Content
- Causes and ways of infection of jaundice
- Conditions affecting red blood cells
- Conditions affecting liver cells
- Conditions affecting the bile ducts
- Conditions affecting the common bile duct
- Types of jaundice
- Hemolytic (prehepatic) jaundice
- Hepatic jaundice
- Cholestatic (post-hepatic) jaundice
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Diet and lifestyle advice
- Home remedies
- Is jaundice dangerous, the consequences
- Adult jaundice videos
In adults jaundice cannot be considered a disease, it is a symptom that is caused by various reasons. The syndrome occurs when too much bilirubin is produced in the body.
Causes and ways of infection of jaundice
Jaundice is a yellowish discoloration of the skin, sclera (whites of the eyes) and mucous membranes due to bilirubin. There are millions of red blood cells in the bloodstream. Each blood cell lives for about 120 days, and then it breaks down into various chemical waste. New red blood cells are constantly being created to replace the destroyed ones.
Bilirubin (yellow-orange pigment) is one of the chemicals that are produced when red blood cells break down and is carried through the bloodstream. When blood flows through the liver, its cells absorb bilirubin. Chemicals in liver cells slightly alter the structure of the pigment, making it water-soluble or conjugated. The pigment in the blood before it is absorbed by the liver cells is called unconjugated.
Liver cells secrete conjugated bilirubin into tiny tubes called bile ducts. Thus, bilirubin is part of bile. Bile is a mixture of various chemical wastes secreted by liver cells. One of the functions of liver cells is to get rid of a number of unnecessary chemicals in the bile.
The liver has a network of bile ducts. They join together (like the branches of a tree) to form a larger common bile duct. Bile constantly flows through tiny bile ducts into the common bile duct and into the first part of the intestine known as the duodenum.
The gallbladder lies under the liver. It looks like a sac that stores bile. The bubble shrinks when the person eats. This flushes the accumulated bile back into the common bile duct and into the duodenum. The bilirubin in the bile gives the stool its typical brown color. Therefore, getting rid of bilirubin is a normal process.
Jaundice in adults (caused by liver dysfunction) usually occurs when blood bilirubin levels exceed 2.5–3 mg / dL.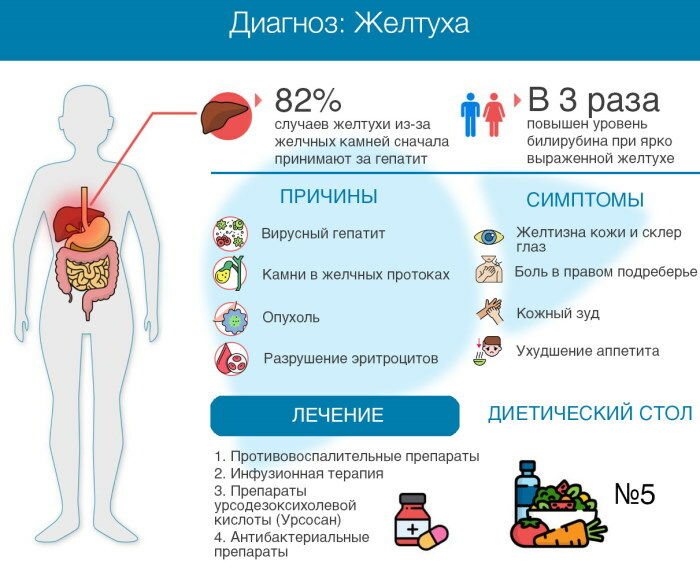
And this can happen for various reasons:
- Conditions affecting red blood cells.
- Conditions affecting liver cells.
- Diseases affecting the tiny bile ducts in the liver.
- Conditions affecting the common bile duct outside the liver.
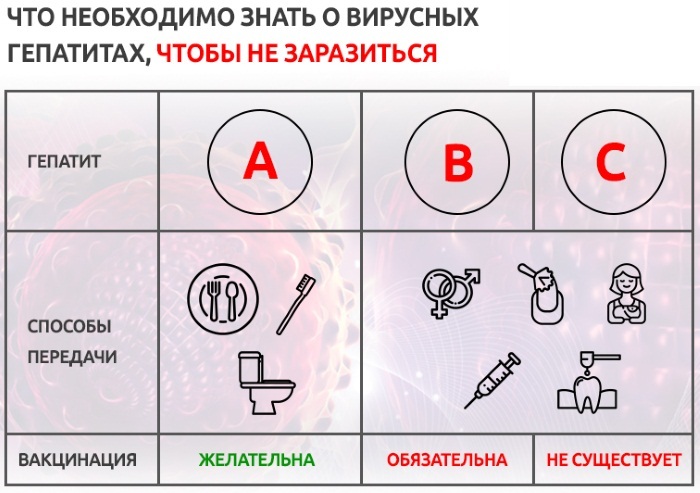
Not all types of diseases are contagious. This only applies to viral hepatitis.
However, there are several types of jaundice transmission:
- Contaminated food and water - fecal-oral route. The incubation period lasts 10-45 days.
- Parenteral route. Such jaundice can become chronic, and the incubation period lasts from 6 weeks to 6 months.
- Through the blood. The patient can become infected through a blood transfusion or during childbirth.
- Sexual. Transmission of jaundice or hepatitis C is possible with this method.
Conditions affecting red blood cells
Various causes cause an increased rate of destruction of red blood cells. As a result, more bilirubin is produced than normal and circulates in the blood. Liver cells do not have time to process excess bilirubin. Consequently, a store of pigment accumulates in the blood, waiting for the liver cells to process it. This increased amount of bilirubin then travels to body tissues, causing jaundice.
Conditions that cause an increased rate of destruction of red blood cells include:
- Certain genetic diseases such as sickle cell disease, thalassemia, spherocytosis.
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome.
- Malaria.
Conditions affecting liver cells
In some cases, liver cells cannot absorb bilirubin well, so pigment builds up in the bloodstream. This occurs when there are problems with the excretion of processed bilirubin by the liver cells into the bile ducts or when cells are damaged.
Conditions that affect liver cells that can cause jaundice include:
- Hepatitis A or B.
- Some infections caused by microbes.
- Alcoholic hepatitis.
- Inflammation caused by poisons or side effects of certain medications.
- Autoimmune hepatitis.
- Cirrhosis. It is a condition in which normal liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue (fibrosis). It tends to progress slowly and often does not cause symptoms in the early stages. However, as liver function gradually deteriorates, serious problems and jaundice can develop.
- Hereditary defects in enzymes that process bilirubin in liver cells. This occurs with Gilbert, Dubin-Johnson, Rotor syndrome. Gilbert's syndrome is very common, affecting about 1 in 20 people, with occasional mild jaundice. Other inherited defects are rare.
Conditions affecting the bile ducts
If the tiny bile ducts in the liver become damaged or narrowed, the flow of bile is limited. The accumulated bile (containing bilirubin) then enters the bloodstream. Primary biliary cirrhosis, cholangitis, or certain medications can affect or damage your bile ducts.
Conditions affecting the common bile duct
Bile from all the small bile ducts in the liver drains into the common bile duct. If the duct is narrowed or blocked (blocked), bile containing bilirubin can leak into the bloodstream and cause jaundice. This is sometimes called obstructive jaundice.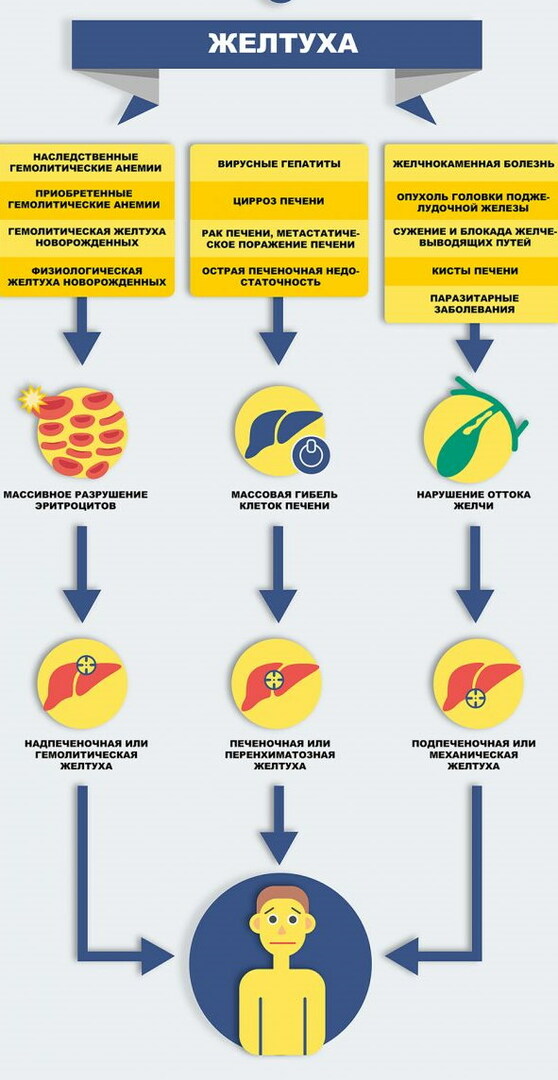
Conditions that can cause this condition include:
- Gallstones.
- Pancreas cancer.
- Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
- Biliary atresia. In this condition, some or all of the bile ducts become inflamed.
- Gallbladder cancer.
Types of jaundice
Jaundice in adults (the reasons for the accumulation of bilirubin in the body determine the different types of symptom) is subdivided into into 3 types, which are classified depending on what interferes with the normal removal of bilirubin from organism.
Hemolytic (prehepatic) jaundice
If the cause of the jaundice is a blood disorder, it is called hemolytic jaundice. It is a condition in which red blood cells are destroyed and removed from the bloodstream before their normal life cycle is completed.
The term "anemia" usually refers to a decreased number of red blood cells. Sometimes it also refers to low levels of hemoglobin, a protein that allows red blood cells to carry oxygen. Hemolytic anemia is characterized by increased levels of indirect bilirubin in the bloodstream.
Triggers for hemolytic anemia vary and can be inherited or self-acquired:
- Hereditary hemolytic anemia includes gene disorders such as glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency (the most common enzyme deficiency in people), hereditary spheroid cell anemia (a defect in the proteins of the walls of red blood cells) and sickle cell anemia (abnormal hemoglobin in red blood cells).
- Acquired hemolytic anemia can be caused by medications such as paracetamol, penicillin, and oral contraceptives. It also develops after infections such as malaria or autoimmune diseases such as lupus.
Hepatic jaundice
Jaundice in adults, the causes of which are in the area of the liver, develops due to damage or dysfunction of this organ. One of the functions of the liver is to chemically convert bilirubin and transfer it to the gallbladder. If these processes are disrupted, the liver can no longer carry out further processing. The pigment accumulates in the blood and then is deposited in tissues: eyes, skin and mucous membranes.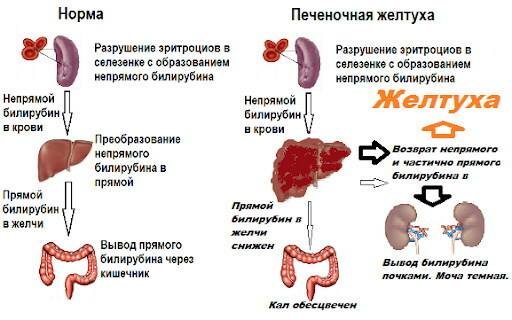
The main stimuli that trigger jaundice are:
- cirrhosis of the liver;
- viral hepatitis;
- liver cancer;
- poisoning;
- right ventricular failure;
- poisoning during pregnancy (gestosis);
- fatty liver;
- Pfeiffer's glandular fever;
- liver metastases;
- medicines;
- congenital hyperbilirubinemia, such as Meilengracht disease;
- yellow fever.
Cholestatic (post-hepatic) jaundice
In this form, a violation of the metabolism of bilirubin occurs only after its passage through the liver. The cause of the violation is a blockage of the main bile duct. Bile and bilirubin accumulate in the gallbladder and cannot enter the duodenum. Posthepatic jaundice usually occurs due to impaired outflow of bile.
Causes of posthepatic jaundice in adults:
- Gallstones in the gallbladder or bile duct.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis.)
- Inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
- Tumors of the gallbladder, duodenum, or pancreas.
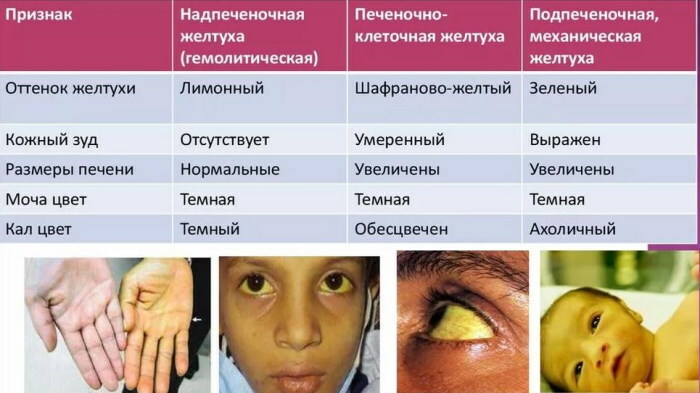
Posthepatic or obstructive jaundice is the most common form of the disease that is not diagnosed only in adults, but also in children, is accompanied by an increase in the level of conjugated bilirubin in the blood or urine. In addition to these symptoms, jaundice can cause headaches, diarrhea, itching, drowsiness, nausea, and vomiting.
Symptoms
If the level of bilirubin in the blood is slightly high, the eyes turn yellow at first. If the value continues to rise, the skin and mucous membranes also change color. Further development leads to hyperbilirubinemia.
Patients with jaundice may be asymptomatic or the syndrome can lead to a life-threatening condition. The wide range of possibilities depends on many underlying causes and the rate at which the disease progresses.
- Patients with acute illness, which is often caused by infection, may seek medical attention for fever, chills, abdominal pain, and flu-like symptoms.
- Patients with non-infectious jaundice may complain of weight loss and itching.
- Abdominal pain is the most common symptom in patients with pancreatic or biliary cancer.
- Even such a non-specific thing as depression can be a complaint in patients with chronic infectious hepatitis and in patients with a history of alcoholism.
Sometimes, excessive consumption of foods rich in beta-carotene (zucchini, melons and carrots) leads to the development of pseudo-jaundice. Unlike true jaundice, carotenemia does not lead to yellowing of the sclera or increased bilirubin levels.
Jaundice in adults (the causes can be both infectious and mechanical) is not a disease, so it is not contagious. But it can be transmitted from person to person against the background of hepatitis, infections.
Diagnostics
The attending physician will first ask in detail about the medical history, current complaints and lifestyle. Also important is information about possible pregnancy, medication, diet. Stay abroad and alcohol consumption are included in the history. Then follow the further steps of the survey.
Physical examination:
- The doctor palpates the abdominal wall to look for any changes in the liver. For example, if the surface of the liver is small, hard, and uneven, the patient may have cirrhosis.
- If the gallbladder is affected, the patient feels pain immediately after palpation.
- An enlarged spleen can cause excessive destruction of blood cells.
Laboratory examination:
- A blood test is relevant for jaundice. In this case, the level of bilirubin is determined. If it is above 2 mg / dL, then the suspicion of jaundice is confirmed.
- Elevated ALT (lutamate pyruvate transaminase) values indicate liver damage, inflammation, or gallbladder disease. But this value also indicates chronic alcohol abuse or even a heart attack.
- An increased value of GT (gamma glutamyl transferase) also indicates chronic alcohol use. If the pancreas becomes inflamed, the level of alpha-amylase in the blood rises.
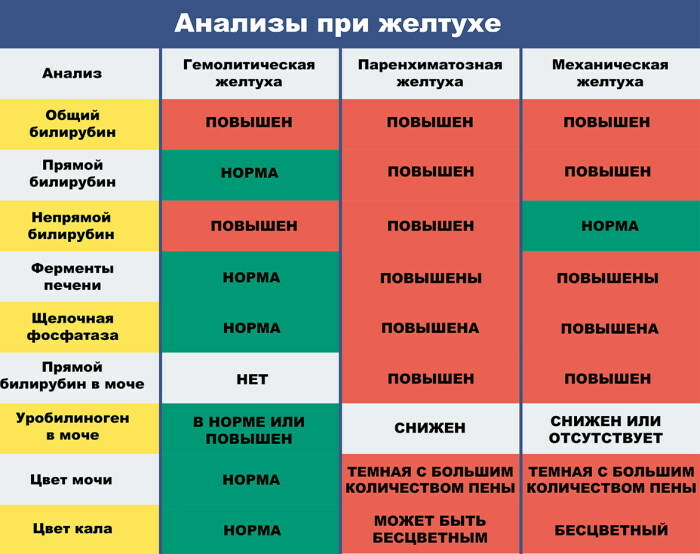
Imaging procedures:
- Ultrasound examination (abdominal sonography) detects pathological changes in organs in the abdominal cavity.
- If cancer is suspected, more sophisticated imaging using MRI or CT is done.
- If a tumor is suspected, a biopsy (taking a tissue sample) is done.
Treatment
Depending on the diagnosis, a suitable therapy is prescribed after the examination. If necessary, the patient is referred to a specialist or to a specialized department of the hospital for further treatment. If the cause of jaundice is not dangerous, then it is enough to change the diet or prescribe medications.
Jaundice in adults with diagnosed causes is treated with medication, a healthy diet, and sometimes surgery.
| Type of jaundice | Therapy |
| Prehepatic | The goal of treatment is to prevent the rapid destruction of red blood cells, causing an increase in the level of bilirubin in the blood. In cases where prehepatic jaundice is caused by an infection, medications are recommended to treat the underlying infection. For genetic blood disorders, a blood transfusion may be required to replace red blood cells. Gilbert's syndrome usually does not require treatment because the associated jaundice does not pose a serious health threat. |
| Hepatic | The goal of treatment is to prevent further liver damage. If it is caused by an infection, such as viral hepatitis or glandular fever, antiviral drugs are used. If the damage is caused by alcohol or exposure to harmful substances, it is recommended to reduce alcohol consumption or avoid further exposure to the substance. In severe cases, a liver transplant is another option. |
| Posthepatic | Treatment includes surgery to unblock the bile duct. Removal of the gallbladder, part of the bile duct system, or part of the pancreas may be necessary to prevent further blockage. The tactic of 2-stage treatment is applied. At stage 1, cholestasis is eliminated, while minimally invasive interventions and conservative treatment are used. At the 2nd stage, as the jaundice subsides, surgical methods are used. |
If the cause is found quickly, pigmentation may disappear shortly after starting therapy.
In treatment, hepatoprotectors are often used:
-
Ursosan. The drug binds toxic substances, strengthens liver cells.
Ursosan for jaundice of newborns - Ursofalk. Bile acid medicine affects the circulation of bile salts, helps dissolve cholesterol gallstones.
How long jaundice persists in adults depends on the method of treatment and the time of initiation of therapy.
Diet and lifestyle advice
Preventive measures for jaundice include preventing the diseases that cause it. To protect yourself from this pathology, you need to carefully monitor your personal hygiene.
The liver is one of the most easily damaged organs. It is not always possible to prevent jaundice (as it is caused by a wide range of possible causes), but taking some precautions can minimize the risk.
- Maintaining good hygiene and sanitation. Do not eat in unsanitary conditions, wash your hands more often.
- Do not abuse alcohol. This will not only help relieve the symptoms of jaundice, but it will also protect you from alcohol-related liver diseases such as cirrhosis. The recommended daily limit for women is 2-3 units of alcohol. For men, the recommended daily limit is 3-4 units. Reference point: one bottle of wine contains 9-10 units of alcohol.
- Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet.
- Cholesterol management. Controlling your cholesterol levels will not only prevent jaundice but also help maintain overall health. You can control it with a healthy diet and exercise or medication. Eating more soluble fiber, healthy fats, and foods high in omega-3 fatty acids lowers cholesterol levels.
Home remedies
Recipes based on medicinal plants:
- Mix 1 tsp. l. roasted barley powder with a glass of water. Add 1 tsp to it. l. honey and take twice a day.
- Add 1 tsp. l. paste from basil leaves into a glass of radish juice. Take the drink 2 times a day for 15-20 days.
- Take 1 tsp. l. Indian aloe vera pulp with black salt and dry ginger powder every morning for 10 days.
- Mash the bitter Chinese gourd (Momordica charantia) and extract the juice from it. Take 1/4 cup of juice daily early in the morning. You can use capsules made from this plant.
Is jaundice dangerous, the consequences
Jaundice is difficult to prevent on purpose as it is just a symptom of many different diseases, but subject to certain hygienic conditions and health control, it is possible to minimize the development of symptoms.
If the disease causing the symptoms of jaundice is left untreated, it can be dangerous or even fatal to the patient. Inflammation of the liver and gallbladder should be treated as quickly as possible with appropriate therapy.
The vaccine against jaundice is not given because it is not a separate disease, but just a symptom. To date, vaccines have been developed against viral hepatitis, which is a common cause of jaundice.
Jaundice itself is not a disease, but a clinical outward sign. It underlies many pathologies. Therefore, in order to understand whether a symptom can be cured, it is important to understand the entire metabolic process of the disease.
If a person can overcome the disease, then the symptom will go away. Various diseases are associated with it, so only a thorough examination can shed light on the cause of jaundice. For example, an infection can be a trigger, but sometimes other conditions are behind it, such as cirrhosis, fatty liver, gallstones, or pancreatitis.
Jaundice in adults is a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that requires proper diagnosis, clarification of all causes and urgent treatment.
Adult jaundice videos
Colored diseases. Jaundice: