (corresponds to the period from 1st to 13th day). Sometimes the menstrual phase is distinguished in it (1-6th day) | 1,1—11,6 |
| Ovulatory phase (13-15 days) | 17,0—77,0 |
| Luteal phase (15th day, onset of menstruation) | Less than 14.7 |
| Postmenopause | 11,3—39,8 |

If pregnancy occurs, LH and FSH levels remain at the luteal phase. Due to this, maturation of follicles and ovulation become impossible during the entire period, and the onset of a new pregnancy is postponed. Too low a concentration of LH is dangerous: along with lutotropin, the level of progesterone, which is necessary to maintain pregnancy, also falls.
When assessing the level of LH in a particular woman, a number of circumstances are taken into account. In particular, LH levels fall below 8 U / L while taking oral contraceptives is normal.
The hormone level is influenced by too long a menstrual cycle (more than 35 days), a recent abortion, or vaginal bleeding between periods.
An increase in indicators, if they are not associated with the period of menopause, is accompanied by diseases such as pituitary tumors or polycystic ovaries. A persistent increase in LH and FSH concentrations in combination with a reduced level of estradiol indicates the onset of menopause.
LH to FSH ratio
FSH is a stimulant of follicular development in women. Acting in conjunction, LH and FSH control the menstrual cycle at every stage, ensuring the well-coordinated work of the gonads. Discoordination in the synthesis of FSH and LH disrupts the cycle and maturation of eggs, which reduces the possibility of conception. Therefore, it is important to compare their values and determine the proportions between them.
The ratio of luteinizing hormone to follicle-stimulating hormone (LH / FSH) is normal:
- 1 - before the establishment of the menstrual cycle;
- 1-1.5 - after a year of regular menstruation;
- 1.5-2 - from 2 years of normal menstrual function to menopause;
- less than 1 - menopause.
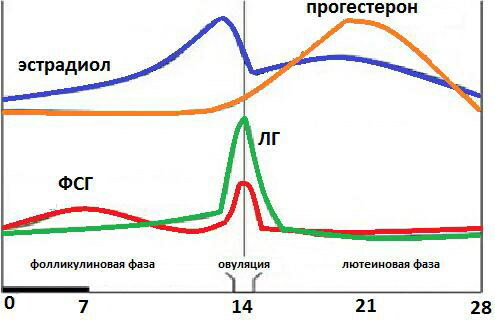
Luteinizing hormone normally prevails over FSH in women of childbearing age. In girls, the concentration of these hormones is approximately the same. With menopause, FSH values are higher than LH.
Menopause is accompanied by significant hormonal changes: first of all, the level of the main female sex hormone, estradiol, decreases. It is he who suppresses the production of FSH and stimulates the synthesis of LH during ovulation. Therefore, although both hormones increase during menopause, FSH increases more significantly than LH.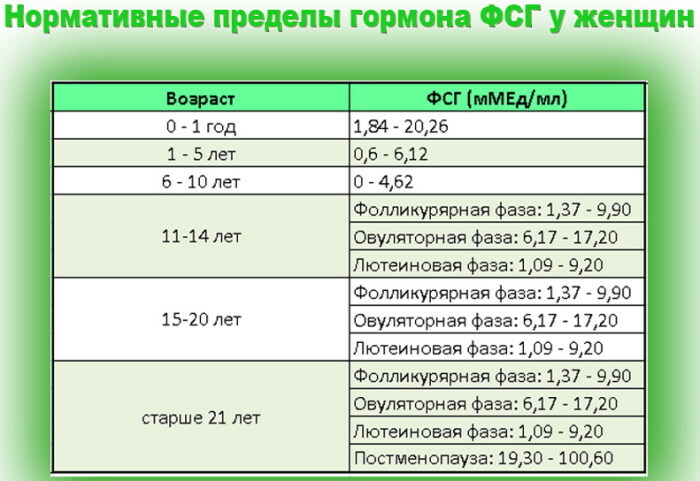
For assessment, hormone indicators are taken at the very beginning of the menstrual cycle - they are considered basic.
The ratio should not be more than 2 or more. Otherwise, we are talking about the possible presence of pituitary tumors, PCOS (polycystic ovary syndrome) or other pathologies. The diagnosis is made after additional research.
How to determine the level of LH, what tests to take
The main method for determining the level of LH is a blood test for the content of luteinizing hormone. The referral is issued by a gynecologist or reproductologist after taking an anamnesis.
A study is recommended to assess ovarian function when planning a pregnancy. Data is required for miscarriage, uterine bleeding in the second half of the cycle, for cysts and ovarian tumors. The level of the hormone is necessary to know during hormone therapy, which is carried out in order to stimulate the ovaries to increase the chance of natural conception.
A blood test for LH levels is included in the recommended periodic examinations of women from 30 years of age and 50 years of age, with menopause.
Along with other hormones, lutotropin is studied with visible manifestations of violations of the hormonal status of a woman:
- amenorrhea and oligomenorrhea;
- acne;
- excessive hair growth (growth of dark, coarse male-pattern hair);
- infertility;
- violations in the genital area.
Since the hormone is found not only in the blood, but also in the urine, there are home tests to determine ovulation. It is used by couples planning to conceive a child to determine the most favorable days for intercourse. It is based on a surge in LH levels after the release of the egg from the follicle, which persists for 48 hours and precedes ovulation. The test does not give exact numbers: it only indicates an increase in the level of the hormone.
Preparing for a blood test for LH hormone
The general recommendation is to carry out the analysis on the 6-7th day of the menstrual cycle. In some cases, the attending physician may specify other terms.
Many factors affect the validity of the analysis, including stress or exercise. So, fasting or sports training increases LH values, and reduces psychological stress. You should inform your doctor about taking any medications, especially hormonal ones.
Blood sampling is carried out from a vein, on an empty stomach.
To obtain reliable results, the patient should follow these recommendations:
- Eliminate increased physical activity 3 days before the procedure.
- Refrain from smoking for 1 hour before submitting the biomaterial.
- It is recommended to avoid anxiety, conflict and stressful situations. It is important to calm down before visiting the treatment room.
Before the analysis, the patient is advised to report the date of her last menstrual period or the duration of pregnancy. This data will be entered into her card.
Decoding indicators
The result of the study may be the determination of increased, decreased or normal levels of LH in the blood plasma. At the next appointment, the doctor will make a conclusion based on the data obtained. Violation of the concentration of lutotropin in the blood can be both a sign and a cause of the disease.
Signs and reasons for lowering the level
A decrease in the hormone is associated with the following conditions and diseases:
- secondary amenorrhea, including "sportswomen's amenorrhea";
- delayed puberty in girls;
- pathological increase in the level of prolactin in the blood - hyperprolactinemia;
- hereditary and acquired diseases associated with damage to the pituitary gland or anomalies of its development (Sheehan's syndrome, dwarfism, growth retardation, Simmonds disease);
- tumors and injuries of the hypothalamus;
- insufficiency of the luteal phase;
- obesity.
Luteinizing hormone (the norm in women is not achieved when taking medications containing estrogens or progesterone, some anticonvulsants (valproic acid, carbamazepine), anabolic steroids) may be reduced due to smoking, recent surgery or stay in prolonged stress.
A decrease in the hormone is manifested by the absence of menstruation or their frequent delays.
Symptoms and causes of elevated LH
A high level of luteinizing hormone in the blood is observed in the following cases:
- pituitary tumors that disrupt the secretory function of the gland;
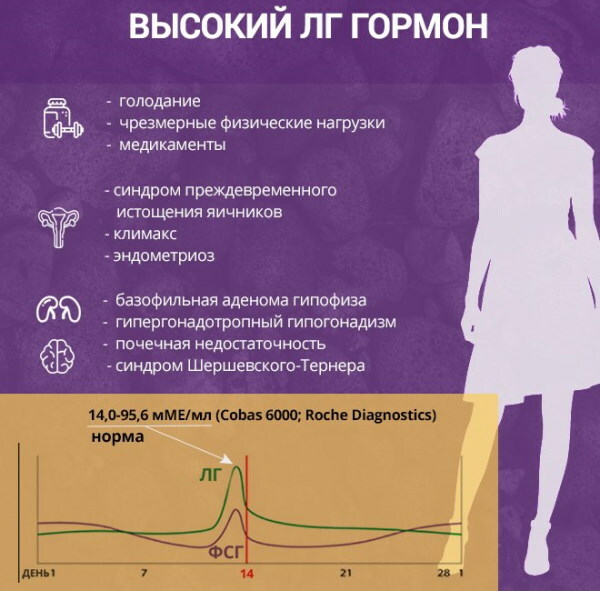
- ovarian wasting syndrome, causing early menopause and associated symptoms: hot flashes, delays, fluctuations in blood pressure;
- polycystic ovary disease, in which the eggs do not leave the follicles and turn into small cysts;
- endometriosis - abnormal proliferation of the endometrium, causing bleeding between periods;
- renal failure (except for LH, with the disease, growth hormones, FSH and prolactin are increased).
An increase in the level of the hormone is caused by the intake of drugs such as ketoconazole, troleandomycin, naloxone.
How to get hormone levels back to normal?
It is important to know the reason for the change in LH values. By acting on it, you can achieve the return of the hormone to normal levels.
How to raise
Luteinizing hormone, the norm in women of which fluctuates in values corresponding to her age and condition, during in many cases, it quickly returns to normal values with the rationalization of nutrition and the organization of a full recreation. Often the reason for the violation of the ovulation process is the lack of micronutrients and some amino acids in the diet. In such a situation, taking cyclic vitamin therapy (Cyclovita) will gently help to adjust the hormonal background correctly.
If LH is lowered in the second phase of the cycle due to the suppressive effect of prolactin in hyperprolactinemia, it is useful to take drugs with the extract of the fruits of the sacred Vitex plant. Dopamine lowers prolactin levels, and the active substances derived from Vitex have a similar effect to dopamine. As a result, prolactin will decrease, and LH will return to normal.
Sometimes hormone replacement therapy is required.
The analogue of LH is gonadotropin. Preparations based on it create a physiological cyclicity of the production of luteinizing hormone. In some situations, drugs that stimulate the release of hormone into the blood (Clomiphene) are used.
How to downgrade
Increased LH in the first phase of the cycle interferes with the maturation of follicles and makes it impossible to switch to ovulation. This situation is common in PCOS. In these cases, doctors carry out a rather subtle therapy. To lower LH, hormones agonists or vice versa, analogs of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (leuprorelin, triptorelin) can be prescribed; contraceptive drugs based on estrogen and gestagen (Diane-35).
The treatment regimen depends on the presence or absence of ovulation, on the general condition of the patient and concomitant diseases. An irrational decrease in LH levels with the help of artificial hormones carries great risks and cannot be carried out in any other way than with the conscientious consultation of the attending physician.
It is important to avoid factors such as fasting and excessive exercise.
What are the consequences if the hormone level does not correspond to the norm?
Anxiety is caused by a deviation of the LH level from the norm, if it is caused by any disease or pathological condition. In this case, the hormonal status is normalized only after successful treatment of the underlying disease. The compliance of lutotropin with the physiological norm is of exceptional importance for female infertility and preparation for conception, especially with the help of the IVF procedure. If it is not possible to bring the concentration of LA to the required values, the chance of getting pregnant decreases.
In most cases, a timely visit to a doctor and an adequately selected treatment will allow the luteinizing hormone to return to normal and save a woman from the problems existing in the reproductive sphere.
Luteinizing Hormone Video
What is the LH hormone for:



