Content
- What is ventricular premature beats and the causes of development
- Symptoms of pathology
- Classification and stages of development
- Ryan Graduation
- How is ventricular extrasystole diagnosed using an ECG
- Signs of the disease on the ECG, norms and interpretation of indicators
- Alternative diagnostic method - Holter monitoring
- Treatment of ventricular extrasystole
- How to relieve an attack
- When is it necessary to do the operation
- Forecast
- Video about extrasystole
Ventricular premature beats - This is a type of heart disease, characterized by the occurrence of premature organ contractions. Pathology is often detected during a planned ECG and accompanies most heart diseases.
What is ventricular premature beats and the causes of development
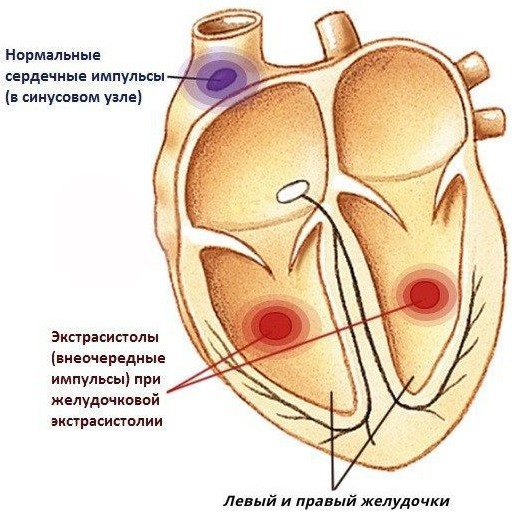
The violation occurs as a result of excitations formed in the Purkinje fibers or in the area remote from the legs of the bundle of His.
The lower conducting system of the heart can also lead to the appearance of electrical impulses. Excessive activity of such a system creates disruptions in the heart rhythm, which causes the development of pathology.
The disease owes its name to the development of areas of excitation in the left or right ventricle. The disorder, for the most part, occurs in elderly patients, but is often found in young people (in 5% of cases).
The reasons for the development of pathology are divided into several main types:
- Organic (cardinal). The disorder develops as a result of other heart diseases - ischemic heart disease, peri- and myocarditis, congenital malformations, cardiomyopathy, organ failure, cardiosclerosis caused by a previous heart attack.
- Extracardiac (noncardinal). The cause of the pathology can be vegetative-vascular dystonia, hyperthyroidism, disruptions in the functioning of the digestive tract, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. In more rare cases, the disease can develop during pregnancy, in violation of the concentration of potassium in the blood, as well as when taking certain medications (diuretics, sympathomimetics).
- Functional reasons. They are caused by the influence of external provoking factors - smoking, stressful situations, overwork, drinking alcohol or coffee, excessive physical activity, pregnancy.
- Idiopathic. In this case, the disease has nothing to do with other internal disorders or provoking factors.
 By identifying the cause, it is possible to find a suitable and effective treatment.
By identifying the cause, it is possible to find a suitable and effective treatment.
Symptoms of pathology
Single interruptions in the heart can occur without any other symptoms. However, in most cases, the patient experiences fading or interruptions in the organ, small tremors and pain. The symptomatology of the pathology also depends on the reasons that caused its development.
Signs:
- fatigue, general weakness;
- dizziness;
- the development of shortness of breath, a feeling of lack of oxygen;
- irritability;
- impaired consciousness - pre-syncope, fainting;
- lowering blood pressure;
- hyperhidrosis (increased sweating);
- numbness of the limbs;
- migraine;
- soreness in the cervical region;
- somatic disorders - anxiety, fear, panic attacks.
In some cases, there is a decrease in stamina during physical activity. At the same time, in patients with diseases that have a functional nature of origin, the symptoms are more pronounced than with organic causes of the disorder.
Classification and stages of development
Ventricular extrasystole on the ECG displays graphical data, on the basis of which the stage and degree of danger of pathology can be assumed. Diagnostics is good because it allows you to accurately determine the presence of a violation.
The disease has a complex classification and stages. Moreover, it is divided into several main types, due to which it is possible to establish the exact cause of the origin of the pathology.
| Classification | Varieties | Description / characteristic |
| By frequency of occurrence | Rare | Up to 5 per minute |
| Average | No more than 16 / min | |
| Frequent | Over 16 and more | |
| By density | Single. Paired Group |
|
| By location (occurrence) | Right ventricular Left ventricular |
|
| By the area of excitement | Monomorphic (monotopic) | Have one focus of occurrence |
| Polymorphic (polytopic) | Have different places of origin | |
| By the rhythm of manifestation | Bigeminia | Every second contraction is pathology |
| Trigeminia | Every third cut | |
| Evadrigeminia | Every fourth | |
| Sporadic | There is no sequence | |
| According to the degree of danger | Benign | Absence of damage to the heart muscle and impairment of consciousness. The frequency of occurrence varies from 1 to 10 per hour. |
| Potentially malignant | Accompanied by hypertrophic changes in the left ventricle. Feeling of interruptions in the heart. In this case, loss of consciousness and cardiac arrest do not occur. The frequency of occurrence per minute is from 10 and more. | |
| Malignant | Loss of consciousness or cardiac arrest may occur. Ventricular tachycardia develops. The frequency of occurrence is from 10 to 100 per hour. |
Ryan Graduation
The classification was proposed by M. Ryan back in 1975 and is intended for patients with myocardial infarction.
Gradation:
- 0 - there are no interruptions (extrasystoles).
- 1 - single interruptions, rarely occur (no more than 30 per hour).
- 2 - solitary, occur frequently (over 30 per hour).
- 3 - polymorphic extrasystoles.
- 4A - paired, monotropic.
- 4B - paired, polymorphic, there are signs of flutter and flickering.
- 5 - early, often lead to the development of paroxysm of ventricular tachycardia.
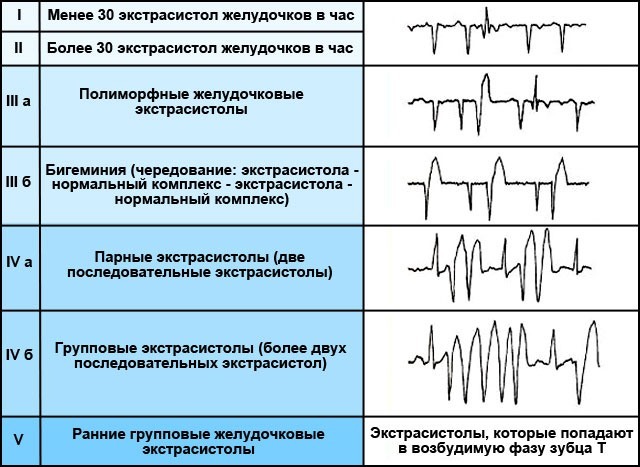
The greatest danger is the 5th stage, since the violation leads to the fact that the heart is not able to completely relax until the next contraction.
How is ventricular extrasystole diagnosed using an ECG
Ventricular extrasystole on the ECG is often found in conjunction with other violations of the conduction of electrical impulses of the heart. In most cases, this is due to the fact that the pathology arose against the background of another heart disease.
Electrocardiography is the most effective and accurate way to detect cardiac arrhythmias. However, diagnostics are not able to detect the cause of the disease, since additional excitement does not always develop during research.
Before diagnosis, the patient should undress to the waist and lie on the couch. After that, the specialist attaches special electrodes (sensors) to the patient's chest, which will transmit information about the impulses in the form of graphic information.
Before mounting the electrodes are treated with isotonic sodium chloride solution. The patient's chest is defatted using a gel base, which further improves the sensitivity of the sensors. After that, the doctor turns on the device, and the equipment begins to record and display heart impulses on special paper.
During the study, the patient should be calm. At this time, you should not move, take deep breaths or other actions that may affect the result. The procedure takes several minutes, after which the received data is transmitted to the cardiologist for decryption.
Signs of the disease on the ECG, norms and interpretation of indicators
During decoding, the specialist estimates the width and height of the teeth. Thus, the heart rate, intervals between contractions and other characteristics of the heart are determined.

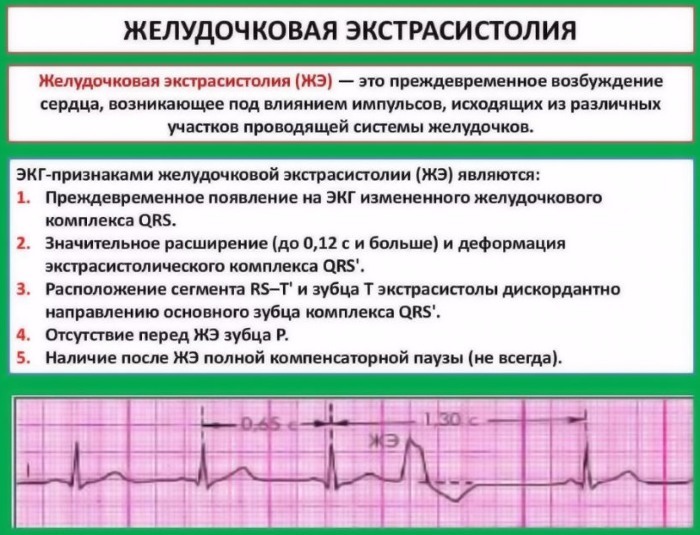
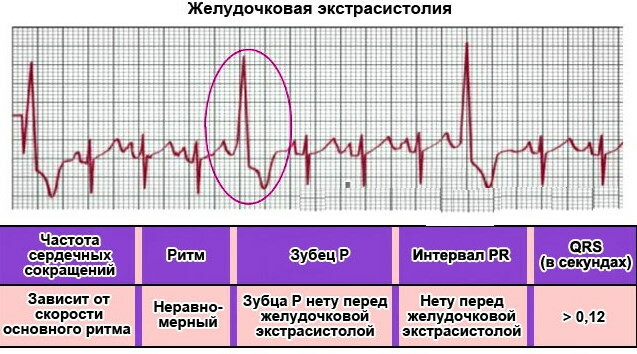
The characteristic signs of the disorder are the disappearance of the atrial P wave. In this case, a change and expansion of the ventricular complex also occurs. The T wave changes its position to the opposite in relation to the QRS complex. After this complex, the emergence of a straight line (isoline) is noted.
Other signs of the disease when decoding:
- The excitations coming from the left ventricle in the diagram have a high and wide R wave, followed by a deep and negative T wave in lead 3, aVF, V1 and V2. In this case, the S wave has a wider and deeper appearance. T - high in 1st and 2nd leads, as well as in V5 and V.
- Complexes from the right ventricle have opposite data. Positive R and negative T are located in the 1st, 2nd, and also in the left chest leads. Indicators in the right leads and aVF.
- Deformed QRS complex. It is characterized by the absence of a compensatory pause. Moreover, it is located between the two usual contractions.
Thanks to the study, it is possible to establish from which ventricle the extrasystoles emanate.
Alternative diagnostic method - Holter monitoring
Ventricular premature beats can also be detected with a 24-hour mount or Holter study. It is used as an additional diagnosis after an ECG.
Holter ECG is a special device in cardiology that allows you to track cardiac activity during various states of the body.
What the study helps to establish:
- Determination of the exact number of arising extrasystoles per day.
- Establishing the cause of origin.
- Counting paired, group extrasystoles.
- Determination of the relationship between the resulting violation and provoking factors.
- Establishing the dependence of pathology during night rest and at the time of rest.
- Tracking the effectiveness of the applied treatment.
- Checking the patient for other disorders of the cardiovascular system.
The patient is required to write down the daily readings of the device in a special diary on a daily basis, taking into account time intervals.
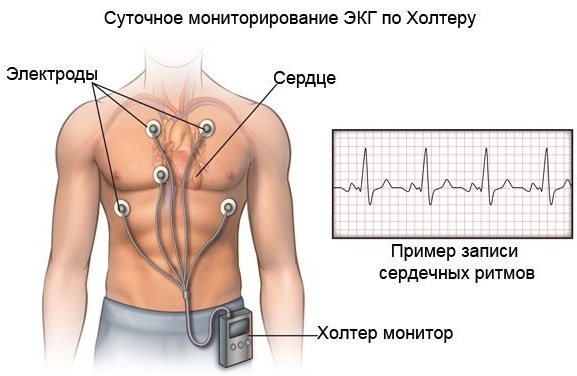
Thus, data is recorded in the following time periods:
- sleep state (at night);
- rest time (during the day);
- while eating food;
- with physical activity and stress;
- when the condition worsens.
During the research, it is necessary to refrain from drinking and smoking. Necessary medications are allowed. The cardiologist is also involved in decoding the results and indicators.
Treatment of ventricular extrasystole
Ventricular extrasystole on an ECG allows you to establish the presence of pathology with high accuracy, which, in turn, helps to choose the most appropriate treatment option.
Therapy of the disease is selected taking into account the clinical picture and the presence of dangerous types of extrasystole. Moreover, it can be both medicinal and surgical (depending on life-threatening conditions).
With the development of a disorder against the background of provoking factors, they must be completely eliminated. Such patients should be excluded from the diet of coffee, alcoholic beverages, and quit smoking. You should also adhere to the daily routine and observe the sleep-wake regimes. In stressful situations, it is recommended to use sedatives - motherwort tincture, Valerian.
Patients with a benign form of pathology in the absence of hemodynamic disturbances are prescribed drug therapy. Beta-blockers are most effective - Valocordin, Bisoprolol.
With the threat of hemodynamic disturbances and the development of complications, antiarrhythmic therapy is performed. Class 1 agents are preferred. Additionally, treatment is prescribed for the main disease that led to the development of the disorder.
In the malignant form of the disease, medications such as Amiodarone and Sotalol are prescribed. However, they are recommended to be used in conjunction with beta-blockers. Therapy in this case should be carried out only in a medical institution under the supervision of specialists and with constant ECG monitoring. This will allow, if necessary, to adjust the therapy and avoid death or other life-threatening conditions.
In malignant forms of the disease, drug therapy can be carried out for life. It should be borne in mind that some antiarrhythmic drugs can lead to the development of more dangerous types of arrhythmias. In this connection, such drugs should be taken only on the recommendation of a doctor and under his supervision.
How to relieve an attack
Often, pathology occurs against the background of a rapidly developing myocardial infarction. The condition is dangerous by the development of complications (fibrillations), therefore, requires urgent assistance.
Relief of an attack:
- The use of lidocaine. The drug is administered intravenously, after which they switch to infusion.
- In the absence of a therapeutic effect, Novocainamide or Etacizin is used.
- In the presence of palpitations, it is recommended to use Cordaron and b-blockers.
- In case of pathology resulting from bradycardia, it is necessary to use drugs such as Etmozin or Ritmilen.
It should be borne in mind that antiarrhythmic drugs can be combined with each other only if absolutely necessary, since such a reception can lead to various complications.
When is it necessary to do the operation
Ventricular extrasystole on an ECG can only be determined by a specialist with high skills in decoding data. The patient's life may depend on this, as in severe cases, an urgent operation may be required.
Surgical intervention can only be carried out according to the indications of a doctor in severe cases. Most often, operations are prescribed to patients who have frequent episodes of extrasystoles, and also in case of intolerance or lack of possibility of prolonged use of medicinal drugs.
The technique of radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is often used, which implies the introduction of a special catheter into the region of the heart through a large vessel.
After that, the specialist, using the equipment, determines the pathological area and acts on it with radio frequency radiation. The operation allows you to completely eliminate (burn) the problem area. The effectiveness of the procedure depends on the correctness of its implementation and allows you to eliminate the violation in more than 90% of cases.
In some cases, a pacemaker may be installed. The essence of the technique is to install a special device in the atrium or ventricle. The device is attached with electrodes, which, if necessary, supply electrical impulses and force the heart muscle to contract.
Myocardial revascularization (shunting, stent placement) is effective in ischemic disorders. The operation allows you to improve the conductivity of electrical impulses and significantly reduce the risks of developing pathology.
In rare cases, with the threat of sudden death, patients may need a heart transplant.
Forecast
The prognosis depends on the form of the disorder, the presence of complications and the cause of the development. With functional and idiopathic types of the disease, there is no threat to the patient's life.
With organic lesions of the heart in the absence of timely therapy, pathology can lead to the development of heart failure, which, in turn, can lead to sudden death.
Therefore, if you suspect a ventricular extrasystole, you should immediately consult a specialist. It is also recommended to undergo annual preventive examinations with a doctor and ECG diagnostics. This will reduce the risks of a violation and exclude the development of complications.
Video about extrasystole
ECG with extrasystole: