Content
- Indications for research
- Preparation for analysis
- Analysis
- Decoding the results
- HCG (hormonal substance human chorionic gonadotropin)
- Plasma protein associated with pregnancy
- Alpha-fetoprotein
- Unconjugated estriol (NE)
- Symptoms of abnormalities
- Reasons for deviations
- Delay in the physical development of the fetus
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Down Syndrome
- Fetal neural tube defect
- Non-developing pregnancy
- Chromosomal abnormalities
- How to bounce back
- Biochemical Screening Video
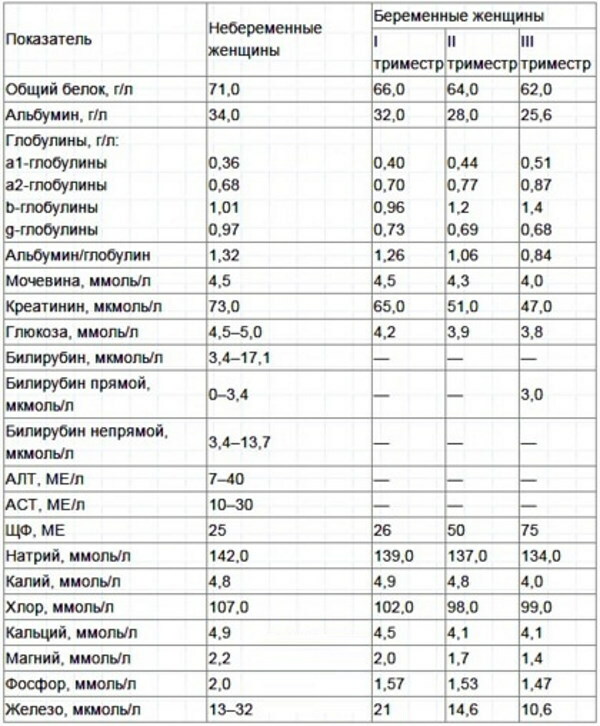
Biochemical maternal serum analysis - This is one of the methods of laboratory examination of the venous blood of a pregnant woman, which reflects the dynamics and quality of the development of the embryo.
This type of examination is distinguished by a high level of information content, and its conduct is indicated for women in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimester of the formation of a child. The deciphering of the biochemical analysis of maternal serum is dealt with by a gynecologist. Diagnostic results allow timely detection of intrauterine fetal malformations.
Indications for research
Biochemistry of maternal serum in the 1-2-3 trimester of pregnancy is prescribed for women with a potential risk group who may have a child with genetic disorders. The analysis is deciphered by the doctor in the first 1-2 days after the completion of laboratory diagnostics.
There are the following mandatory indications for testing the biochemistry of maternal serum:
- the pregnant woman has objective suspicions of the presence of fetal neural tube pathology;
- the age of the expectant mother is over 35 years old;
- after a preliminary examination of the woman, a high probability was established that a developing child would develop trisomy 21 (Down's syndrome);
- in the early stages of pregnancy, spontaneous abortions occurred, the causes of which were not established based on the results of diagnostics;
- found a family carriage of genetic diseases and chromosomal rearrangements;
- a child with Down syndrome was born in the family;
- in the early stages of pregnancy, a woman took potent drugs that are contraindicated for taking in the 1st and 2nd trimesters of fetal development;
- the closest blood relatives were diagnosed with genetic diseases;
- one, or both spouses were exposed to ionizing radiation of a man-made nature;
- during pregnancy, the woman had hepatitis, cytomegalovirus, rubella or herpes infection.
 Biochemistry of maternal serum in the 1-2-3 trimester (decoding of the analysis results takes no more than 30 minutes) is indicated for women who are interested in having a healthy child, and also want to minimize the risk of developing genetic pathology. According to international statistics, 4% of pregnant women over 35 years old are diagnosed with fetal anomalies.
Biochemistry of maternal serum in the 1-2-3 trimester (decoding of the analysis results takes no more than 30 minutes) is indicated for women who are interested in having a healthy child, and also want to minimize the risk of developing genetic pathology. According to international statistics, 4% of pregnant women over 35 years old are diagnosed with fetal anomalies.
Preparation for analysis
Conducting a biochemical study of maternal serum does not require complex preparatory measures. A woman who is assigned this type of diagnosis needs to come to an appointment with a specialist at a strictly appointed time, and also not to eat food in the morning. This analysis is given on an empty stomach.
Analysis
Biochemical examination of biological material to detect possible fetal pathologies is classified into invasive and non-invasive. The table below describes these methods of examining women in the 1st and 2nd trimester of pregnancy.
| Diagnostics type | Features of the analysis |
| Invasive | The use of an invasive biochemical study method allows obtaining the maximum amount of data on the course of pregnancy. This type of diagnosis is carried out according to the following algorithm of actions: 1. The patient goes to the treatment room, where she lies down on the couch. 2. The doctor performs a puncture of the abdominal wall of a pregnant woman using a special needle. 3. The embryo's genetic material is taken for diagnostics. 4. The selected tissues are sent to the laboratory for their further examination for genetic pathologies. In the 1st trimester of pregnancy, a chorionic villus biopsy is performed. In the 2nd trimester of fetal development, amniocentesis and cordocentesis are performed. The advantage of this diagnostic method is a high level of information content. The disadvantage of invasive fetal examination is the risk of developing post-procedural complications. |
| Non-invasive | A non-invasive biochemical study of the dynamics and quality of the course of pregnancy involves the collection of venous blood. This diagnostic method is carried out as follows: 1. The woman goes to the manipulation room, where she sits down on the couch, and puts her right hand on the table for blood sampling. 2. The nurse, using a tourniquet, pulls the upper limb of the pregnant woman in the bicep area. 3. A sterile disposable syringe is used to puncture the ulnar vein. 4. The venous blood of a pregnant woman is taken in an amount of 20 ml. 5. The collected biological material is sent to the laboratory for biochemical research, the results of which will indicate the presence or absence of genetic pathologies in developing fetus. This method of prenatal diagnosis is used when a woman is 11-14 weeks pregnant. If, according to the results of this examination, signs of chromosomal abnormalities are found in a developing child, then the patient is mandatorily assigned to undergo invasive diagnostics. |
 A control biochemical analysis of venous blood is performed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. At this stage of diagnosis, the level of sex hormones is analyzed, which are responsible for the rate of fetal formation and the general condition of a woman.
A control biochemical analysis of venous blood is performed in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. At this stage of diagnosis, the level of sex hormones is analyzed, which are responsible for the rate of fetal formation and the general condition of a woman.
Decoding the results
Biochemistry of maternal serum in the 1-2-3 trimester (the analysis is deciphered by a gynecologist) - it is a modern method of laboratory examination that allows detecting genetic abnormalities fetus. The object of the study is the level of the hormone beta-hCG, AFP, as well as unconjugated estriol.
Biochemistry of maternal serum is performed during gestation periods from 9 to 14, from 15 to 20, as well as from 16 to 18 weeks of fetal development. During this analysis, special attention is paid to the characterization of the marker proteins. In the process of decoding the results of this diagnostic method, the concentration of all biochemical components that affect the course of pregnancy is taken into account.
HCG (hormonal substance human chorionic gonadotropin)
HCG is a type of glycoprotein that is synthesized by the trophoblast of the placenta of a pregnant woman. This hormone maintains an optimal level of activity of the corpus luteum from the 8th day of ovulation, and is also considered the basic hormone of early pregnancy.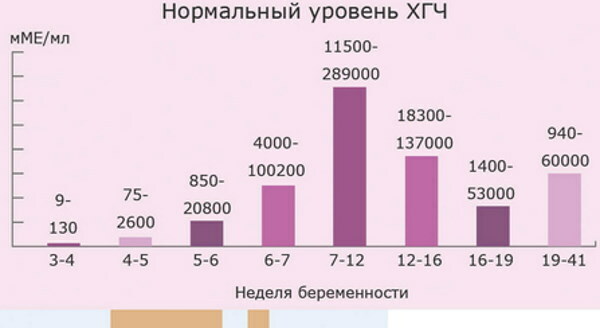
According to the biochemical composition, hCG is a protein component that is found in the composition of venous blood with 10-12 days of pregnancy, and then its concentration gradually increases until the end of the 1st trimester of development fetus.
The table below shows the norms of chorionic gonadotropin, which correspond to a particular week of pregnancy.
| Fetal development period | The norm of the concentration of hCG in the blood of a pregnant woman (units. measurements of honey per 1 ml of biological material) |
| from 1 to 2 weeks | from 25 to 300 |
| from 2 to 3 weeks | from 1500 to 5000 |
| from 3 to 4 weeks | from 10,000 to 30,000 |
| from 4 to 5 weeks | from 20,000 to 100,000 |
| from 5 to 6 weeks | from 50,000 to 200,000 |
| from 6 to 7 weeks | from 50,000 to 200,000 |
| from 7 to 8 weeks | from 20,000 to 200,000 |
| from 8 to 9 weeks | from 20,000 to 100,000 |
| from 9 to 10 weeks | from 20,000 to 95,000 |
| from 11 to 12 weeks | from 20,000 to 90,000 |
| from 13 to 14 weeks | from 15,000 to 60,000 |
| from 15 to 25 weeks | from 10,000 to 35,000 |
| from 26 to 37 weeks | from 10,000 to 60,000 |
During the biochemical analysis of maternal serum, the alpha and beta subunits of the hCG hormone are released. The use of immunochemiluminescent techniques allows you to determine even the lowest levels of human chorionic gonadotropin.
Plasma protein associated with pregnancy
The concentration of this substance is also determined during the biochemical study of maternal serum. This component is a glycoprotein that is produced by the placental trophoblast throughout the entire period of pregnancy.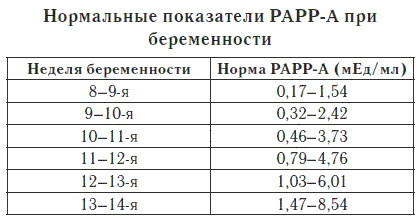
Plasma protein levels increase in proportion to fetal development. According to the results of scientific research, the concentration of this substance between 8 and 13 weeks of pregnancy is 2.5 times lower than the norm in women who are carrying a child with Down syndrome.
The table below shows the optimal plasma protein levels associated with pregnancy.
| Fetal development period | The rate of concentration of plasma protein associated with the state of pregnancy (units. measurements of honey per 1 ml of biological material) |
| from 8 to 9 weeks | from 0.17 to 1.54 |
| from 9 to 10 weeks | from 0.32 to 2.42 |
| from 10 to 11 weeks | from 0.46 to 3.73 |
| from 11 to 12 weeks | 0.7 to 4.76 |
| from 12 to 13 weeks | 1.03 to 6.01 |
| from 13 to 14 weeks | 1.47 to 8.54 |
 The concentration of plasma protein associated with pregnancy changes under the influence of the following factors:
The concentration of plasma protein associated with pregnancy changes under the influence of the following factors:
- body weight of a pregnant woman;
- therapy with potent drugs;
- the presence of diabetes mellitus;
- the onset of pregnancy by IVF.
In a pregnant woman's body, plasma protein performs a protease function. A decrease or increase in the level of this component indicates the presence of disorders in the work of the mother's endocrine system, and also indicates the development of genetic abnormalities of the fetus.
Alpha-fetoprotein
Alpha-fetoprotein is a biologically active substance, which is also determined in the process of biochemical examination of maternal blood serum. AFP is a protein produced by the embryonic liver and yolk sac. Alpha-fetoprotein is determined only from the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. The change in AFP indicators is recorded from 14-15 weeks of fetal formation, when the placentation period ends.
The table below shows the rate of alpha-fetoprotein in women at different stages of pregnancy:
| Fetal development period | Normal concentration of AFP (units. measurements of IU per 1 ml of venous blood) |
| from 15 to 19 weeks | from 15 to 95 |
| from 20 to 24 weeks | from 27 to 125 |
| from 25 to 27 weeks | from 52 to 140 |
| from 28 to 30 weeks | from 67 to 150 |
| from 31 to 32 weeks | from 100 to 250 |
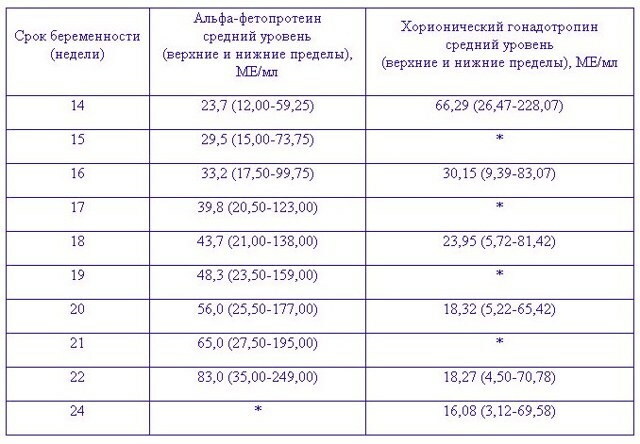 A sharp increase in the level of alpha-fetoprotein in the venous blood of a pregnant woman indicates malformations of the child's physical development. It should be noted that if the fetus has a genetic pathology in the form of Down's syndrome, the AFP concentration in the maternal serum is significantly reduced.
A sharp increase in the level of alpha-fetoprotein in the venous blood of a pregnant woman indicates malformations of the child's physical development. It should be noted that if the fetus has a genetic pathology in the form of Down's syndrome, the AFP concentration in the maternal serum is significantly reduced.
A similar result of too low levels of alpha-fetoprotein is recorded in pregnant women who are carrying children with other chromosomal abnormalities. For example, with Klinefelter's syndrome, as well as deletion of the 18th chromosome.
Unconjugated estriol (NE)
Biochemistry of maternal serum in the 1st trimester (deciphering the results of this study is important value in the early diagnosis of genetic pathologies) allows you to determine the level of unconjugated estriol.
It is a type of estrogen that is synthesized by the developing embryo. The synthesis of this substance occurs in the adrenal glands of the child, and then undergoes a complex metabolic process with the participation of liver tissue. Intrauterine synthesis of estriol leads to a proportional increase in this hormone in the blood of the expectant mother.
The table below shows the optimal values for unconjugated estriol:
| Fetal development period | Normal NE concentration (units. measurements of ng per 1 ml of venous blood) |
| from 14 to 16 weeks | 0.13 to 0.99 |
| from 16 to 18 weeks | from 0.34 to 1.59 |
| from 18 to 20 weeks | from 0.700 to 3.23 |
| from 20 to 22 weeks | 1.09 to 2.88 |
| from 22 to 23 weeks | from 1.29 to 3.75 |
| from 23 to 25 weeks | from 1.41 to 4.04 |
| from 25 to 27 weeks | from 1.53 to 4.62 |
| from 27 to 29 weeks | from 2.31 to 6.92 |
| from 29 to 31 weeks | from 2.31 to 8.65 |
Too high maternal serum levels of unconjugated estriol are indicative of the following factors:
- excessively large fruit;
- several embryos develop in a woman's uterus at once;
- the beginning of labor is approaching.

A decrease in the indicators of unconjugated estriol in the blood of a pregnant woman indicates the possible presence of the following fetal pathologies:
- chromosomal abnormalities;
- delay in the physical development of the fetus;
- the child has defects in certain parts of the body.
The unconjugated form of estriol accounts for only 9% of all biochemical forms of female estriol in maternal serum. The concentration of this substance reflects the activity of fetoplacental synthesis.
Symptoms of abnormalities
Biochemistry of maternal serum in the 1-2 trimester (decoding of this analysis is one of the stages prenatal diagnosis) allows you to detect pathologies of the physical development of the fetus and genetic anomalies. Most of the congenital diseases of this type are not manifested by external symptoms.
Only if the fetus dies, the following signs are diagnosed in a pregnant woman:
- deterioration in general health;
- an increase in body temperature to a level of 37-38 degrees Celsius;
- bloody vaginal discharge;
- decrease in the volume of the abdomen;
- prolonged aching pain in the lumbar region and lower abdominal cavity;
- chills and a state of fever;
- lack of fetal mobility;
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness.
A pregnant woman who has the above symptoms should be hospitalized in a gynecological department. Delay in the provision of medical care is fraught with the development of acute intra-abdominal inflammation, loss of fertility, and blood poisoning.
Reasons for deviations
Violation of the norms in the results of biochemical analysis of maternal serum is caused by genetic diseases and physical defects in the development of the fetus. Laboratory and hardware diagnostics, carried out in the 1st and 2nd trimester of pregnancy, allows you to timely detect the presence of these pathologies.
Delay in the physical development of the fetus
Fetal growth retardation is an intrauterine disorder, which is manifested by a lag in the physical development of the tissues of the embryo. The incidence of this syndrome is in the range of 5-17%. In the presence of this pathology, a low level of unconjugated estriol in the blood is diagnosed in a pregnant woman.
Ectopic pregnancy
An ectopic pregnancy is a complicated pregnancy in which a fertilized egg is attached outside the uterine cavity. This condition of a woman's reproductive system is dangerous due to the high probability of opening internal bleeding, as well as rupture of the fallopian tube. 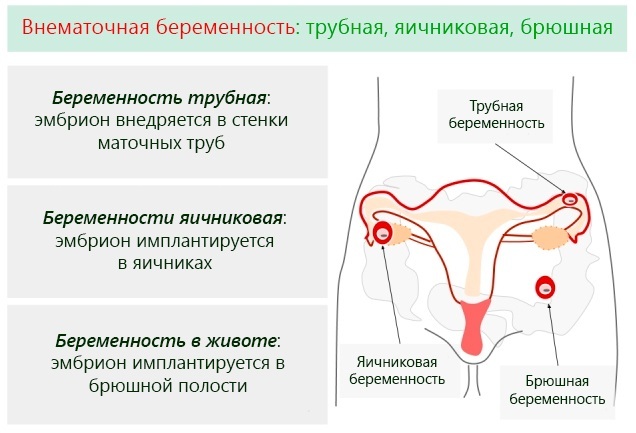 In women with signs of ectopic pregnancy, a sharp decrease in human chorionic gonadotropin is found in the venous blood. The patient needs urgent medical attention.
In women with signs of ectopic pregnancy, a sharp decrease in human chorionic gonadotropin is found in the venous blood. The patient needs urgent medical attention.
Down Syndrome
Down syndrome is a congenital genetic disease of the human body that causes mental and physical retardation. Children born with this defect suffer from disorders in the work of the heart, thyroid gland, the organ of vision and hearing. Down syndrome is a consequence of chromosome 21 trisomy.
This is a genomic pathology, the karyotype of which contains 47 chromosomes instead of 46. The presence or absence of this disease in a developing child can be detected between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy. A decrease in plasma protein levels associated with pregnancy is one of the hallmarks of Down syndrome.
Fetal neural tube defect
Fetal neural tube malformation is a congenital disease of the brain, spinal cord, and spine. This anomaly of intrauterine development leads to partial or total damage to peripheral nerves, dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system and internal organs, causes paralysis and death child.
Fetal neural tube defect is determined by biochemical examination of maternal serum. This pathology is manifested by a change in the level of plasma protein in the direction of its decrease.
Non-developing pregnancy
Non-developing pregnancy is a pathological condition of the female reproductive system, which is manifested by the fading of the fetus. The death of the embryo occurs in the 1st trimester. A distinctive feature of a non-developing pregnancy is the absence of a miscarriage.
To save the woman's life, the frozen fetus is surgically removed. This pathology is detected using ultrasound and maternal serum biochemistry. In this case, a decrease in the concentration of chorionic gonadotropin is recorded.
Chromosomal abnormalities
Chromosomal abnormalities are a complex of genetic disorders that lead to mental and physical developmental defects in a child. Trisomies are most often diagnosed when an extra chromosome appears in the human genome. The presence of this pathology is detected in the 1st and 2nd trimester of pregnancy according to the results of a biochemical study of the woman's venous blood.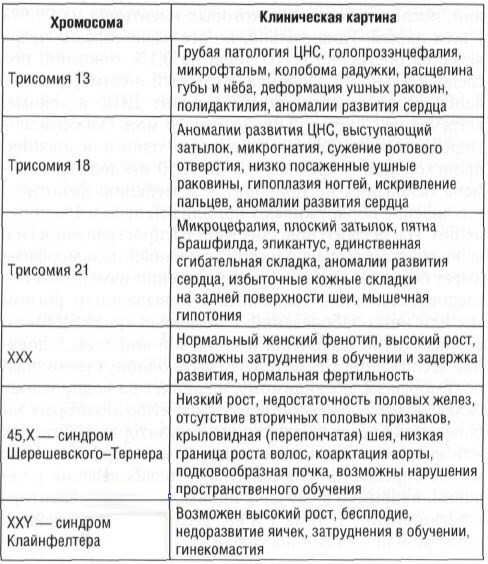
According to statistics, chromosomal abnormalities appear in 1 out of 700 newborn babies. If at the stage of intrauterine development in the fetus there are genetic errors in the genome, then in maternal serum biochemical test results show an abnormally low level alpha-fetoprotein.
How to bounce back
Biochemical screening of maternal serum is just one of many tests that are prescribed to a woman at different stages of pregnancy. Using this research method, it is possible to isolate the key hormones that affect the stable development of the fetus.
Alpha-fetoprotein, unconjugated form of estriol, human chorionic gonadotropin, plasma protein - these are just protein markers that indicate the possible presence of congenital pathologies. In the case of a decrease or increase in the concentration of these substances, a pregnant woman is not prescribed additional drug therapy to stabilize their level.
In this case, the attending gynecologist decides to conduct an additional examination. patients using ultrasound diagnostics, as well as invasive extraction of genetic material embryo. In case of confirmation of the fact that the child has chromosomal abnormalities, physical and mental development, a woman independently makes a decision on the preservation or early interruption pregnancy.
Biochemistry of maternal serum is an informative method for laboratory examination of venous blood, which is used in the 1st, 2nd and 3rd trimesters of pregnancy. This diagnostic method is used for the timely detection of genetic diseases, mental and physical defects that may be present in the fetus.
The analysis is deciphered by a gynecologist. A decrease or increase in the level of chorionic gonadotropin, alpha-fetoprotein, plasma protein indicates anomalies in the intrauterine development of the fetus.
Biochemical Screening Video
First screening. Decoding of ultrasound and blood:



