Content
- What parts does the human hearing organ consist of?
- Outer ear
- Middle ear
- Inner ear
- The structure and anatomy of the inner ear
- Snail
- The vestibule
- Semicircular canals
- Development
- Function and mechanism of operation of the inner ear
- Inner ear cavity dimensions
- What is the cavity of the inner ear filled with, what is the fluid for?
- Inner ear video
Inner ear - one of the parts of the hearing organs, which has the most complex structure and is often influenced by various negative factors. The cavity is filled with a special liquid that prevents the development of disorders. However, with an excessive increase in its amount, you should consult a specialist.
What parts does the human hearing organ consist of?
The organ of hearing consists of 3 main parts, each of which has its own characteristics and functions.
The body has departments:
- The part that picks up sounds (outer ear).
- Sound transmission structure (middle ear).
- Departments responsible for the perception of sound (inner ear).
Thanks to all systems, a person is able to perceive, distinguish and determine the source of sound vibrations. At the same time, protective properties are also observed, which does not allow foreign objects or infectious agents to penetrate into the cavity of the auditory system.
Outer ear
This element got its name due to the fact that it is located outside.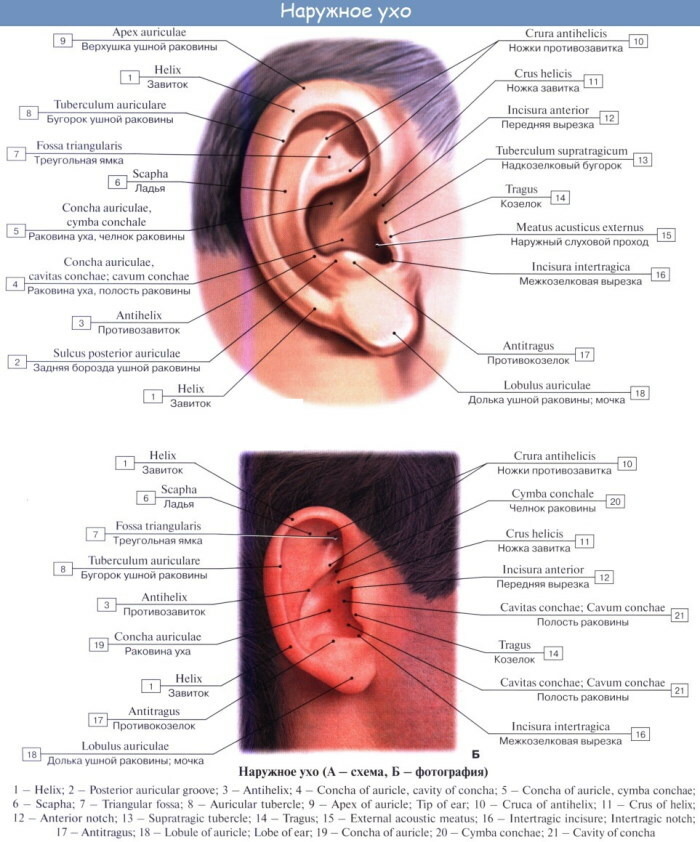
The body consists of 3 main structures:
- Auricle - is an elastic cartilage covered with skin. The lobe is located at the bottom. The auricle is responsible for the transmission of sounds through their transmission through the external auditory canal. Moreover, it is only found in mammals and acts as an auditory receiver.
- Ear canal - transmits sounds to the middle ear to the tympanic cavity. The passage has various lengths (in adults, its dimensions reach 2.6 cm, and its width - up to 0.7 cm). Sebaceous glands are located on the surface of the element, the function of which is to produce earwax and protect against the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms.
- Eardrum - this part acts as a septum that separates the outer and middle ear. It also prevents foreign objects from entering the tympanic cavity. Consists of inner, outer and middle layers. It is oval (in adults) and round (in children).
The ear canal, in turn, has 4 walls. Each department has a complex structure and relationship with the rest of the general auditory system.
Classification:
- Lower - adjoins the salivary gland, located in the area of the organ of hearing, which is caused by the overflow of inflammatory diseases from one cavity to another.
- Upper - this area separates the outer ear from the fossa located in the region of the skull, therefore, with craniocerebral trauma, exudate (cerebrospinal fluid, blood) is often formed, which flows out of the ear.
- Front - located in the area of the temporomandibular articular system. This explains the presence of pain in inflammatory diseases during chewing.
-
Back - is closely interconnected with some structures of the mastoid process. In this connection, it is often affected by purulent inflammation.
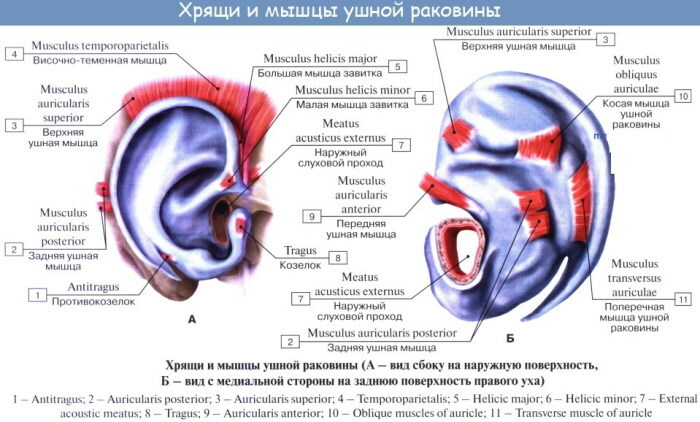
The outer ear has similar functions to the rest of the auditory system. It performs a protective function, and is also responsible for the localization and conduction of sound vibrations.
Middle ear
The inner ear cavity is filled with a special lymphatic fluid that has several functions in the body. All parts of the hearing aid, including the middle ear, take part in the process, since all parts and cavities of the departments are interconnected. This is necessary for the complete and correct operation of the entire system.
The middle ear is located behind the tympanic membrane and is a small cavity filled with air. This structure is connected to the nasopharynx by means of the Eustachian tube, which is responsible for the distribution of pressure behind and in front of the tympanic membrane.
When the pressure changes in a person, as a rule, the ears are blocked, which leads to the appearance of the yawning reflex. This suggests that yawning in conjunction with swallowing movements can help eliminate congestion. In doing so, it is also recommended to pinch the nose on both sides.
The organ also contains small bone structures, the presence of which is due to various evolutionary transformations. These structures are necessary for the full functioning of the hearing organs.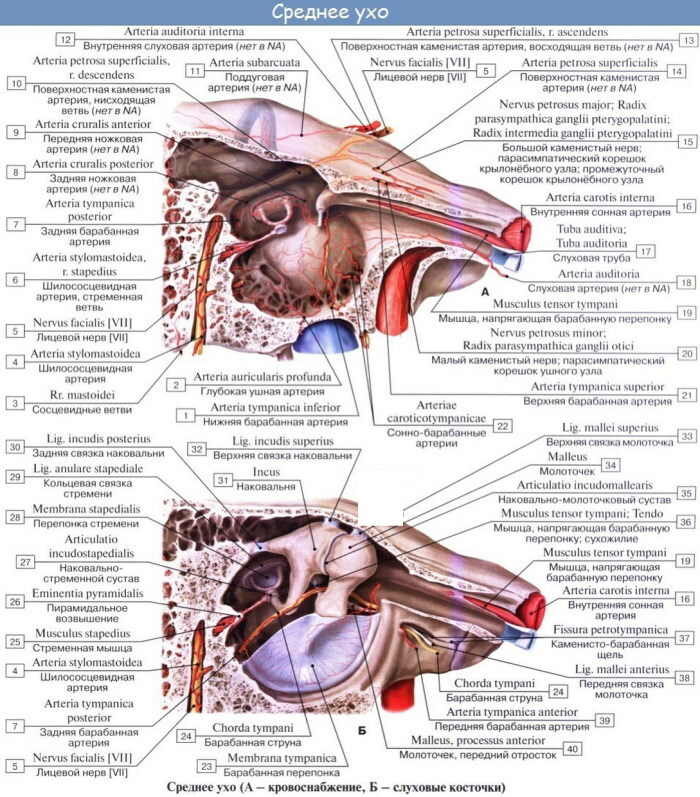
| Department | Description |
| Hammer | The main task of the department is to transmit sound vibrations to other parts of the middle ear. The malleus originated in the process of evolution in mammals. When sound vibrations arrive, the component transmits information to the anvil and stapes |
| Anvil | This part is located between the stirrup and the hammer and transmits sound vibrations from one to another. Bone is present only in mammals and comes from the square bone of reptiles as a result of an evolutionary transformation of the bone structures of mammals |
| Stapes | It is considered the smallest bone. It comes from the upper part of the hyoid lip, which has been transformed in the process of evolution. Its size is 4 mm, its weight barely reaches 2.5 g |
Their main function is to transmit and amplify sound from the outer ear to the inner ear. The close interconnection of the departments ensures adequate perception of sound and its location.
The ear ossicles are also located here, which transmit sound vibrations further along the hearing aid. The base of the malleus is attached with the tympanic membrane. Its main part is closely connected to the anvil, which, in turn, is attached to the anvil.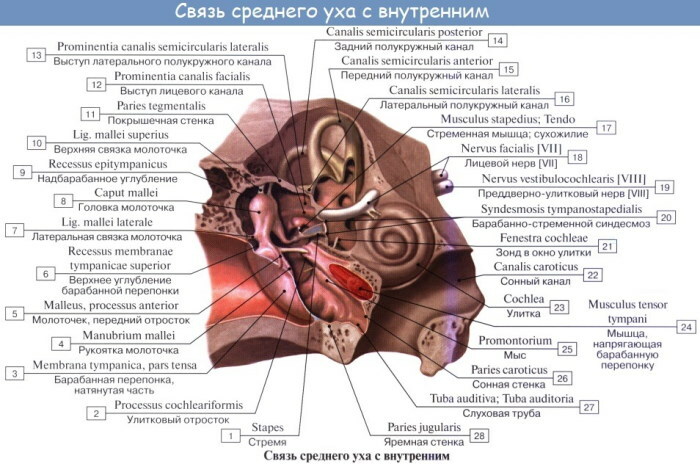
The middle ear is sensitive to sound vibrations, so it is often recommended that the military keep their mouth open when an expected explosion occurs. This will help prevent strong pressure on the eardrum and prevent damage (rupture).
Inner ear
The inner ear cavity is filled with lymphatic fluid on both sides, which allows you to evenly distribute pressure and not lose balance and the feeling of your own body in space. The filling level for each person is individual, but must be within the permissible limits.
The inner ear is otherwise called a labyrinth and is located in the thickness of the temporal bone. It, receiving sound vibrations from the stapes, converts them into electrical nerve impulses.
This area of the organ of hearing consists of 3 parts - the cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals. Each of the departments performs its own functions and role in the perception and conduct of sounds.
The human ear is able to perceive sounds in the range of 16-21 thousand. Hz. However, with age, the perceived frequency of sound waves decreases to 5 thousand. Hz. This is associated not only with the production of lymphatic intra-ear fluid, but also with a decrease in the work of other organs and systems, which is caused by aging (wear) of the body.
The structure and anatomy of the inner ear
The inner ear has a complex structure and structure. It includes various cavities and channels that communicate with each other. This system is called a labyrinth, which is divided into 3 sections - middle, front and back.
Some people have congenital anomalies in the structure of the organ, which do not always lead to disturbances in the functioning of the rest of the hearing aid. However, there are generally accepted norms, the deviation of which (with the exception of hereditary mutations) can cause disruptions in the production of cerebrospinal fluid and other lymph fluids filling the cavity of organs hearing.
Snail
The inner ear is located deeper than all other parts of the auditory system. It includes many different parts, structural elements. In addition, the cavity is also filled with lymphatic fluid, which plays a large role in the functioning of other parts of the system.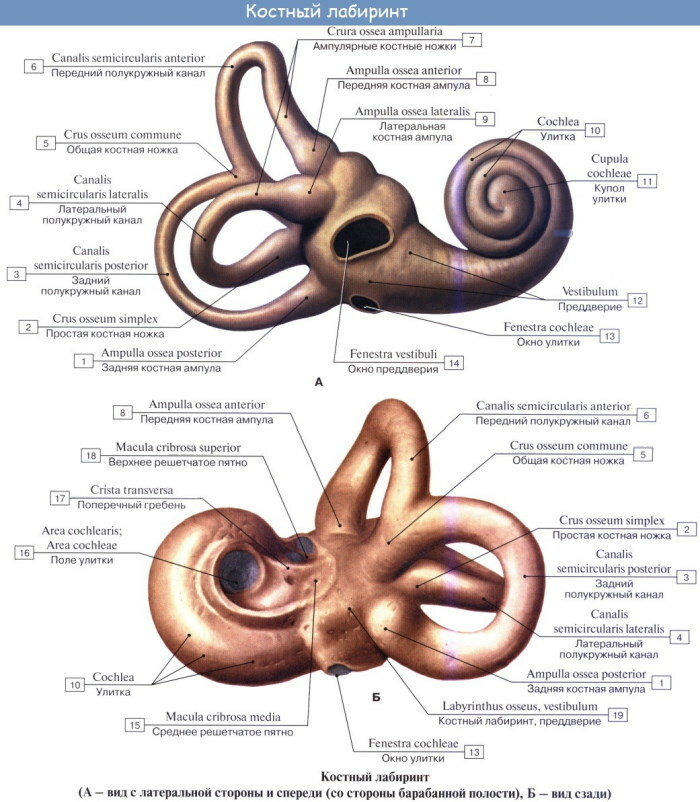
The cochlea is the anterior part of the labyrinth - a bony spiral canal, which is located around the bone rod and turns about 2.5 turns. A spiral bone plate extends from this channel into the internal cavity.
The width of the base of the snail (in section) is 9 mm, the height is approximately 5 mm. The very same length of the bony spiral canal is about 3.2 cm.
The cochlear canal is subdivided into 2 corridors - upper and lower. Both are also involved in the transmission of sound vibrations.
The bony cochlea is filled with fluid (perilymph) and connects to the tympanic membrane through an oval and round window. The first window is closed by a foot plate emanating from the stapes. The round window is covered with the thinnest membrane.
In the process of transmitting sound vibrations to the inner ear, the perilymph flows over. A round window is also included in the process.
In the area of attachment of the basilar membrane, another membrane is attached, which is otherwise called vestibular or reynsser. Its function is to separate an independent canal called the cochlear duct. This duct has the form of a spiral and is filled with endolymph.
In the area of the cochlear duct, the organ of Corti is located - an accumulation of various cells (including epithelial), which are responsible for the perception and transmission of sound vibrations in the form of nerve impulses. Subsequently, these impulses are transmitted to the cortical region of the brain, where the auditory center is located.
The vestibule
The vestibule is located in the center of the maze and forks into 2 pockets. One of them has the shape of a sphere and is located close to the snail. Another pocket is presented in the form of an ellipse and is adjacent to the semicircular canals. The vestibule is supplied with blood through an artery located in the labyrinth.
Types of vestibules:
- Lateral wall - directed towards the tympanic cavity. The ends of both branches of the semicircular canal are adjacent to it.
- The lower one is bounded on all sides by a snail plate.
- Medial - there are 4 pits or pockets on its surface.
- Back - not far from it is the mouth of the common leg of the semicircular canals. A simple opening of the external semicircular canal can be seen in the anterior part.
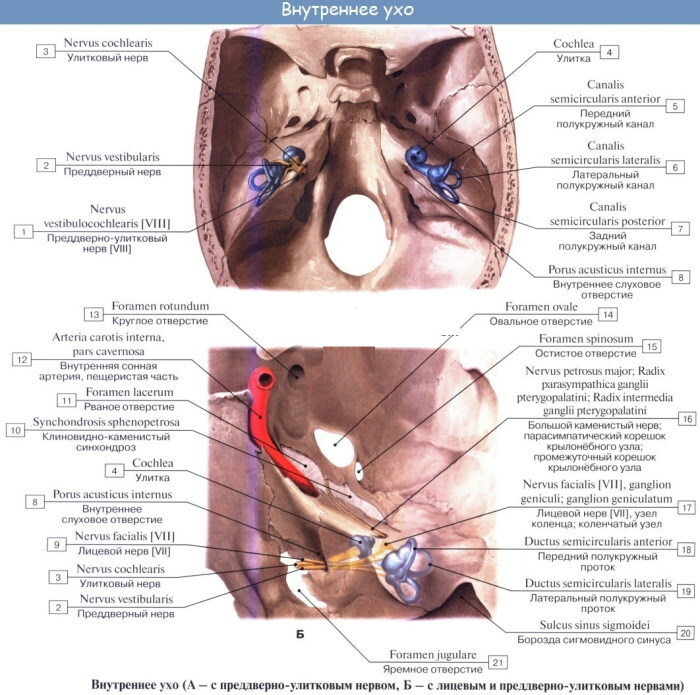
Inner ear
The length of the vestibule section itself is 0.6 cm, height - 0.5 cm, width - no more than 0.3-0.4 cm.
Semicircular canals
The inner ear cavity is filled not only with lymph, but also with other structural elements that represent a single system of the hearing aid. Without these parts, the full-fledged work of the hearing organs is impossible. In this case, in the event of damage or damage to the structural divisions, a violation of the production of intracavitary fluid may occur.
The semicircular canals are filled with a gelatinous fluid inside. Sensitive hairs are located within these systems. During movement, the fluid moves, resulting in pressure on the hairs. This leads to the emergence of nerve impulses that transmit information to the vestibular nerves, from where they are redistributed to the center of the brain.
This structure is responsible for vestibular and auditory function. She is responsible for the transmission and recognition of sound information, and also participates in somatic and sensory reactions - changing the position of the body, orientation in space.
Development
The first signs of the formation of the internal part of the hearing organs can be seen in the fetus during pregnancy during routine diagnostics (ultrasound). As a rule, the formation begins from the very moment of the development of the fetus. However, the first distinctive features can be seen as early as the 4th week of pregnancy.
At this stage, the organ looks like a thickening of the ectoderm located in the region of the brain (rhomboid).
At the 8th week, some structures are formed, which in the future will be presented in the form of an ear cochlea.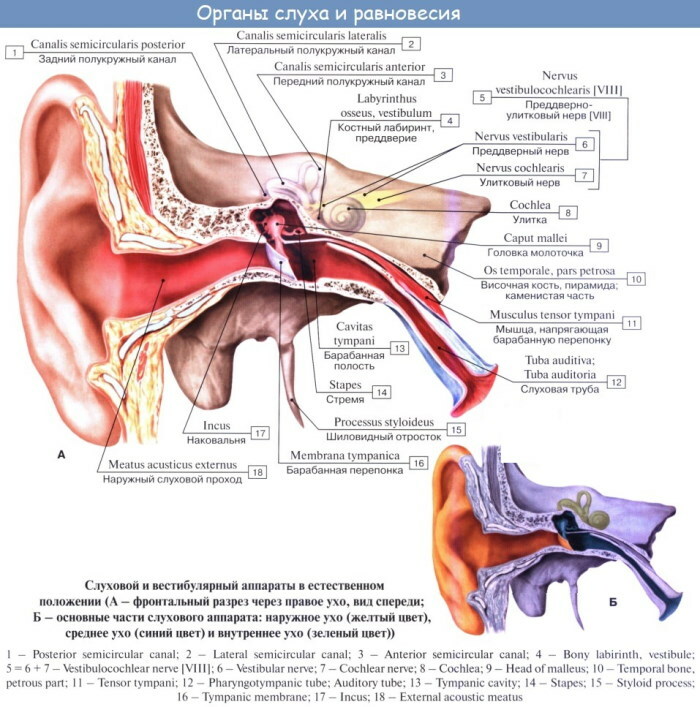
By the 9th week of pregnancy, the inner ear is almost completely formed. At the same time, the labyrinth continues its formation, which ends only after a year.
By the 11-12th week, the fetus already has 2 snail curls and the formation of a membranous labyrinth begins.
At the 20th week, the organ is already fully mature and reaches the size of an adult. And only by the 37th week in the fetus, all the main sections and structures of the ear - inner, outer and middle - are fully formed. However, their functional ability remains not fully developed.
The inner ear is fully formed and almost reaches the size of an adult by the age of 7 years. In the future, the system gradually develops and reaches full functionality by the age of 20.
Function and mechanism of operation of the inner ear
The inner ear cavity is filled with lymph of various types. Such fluid is needed for the formation of nerve impulses, which play a direct role in capturing, transmitting and recognizing sound vibrations. In case of disturbances in the formation of lymphatic fluid, the hearing aid can be exposed to various negative influences from the outside.
The main functions of the inner ear are the perception of sound vibrations and balance. Sound information coming from the labyrinth is transmitted to the brain through nerve impulses. The conductor of such information is the vestibulo-cochlear nerve, which has 2 main branches.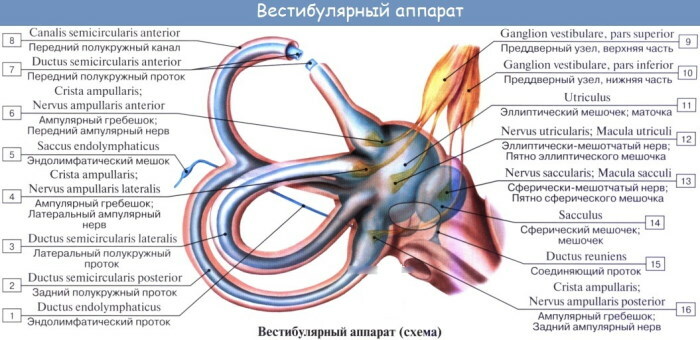
With the help of the first branch, information is transmitted from the organs of hearing, with the help of the second, impulses from the organs of balance. With the development of any violations, the incoming information is distorted and does not correspond to reality.
The inner ear also protects the person from the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms (infection) and loud noises that can damage your hearing (eardrum, external ear).
Working mechanism:
- The entry of sound information into the external auditory canal, followed by entry into the area of the tympanic membrane.
- The emergence of vibrations in the membrane located in the area of the tympanic membrane.
- Transfer of vibration to the cochlea. In this case, information passes through the auditory ossicles, which are located in the middle ear cavity.
- Endolymph displacement and increased pressure on hair cells.
- The production of nerve impulses (electrical signals) by hair cells.
- The entry of nerve impulses into the brain through the auditory nerve.
- Perception and processing of sound information by the centers of the brain responsible for the organs of hearing.
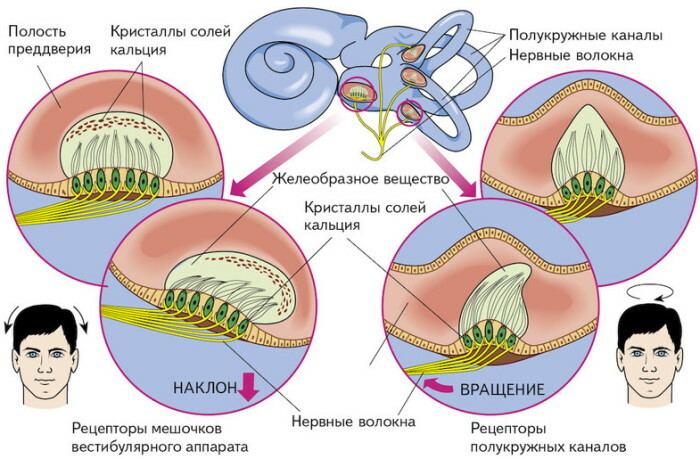
Vestibular apparatus
Thanks to this mechanism of action, a person perceives sound information coming from the surrounding external world. It also allows you to navigate in space and feel changes in the position of the head or body.
Inner ear cavity dimensions
The size of the inner ear may vary slightly within acceptable limits, with the exception of congenital anomalies and defects in the structure of the hearing organs.
Since the inner ear consists of 3 sections, its dimensions are difficult to determine. For example, the base of a snail is 0.9 cm thick. The height of this structure varies within 0.5 cm. The canal length is about 3.2 cm.
All sizes of departments for each person may be different, but vary approximately in the indicated ranges.
What is the cavity of the inner ear filled with, what is the fluid for?
The inner ear cavity is filled with endolymph and perilymph - fluids that differ in composition and function. In this case, the first type of liquid fills the cavity of the labyrinth inside, and the second - fills the organ from the outside.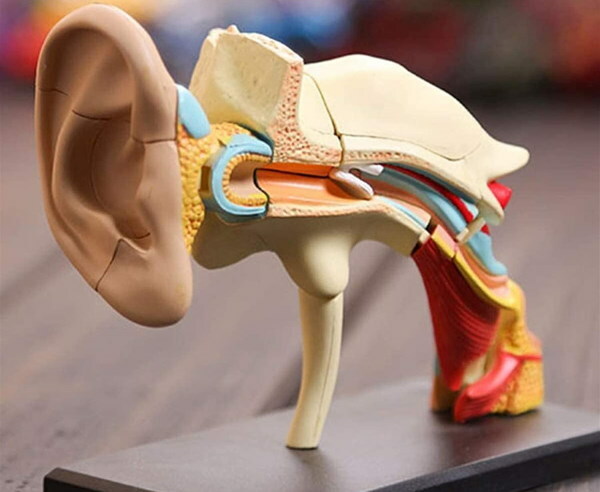
These fluids are required to conduct sound vibrations. With its lack or overabundance, various pathological processes can occur - dizziness, hearing loss, distortion incoming sound information, the penetration of pathogenic microflora and, as a result, damage to the auditory and other neighboring organs and systems.
In order for the hearing organs to function properly and perceive sound vibrations, a sufficient level of fluid is required in the inner ear, as well as in other parts of it. In the case of a deficiency in filling the cavity, various auditory disorders can occur. If such symptoms occur, you should consult a specialist for diagnosis and determination of the cause of the disorders.
Inner ear video
Inner ear: