Content
- Generations of antipsychotics
- 1st generation antipsychotics
- 2nd generation antipsychotics
- New generation antipsychotics
- The mechanism of action of antipsychotics
- Complete blockade of dopamine receptors
- Partial inhibition of dopamine receptors
- Serotonin receptor blockade
- Multi-receptor blockade
- Indications for use in psychiatry
- Contraindications and combinations with other substances
- Side effects
- The principles of treatment with antipsychotics
- Video about antipsychotics
In the pharmacological group of antipsychotics includes drugs that have a pronounced effect on higher nervous activity. Such substances have a complex and diverse mechanism of biochemical and physiological effects. The indications for their use are not limited to psychiatric practice.
Generations of antipsychotics
The basic principle of the classification of such medicines is based on the chemical structure of the molecules of the active substance and the mechanism of therapeutic action. The first drugs for this purpose were developed in the 1930s.
Each generation of antipsychotics differs in biochemical characteristics and the number of severe side effects. A total of 3 generations of antipsychotic medications have been created. The newest generation has a number of fundamental differences from the previous ones.
1st generation antipsychotics
Such antipsychotic drugs are called typical. The active ingredients of 1st generation antipsychotics still used in psychiatric in stations to suppress incurable conditions, the derivatives are:
- thioxanthene;
- phenothiazine;
- buterophenone.
Such drugs demonstrate high efficiency and speed of therapeutic effect, but have a number of non-core effects. Antipsychotic agents are divided into 3 clinical categories according to the mechanism of inhibition of the cerebral divisions and receptors.
Antipsychotics (indications for the use of 1st generation drugs are limited to exclusive psychiatry) based on thioxanthene, phenothiazine derivatives or buterophenone, depending on the drug group, have a different degree of affinity for dopamine-secreting physiological structures.
They enter into a stable and irreversible bond with histamine, muscarinic and alpha-adrenergic receptors. These properties are responsible for the strong antipsychotic effect of 1st generation neuroleptics. Such drugs are unable to suppress schizophrenic manifestations in 3 out of every 10 patients.
The 1st generation antipsychotics used so far include:
- Haloperidol. The drug was developed back in 1958. Belgian pharmaceutical concern Janssen Pharmaceutica and is currently successfully used in psychiatric hospitals.
- Chlorprethixene. The drug is distinguished by high antipsychotic activity combined with a mild therapeutic effect in comparison with most analogues.
- Sulpiride. The drug has a combined effect on the function of the central nervous system, moderate antidepressant and weak psychostimulating effects.
- Chlorpromazine. The first synthetic-based antipsychotic drug. A typical representative of aliphatic phenothiazines.
In most cases, such medications relieve the most severe psychiatric syndromes without causing the patient feels chronic fatigue, but slightly reducing muscle tone against the background of regular reception.
2nd generation antipsychotics
When choosing the tactics of drug therapy, psychiatrists give preference to drugs of the next generation. Such antipsychotics are called atypical due to a special mechanism of clinical influence.
The active substances of such drugs selectively block dopamine receptors, which significantly reduces the likelihood of developing extrapyramidal disorders.
Unlike 1st generation antipsychotics, improved 2nd generation drugs have the following clinically significant positive effects:
- gently smooth out the negative manifestations of mental disorders;
- reduce the risk of cognitive impairment of varying severity;
- less often provoke extrapyramidal dysfunction;
- do not cause tardive (tardive) dyskinesia - involuntary motor reactions and spontaneous muscle contractions that develop against the background of prolonged use of dopamine receptor blockers.
Certain 2nd generation antipsychotics are effective in treating suicidal ideation through sedation. The drugs of this pharmaceutical group relieve anxiety syndrome and improve sleep.
New generation antipsychotics
Modern developments are fundamentally different from antipsychotic medicines of previous generations in the principle of biochemical effects and physiological effects. Substances of previous generations effectively and quickly suppress exacerbations.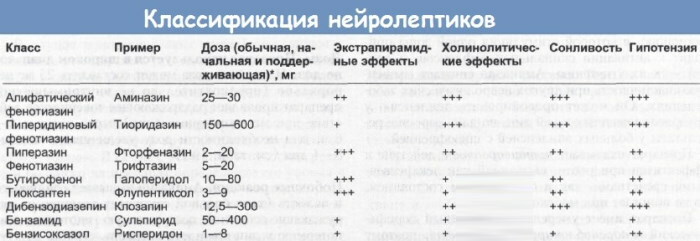
Antipsychotics of the 1st and 2nd generation are suitable for the correction and regulation of incurable conditions. They have a large number of residual symptoms combined with an individual profile of unwanted effects and side effects.
Added to this are the difficulties with targeted selection of the appropriate drug, which did not allow such drugs to become the standard of the psychiatric industry. The latest developments of pharmacologists and biochemists are partially devoid of these disadvantages.
Antipsychotics have numerous indications for use. 3rd generation medicines are used to treat somatic pathologies. They have selective and partial antagonism to dopamine receptors.
3rd generation antipsychotics interact with D2 and D3 physiological elements.
The use of such medicines provides a sustainable reduction:
- symptoms of mental disorders;
- cognitive impairment;
- neurological syndromes;
- metabolic disorders;
- dysfunctions of the endocrine glands.
These drugs increase mental capacity. 3rd generation antipsychotics have an extended therapeutic range, an improved safety profile, and good tolerance for most target patients.
Partial antagonism to dopamine receptors provides innovative possibilities in the treatment of a wide range of mental disorders and somatic pathologies.
Such drugs take the treatment of schizophrenic conditions to a new level of clinical efficacy.
3rd generation antipsychotics:
- stop positive symptoms no less reliably than drugs of previous generations;
- allow to achieve a therapeutic goal by selectively influencing dopamine receptors altered by pathology without irreversible blocking of the entire cluster of biological structures;
- provide a therapeutic effect with mild decompensation of neurotransmitter and dopaminegric mechanisms, which is not available for antipsychotics of previous generations;
- minimize or completely eliminate the risk of extrapyramidal disorders;
- have significantly improved individual susceptibility.
These medications include Aripiprazole, which has been used in psychiatric practice since 2002. Even more modern developments are Brexiprazole and Karipzazin, created in 2015. The list of 3rd generation antipsychotics is constantly expanding.
The mechanism of action of antipsychotics
The therapeutic effect of such drugs is due to the suppression of excess dopamine activity in the mesolimbic tract, which binds the ventral cortex of the middle cerebral lobe and the so-called substantia nigra with organic limbic structures systems.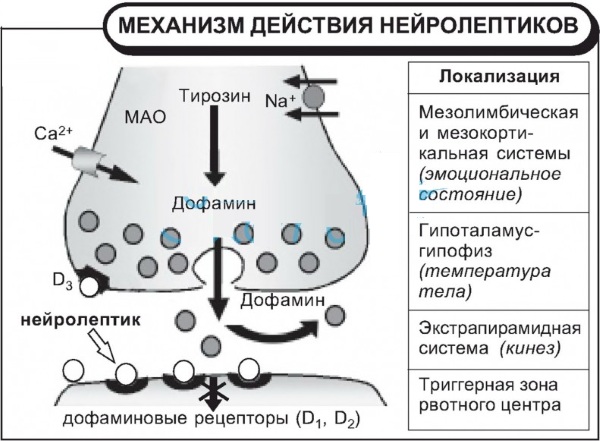
The channel that conducts nerve impulses is involved in physiological reactions:
- endocrine regulation;
- psycho-emotional state;
- ability to memorize information;
- learning;
- experiences of pleasure;
- affective variations.
The mesolimbic tract partially regulates the coordination of movements, the work of baroreceptors. Do not prescribe the simultaneous use of different antipsychotics, since they have synergy.
Complete blockade of dopamine receptors
The leading mechanism of the therapeutic effect of antipsychotic drugs. An increased concentration of a neurotransmitter in the channel is considered a key cause of mental abnormalities with a productive symptomatic complex.
These signs include:
- delusional states;
- obsession;
- auditory and visual hallucinations;
- tactile sensations;
- causeless anxiety.
Typical antipsychotics suppress dopamine activity by blocking at least 65% of the perceiving neurotransmitter of D2 receptors, which leads to the reduction of positive neuropsychiatric symptoms.
The mechanism of the clinical effect of 1st generation drugs is associated with the manifestation of numerous non-core effects:
- motor restlessness;
- uncontrolled muscle contractions;
- depression;
- emotional depression;
- the occurrence of anhedonia - a decrease or complete loss of the ability to have pleasure.
Antipsychotics that cause such conditions require constant dose adjustments to reduce the negative effects of taking. Indications for use necessitate symptomatic treatment.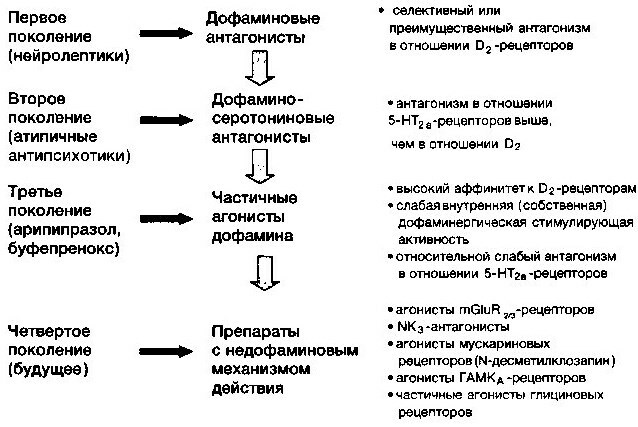
Mechanism of action based on long-term and persistent blockade of dopamine receptors in the mesolimbic tract antipsychotic drugs provoke an increase in the sensitivity of target organic elements and their growth number.
This effect is caused by the attempts of neurons to restore the cropped connections between synapses. An increase in receptor susceptibility, provoked by prolonged use of antipsychotics, increases the potential danger of developing previously unrecorded psychoses.
Partial inhibition of dopamine receptors
Certain antipsychotic drugs targeting D2 elements mimic a weakened form of the neurotransmitter. This mechanism of clinical action is characteristic of the 2nd generation drugs.
The drugs are characterized by a mild correction of dopamine activity, which reduces the reduction of positive symptoms and significantly reduces the likelihood of non-core manifestations.
Serotonin receptor blockade
The target objects of biochemical action for drugs based on this principle of therapeutic action are elements of the types 5-HT2A, 5-HT1A and 5-HT2C.
Interacting with these receptors, the active substance of the drug indirectly regulates the concentration of dopamine in the mesolimbic pathway. The sensitivity of neurotransmitter neurons is reduced due to the inhibition of the production of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA).
The biochemical compound is a key component of the system for inhibiting higher nervous activity. This mechanism of action is inherent in 3rd generation antipsychotics. Some antipsychotics achieve a similar physiological effect by mimicking the effect of serotonin on receptor elements such as 5-HT1A.
Other 3rd generation antipsychotics are aimed at blocking the functions of organic structures of the 5-HT2C class. This biochemical mechanism activates special reactions in intermediate GABA neurons that lead to a decrease in dopamine secretion.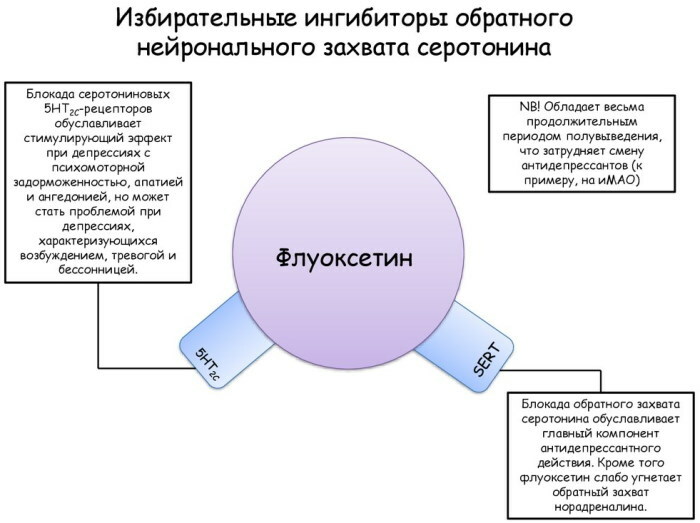
Antipsychotics that inhibit α2-adrenergic receptors act in a similar way. Violation of their basic physiological functions causes the release of an increased portion of norepinephrine with inhibition of the reuptake of the hormone and an increase in its biochemical activity.
Multi-receptor blockade
This property is inherent in the most modern, progressive and innovative pharmacological developments.
Their mechanism of action is based on the simultaneous involvement of the following systems in the inhibition process:
- dopamine;
- serotonin;
- cholinergic;
- adrenergic.
Antipsychotics (indications for the use of such drugs are significantly expanded) are distinguished by an increased profile of therapeutic effect with relief of positive symptoms and reduction of negative manifestations.
When used in clinical practice, non-core effects are few and far between. General and basic properties of antipsychotic medications due to the mechanism of action are presented in the table.
| the effect | Clinical characteristics |
| Antipsychotic | The ability of the active substance to suppress the excessive activity of cerebral structures, which causes inadequate psychomotor agitation. |
| Sedative | Drug-induced drowsiness, mild lethargy. |
| Incisive | Uniform reduction of manifestations of psychosis, counteraction to the progression of pathology. |
| Anti-deficiency | Mitigating signs of mental illness and mental deficiency. The anti-deficiency effect has a therapeutic value in conditions associated with depletion of emotions, loss of motivation, impaired attention, weakening of memory, mental disorganization. |
| Potentiating | Strengthens the effect of other medicines used in complex therapy. |
| Prophylactic | Prevention of repeated exacerbations and prolongation of the period of remission after a course of therapy in a neuropsychiatric hospital. |
Some drugs in the category of antipsychotics in medium therapeutic or high dosages have activating influence aimed at controlling severe negative symptoms, improving cognitive abilities.
Indications for use in psychiatry
Such potent drugs are prescribed in emergencies and in special categories of patients.
Standard indications for use in psychiatric practice are:
- functional disorders of higher nervous activity;
- excessive psychomotor agitation - a pathological condition associated with motor restlessness of various severity, speech disorders, affective manifestations;
- psychosis associated with a distorted perception of reality and inadequate responses to external stimuli;
- withdrawal symptoms associated with the systematic use of drugs or drugs with an addictive effect;
- delirium - a violation of brain activity, accompanied by a clouding of consciousness, emotional and mental disorders;
- schizophrenia of any form and variety;
- indomitable phobic states;
- intellectual and mental disorders;
- bipolar disorders;
- anxiety unexplained by somatic reasons;
- suicidal mood;
- genetic related mental retardation.
Antipsychotics are used to reduce the symptoms of Tourette's syndrome and to relieve numerous reactive conditions. These drugs are indicated for most mental disorders. Only the dosage regimen differs.
Contraindications and combinations with other substances
Antipsychotics have numerous indications for use. Equally extensive is the list of absolute clinical prohibitions and situational restrictions on their use.
Antipsychotic medications are contraindicated for:
- glaucoma;
- individual hypersensitivity to any component of the drug;
- hepatobiliary pathologies;
- acute heart failure;
- peptic ulcer;
- renal dysfunction;
- febrile conditions;
- active infectious process;
- hematological diseases;
- endocrine disruption;
- pulmonary tuberculosis;
- immunodeficiency syndrome;
- anorexia;
- physical exhaustion;
- anemic conditions;
- oncological neoplasms in the stage of metastasis.
It is strictly forbidden to take antipsychotics when carrying a child and during lactation. The combination of antipsychotic medications with antidepressants causes impaired bowel movements and increases intravascular pressure.
The simultaneous use of antipsychotics and drugs based on benzodiazepine derivatives provokes respiratory failure. It is forbidden in the framework of complex therapy to combine the intake of antipsychotic drugs and antiallergic drugs.
Such a drug combination can cause dysfunction of the central nervous system. The neuroleptic effect reduces the presence of alcohol, insulin, anticonvulsants.
The combination of antipsychotics with tetracycline antimicrobial drugs leads to extensive damage to hepatocyte cells. Such medicines increase the toxic properties of each other.
Side effects
Antipsychotics are taken exclusively for medical prescription with strict adherence to the dosage regimen specified by the psychiatrist. These medications have numerous severe side effects.
They directly depend on the duration of the course, the volume of the drug, the patient's age, and other influencing factors.
Commonly reported side effects of antipsychotics:
- depression or a sharp increase in appetite;
- endocrine dysfunction;
- pathological drowsiness;
- bradycardia;
- deterioration in visual perception;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- difficulty in deurination and defecation;
- violation of salivation;
- erectile dysfunction in men.
Extrapyramidal disorders are manifested by hyper- or hypokinetic disorders, which are muscle stiffness in combination with a limitation of the motor range or vice versa uncontrolled contractions musculature.
The principles of treatment with antipsychotics
There are various regimens for the use of antipsychotic drugs. Each is selected individually depending on the goals of therapy, the age and gender of the patient.
The so-called rapid method of relieving a symptom involves a progressive increase in dosage for 1-2 days. It is used for schizophrenic disorders.
With a zigzag scheme of therapy, a maximum daily dose is prescribed with a sharp decrease in it for 1-2 days. Treatment with pauses provides for breaks of 5-6 days. With shock therapy, a neuroleptic is taken 2 times a week at the maximum possible dosage. This scheme is used to suppress acute psychosis.
The signs of sluggish mental disorders are eliminated by a slow method. The dose of the neuroleptic is gradually increased over 5-7 days. Typical indications for the application of this principle of treatment are mental retardation, delusional states, impoverishment of emotions.
Video about antipsychotics
What are antipsychotics:
